This research disentangles the causal effects of pre-training, mid-training, and reinforcement learning (RL) on language model reasoning using a controlled synthetic task framework. It establishes that RL extends reasoning capabilities only under specific conditions of pre-training exposure and data calibration, with mid-training playing a crucial role in bridging training stages and improving generalization.
09 Dec 2025
The paper empirically investigates the performance of multi-agent LLM systems across diverse agentic tasks and architectures, revealing that benefits are highly contingent on task structure rather than universal. It establishes a quantitative scaling principle, achieving 87% accuracy in predicting optimal agent architectures for unseen tasks based on model capability, task properties, and measured coordination dynamics.
The Native Parallel Reasoner (NPR) framework allows Large Language Models to autonomously acquire and deploy genuine parallel reasoning capabilities, without relying on external teacher models. Experiments show NPR improves accuracy by up to 24.5% over baselines and delivers up to 4.6 times faster inference, maintaining 100% parallel execution across various benchmarks.
Wan-Move presents a framework for motion-controllable video generation that utilizes latent trajectory guidance to directly edit image condition features within a pre-trained image-to-video model. This method yields superior visual quality and precise motion adherence compared to state-of-the-art academic approaches and rivals commercial solutions, while also establishing MoveBench, a new comprehensive evaluation benchmark.
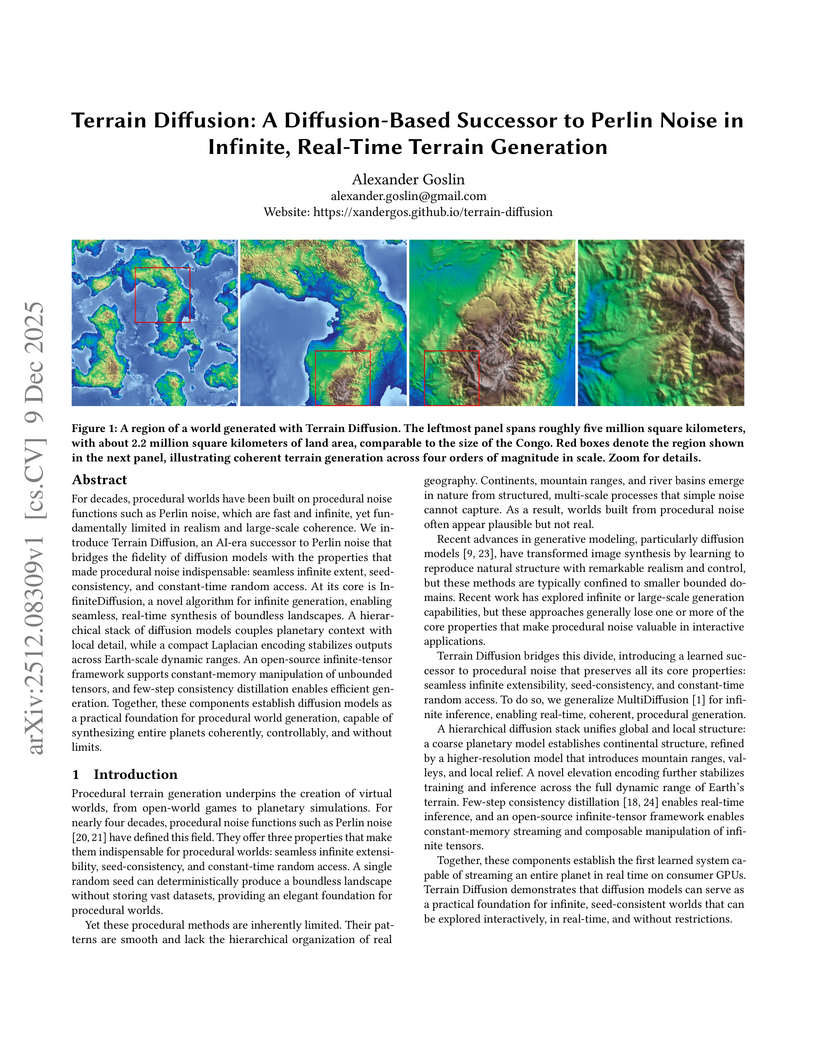
Terrain Diffusion introduces a diffusion-based framework for generating infinite, real-time procedural terrain, delivering highly realistic, boundless virtual worlds with seed-consistency and constant-time random access. The system achieves competitive FID scores and real-time generation latency on consumer hardware, demonstrating its practical applicability.
Astra, a collaborative effort from Tsinghua University and Kuaishou Technology, introduces an interactive general world model using an autoregressive denoising framework to generate real-world futures with precise action interactions. The model achieves superior performance in instruction following and visual fidelity across diverse simulation scenarios while efficiently extending a pre-trained video diffusion backbone.
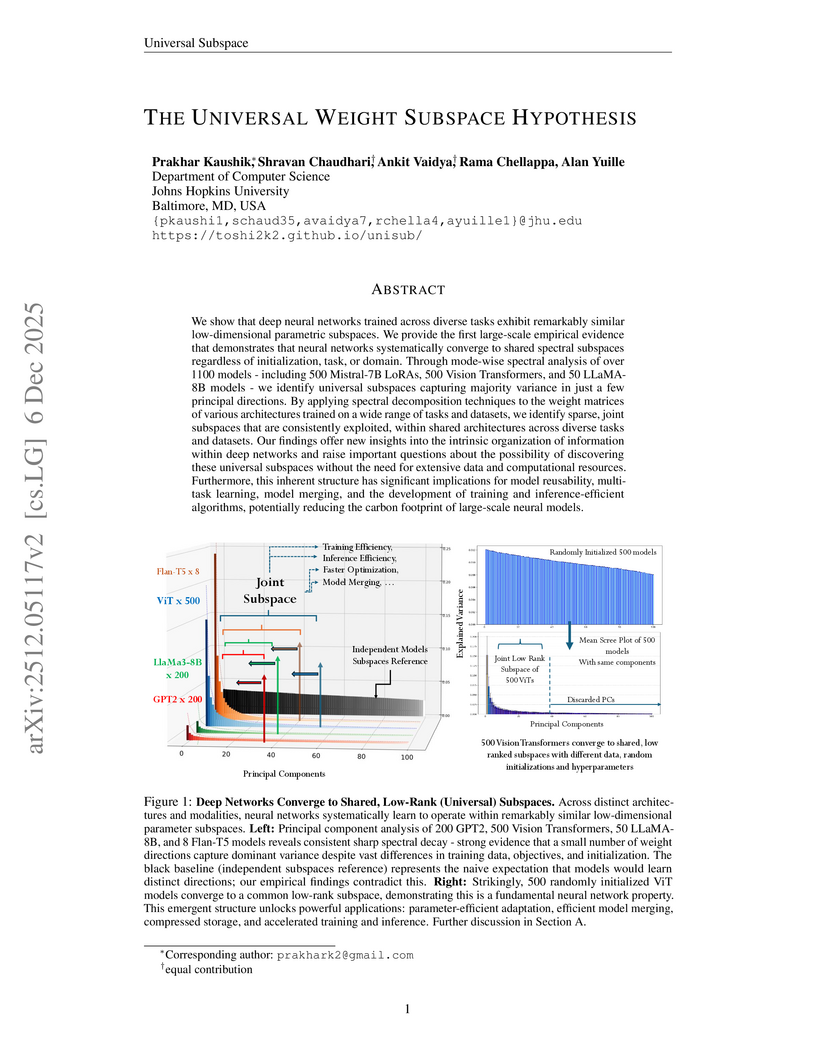
This paper presents the Universal Weight Subspace Hypothesis, demonstrating empirically that deep neural networks trained across diverse tasks and modalities converge to shared low-dimensional parametric subspaces. This convergence enables significant memory savings, such as up to 100x for Vision Transformers and LLaMA models, and 19x for LoRA adapters, while preserving model performance and enhancing efficiency in model merging and adaptation.
Apple researchers introduced FAE (Feature Auto-Encoder), a minimalist framework using a single attention layer and a double-decoder architecture to adapt high-dimensional self-supervised visual features into compact, generation-friendly latent spaces. FAE achieves competitive FID scores on ImageNet (1.29) and MS-COCO (6.90) for image generation while preserving semantic understanding capabilities of the original pre-trained encoders.
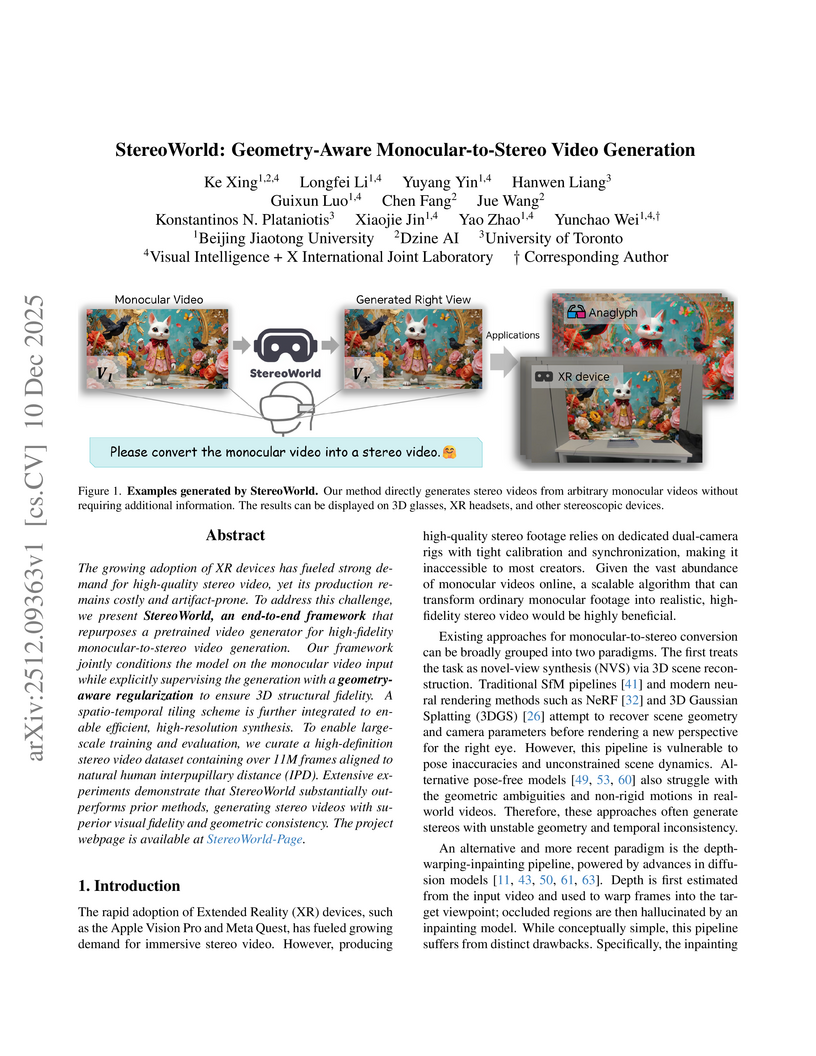
StereoWorld introduces an end-to-end diffusion framework for converting monocular videos into high-fidelity, geometry-aware stereo videos. The method utilizes a novel geometry-aware regularization, integrating disparity and depth supervision, and introduces the large-scale, IPD-aligned StereoWorld-11M dataset, achieving superior visual quality and geometric accuracy, with markedly lower LPIPS and EPE scores compared to prior methods.
10 Dec 2025
Researchers from Columbia University and NYU introduced Online World Modeling (OWM) and Adversarial World Modeling (AWM) to mitigate the train-test gap in world models for gradient-based planning (GBP). These methods enabled GBP to achieve performance comparable to or better than search-based planning algorithms like CEM, while simultaneously reducing computation time by an order of magnitude across various robotic tasks.
10 Dec 2025
UniUGP presents a unified framework for end-to-end autonomous driving, integrating scene understanding, future video generation, and trajectory planning through a hybrid expert architecture. This approach enhances interpretability with Chain-of-Thought reasoning and demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in challenging long-tail scenarios and multimodal capabilities across various benchmarks.
The Astribot Team developed Lumo-1, a Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model that explicitly integrates structured reasoning with physical actions to achieve purposeful robotic control on their Astribot S1 bimanual mobile manipulator. This system exhibits superior generalization to novel objects and instructions, improves reasoning-action consistency through reinforcement learning, and outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in complex, long-horizon, and dexterous tasks.
Researchers from Fudan University and Shanghai Innovation Institute introduced RoPE++, an extension of Rotary Position Embeddings that re-incorporates the previously discarded imaginary component of attention scores to improve long-context modeling in Large Language Models. This method consistently outperforms standard RoPE on various benchmarks and offers significant KV-cache and parameter efficiency.
09 Dec 2025
This work presents a comprehensive engineering guide for designing and deploying production-grade agentic AI workflows, offering nine best practices demonstrated through a multimodal news-to-media generation case study. The approach improves system determinism, reliability, and responsible AI integration, reducing issues like hallucination and enabling scalable, maintainable deployments.
Meituan's LongCat-Image introduces an open-source, bilingual foundation model for image generation and editing, achieving state-of-the-art performance with a compact 6B parameter architecture. The model establishes new industry standards for Chinese character rendering, reaching 90.7% accuracy on a custom benchmark, and demonstrates robust image editing capabilities, often outperforming larger models.
The DEMOCRITUS system establishes a new framework for building large causal models (LCMs) by extracting and structuring textual knowledge from Large Language Models (LLMs) across diverse domains. It leverages a Geometric Transformer to embed and organize vast causal claims into coherent, navigable manifolds, which, unlike raw LLM outputs, exhibit global causal coherence and interpretable local structures.
InfiniteVL, a collaboration between Huazhong University of Science and Technology and Horizon Robotics, introduces a hybrid Vision-Language Model that synergizes linear and sparse attention to enable unlimited multimodal input processing with constant latency and memory footprint. The model achieves performance competitive with Transformer-based VLMs on diverse benchmarks, including information-intensive tasks, while demonstrating significant inference speedups and robust real-time streaming capabilities.
09 Dec 2025
The DualVLN framework addresses Vision-Language Navigation by asynchronously integrating a slow VLM for high-level reasoning and a fast diffusion policy for real-time local control. This "Ground Slow, Move Fast" approach yields enhanced generalization and robust performance, including dynamic obstacle avoidance, across various simulated and real-world robotic platforms.
08 Dec 2025
Researchers from Harvard University and Perplexity conducted a large-scale field study on the real-world adoption and usage of general-purpose AI agents, leveraging hundreds of millions of user interactions with Perplexity's Comet AI-powered browser and its integrated Comet Assistant. The study provides foundational evidence on who uses these agents, their usage intensity, and a detailed breakdown of use cases via a novel hierarchical taxonomy.
Researchers at The Chinese University of Hong Kong and the University of Wisconsin-Madison developed an efficient framework for video multimodal large language models, significantly reducing computational overhead by employing concise reasoning and trainable visual token compression. This approach achieved state-of-the-art performance across video understanding benchmarks while eliminating the need for expensive Chain-of-Thought annotations and supervised fine-tuning.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.