Eindhoven Artificial Intelligence Systems Institute
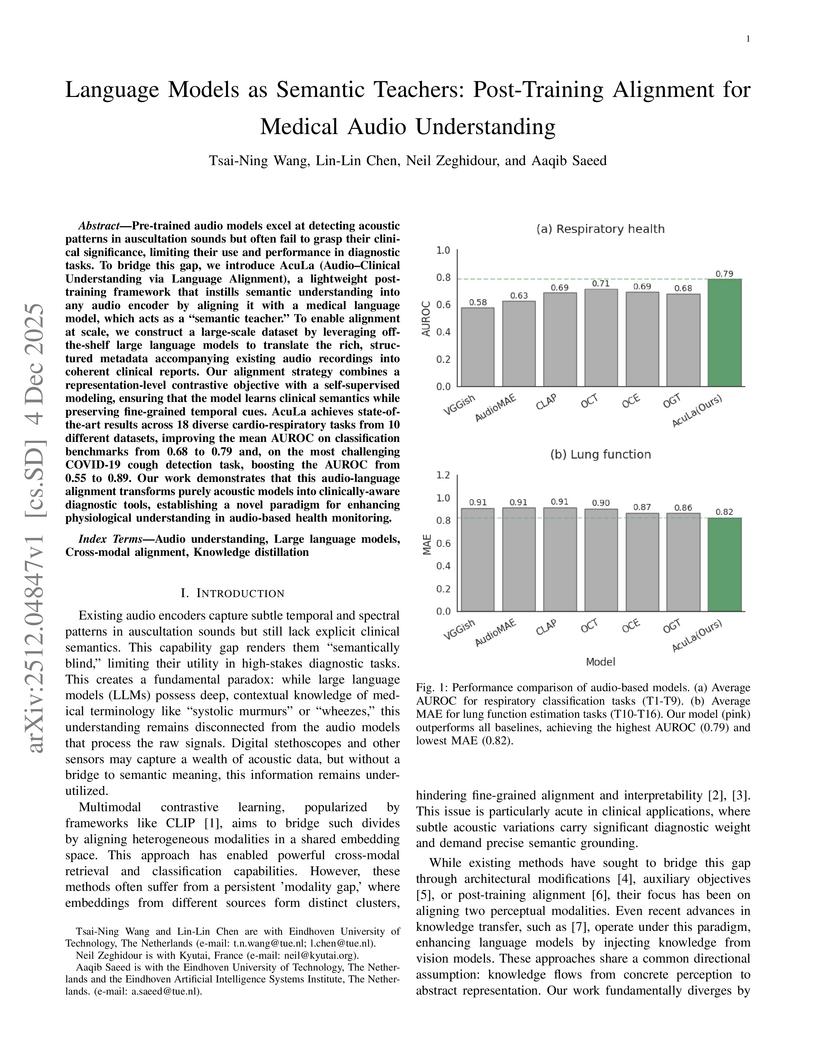
Pre-trained audio models excel at detecting acoustic patterns in auscultation sounds but often fail to grasp their clinical significance, limiting their use and performance in diagnostic tasks. To bridge this gap, we introduce AcuLa (Audio-Clinical Understanding via Language Alignment), a lightweight post-training framework that instills semantic understanding into any audio encoder by aligning it with a medical language model, which acts as a "semantic teacher." To enable alignment at scale, we construct a large-scale dataset by leveraging off-the-shelf large language models to translate the rich, structured metadata accompanying existing audio recordings into coherent clinical reports. Our alignment strategy combines a representation-level contrastive objective with a self-supervised modeling, ensuring that the model learns clinical semantics while preserving fine-grained temporal cues. AcuLa achieves state-of-the-art results across 18 diverse cardio-respiratory tasks from 10 different datasets, improving the mean AUROC on classification benchmarks from 0.68 to 0.79 and, on the most challenging COVID-19 cough detection task, boosting the AUROC from 0.55 to 0.89. Our work demonstrates that this audio-language alignment transforms purely acoustic models into clinically-aware diagnostic tools, establishing a novel paradigm for enhancing physiological understanding in audio-based health monitoring.
Automating the current bridge visual inspection practices using drones and
image processing techniques is a prominent way to make these inspections more
effective, robust, and less expensive. In this paper, we investigate the
development of a novel deep-learning method for the detection of fatigue cracks
in high-resolution images of steel bridges. First, we present a novel and
challenging dataset comprising of images of cracks in steel bridges. Secondly,
we integrate the ConvNext neural network with a previous state-of-the-art
encoder-decoder network for crack segmentation. We study and report, the
effects of the use of background patches on the network performance when
applied to high-resolution images of cracks in steel bridges. Finally, we
introduce a loss function that allows the use of more background patches for
the training process, which yields a significant reduction in false positive
rates.
Evaluating feature attribution methods represents a critical challenge in
explainable AI (XAI), as researchers typically rely on perturbation-based
metrics when ground truth is unavailable. However, recent work demonstrates
that these evaluation metrics can show different performance across predicted
classes within the same dataset. These "class-dependent evaluation effects"
raise questions about whether perturbation analysis reliably measures
attribution quality, with direct implications for XAI method development and
the trustworthiness of evaluation techniques. We investigate under which
conditions these class-dependent effects arise by conducting controlled
experiments with synthetic time series data where ground truth feature
locations are known. We systematically vary feature types and class contrasts
across binary classification tasks, then compare perturbation-based degradation
scores with ground truth-based precision-recall metrics using multiple
attribution methods. Our experiments demonstrate that class-dependent effects
emerge with both evaluation approaches even in simple scenarios with temporally
localized features, triggered by basic variations in feature amplitude or
temporal extent between classes. Most critically, we find that
perturbation-based and ground truth metrics frequently yield contradictory
assessments of attribution quality across classes, with weak correlations
between evaluation approaches. These findings suggest that researchers should
interpret perturbation-based metrics with care, as they may not always align
with whether attributions correctly identify discriminating features. These
findings reveal opportunities to reconsider what attribution evaluation
actually measures and to develop more comprehensive evaluation frameworks that
capture multiple dimensions of attribution quality.
Understanding the dynamics of pedestrian crowds is an outstanding challenge crucial for designing efficient urban infrastructure and ensuring safe crowd management. To this end, both small-scale laboratory and large-scale real-world measurements have been used. However, these approaches respectively lack statistical resolution and parametric controllability, both essential to discovering physical relationships underlying the complex stochastic dynamics of crowds. Here, we establish an investigation paradigm that offers laboratory-like controllability, while ensuring the statistical resolution of large-scale real-world datasets. Using our data-driven Neural Crowd Simulator (NeCS), which we train on large-scale data and validate against key statistical features of crowd dynamics, we show that we can perform effective surrogate crowd dynamics experiments without training on specific scenarios. We not only reproduce known experimental results on pairwise avoidance, but also uncover the vision-guided and topological nature of N-body interactions. These findings show how virtual experiments based on neural simulation enable data-driven scientific discovery.
In this paper, we demonstrate that controllers designed by artificial
potential fields (APFs) can be derived from reciprocal control barrier function
quadratic program (RCBF-QP) safety filters. By integrating APFs within the
RCBF-QP framework, we explicitly establish the relationship between these two
approaches. Specifically, we first introduce the concepts of tightened control
Lyapunov functions (T-CLFs) and tightened reciprocal control barrier functions
(T-RCBFs), each of which incorporates a flexible auxiliary function. We then
utilize an attractive potential field as a T-CLF to guide the nominal
controller design, and a repulsive potential field as a T-RCBF to formulate an
RCBF-QP safety filter. With appropriately chosen auxiliary functions, we show
that controllers designed by APFs and those derived by RCBF-QP safety filters
are equivalent. Based on this insight, we further generalize the APF-based
controllers (equivalently, RCBF-QP safety filter-based controllers) to more
general scenarios without restricting the choice of auxiliary functions.
Finally, we present a collision avoidance example to clearly illustrate the
connection and equivalence between the two methods.
09 Jun 2023
Dynamic task assignment involves assigning arriving tasks to a limited number
of resources in order to minimize the overall cost of the assignments. To
achieve optimal task assignment, it is necessary to model the assignment
problem first. While there exist separate formalisms, specifically Markov
Decision Processes and (Colored) Petri Nets, to model, execute, and solve
different aspects of the problem, there is no integrated modeling technique. To
address this gap, this paper proposes Action-Evolution Petri Nets (A-E PN) as a
framework for modeling and solving dynamic task assignment problems. A-E PN
provides a unified modeling technique that can represent all elements of
dynamic task assignment problems. Moreover, A-E PN models are executable, which
means they can be used to learn close-to-optimal assignment policies through
Reinforcement Learning (RL) without additional modeling effort. To evaluate the
framework, we define a taxonomy of archetypical assignment problems. We show
for three cases that A-E PN can be used to learn close-to-optimal assignment
policies. Our results suggest that A-E PN can be used to model and solve a
broad range of dynamic task assignment problems.
The Dynamic Task Assignment Problem (DTAP) concerns matching resources to
tasks in real time while minimizing some objectives, like resource costs or
task cycle time. In this work, we consider a DTAP variant where every task is a
case composed of a stochastic sequence of activities. The DTAP, in this case,
involves the decision of which employee to assign to which activity to process
requests as quickly as possible. In recent years, Deep Reinforcement Learning
(DRL) has emerged as a promising tool for tackling this DTAP variant, but most
research is limited to solving small-scale, synthetic problems, neglecting the
challenges posed by real-world use cases. To bridge this gap, this work
proposes a DRL-based Decision Support System (DSS) for real-world scale DTAPS.
To this end, we introduce a DRL agent with two novel elements: a graph
structure for observations and actions that can effectively represent any DTAP
and a reward function that is provably equivalent to the objective of
minimizing the average cycle time of tasks. The combination of these two
novelties allows the agent to learn effective and generalizable assignment
policies for real-world scale DTAPs. The proposed DSS is evaluated on five DTAP
instances whose parameters are extracted from real-world logs through process
mining. The experimental evaluation shows how the proposed DRL agent matches or
outperforms the best baseline in all DTAP instances and generalizes on
different time horizons and across instances.
Sontag's universal formula is a widely used technique for stabilizing control through control Lyapunov functions. Recently, it has been extended to address safety-critical control by incorporating control barrier functions (CBFs). However, deriving a universal formula that satisfies requirements on essential properties, including safety, smoothness, and robustness against input disturbances, is still an open problem. To address this challenge, this paper introduces a novel solution - a tunable universal formula - by incorporating a (state-dependent) tunable term into Sontag's formula. This tunable term enables the regulation of safety-critical control performances, allowing the attainment of desired properties through a proper selection of tunable terms. Generally, the tunable universal formula can be seen as a controller that improves the quadratic program (QP)-synthesized controllers in terms of robustness and smoothness, while also reducing the conservatism (corresponding to robustness) in Sontag's formula. Furthermore, we extend the tunable universal formula to address safety-critical control problems with norm-bounded input constraints, showcasing its applicability across diverse control scenarios. Finally, we demonstrate the efficacy of our method through a two-link manipulator safe tracking example, investigating the essential properties including safety, smoothness, and robustness against input disturbances under various tunable terms.
Dynamic task assignment concerns the optimal assignment of resources to tasks in a business process. Recently, Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) has been proposed as the state of the art for solving assignment problems. DRL methods usually employ a neural network (NN) as an approximator for the policy function, which ingests the state of the process and outputs a valuation of the possible assignments. However, representing the state and the possible assignments so that they can serve as inputs and outputs for a policy NN remains an open challenge, especially when tasks or resources have features with an infinite number of possible values. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a method for representing and solving assignment problems with infinite state and action spaces. In doing so, it provides three contributions: (I) A graph-based feature representation of assignment problems, which we call assignment graph; (II) A mapping from marked Colored Petri Nets to assignment graphs; (III) An adaptation of the Proximal Policy Optimization algorithm that can learn to solve assignment problems represented through assignment graphs. To evaluate the proposed representation method, we model three archetypal assignment problems ranging from finite to infinite state and action space dimensionalities. The experiments show that the method is suitable for representing and learning close-to-optimal task assignment policies regardless of the state and action space dimensionalities.
Distal myopathy represents a genetically heterogeneous group of skeletal muscle disorders with broad clinical manifestations, posing diagnostic challenges in radiology. To address this, we propose a novel multimodal attention-aware fusion architecture that combines features extracted from two distinct deep learning models, one capturing global contextual information and the other focusing on local details, representing complementary aspects of the input data. Uniquely, our approach integrates these features through an attention gate mechanism, enhancing both predictive performance and interpretability. Our method achieves a high classification accuracy on the BUSI benchmark and a proprietary distal myopathy dataset, while also generating clinically relevant saliency maps that support transparent decision-making in medical diagnosis. We rigorously evaluated interpretability through (1) functionally grounded metrics, coherence scoring against reference masks and incremental deletion analysis, and (2) application-grounded validation with seven expert radiologists. While our fusion strategy boosts predictive performance relative to single-stream and alternative fusion strategies, both quantitative and qualitative evaluations reveal persistent gaps in anatomical specificity and clinical usefulness of the interpretability. These findings highlight the need for richer, context-aware interpretability methods and human-in-the-loop feedback to meet clinicians' expectations in real-world diagnostic settings.
Distal myopathy represents a genetically heterogeneous group of skeletal muscle disorders with broad clinical manifestations, posing diagnostic challenges in radiology. To address this, we propose a novel multimodal attention-aware fusion architecture that combines features extracted from two distinct deep learning models, one capturing global contextual information and the other focusing on local details, representing complementary aspects of the input data. Uniquely, our approach integrates these features through an attention gate mechanism, enhancing both predictive performance and interpretability. Our method achieves a high classification accuracy on the BUSI benchmark and a proprietary distal myopathy dataset, while also generating clinically relevant saliency maps that support transparent decision-making in medical diagnosis. We rigorously evaluated interpretability through (1) functionally grounded metrics, coherence scoring against reference masks and incremental deletion analysis, and (2) application-grounded validation with seven expert radiologists. While our fusion strategy boosts predictive performance relative to single-stream and alternative fusion strategies, both quantitative and qualitative evaluations reveal persistent gaps in anatomical specificity and clinical usefulness of the interpretability. These findings highlight the need for richer, context-aware interpretability methods and human-in-the-loop feedback to meet clinicians' expectations in real-world diagnostic settings.
We consider the problem of estimating a temperature-dependent thermal
conductivity model (curve) from temperature measurements. We apply a Bayesian
estimation approach that takes into account measurement errors and limited
prior information of system properties. The approach intertwines system
simulation and Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) sampling. We investigate the
impact of assuming different model classes - cubic polynomials and piecewise
linear functions - their parametrization, and different types of prior
information - ranging from uninformative to informative. Piecewise linear
functions require more parameters (conductivity values) to be estimated than
the four parameters (coefficients or conductivity values) needed for cubic
polynomials. The former model class is more flexible, but the latter requires
less MCMC samples. While parametrizing polynomials with coefficients may feel
more natural, it turns out that parametrizing them using conductivity values is
far more natural for the specification of prior information. Robust estimation
is possible for all model classes and parametrizations, as long as the prior
information is accurate or not too informative. Gaussian Markov random field
priors are especially well-suited for piecewise linear functions.
Safe stabilization is a significant challenge for quadrotors, which involves
reaching a goal position while avoiding obstacles. Most of the existing
solutions for this problem rely on optimization-based methods, demanding
substantial onboard computational resources. This paper introduces a novel
approach to address this issue and provides a solution that offers fast
computational capabilities tailored for onboard execution. Drawing inspiration
from Sontag's universal formula, we propose an analytical control strategy that
incorporates the conditions of control Lyapunov functions (CLFs) and control
barrier functions (CBFs), effectively avoiding the need for solving
optimization problems onboard. Moreover, we extend our approach by
incorporating the concepts of input-to-state stability (ISS) and input-to-state
safety (ISSf), enhancing the universal formula's capacity to effectively manage
disturbances. Furthermore, we present a projection-based approach to ensure
that the universal formula remains effective even when faced with control input
constraints. The basic idea of this approach is to project the control input
derived from the universal formula onto the closest point within the control
input domain. Through comprehensive simulations and experimental results, we
validate the efficacy and highlight the advantages of our methodology.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.