Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss
Accurate weather forecasts are essential for supporting a wide range of
activities and decision-making processes, as well as mitigating the impacts of
adverse weather events. While traditional numerical weather prediction (NWP)
remains the cornerstone of operational forecasting, machine learning is
emerging as a powerful alternative for fast, flexible, and scalable
predictions. We introduce PeakWeather, a high-quality dataset of surface
weather observations collected every 10 minutes over more than 8 years from the
ground stations of the Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology
MeteoSwiss's measurement network. The dataset includes a diverse set of
meteorological variables from 302 station locations distributed across
Switzerland's complex topography and is complemented with topographical indices
derived from digital height models for context. Ensemble forecasts from the
currently operational high-resolution NWP model are provided as a baseline
forecast against which to evaluate new approaches. The dataset's richness
supports a broad spectrum of spatiotemporal tasks, including time series
forecasting at various scales, graph structure learning, imputation, and
virtual sensing. As such, PeakWeather serves as a real-world benchmark to
advance both foundational machine learning research, meteorology, and
sensor-based applications.
LDCast presents a precipitation nowcasting system leveraging latent diffusion models to generate realistic, diverse, and probabilistic forecasts. The model produces forecasts with improved accuracy and significantly better uncertainty quantification when compared to state-of-the-art GAN-based and statistical nowcasting methods.
27 Sep 2022
A deep learning model is presented to nowcast the occurrence of lightning at a five-minute time resolution 60 minutes into the future. The model is based on a recurrent-convolutional architecture that allows it to recognize and predict the spatiotemporal development of convection, including the motion, growth and decay of thunderstorm cells. The predictions are performed on a stationary grid, without the use of storm object detection and tracking. The input data, collected from an area in and surrounding Switzerland, comprise ground-based radar data, visible/infrared satellite data and derived cloud products, lightning detection, numerical weather prediction and digital elevation model data. We analyze different alternative loss functions, class weighting strategies and model features, providing guidelines for future studies to select loss functions optimally and to properly calibrate the probabilistic predictions of their model. Based on these analyses, we use focal loss in this study, but conclude that it only provides a small benefit over cross entropy, which is a viable option if recalibration of the model is not practical. The model achieves a pixel-wise critical success index (CSI) of 0.45 to predict lightning occurrence within 8 km over the 60-min nowcast period, ranging from a CSI of 0.75 at a 5-min lead time to a CSI of 0.32 at a 60-min lead time.
21 Aug 2025
Issuing timely severe weather warnings helps mitigate potentially disastrous consequences. Recent advancements in Neural Weather Models (NWMs) offer a computationally inexpensive and fast approach for forecasting atmospheric environments on a 0.25° global grid. For thunderstorms, these environments can be empirically post-processed to predict wind gust distributions at specific locations. With the Pangu-Weather NWM, we apply a hierarchy of statistical and deep learning post-processing methods to forecast hourly wind gusts up to three days ahead. To ensure statistical robustness, we constrain our probabilistic forecasts using generalised extreme-value distributions across five regions in Switzerland. Using a convolutional neural network to post-process the predicted atmospheric environment's spatial patterns yields the best results, outperforming direct forecasting approaches across lead times and wind gust speeds. Our results confirm the added value of NWMs for extreme wind forecasting, especially for designing more responsive early-warning systems.
The distance to the Vela Junior supernova remnant (RX J0852.0-4622 or G266.2-1.2) has long remained uncertain, limiting our understanding of its physical properties. Using VLT/MUSE integral field spectroscopy, we uncover chemical and kinematic connections between the nebula surrounding its Central Compact Object (CXOU J085201.4-461753) and the nearby Herbig-Haro outflow of Ve 7-27 (Wray 16-30), indicating a shared nitrogen-rich, Fe-peak-enhanced environment. This link ties stellar birth and death, with the young star Ve 7-27 embedded in material expelled by Vela Junior's massive progenitor, and the remnant's blast wave is expanding through the same medium. Adopting the Gaia-based distance to Ve 7-27, we revise Vela Junior's distance to 1.41±0.14 kpc. At this distance, the remnant's physical radius is 23.3±2.3 pc, and X-ray proper motions of the northwestern rim correspond to shock speeds of (2.8±0.7)×103 to (5.6±1.5)×103 km s−1. These imply an age of ∼1.6-3.3 kyr and a very low ambient density, indicating that Vela Junior is expanding within a highly rarefied wind-blown cavity carved by a massive progenitor -- consistent with the non-detection of strong thermal X-ray emission. This distance update also resolves long-standing inconsistencies, with major implications for its energy budget, particle acceleration efficiency, and compact object evolution.
 Karlsruhe Institute of TechnologyMet OfficeFinnish Meteorological InstituteNorwegian Meteorological InstituteFederal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwissMétéo-FranceEuropean Center for Medium-Range Weather ForecastsRoyal Meteorological Institute of BelgiumDeutscher WetterdienstRoyal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI)Zentralanstalt für Meteorologie und GeodynamikCroatian Meteorological and Hydrological ServiceMetOffice@ReadingEuropean Meteorological Network (EUMETNET)
Karlsruhe Institute of TechnologyMet OfficeFinnish Meteorological InstituteNorwegian Meteorological InstituteFederal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwissMétéo-FranceEuropean Center for Medium-Range Weather ForecastsRoyal Meteorological Institute of BelgiumDeutscher WetterdienstRoyal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI)Zentralanstalt für Meteorologie und GeodynamikCroatian Meteorological and Hydrological ServiceMetOffice@ReadingEuropean Meteorological Network (EUMETNET)A comprehensive review synthesizes the state-of-the-art in statistical postprocessing techniques for weather forecasts, emphasizing methods for ensemble predictions within a Big Data context and detailing current challenges and future research directions.
Weather forecasting centers currently rely on statistical postprocessing
methods to minimize forecast error. This improves skill but can lead to
predictions that violate physical principles or disregard dependencies between
variables, which can be problematic for downstream applications and for the
trustworthiness of postprocessing models, especially when they are based on new
machine learning approaches. Building on recent advances in physics-informed
machine learning, we propose to achieve physical consistency in deep
learning-based postprocessing models by integrating meteorological expertise in
the form of analytic equations. Applied to the post-processing of surface
weather in Switzerland, we find that constraining a neural network to enforce
thermodynamic state equations yields physically-consistent predictions of
temperature and humidity without compromising performance. Our approach is
especially advantageous when data is scarce, and our findings suggest that
incorporating domain expertise into postprocessing models allows to optimize
weather forecast information while satisfying application-specific
requirements.
Surface albedo is an important parameter in radiative transfer simulations of
the Earth's system, as it is fundamental to correctly calculate the energy
budget of the planet. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS)
instruments on NASA's Terra and Aqua satellites continuously monitor daily and
yearly changes in reflection at the planetary surface. The MODIS Surface
Reflectance black-sky albedo dataset (MCD43D, version 6.1) gives detailed
albedo maps in seven spectral bands in the visible and near-infrared range.
These albedo maps allow us to classify different Lambertian surface types and
their seasonal and yearly variability and change, albeit only in seven spectral
bands. However, a complete set of albedo maps covering the entire wavelength
range is required to simulate radiance spectra, and to correctly retrieve
atmospheric and cloud properties from Earth's remote sensing. We use a
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) regression algorithm to generate
hyperspectral albedo maps of Earth. Combining different datasets of
hyperspectral reflectance laboratory measurements for various dry soils,
vegetation surfaces, and mixtures of both, we reconstruct the albedo maps in
the entire wavelength range from 400 to 2500~nm. The PCA method is trained with
a 10-years average of MODIS data for each day of the year. We obtain
hyperspectral albedo maps with a spatial resolution of 0.05{\deg} in latitude
and longitude, a spectral resolution of 10~nm, and a temporal resolution of
1~day. Using the hyperspectral albedo maps, we estimate the spectral profiles
of different land surfaces, such as forests, deserts, cities and icy surfaces,
and study their seasonal variability. These albedo maps shall enable to refine
calculations of Earth's energy budget, its seasonal variability, and improve
climate simulations.
The coarse spatial resolution of gridded climate models, such as general circulation models, limits their direct use in projecting socially relevant variables like extreme precipitation. Most downscaling methods estimate the conditional distributions of extremes by generating large ensembles, complicating the assessment of robustness under distributional shifts, such as those induced by climate change. To better understand and potentially improve robustness, we propose super-resolving the parameters of the target variable's probability distribution directly using analytically tractable mappings. Within a perfect-model framework over Switzerland, we demonstrate that vector generalized linear and additive models can super-resolve the generalized extreme value distribution of summer hourly precipitation extremes from coarse precipitation fields and topography. We introduce the notion of a "robustness gap", defined as the difference in predictive error between present-trained and future-trained models, and use it to diagnose how model structure affects the generalization of each quantile to a pseudo-global warming scenario. By evaluating multiple model configurations, we also identify an upper limit on the super-resolution factor based on the spatial auto- and cross-correlation of precipitation and elevation, beyond which coarse precipitation loses predictive value. Our framework is broadly applicable to variables governed by parametric distributions and offers a model-agnostic diagnostic for understanding when and why empirical downscaling generalizes to climate change and extremes.
21 Aug 2025
Issuing timely severe weather warnings helps mitigate potentially disastrous consequences. Recent advancements in Neural Weather Models (NWMs) offer a computationally inexpensive and fast approach for forecasting atmospheric environments on a 0.25° global grid. For thunderstorms, these environments can be empirically post-processed to predict wind gust distributions at specific locations. With the Pangu-Weather NWM, we apply a hierarchy of statistical and deep learning post-processing methods to forecast hourly wind gusts up to three days ahead. To ensure statistical robustness, we constrain our probabilistic forecasts using generalised extreme-value distributions across five regions in Switzerland. Using a convolutional neural network to post-process the predicted atmospheric environment's spatial patterns yields the best results, outperforming direct forecasting approaches across lead times and wind gust speeds. Our results confirm the added value of NWMs for extreme wind forecasting, especially for designing more responsive early-warning systems.
Real-time bioaerosol monitoring is improving the quality of life for people
affected by allergies, but it often relies on deep-learning models which pose
challenges for widespread adoption. These models are typically trained in a
supervised fashion and require considerable effort to produce large amounts of
annotated data, an effort that must be repeated for new particles, geographical
regions, or measurement systems. In this work, we show that self-supervised
learning and few-shot learning can be combined to classify holographic images
of bioaerosol particles using a large collection of unlabelled data and only a
few examples for each particle type. We first demonstrate that self-supervision
on pictures of unidentified particles from ambient air measurements enhances
identification even when labelled data is abundant. Most importantly, it
greatly improves few-shot classification when only a handful of labelled images
are available. Our findings suggest that real-time bioaerosol monitoring
workflows can be substantially optimized, and the effort required to adapt
models for different situations considerably reduced.
The Weather4cast 2021 competition gave the participants a task of predicting the time evolution of two-dimensional fields of satellite-based meteorological data. This paper describes the author's efforts, after initial success in the first stage of the competition, to improve the model further in the second stage. The improvements consisted of a shallower model variant that is competitive against the deeper version, adoption of the AdaBelief optimizer, improved handling of one of the predicted variables where the training set was found not to represent the validation set well, and ensembling multiple models to improve the results further. The largest quantitative improvements to the competition metrics can be attributed to the increased amount of training data available in the second stage of the competition, followed by the effects of model ensembling. Qualitative results show that the model can predict the time evolution of the fields, including the motion of the fields over time, starting with sharp predictions for the immediate future and blurring of the outputs in later frames to account for the increased uncertainty.
Outdoor webcam images are an information-dense yet accessible visualization
of past and present weather conditions, and are consulted by meteorologists and
the general public alike. Weather forecasts, however, are still communicated as
text, pictograms or charts. We therefore introduce a novel method that uses
photographic images to also visualize future weather conditions.
This is challenging, because photographic visualizations of weather forecasts
should look real, be free of obvious artifacts, and should match the predicted
weather conditions. The transition from observation to forecast should be
seamless, and there should be visual continuity between images for consecutive
lead times. We use conditional Generative Adversarial Networks to synthesize
such visualizations. The generator network, conditioned on the analysis and the
forecasting state of the numerical weather prediction (NWP) model, transforms
the present camera image into the future. The discriminator network judges
whether a given image is the real image of the future, or whether it has been
synthesized. Training the two networks against each other results in a
visualization method that scores well on all four evaluation criteria.
We present results for three camera sites across Switzerland that differ in
climatology and terrain. We show that users find it challenging to distinguish
real from generated images, performing not much better than if they guessed
randomly. The generated images match the atmospheric, ground and illumination
conditions of the COSMO-1 NWP model forecast in at least 89 % of the examined
cases. Nowcasting sequences of generated images achieve a seamless transition
from observation to forecast and attain visual continuity.
12 May 2023
Solar energy supply is usually highly volatile which limits its integration
in the power grid. Accurate probabilistic intraday forecasts of solar resources
are essential to increase the share of photovoltaic (PV) energy in the grid and
enable cost-efficient balancing of power demand and supply. Solar PV production
mainly depends on downwelling surface solar radiation (SSR). By estimating SSR
from geostationary satellites, we can cover large areas with high spatial and
temporal resolutions, allowing us to track cloud motion. State-of-the-art
probabilistic forecasts of solar resources from satellite imagery account only
for the advective motion of clouds. They do not consider the evolution of
clouds over time, their growth, and dissipation, even though these are major
sources of forecast uncertainty. To address the uncertainty of cloudiness
evolution, we present SolarSTEPS, the first optical-flow probabilistic model
able to simulate the temporal variability of cloudiness. We demonstrate that
forecasting the autocorrelated scale-dependent evolution of cloudiness
outperforms state-of-the-art probabilistic advection-based forecasts by 9% in
continuous ranked probability score (CRPS). This corresponds to an extension of
the forecast lead time by about 45 minutes at constant CRPS. Our work is
motivated by the scale-dependent predictability of cloud growth and decay. We
demonstrate that cloudiness is more variable in time at smaller spatial scales
than at larger ones. Specifically, the temporal autocorrelation of cloudiness
is related to its spatial scale by a rational function. We also demonstrate
that decomposing cloudiness into multiple spatial scales in the forecasts
further improves the forecast skill, reducing the CRPS by 10% and the RMSE by
9%.
16 Sep 2023
 ETH ZurichUniversity of Bern
ETH ZurichUniversity of Bern NVIDIAUniversity of LeedsUniversity of TennesseeUniversity of ReadingUniversität HamburgCommonwealth Scientific Industrial Research OrganisationFederal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwissGerman Climate Computing Center DKRZNational Center for Atmospheric ResearchSwiss National Supercomputing CenterCSC-IT Center for ScienceMax-Planck Institute for Meteorology
NVIDIAUniversity of LeedsUniversity of TennesseeUniversity of ReadingUniversität HamburgCommonwealth Scientific Industrial Research OrganisationFederal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwissGerman Climate Computing Center DKRZNational Center for Atmospheric ResearchSwiss National Supercomputing CenterCSC-IT Center for ScienceMax-Planck Institute for MeteorologyParticipants of the Berlin Summit on Earth Virtualization Engines (EVEs)
discussed ideas and concepts to improve our ability to cope with climate
change. EVEs aim to provide interactive and accessible climate simulations and
data for a wide range of users. They combine high-resolution physics-based
models with machine learning techniques to improve the fidelity, efficiency,
and interpretability of climate projections. At their core, EVEs offer a
federated data layer that enables simple and fast access to exabyte-sized
climate data through simple interfaces. In this article, we summarize the
technical challenges and opportunities for developing EVEs, and argue that they
are essential for addressing the consequences of climate change.
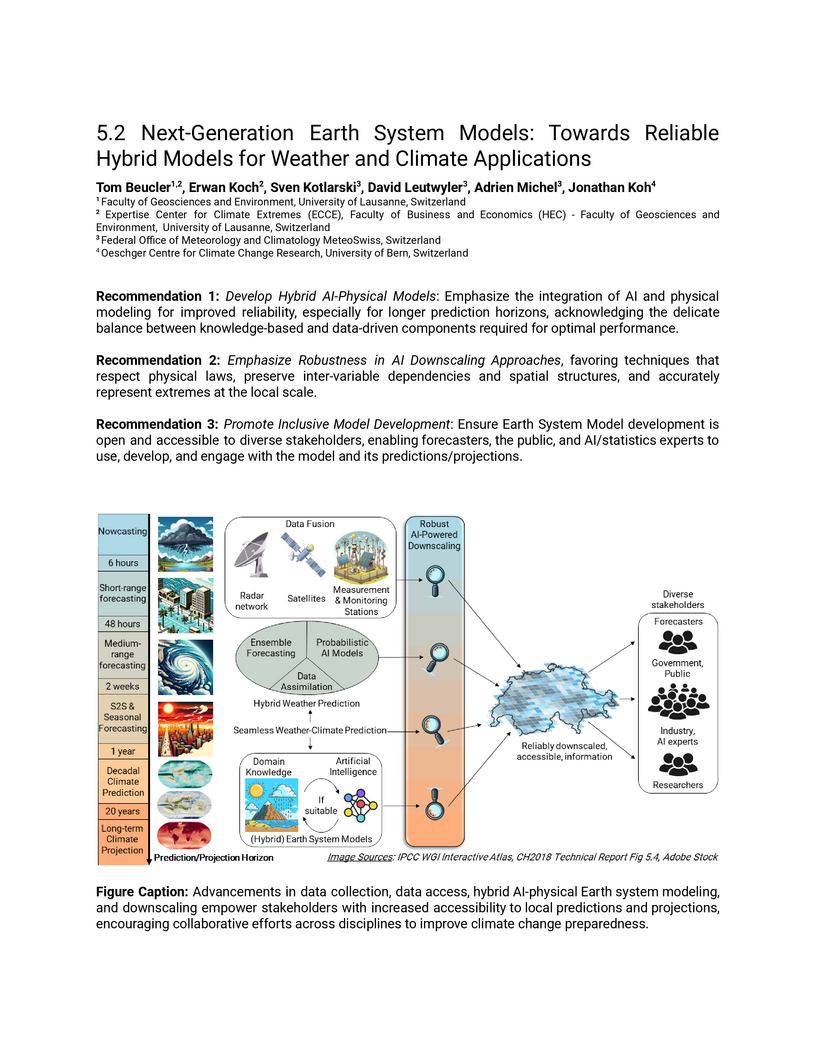
We review how machine learning has transformed our ability to model the Earth
system, and how we expect recent breakthroughs to benefit end-users in
Switzerland in the near future. Drawing from our review, we identify three
recommendations.
Recommendation 1: Develop Hybrid AI-Physical Models: Emphasize the
integration of AI and physical modeling for improved reliability, especially
for longer prediction horizons, acknowledging the delicate balance between
knowledge-based and data-driven components required for optimal performance.
Recommendation 2: Emphasize Robustness in AI Downscaling Approaches, favoring
techniques that respect physical laws, preserve inter-variable dependencies and
spatial structures, and accurately represent extremes at the local scale.
Recommendation 3: Promote Inclusive Model Development: Ensure Earth System
Model development is open and accessible to diverse stakeholders, enabling
forecasters, the public, and AI/statistics experts to use, develop, and engage
with the model and its predictions/projections.
This paper presents the neural network model that was used by the author in the Weather4cast 2021 Challenge Stage 1, where the objective was to predict the time evolution of satellite-based weather data images. The network is based on an encoder-forecaster architecture making use of gated recurrent units (GRU), residual blocks and a contracting/expanding architecture with shortcuts similar to U-Net. A GRU variant utilizing residual blocks in place of convolutions is also introduced. Example predictions and evaluation metrics for the model are presented. These demonstrate that the model can retain sharp features of the input for the first predictions, while the later predictions become more blurred to reflect the increasing uncertainty.
17 Apr 2025
In neutrino physics, analyses often depend on large simulated datasets, making it essential for models to generalise effectively to real-world detector data. Contrastive learning, a well-established technique in deep learning, offers a promising solution to this challenge. By applying controlled data augmentations to simulated data, contrastive learning enables the extraction of robust and transferable features. This improves the ability of models trained on simulations to adapt to real experimental data distributions. In this paper, we investigate the application of contrastive learning methods in the context of neutrino physics. Through a combination of empirical evaluations and theoretical insights, we demonstrate how contrastive learning enhances model performance and adaptability. Additionally, we compare it to other domain adaptation techniques, highlighting the unique advantages of contrastive learning for this field.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.