Alibaba Inc.
The Qwen Team at Alibaba Inc. developed a theoretical formulation that justifies token-level optimization for sequence-level rewards in Large Language Model (LLM) reinforcement learning, identifying training–inference discrepancy and policy staleness as key instability factors. Their work also provides empirically validated strategies, including Routing Replay and clipping, to achieve stable and high-performing RL training for Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) LLMs.
Group Sequence Policy Optimization (GSPO) introduces a sequence-level approach to importance sampling in reinforcement learning, stabilizing the training of large language models and enabling more efficient policy updates. This method resolves the instability and model collapse observed in prior token-level algorithms, particularly benefiting Mixture-of-Experts architectures by simplifying their training infrastructure, and has been applied to Qwen3 models.
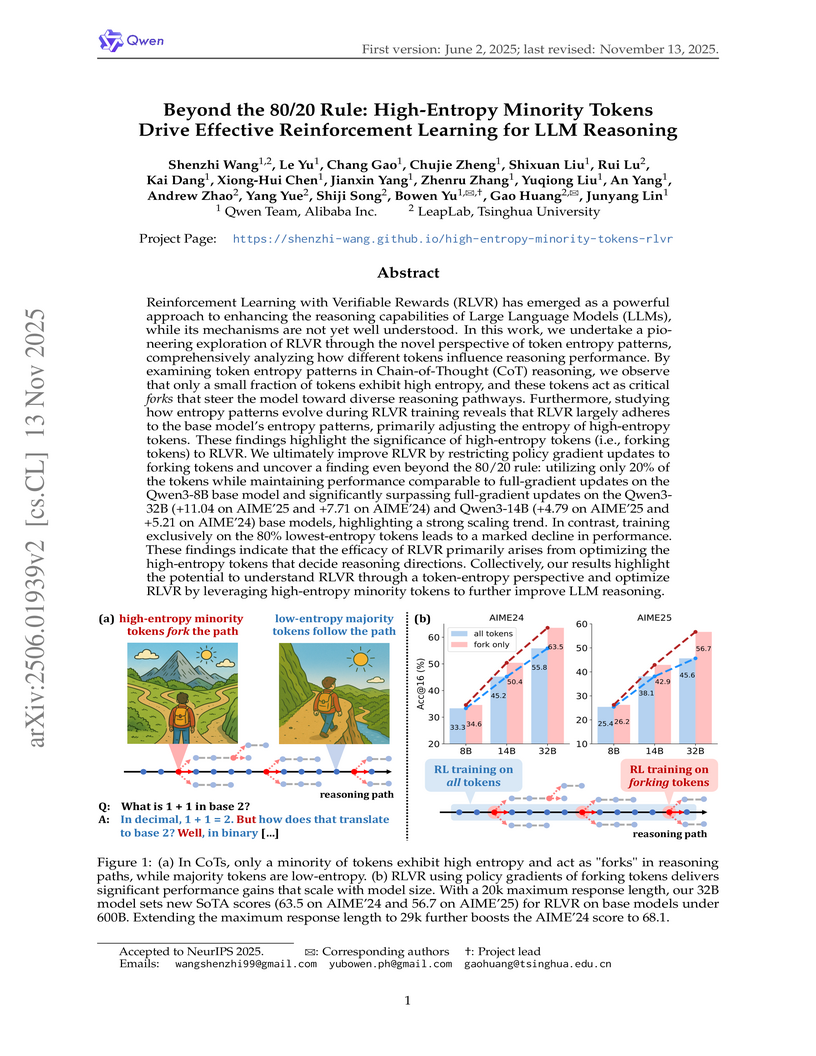
Research from Alibaba Inc.'s Qwen Team and Tsinghua University's LeapLab reveals that in large language models, only a small fraction of high-entropy tokens are critical for reasoning improvements during Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR). By focusing policy gradient updates exclusively on these minority tokens, models achieve superior performance, including setting new state-of-the-art scores on mathematical benchmarks while reducing computational overhead and improving generalization.
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Zhejiang UniversityHunan UniversityAgency for Science, Technology and ResearchAlibaba Inc.Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of MedicineZhejiang University School of MedicineAngelalign Technology Inc.Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Medical Imaging Artificial IntelligenceChina Mobile Group Zhejiang Company Limited
Zhejiang UniversityHunan UniversityAgency for Science, Technology and ResearchAlibaba Inc.Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of MedicineZhejiang University School of MedicineAngelalign Technology Inc.Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Medical Imaging Artificial IntelligenceChina Mobile Group Zhejiang Company LimitedHulu-Med introduces a transparent generalist model for comprehensive medical vision-language understanding across diverse modalities including text, 2D images, 3D volumes, and videos. The model surpassed existing open-source models on 27 of 30 benchmarks and outperformed proprietary systems like GPT-4o on 16 benchmarks, demonstrating competitive performance with accessible training costs.
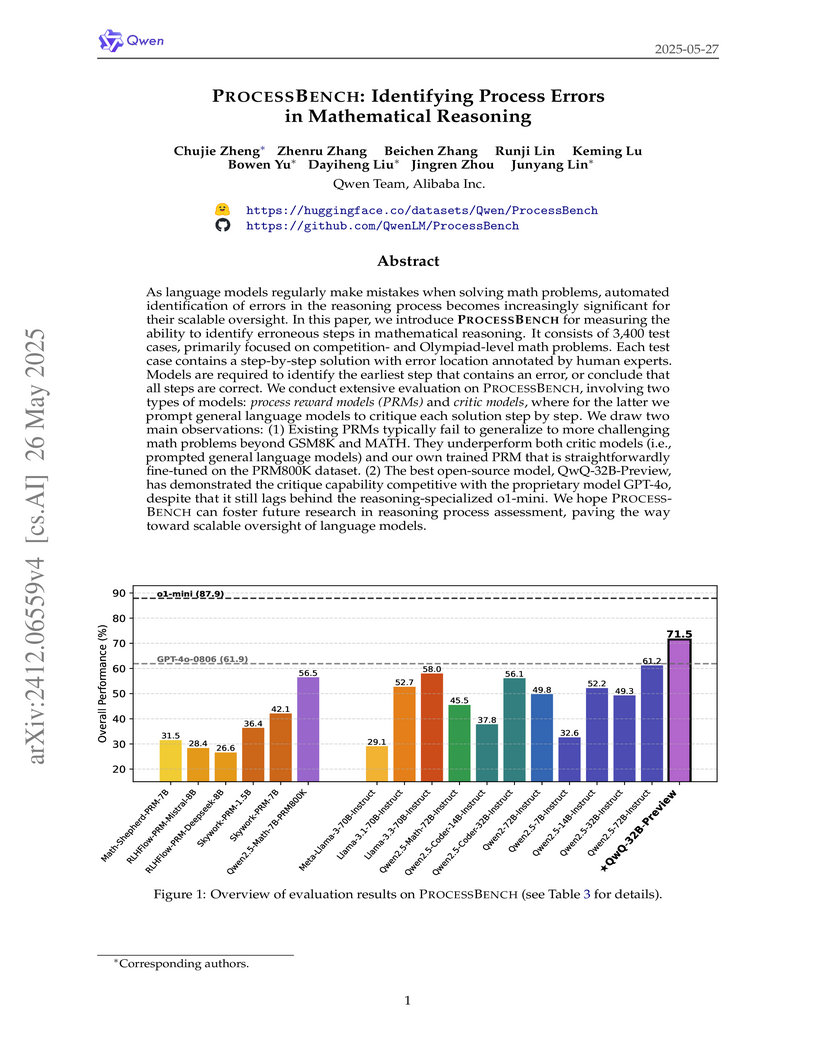
PROCESSBENCH is a new benchmark featuring 3,400 rigorously human-annotated, challenging math problems designed to evaluate language models' ability to identify the earliest erroneous step in a solution. Evaluations indicate that most current process reward models underperform general language models acting as critics, and human-annotated training data is crucial for robust performance in error identification.
Shenzhen Research Institute of Big Data University of Science and Technology of ChinaThe Chinese University of Hong Kong, ShenzhenAlibaba Inc.Shenzhen International Center for Industrial and Applied MathematicsShenzhen International Center for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Shenzhen Research Institute of Big Data
University of Science and Technology of ChinaThe Chinese University of Hong Kong, ShenzhenAlibaba Inc.Shenzhen International Center for Industrial and Applied MathematicsShenzhen International Center for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Shenzhen Research Institute of Big Data
 University of Science and Technology of ChinaThe Chinese University of Hong Kong, ShenzhenAlibaba Inc.Shenzhen International Center for Industrial and Applied MathematicsShenzhen International Center for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Shenzhen Research Institute of Big Data
University of Science and Technology of ChinaThe Chinese University of Hong Kong, ShenzhenAlibaba Inc.Shenzhen International Center for Industrial and Applied MathematicsShenzhen International Center for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Shenzhen Research Institute of Big DataCoRT (Code-Optimized Reasoning Training) is a post-training framework that teaches Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) to efficiently integrate computational tools, specifically Code Interpreters, for complex mathematical problem-solving. Developed by researchers from Alibaba, USTC, and CUHK Shenzhen, the framework achieved substantial improvements in accuracy and reduced token usage by 30-50% across challenging benchmarks, demonstrating a qualitative shift to proactive tool utilization.
12 Jun 2025
The CoRT framework enables Large Reasoning Models to efficiently leverage Code Interpreters for complex mathematical reasoning, achieving higher accuracy and significantly reducing token usage by optimizing interaction patterns. It introduces a novel hint-engineering data synthesis method and an end-to-end training pipeline combining supervised, rejection, and reinforcement learning.
The AUTOIF method, developed by the Qwen Team at Alibaba Inc., introduces a scalable and reliable approach for automatically generating high-quality training data to enhance the instruction-following capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). This framework allows LLMs to achieve state-of-the-art performance, including the first instance of an LLM surpassing 90% accuracy on the IFEval benchmark, while preserving general abilities.
Researchers from Alibaba, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, and Fudan University developed AI Hospital, a multi-agent simulator for benchmarking Large Language Models in dynamic medical diagnostic scenarios. Their evaluation revealed a substantial performance gap for LLMs in interactive settings compared to single-step methods, yet demonstrated improved accuracy through collaborative diagnosis.
This framework introduces a robust Text-to-SQL generation method that addresses schema linking risks, achieving 67.21% execution accuracy on the BIRD dataset and 87.9% on Spider using GPT-4o, and maintaining strong performance with cost-effective DeepSeek models by significantly reducing token consumption.
Click-through rate~(CTR) prediction, whose goal is to estimate the
probability of the user clicks, has become one of the core tasks in advertising
systems. For CTR prediction model, it is necessary to capture the latent user
interest behind the user behavior data. Besides, considering the changing of
the external environment and the internal cognition, user interest evolves over
time dynamically. There are several CTR prediction methods for interest
modeling, while most of them regard the representation of behavior as the
interest directly, and lack specially modeling for latent interest behind the
concrete behavior. Moreover, few work consider the changing trend of interest.
In this paper, we propose a novel model, named Deep Interest Evolution
Network~(DIEN), for CTR prediction. Specifically, we design interest extractor
layer to capture temporal interests from history behavior sequence. At this
layer, we introduce an auxiliary loss to supervise interest extracting at each
step. As user interests are diverse, especially in the e-commerce system, we
propose interest evolving layer to capture interest evolving process that is
relative to the target item. At interest evolving layer, attention mechanism is
embedded into the sequential structure novelly, and the effects of relative
interests are strengthened during interest evolution. In the experiments on
both public and industrial datasets, DIEN significantly outperforms the
state-of-the-art solutions. Notably, DIEN has been deployed in the display
advertisement system of Taobao, and obtained 20.7\% improvement on CTR.
The paper provides a comprehensive survey of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) applied to recommender systems, categorizing over 100 representative studies based on information types and recommendation tasks. It systematically reviews methodologies, identifies common design principles, and outlines nine key future research directions for the field.
15 Oct 2025
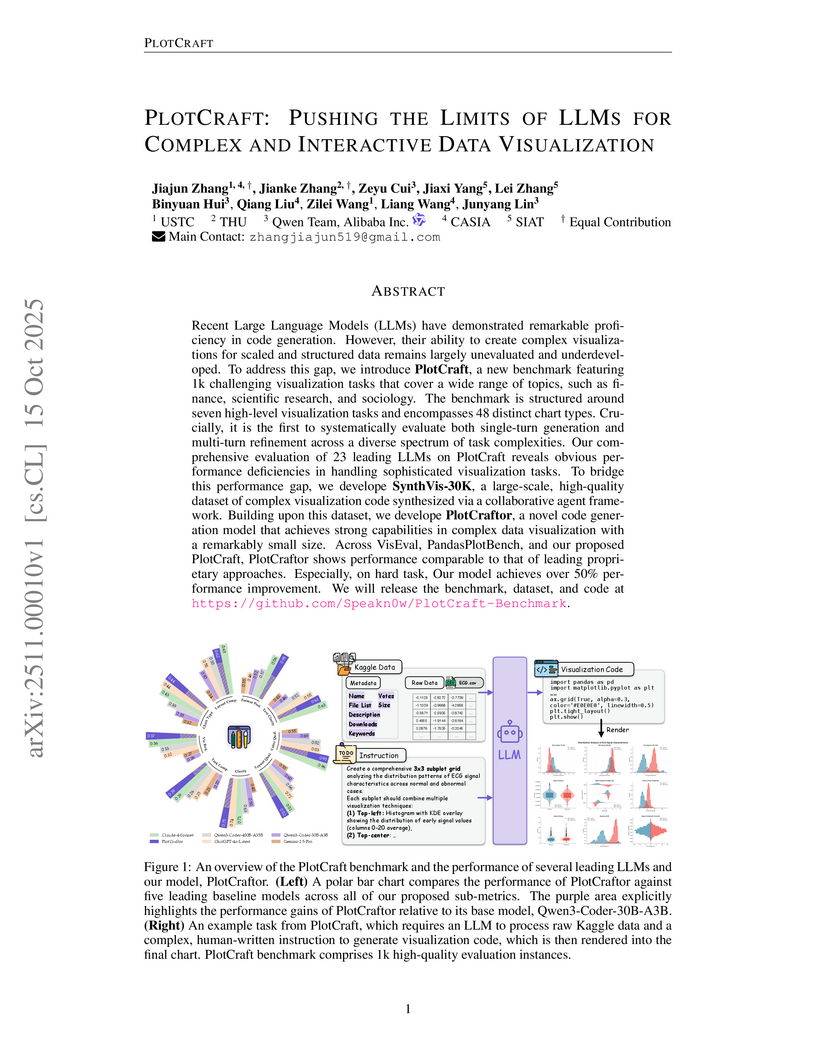
Recent Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable profi- ciency in code generation. However, their ability to create complex visualiza- tions for scaled and structured data remains largely unevaluated and underdevel- oped. To address this gap, we introduce PlotCraft, a new benchmark featuring 1k challenging visualization tasks that cover a wide range of topics, such as fi- nance, scientific research, and sociology. The benchmark is structured around seven high-level visualization tasks and encompasses 48 distinct chart types. Cru- cially, it is the first to systematically evaluate both single-turn generation and multi-turn refinement across a diverse spectrum of task complexities. Our com- prehensive evaluation of 23 leading LLMs on PlotCraft reveals obvious per- formance deficiencies in handling sophisticated visualization tasks. To bridge this performance gap, we develope SynthVis-30K, a large-scale, high-quality dataset of complex visualization code synthesized via a collaborative agent frame- work. Building upon this dataset, we develope PlotCraftor, a novel code gener- ation model that achieves strong capabilities in complex data visualization with a remarkably small size. Across VisEval, PandasPlotBench, and our proposed PlotCraft, PlotCraftor shows performance comparable to that of leading propri- etary approaches. Especially, on hard task, Our model achieves over 50% per- formance improvement. We will release the benchmark, dataset, and code at this https URL.
31 Aug 2021
Researchers at Alibaba Supply Chain Platform deployed deep reinforcement learning (DRL) for dynamic pricing on Tmall.com, a large-scale e-commerce platform. Field experiments demonstrated that DRL agents, particularly those using continuous pricing with DDPG, consistently outperformed human expert pricing strategies, achieving higher revenue and profit conversion rates for thousands of products over several months.
12 Oct 2020
Researchers from Alibaba Inc. and UC Santa Cruz developed unsupervised graph-based algorithms, Swing and Surprise, to construct large-scale product graphs capturing substitute and complementary relationships for e-commerce recommendations. These algorithms led to substantial improvements in online metrics on Taobao, including a +33.2% increase in Click Through Rate and a +62.9% increase in Payment Per Thousand Impressions in a hybrid application.
Large language model (LLM) role-playing has gained widespread attention.
Authentic character knowledge is crucial for constructing realistic LLM
role-playing agents. However, existing works usually overlook the exploration
of LLMs' ability to detect characters' known knowledge errors (KKE) and unknown
knowledge errors (UKE) while playing roles, which would lead to low-quality
automatic construction of character trainable corpus. In this paper, we propose
RoleKE-Bench to evaluate LLMs' ability to detect errors in KKE and UKE. The
results indicate that even the latest LLMs struggle to detect these two types
of errors effectively, especially when it comes to familiar knowledge. We
experimented with various reasoning strategies and propose an agent-based
reasoning method, Self-Recollection and Self-Doubt (S2RD), to explore
further the potential for improving error detection capabilities. Experiments
show that our method effectively improves the LLMs' ability to detect error
character knowledge, but it remains an issue that requires ongoing attention.
Online Merging Optimizers, developed by the Qwen Team at Alibaba Inc., improve Large Language Model (LLM) alignment by simultaneously boosting human preference rewards and mitigating the "alignment tax." This is achieved by integrating model merging directly into each optimization step of Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), demonstrating superior performance across various LLM architectures and sizes compared to existing methods.
Researchers developed the Trajectory Volatility (TV) Score, a method for out-of-distribution (OOD) detection in generative language models performing mathematical reasoning. The TV Score leverages the dynamic shifts of embedding representations across model layers to address limitations of static embedding methods and improves OOD detection AUROC by over 10 percentage points and reduces FPR95 by over 80% in far-shift scenarios compared to baselines.
The rapid development of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) has exposed vulnerabilities to various adversarial attacks. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of jailbreaking research targeting both LLMs and MLLMs, highlighting recent advancements in evaluation benchmarks, attack techniques and defense strategies. Compared to the more advanced state of unimodal jailbreaking, multimodal domain remains underexplored. We summarize the limitations and potential research directions of multimodal jailbreaking, aiming to inspire future research and further enhance the robustness and security of MLLMs.
Researchers from Zhejiang University, State Street Technology, and Salesforce Research systematically evaluated Transformer architectures for long-term time series forecasting, identifying key design choices for optimal performance. The study found that bi-directional attention with joint-attention, complete forecasting aggregation, and a direct-mapping paradigm consistently yield superior results. A combined model built on these principles outperformed several existing state-of-the-art models.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.