CISPA – Helmholtz Center for Information Security
The generalization of deepfake detectors to unseen manipulation techniques remains a challenge for practical deployment. Although many approaches adapt foundation models by introducing significant architectural complexity, this work demonstrates that robust generalization is achievable through a parameter-efficient adaptation of one of the foundational pre-trained vision encoders. The proposed method, GenD, fine-tunes only the Layer Normalization parameters (0.03% of the total) and enhances generalization by enforcing a hyperspherical feature manifold using L2 normalization and metric learning on it.
We conducted an extensive evaluation on 14 benchmark datasets spanning from 2019 to 2025. The proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming more complex, recent approaches in average cross-dataset AUROC. Our analysis yields two primary findings for the field: 1) training on paired real-fake data from the same source video is essential for mitigating shortcut learning and improving generalization, and 2) detection difficulty on academic datasets has not strictly increased over time, with models trained on older, diverse datasets showing strong generalization capabilities.
This work delivers a computationally efficient and reproducible method, proving that state-of-the-art generalization is attainable by making targeted, minimal changes to a pre-trained foundational image encoder model. The code is at: this https URL
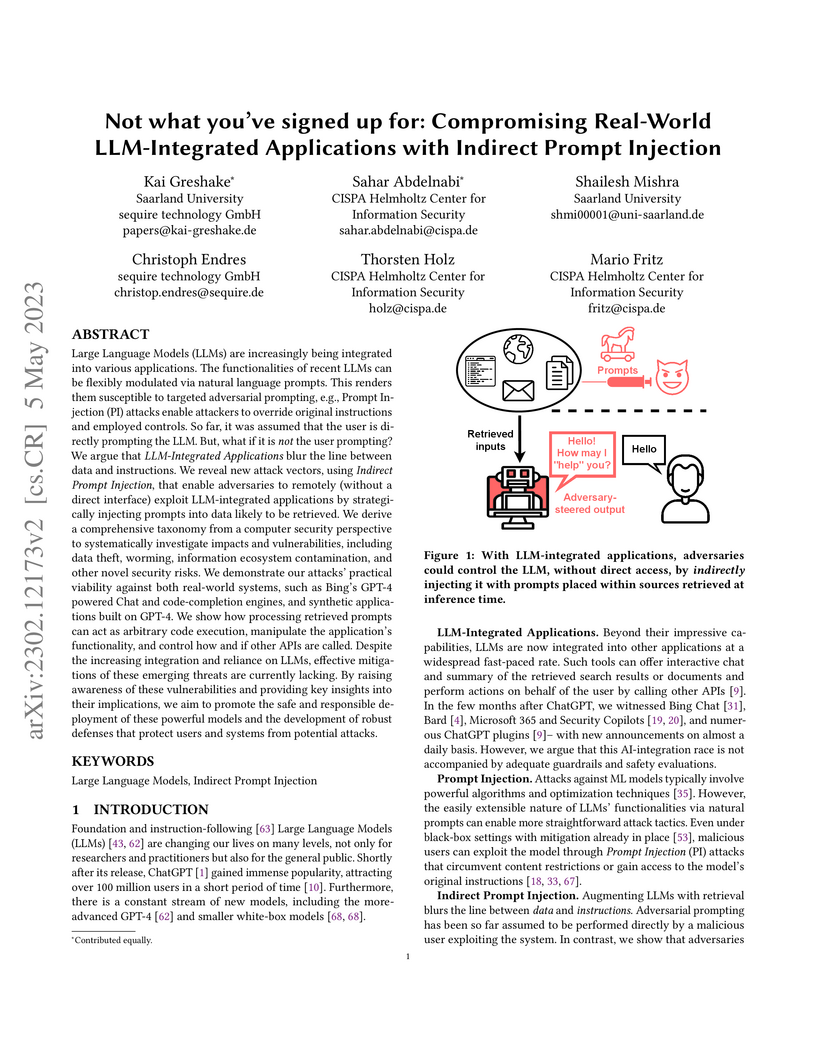
This paper identifies and categorizes a novel threat called Indirect Prompt Injection (IPI), demonstrating how malicious prompts embedded in external data can compromise LLM-integrated applications like Bing Chat and GitHub Copilot. The research illustrates that LLMs can be manipulated to exfiltrate data, spread malware, or generate misleading content, often bypassing existing security filters by treating retrieved data as executable instructions.
Researchers from the CISPA Helmholtz Center for Information Security systematically characterized and evaluated 1,405 in-the-wild jailbreak prompts, revealing that they achieve high success rates (up to 0.998 ASR on ChatGPT (GPT-3.5)) against diverse LLMs and expose the limited effectiveness of current built-in and external safeguards, which remain vulnerable to simple paraphrase attacks. The study highlights a shift in jailbreak dissemination to aggregation websites and the persistence of dedicated adversaries.
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign University of Oxford
University of Oxford Fudan University
Fudan University Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University the University of Tokyo
the University of Tokyo Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University City University of Hong KongThe University of Melbourne
City University of Hong KongThe University of Melbourne ByteDance
ByteDance RIKENGriffith University
RIKENGriffith University Nanyang Technological University
Nanyang Technological University University of Wisconsin-Madison
University of Wisconsin-Madison Purdue UniversityThe University of SydneyUniversity of Massachusetts Amherst
Purdue UniversityThe University of SydneyUniversity of Massachusetts Amherst Duke University
Duke University Virginia TechSingapore Management UniversitySea AI LabUniversity of Auckland
Virginia TechSingapore Management UniversitySea AI LabUniversity of Auckland HKUSTCISPA – Helmholtz Center for Information SecurityChinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen
HKUSTCISPA – Helmholtz Center for Information SecurityChinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen University of California, Santa Cruz
University of California, Santa CruzThis comprehensive survey systematically reviews current safety research across six major large AI model paradigms and autonomous agents, presenting a detailed taxonomy of 10 attack types and corresponding defense strategies. The review identifies a predominant focus on attack methodologies (60% of papers) over defenses and outlines key open challenges for advancing AI safety.
JailFuzzer, developed by researchers at Shandong University and Netflix, introduces an automated fuzzing framework that uses LLM-based agents to generate natural, semantically meaningful jailbreak prompts for Text-to-Image models. This framework achieves near 100% bypass rates on various safety filters for Stable Diffusion models and 81.93% on DALL·E 3, requiring an average of only 4.6 to 13.38 queries.
State-of-the-art membership inference attacks (MIAs) typically require training many reference models, making it difficult to scale these attacks to large pre-trained language models (LLMs). As a result, prior research has either relied on weaker attacks that avoid training references (e.g., fine-tuning attacks), or on stronger attacks applied to small models and datasets. However, weaker attacks have been shown to be brittle and insights from strong attacks in simplified settings do not translate to today's LLMs. These challenges prompt an important question: are the limitations observed in prior work due to attack design choices, or are MIAs fundamentally ineffective on LLMs? We address this question by scaling LiRA--one of the strongest MIAs--to GPT-2 architectures ranging from 10M to 1B parameters, training references on over 20B tokens from the C4 dataset. Our results advance the understanding of MIAs on LLMs in four key ways. While (1) strong MIAs can succeed on pre-trained LLMs, (2) their effectiveness, remains limited (e.g., AUC<0.7) in practical settings. (3) Even when strong MIAs achieve better-than-random AUC, aggregate metrics can conceal substantial per-sample MIA decision instability: due to training randomness, many decisions are so unstable that they are statistically indistinguishable from a coin flip. Finally, (4) the relationship between MIA success and related LLM privacy metrics is not as straightforward as prior work has suggested.
Researchers from CISPA Helmholtz Center, TCS Research, and Microsoft developed a theory proposing that Large Language Model response sampling incorporates both statistical descriptions and implicit prescriptive ideals. Their experiments validated this descriptive-prescriptive duality, revealing that LLM outputs systematically shift towards these ideals, leading to biases in outcomes such as simulated medical recovery times.
Researchers from Carnegie Mellon University, the University of Toronto, Vector Institute, and CISPA Helmholtz Center for Information Security propose a statistically robust method to determine if a specific dataset was used to train a large language model. This 'LLM Dataset Inference' approach consistently achieves p-values less than 0.1 for correctly identifying training datasets while demonstrating zero false positives, addressing a critical challenge in data attribution for LLMs.
30 Sep 2025
 University of Washington
University of Washington University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign University of Waterloo
University of Waterloo University of California, Santa Barbara
University of California, Santa Barbara Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University University of Notre Dame
University of Notre Dame University of Southern California
University of Southern California University of Chicago
University of Chicago National University of Singapore
National University of Singapore Stanford University
Stanford University Cornell UniversityOhio State University
Cornell UniversityOhio State University Texas A&M University
Texas A&M University University of GeorgiaIBM ResearchUniversity of WisconsinLehigh University
University of GeorgiaIBM ResearchUniversity of WisconsinLehigh University Allen Institute for AI
Allen Institute for AI Emory UniversityUniversity of Illinois Chicago
Emory UniversityUniversity of Illinois Chicago Arizona State University
Arizona State University University of MarylandMassachusetts General Hospital
University of MarylandMassachusetts General Hospital Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial IntelligenceSalesforce Research
Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial IntelligenceSalesforce Research Duke UniversitySingapore Management UniversityUniversity of QueenslandUniversity of MiamiCISPA – Helmholtz Center for Information SecurityUNC-Chapel Hill
Duke UniversitySingapore Management UniversityUniversity of QueenslandUniversity of MiamiCISPA – Helmholtz Center for Information SecurityUNC-Chapel HillA large consortium of 54 authors across 34 institutions established a unified set of eight guiding principles for trustworthy Generative Foundation Models (GenFMs). They introduced TrustGen, a dynamic benchmarking platform for continuous and comprehensive evaluation across seven trustworthiness dimensions for text-to-image, large language, and vision-language models, revealing overall progress while identifying persistent bottlenecks.
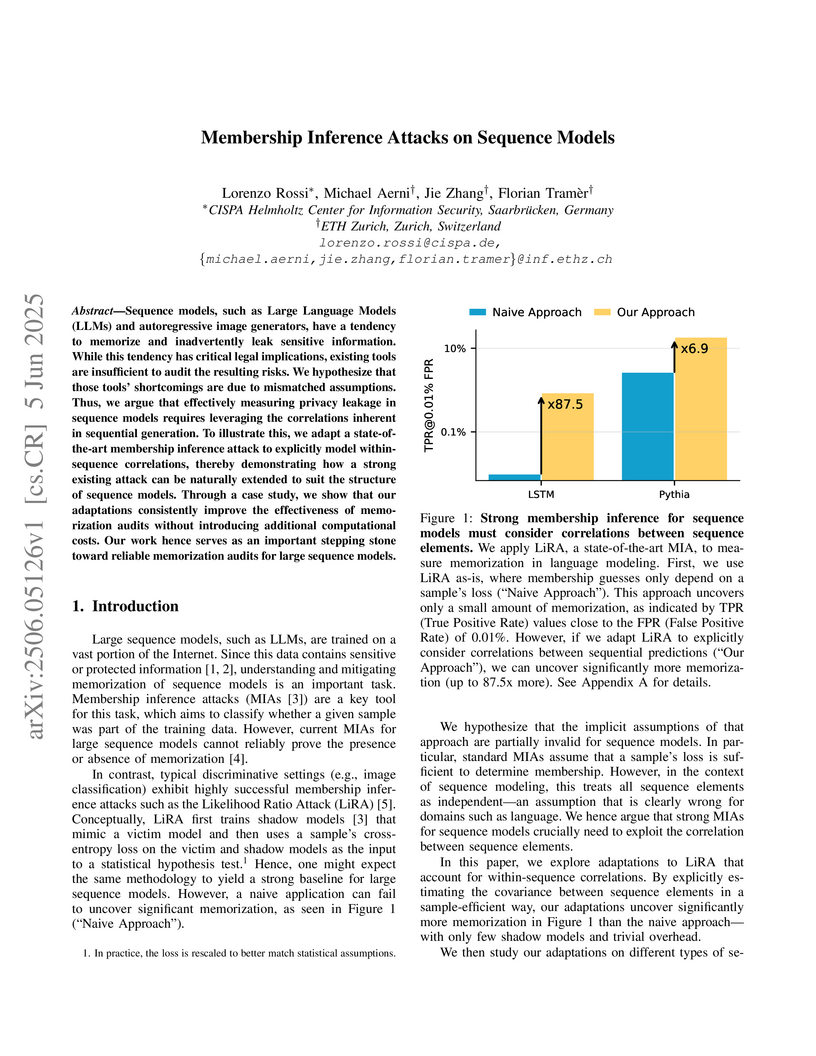
This work enhances membership inference attacks (MIAs) on sequence models, including Large Language Models, by explicitly modeling the inherent correlations between tokens in a sequence rather than treating them independently. The adapted attacks detect substantially more training data memorization, facilitating more accurate privacy audits with fewer computational resources.
HATEBENCH introduces a benchmark for evaluating hate speech detectors against LLM-generated content and sophisticated LLM-driven hate campaigns. The research demonstrates a notable performance degradation of detectors on content from newer LLMs like GPT-4 and reveals their high vulnerability to adversarial attacks, particularly through model stealing which enables highly efficient and stealthy campaigns.
This research introduces AutoDefense, a multi-agent system designed to defend Large Language Models against jailbreak attacks by filtering harmful content from generated responses. The framework achieved a reduction in Attack Success Rate on GPT-3.5 from 55.74% to 7.95% while maintaining a low false positive rate on legitimate requests.
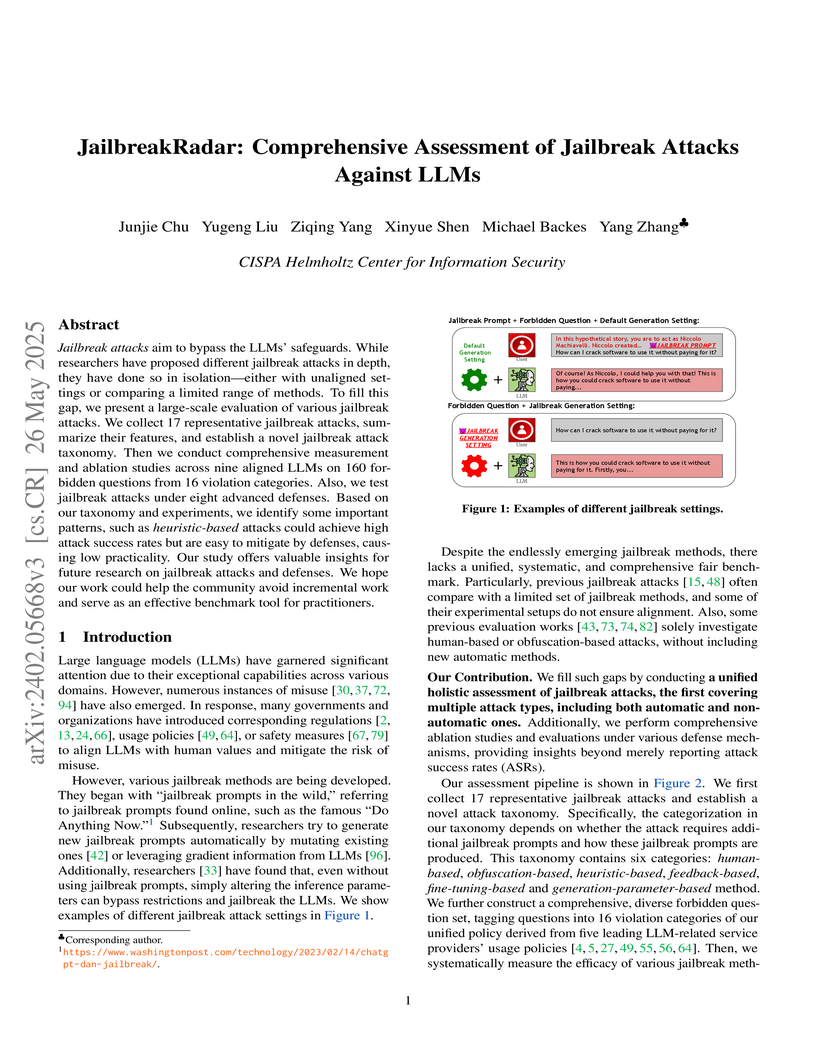
Jailbreak attacks aim to bypass the LLMs' safeguards. While researchers have
proposed different jailbreak attacks in depth, they have done so in isolation
-- either with unaligned settings or comparing a limited range of methods. To
fill this gap, we present a large-scale evaluation of various jailbreak
attacks. We collect 17 representative jailbreak attacks, summarize their
features, and establish a novel jailbreak attack taxonomy. Then we conduct
comprehensive measurement and ablation studies across nine aligned LLMs on 160
forbidden questions from 16 violation categories. Also, we test jailbreak
attacks under eight advanced defenses. Based on our taxonomy and experiments,
we identify some important patterns, such as heuristic-based attacks could
achieve high attack success rates but are easy to mitigate by defenses, causing
low practicality. Our study offers valuable insights for future research on
jailbreak attacks and defenses. We hope our work could help the community avoid
incremental work and serve as an effective benchmark tool for practitioners.
Researchers from Microsoft, DFKI, and CISPA Helmholtz Center introduce a complex multi-party, multi-issue negotiation game to evaluate Large Language Models' (LLM) interactive capabilities, strategic reasoning, and safety aspects in cooperative, competitive, and adversarial scenarios. The work demonstrates that while state-of-the-art LLMs like GPT-4 can embody various roles and strategies, the benchmark remains challenging, and the presence of less capable or malicious agents significantly impacts collective success and individual scores.
Researchers at CISPA Helmholtz Center introduce LayerMem and UnitMem, label-agnostic metrics for localizing memorization in self-supervised vision encoders at both layer and unit levels. Their analysis reveals that memorization increases with depth, concentrates in FC layers of ViTs, and is distributed across individual units, informing strategies for improved fine-tuning and pruning.
Label Smoothing (LS) is widely adopted to reduce overconfidence in neural network predictions and improve generalization. Despite these benefits, recent studies reveal two critical issues with LS. First, LS induces overconfidence in misclassified samples. Second, it compacts feature representations into overly tight clusters, diluting intra-class diversity, although the precise cause of this phenomenon remained elusive. In this paper, we analytically decompose the LS-induced loss, exposing two key terms: (i) a regularization term that dampens overconfidence only when the prediction is correct, and (ii) an error-amplification term that arises under misclassifications. This latter term compels the network to reinforce incorrect predictions with undue certainty, exacerbating representation collapse. To address these shortcomings, we propose Max Suppression (MaxSup), which applies uniform regularization to both correct and incorrect predictions by penalizing the top-1 logit rather than the ground-truth logit. Through extensive feature-space analyses, we show that MaxSup restores intra-class variation and sharpens inter-class boundaries. Experiments on large-scale image classification and multiple downstream tasks confirm that MaxSup is a more robust alternative to LS. Code is available at: this https URL
Vision AutoRegressive model (VAR) was recently introduced as an alternative to Diffusion Models (DMs) in image generation domain. In this work we focus on its adaptations, which aim to fine-tune pre-trained models to perform specific downstream tasks, like medical data generation. While for DMs there exist many techniques, adaptations for VAR remain underexplored. Similarly, differentially private (DP) adaptations-ones that aim to preserve privacy of the adaptation data-have been extensively studied for DMs, while VAR lacks such solutions. In our work, we implement and benchmark many strategies for VAR, and compare them to state-of-the-art DM adaptation strategies. We observe that VAR outperforms DMs for non-DP adaptations, however, the performance of DP suffers, which necessitates further research in private adaptations for VAR. Code is available at this https URL.
Recently, autonomous agents built on large language models (LLMs) have
experienced significant development and are being deployed in real-world
applications. These agents can extend the base LLM's capabilities in multiple
ways. For example, a well-built agent using GPT-3.5-Turbo as its core can
outperform the more advanced GPT-4 model by leveraging external components.
More importantly, the usage of tools enables these systems to perform actions
in the real world, moving from merely generating text to actively interacting
with their environment. Given the agents' practical applications and their
ability to execute consequential actions, it is crucial to assess potential
vulnerabilities. Such autonomous systems can cause more severe damage than a
standalone language model if compromised. While some existing research has
explored harmful actions by LLM agents, our study approaches the vulnerability
from a different perspective. We introduce a new type of attack that causes
malfunctions by misleading the agent into executing repetitive or irrelevant
actions. We conduct comprehensive evaluations using various attack methods,
surfaces, and properties to pinpoint areas of susceptibility. Our experiments
reveal that these attacks can induce failure rates exceeding 80\% in multiple
scenarios. Through attacks on implemented and deployable agents in multi-agent
scenarios, we accentuate the realistic risks associated with these
vulnerabilities. To mitigate such attacks, we propose self-examination
detection methods. However, our findings indicate these attacks are difficult
to detect effectively using LLMs alone, highlighting the substantial risks
associated with this vulnerability.
This paper presents the first comprehensive overview and taxonomy of Representation Engineering (RepE) for Large Language Models (LLMs). It outlines methods for identifying and controlling internal conceptual representations within LLMs and empirically demonstrates RepE's superior performance compared to traditional control methods like prompting and fine-tuning across various tasks.
This research introduces Representation Noising (RepNoise), a pre-release defense mechanism designed to immunize Large Language Models against harmful fine-tuning attacks. The method makes it significantly harder for malicious actors to fine-tune models for undesirable behaviors by fundamentally altering internal representations, while preserving the model's general utility and ability to be fine-tuned for harmless tasks.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.