Cracow University of Technology
Multifractality in time series analysis characterizes the presence of multiple scaling exponents, indicating heterogeneous temporal structures and complex dynamical behaviors beyond simple monofractal models. In the context of digital currency markets, multifractal properties arise due to the interplay of long-range temporal correlations and heavy-tailed distributions of returns, reflecting intricate market microstructure and trader interactions. Incorporating multifractal analysis into the modeling of cryptocurrency price dynamics enhances the understanding of market inefficiencies, may improve volatility forecasting and facilitate the detection of critical transitions or regime shifts. Based on the multifractal cross-correlation analysis (MFCCA) whose spacial case is the multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis (MFDFA), as the most commonly used practical tools for quantifying multifractality, in the present contribution a recently proposed method of disentangling sources of multifractality in time series was applied to the most representative instruments from the digital market. They include Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), decentralized exchanges (DEX) and non-fungible tokens (NFT). The results indicate the significant role of heavy tails in generating a broad multifractal spectrum. However, they also clearly demonstrate that the primary source of multifractality are temporal correlations in the series, and without them, multifractality fades out. It appears characteristic that these temporal correlations, to a large extent, do not depend on the thickness of the tails of the fluctuation distribution. These observations, made here in the context of the digital currency market, provide a further strong argument for the validity of the proposed methodology of disentangling sources of multifractality in time series.
Based on the cryptocurrency market dynamics, this study presents a general methodology for analyzing evolving correlation structures in complex systems using the q-dependent detrended cross-correlation coefficient \rho(q,s). By extending traditional metrics, this approach captures correlations at varying fluctuation amplitudes and time scales. The method employs q-dependent minimum spanning trees (qMSTs) to visualize evolving network structures. Using minute-by-minute exchange rate data for 140 cryptocurrencies on Binance (Jan 2021-Oct 2024), a rolling window analysis reveals significant shifts in qMSTs, notably around April 2022 during the Terra/Luna crash. Initially centralized around Bitcoin (BTC), the network later decentralized, with Ethereum (ETH) and others gaining prominence. Spectral analysis confirms BTC's declining dominance and increased diversification among assets. A key finding is that medium-scale fluctuations exhibit stronger correlations than large-scale ones, with qMSTs based on the latter being more decentralized. Properly exploiting such facts may offer the possibility of a more flexible optimal portfolio construction. Distance metrics highlight that major disruptions amplify correlation differences, leading to fully decentralized structures during crashes. These results demonstrate qMSTs' effectiveness in uncovering fluctuation-dependent correlations, with potential applications beyond finance, including biology, social and other complex systems.
Quantifying the complex/multifractal organization of the brain signals is crucial to fully understanding the brain processes and structure. In this contribution, we performed the multifractal analysis of the electroencephalographic (EEG) data obtained from a controlled multiple sclerosis (MS) study, focusing on the correlation between the degree of multifractality, disease duration, and disability level. Our results reveal a significant correspondence between the complexity of the time series and multiple sclerosis development, quantified respectively by scaling exponents and the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS). Namely, for some brain regions, a well-developed multifractality and little persistence of the time series were identified in patients with a high level of disability, whereas the control group and patients with low EDSS were characterised by persistence and monofractality of the signals. The analysis of the cross-correlations between EEG signals supported these results, with the most significant differences identified for patients with EDSS >1 and the combined group of patients with EDSS ≤1 and controls. No association between the multifractality and disease duration was observed, indicating that the multifractal organisation of the data is a hallmark of developing the disease. The observed complexity/multifractality of EEG signals is hypothetically a result of neuronal compensation -- i.e., of optimizing neural processes in the presence of structural brain degeneration. The presented study is highly relevant due to the multifractal formalism used to quantify complexity and due to scarce resting-state EEG evidence for cortical reorganization associated with compensation.
This paper investigates the temporal patterns of activity in the cryptocurrency market with a focus on Bitcoin, Ethereum, Dogecoin, and WINkLink from January 2020 to December 2022. Market activity measures - logarithmic returns, volume, and transaction number, sampled every 10 seconds, were divided into intraday and intraweek periods and then further decomposed into recurring and noise components via correlation matrix formalism. The key findings include the distinctive market behavior from traditional stock markets due to the nonexistence of trade opening and closing. This was manifest in three enhanced-activity phases aligning with Asian, European, and U.S. trading sessions. An intriguing pattern of activity surge in 15-minute intervals, particularly at full hours, was also noticed, implying the potential role of algorithmic trading. Most notably, recurring bursts of activity in bitcoin and ether were identified to coincide with the release times of significant U.S. macroeconomic reports such as Nonfarm payrolls, Consumer Price Index data, and Federal Reserve statements. The most correlated daily patterns of activity occurred in 2022, possibly reflecting the documented correlations with U.S. stock indices in the same period. Factors that are external to the inner market dynamics are found to be responsible for the repeatable components of the market dynamics, while the internal factors appear to be substantially random, which manifests itself in a good agreement between the empirical eigenvalue distributions in their bulk and the random matrix theory predictions expressed by the Marchenko-Pastur distribution. The findings reported support the growing integration of cryptocurrencies into the global financial markets.
Cellular automata can simulate many complex physical phenomena using the power of simple rules. The presented methodological platform expresses the concept of programmable matter in which Newtons laws of motion are one of examples. Energy has been introduced as the equivalent of the Game of Life mass, which can be treated as first level of approximation. The temperature presence and propagation was calculated for various lattice topology and boundary conditions by using the Shannon entropy measure. The conducted study provides strong evidence that despite not fulfillment the principle of mass and energy conservation, the entropy, mass distribution and temperatures approaches thermodynamic equilibrium. In addition, the described cellular automata system transits from positive to a negative temperatures that stabilizes and can be treated as a signature of system dynamical equilibrium. Furthermore the system dynamics was presented in case of few species of cellular automata competing for maximum presence on given lattice with different boundary conditions.
26 Feb 2025
We present a new model for jet quenching in a quark gluon plasma (QGP). The
jet energy loss has two steps. The initial jet parton with a high virtuality
loses energy by a perturbative vacuum parton shower modified by medium
interactions until it becomes on shell. Subsequent energy loss originates from
elastic and radiative collisions with the medium constituents. Coherency of the
radiative collisions is achieved by starting with virtual gluons that act as
field dressing of the initial jet parton. These are formed according to a
Gunion-Bertsch seed. The QCD version of the LPM effect is obtained by
increasing the phase of the virtual gluons through elastic scatterings with the
medium. Above a phase threshold, the virtual gluons will be formed and can
produce coherent radiation themselves. The model has been implemented in a
Monte Carlo code and is validated by successfully reproducing the BDMPS-Z
prediction for the energy spectrum of radiated gluons in a static medium.
Results for the more realistic case, in which the assumptions of the BDMPS-Z
approach are released, are also shown. We investigate the influence of various
parameters on the energy spectrum and the transverse momentum distribution,
such as the in-medium quark masses, the energy transfer in the recoil process,
and the phase accumulation criteria, especially for low and intermediate energy
gluons.
18 Sep 2017
In this paper the analysis of the result of numerical simulations of pasta phases using algebraic topology methods is presented. These considerations suggest that some phases can be further split into (sub)phases and therefore should be more refined in numerical simulations. The results presented in the paper can also be used to relate the Euler characteristic from numerical simulations to the geometry of the phases. The Betti numbers are used as they provide finer characterization of the phases. It is also shown that different boundary conditions give different outcomes.
Interpretation of electrocardiography (ECG) signals is required for diagnosing cardiac arrhythmia. Recently, machine learning techniques have been applied for automated computer-aided diagnosis. Machine learning tasks can be divided into regression and classification. Regression can be used for noise and artifacts removal as well as resolve issues of missing data from low sampling frequency. Classification task concerns the prediction of output diagnostic classes according to expert-labeled input classes. In this work, we propose a deep neural network model capable of solving regression and classification tasks. Moreover, we combined the two approaches, using unlabeled and labeled data, to train the model. We tested the model on the MIT-BIH Arrhythmia database. Our method showed high effectiveness in detecting cardiac arrhythmia based on modified Lead II ECG records, as well as achieved high quality of ECG signal approximation. For the former, our method attained overall accuracy of 87:33% and balanced accuracy of 80:54%, on par with reference approaches. For the latter, application of self-supervised learning allowed for training without the need for expert labels. The regression model yielded satisfactory performance with fairly accurate prediction of QRS complexes. Transferring knowledge from regression to the classification task, our method attained higher overall accuracy of 87:78%.
22 Sep 2018
Fractal structures pervade nature and are receiving increasing engineering attention towards the realization of broadband resonators and antennas. We show that fractal resonators can support the emergence of high-dimensional chaotic dynamics even in the context of an elementary, single-transistor oscillator circuit. Sierpiński gaskets of variable depth are constructed using discrete capacitors and inductors, whose values are scaled according to a simple sequence. It is found that in regular fractals of this kind each iteration effectively adds a conjugate pole/zero pair, yielding gradually more complex and broader frequency responses, which can also be implemented as much smaller Foster equivalent networks. The resonators are instanced in the circuit as one-port devices, replacing the inductors found in the initial version of the oscillator. By means of a highly simplified numerical model, it is shown that increasing the fractal depth elevates the dimension of the chaotic dynamics, leading to high-order hyperchaos. This result is overall confirmed by SPICE simulations and experiments, which however also reveal that the non-ideal behavior of physical components hinders obtaining high-dimensional dynamics. The issue could be practically mitigated by building the Foster equivalent networks rather than the verbatim fractals. Furthermore, it is shown that considerably more complex resonances, and consequently richer dynamics, can be obtained by rendering the fractal resonators irregular through reshuffling the inductors, or even by inserting a limited number of focal imperfections. The present results draw attention to the potential usefulness of fractal resonators for generating high-dimensional chaotic dynamics, and underline the importance of irregularities and component non-idealities.
12 Jun 2023
We present the Julia package Manifolds.jl, providing a fast and easy-to-use
library of Riemannian manifolds and Lie groups. This package enables working
with data defined on a Riemannian manifold, such as the circle, the sphere,
symmetric positive definite matrices, or one of the models for hyperbolic
spaces. We introduce a common interface, available in ManifoldsBase.jl, with
which new manifolds, applications, and algorithms can be implemented. We
demonstrate the utility of Manifolds.jl using B\'ezier splines, an optimization
task on manifolds, and principal component analysis on nonlinear data. In a
benchmark, Manifolds.jl outperforms all comparable packages for low-dimensional
manifolds in speed; over Python and Matlab packages, the improvement is often
several orders of magnitude, while over C/C++ packages, the improvement is
two-fold. For high-dimensional manifolds, it outperforms all packages except
for Tensorflow-Riemopt, which is specifically tailored for high-dimensional
manifolds.
We comment on a Mazur problem from "Scottish Book" concerning second partial derivatives. It is proved that, if a function f(x,y) of real variables defined on a rectangle has continuous derivative with respect to y and for almost all y the function Fy(x):=fy′(x,y) has finite variation, then almost everywhere on the rectangle there exists the partial derivative f"yx. We construct a separately twice differentiable function, whose partial derivative fx′ is discontinuous with respect to the second variable on a set of positive measure. This solves in the negative the Mazur problem.
26 Feb 2025
In positron emission tomography acquisition (PET), sensitivity along a line
of response can vary due to crystal geometrical arrangements in the scanner
and/or detector inefficiencies, leading to severe artefacts in the
reconstructed image. To mitigate these effects, data must be corrected by a set
of normalization coefficients applied to each line of response. The J-PET
Modular scanner is a PET device made of 50 cm long plastic strips arranged
axially, currently in operation at the Jagiellonian University in Krak\'ow
(Poland).
We have implemented a normalization method for the large field-of-view
plastic-based J-PET Modular scanner using the component-based approach. We
estimated the geometric normalization factors for the J-PET Modular scanner
using Monte Carlo simulations. We also analysed the effects of variations in
detection efficiency. A dedicated cylindrical phantom was simulated to
investigate the impact of various factors on image quality. The image quality
was quantified in terms of radial and axial uniformity metrics, and the
standard deviation to mean intensity ratio, determined for a set of image
slices.
Without normalization, reconstructions of a uniform cylinder exhibit
artefacts. These artefacts were satisfactorily compensated using the
normalization factors. Applying geometrical corrections lowers the
non-uniformity of the image expressed as a standard deviation-to-mean ratio to
a range between 5.5 % to 8.5 %. Computationally, the technique is
straightforward to parallelize, making it time-efficient. Preliminary estimates
suggest that the method is appropriate for use with long axial field-of-view
scanners, such as the total-body J-PET, currently under development at the
Jagiellonian University.
01 Jul 2019
A new class of Random Matrix Ensembles is introduced. The Gaussian orthogonal, unitary, and symplectic ensembles GOE, GUE, and GSE, of random matrices are analogous to the classical Gibbs ensemble governed by Boltzmann's distribution in the coordinate space. The proposed new class of Random Matrix ensembles is an extension of the above Gaussian ensembles and it is analogous to the canonical Gibbs ensemble governed by Maxwell-Boltzmann's distribution in phase space. The thermodynamical magnitudes of partition function, intrinsic energy, free energy of Helmholtz, free energy of Gibbs, enthalpy, as well as entropy, equation of state, and heat capacities, are derived for the new ensemble. The examples of nonideal gas with quadratic potential energy as well as ideal gas of quantum matrices are provided. The distribution function for the new ensembles is derived from the maximum entropy principle.
A comprehensive pharmaceutical recommendation system was designed based on the patients and drugs features extracted from this http URL and this http URL. First, data from these databases were combined, and a dataset of patients and drug information was built. Secondly, the patients and drugs were clustered, and then the recommendation was performed using different ratings provided by patients, and importantly by the knowledge obtained from patients and drug specifications, and considering drug interactions. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first group to consider patients conditions and history in the proposed approach for selecting a specific medicine appropriate for that particular user. Our approach applies artificial intelligence (AI) models for the implementation. Sentiment analysis using natural language processing approaches is employed in pre-processing along with neural network-based methods and recommender system algorithms for modeling the system. In our work, patients conditions and drugs features are used for making two models based on matrix factorization. Then we used drug interaction to filter drugs with severe or mild interactions with other drugs. We developed a deep learning model for recommending drugs by using data from 2304 patients as a training set, and then we used data from 660 patients as our validation set. After that, we used knowledge from critical information about drugs and combined the outcome of the model into a knowledge-based system with the rules obtained from constraints on taking medicine.
An efficient method of exploring the effects of anisotropy in the fractal properties of 2D surfaces and images is proposed. It can be viewed as a direction-sensitive generalization of the multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis (MFDFA) into 2D. It is tested on synthetic structures to ensure its effectiveness, with results indicating consistency. The interdisciplinary potential of this method in describing real surfaces and images is demonstrated, revealing previously unknown directional multifractality in data sets from the Martian surface and the Crab Nebula. The multifractal characteristics of Jackson Pollock's paintings are also analyzed. The results point to their evolution over the time of creation of these works.
12 Jul 2020
The paper focuses on various properties and applications of the homotopy
operator, which occurs in the Poincar\'{e} lemma. In the first part, an
abstract operator calculus is constructed, where the exterior derivative is an
abstract derivative and the homotopy operator plays the role of an abstract
integral. This operator calculus can be used to formulate abstract differential
equations. An example of the eigenvalue problem that resembles the fermionic
quantum harmonic oscillator is presented. The second part presents the dual
complex to the Dolbeault bicomplex generated by the homotopy operator on
complex manifolds.
10 Nov 2015
We consider a few quantities that characterize trading on a stock market in a
fixed time interval: logarithmic returns, volatility, trading activity (i.e.,
the number of transactions), and volume traded. We search for the power-law
cross-correlations among these quantities aggregated over different time units
from 1 min to 10 min. Our study is based on empirical data from the American
stock market consisting of tick-by-tick recordings of 31 stocks listed in Dow
Jones Industrial Average during the years 2008-2011. Since all the considered
quantities except the returns show strong daily patterns related to the
variable trading activity in different parts of a day, which are the best
evident in the autocorrelation function, we remove these patterns by detrending
before we proceed further with our study. We apply the multifractal detrended
cross-correlation analysis with sign preserving (MFCCA) and show that the
strongest power-law cross-correlations exist between trading activity and
volume traded, while the weakest ones exist (or even do not exist) between the
returns and the remaining quantities. We also show that the strongest
cross-correlations are carried by those parts of the signals that are
characterized by large and medium variance. Our observation that the most
convincing power-law cross-correlations occur between trading activity and
volume traded reveals the existence of strong fractal-like coupling between
these quantities.
We study cylindrically symmetric steady-state accretion of polytropic test
matter spiraling onto the symmetry axis in power-law and logarithmic
potentials. The model allows one to qualitatively understand the accretion
process in a symmetry different from that of the classical Bondi accretion. We
study the integral curves as level lines of some Hamiltonian and also apply
this method to Bondi accretion. The isothermal solutions in power-law
potentials (as well as in any radius-dependent potential) can be expressed in
exact form in terms of the Lambert W function, while in the case of logarithmic
potential, exact solutions can be found for any polytropic exponent.
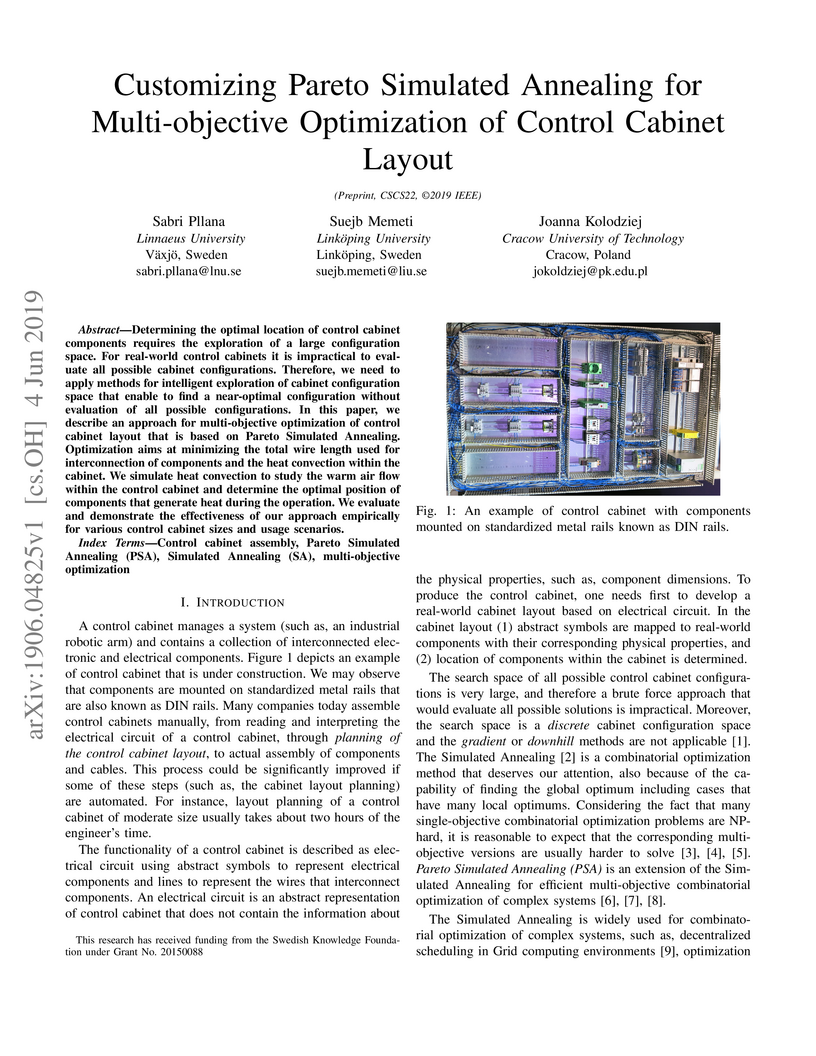
Determining the optimal location of control cabinet components requires the exploration of a large configuration space. For real-world control cabinets it is impractical to evaluate all possible cabinet configurations. Therefore, we need to apply methods for intelligent exploration of cabinet configuration space that enable to find a near-optimal configuration without evaluation of all possible configurations. In this paper, we describe an approach for multi-objective optimization of control cabinet layout that is based on Pareto Simulated Annealing. Optimization aims at minimizing the total wire length used for interconnection of components and the heat convection within the cabinet. We simulate heat convection to study the warm air flow within the control cabinet and determine the optimal position of components that generate heat during the operation. We evaluate and demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach empirically for various control cabinet sizes and usage scenarios.
While modern parallel computing systems offer high performance, utilizing
these powerful computing resources to the highest possible extent demands
advanced knowledge of various hardware architectures and parallel programming
models. Furthermore, optimized software execution on parallel computing systems
demands consideration of many parameters at compile-time and run-time.
Determining the optimal set of parameters in a given execution context is a
complex task, and therefore to address this issue researchers have proposed
different approaches that use heuristic search or machine learning. In this
paper, we undertake a systematic literature review to aggregate, analyze and
classify the existing software optimization methods for parallel computing
systems. We review approaches that use machine learning or meta-heuristics for
software optimization at compile-time and run-time. Additionally, we discuss
challenges and future research directions. The results of this study may help
to better understand the state-of-the-art techniques that use machine learning
and meta-heuristics to deal with the complexity of software optimization for
parallel computing systems. Furthermore, it may aid in understanding the
limitations of existing approaches and identification of areas for improvement.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.