Korea Institute of Energy Technology
Recent research on graph neural networks (GNNs) has explored mechanisms for
capturing local uncertainty and exploiting graph hierarchies to mitigate data
sparsity and leverage structural properties. However, the synergistic
integration of these two approaches remains underexplored. This work introduces
a novel architecture, the Hierarchical Uncertainty-Aware Graph Neural Network
(HU-GNN), which unifies multi-scale representation learning, principled
uncertainty estimation, and self-supervised embedding diversity within a single
end-to-end framework. Specifically, HU-GNN adaptively forms node clusters and
estimates uncertainty at multiple structural scales from individual nodes to
higher levels. These uncertainty estimates guide a robust message-passing
mechanism and attention weighting, effectively mitigating noise and adversarial
perturbations while preserving predictive accuracy on semi-supervised
classification tasks. We also offer key theoretical contributions, including a
probabilistic formulation, rigorous uncertainty-calibration guarantees, and
formal robustness bounds. Extensive experiments on standard benchmarks
demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art robustness and
interpretability.
14 Oct 2025
Quantum magnets offer a unique platform for exploring exotic quantum phases and quantum phase transitions through external magnetic fields. A prominent example is the field-induced Bose--Einstein condensation (BEC) of magnons near the saturation field. While this behavior has been observed in low-spin systems, its realization in high-spin, quasi-two-dimensional magnets -- where multiple on-site excitations are possible -- remains exceptionally rare. Here, we report thermodynamic and density functional theory results on single crystals of the honeycomb-lattice antiferromagnet K4MnMo4O15 with S=5/2. The system undergoes a field-induced transition to a fully polarized state at the critical field μ0Hs=6.4~T. Our results reveal possible thermodynamic signatures of magnon BEC, TN∼(Hs−H)2/d (d=3), expanding the purview of BEC-driven quantum criticality to a high-spin, quasi-two-dimensional antiferromagnets with negligibly small anisotropy.
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) excel on homophilous graphs but often fail under heterophily due to self-reinforcing and phase-inconsistent signals. We propose a Gauge-Equivariant Graph Network with Self-Interference Cancellation (GESC), which replaces additive aggregation with a projection-based interference mechanism. Unlike prior magnetic or gauge-equivariant GNNs that typically focus on phase handling in spectral filtering while largely relying on scalar weighting, GESC introduces a U(1) phase connection followed by a rank-1 projection that attenuates self-parallel components before attention. A sign- and phase-aware gate further regulates neighbor influence, attenuating components aligned with current node states and acting as a local notch on low-frequency modes. Across diverse graph benchmarks, our method consistently outperforms recent state-of-the-art models while offering a unified, interference-aware view of message passing. Our code is available at \href{here}{this https URL}.
Understanding how fluctuations arise and spread in the international trade system can help assess the current state and guide future developments. We analyze the world trade data to investigate strong adverse fluctuations, characterized here as `collapsed trades' -- individual trades that experience significant declines in annual trade volume compared to the previous year. Adopting a hypergraph framework for a fine-scale trade-centric representation of international trade, we find that collapsed trades are clustered similar to infectious disease outbreaks in societies. Moreover, the portion of collapsed trades is found to be negatively correlated with trade volume. We develop a collapse propagation model, an epidemic-like model with a weight-dependent infection rate, that reproduces all the essential empirical features. Through both analytical and numerical analysis, we identify two key factors that synergistically suppress the onset of global collective collapse and serve as a joint stabilizing mechanism for the international economy: i) a positive correlation between a trade's degree (the number of adjacent trades) and its volume and ii) an algebraically decaying infection rate with trade volume. In particular, the second factor weakened during the 2008--2009 global economic recession, possibly explaining the broader spread of collapse.
As a neural network's depth increases, it can improve generalization
performance. However, training deep networks is challenging due to gradient and
signal propagation issues. To address these challenges, extensive theoretical
research and various methods have been introduced. Despite these advances,
effective weight initialization methods for tanh neural networks remain
insufficiently investigated. This paper presents a novel weight initialization
method for neural networks with tanh activation function. Based on an analysis
of the fixed points of the function tanh(ax), the proposed method aims to
determine values of a that mitigate activation saturation. A series of
experiments on various classification datasets and physics-informed neural
networks demonstrates that the proposed method outperforms Xavier
initialization methods~(with or without normalization) in terms of robustness
across different network sizes, data efficiency, and convergence speed. Code is
available at this https URL
In complex networks, many elements interact with each other in different ways. A hypergraph is a network in which group interactions occur among more than two elements. In this study, first, we propose a method to identify influential subgroups in hypergraphs, named (k,q)-core decomposition. The (k,q)-core is defined as the maximal subgraph in which each vertex has at least k hypergraph degrees \textit{and} each hyperedge contains at least q vertices. The method contains a repeated pruning process until reaching the (k,q)-core, which shares similarities with a widely used k-core decomposition technique in a graph. Second, we analyze the pruning dynamics and the percolation transition with theoretical and numerical methods in random hypergraphs. We set up evolution equations for the pruning process, and self-consistency equations for the percolation properties. Based on our theory, we find that the pruning process generates a hybrid percolation transition for either k≥3 \textit{or} q≥3. The critical exponents obtained theoretically are confirmed with finite-size scaling analysis. Next, when k=q=2, we obtain a unconventional degree-dependent critical relaxation dynamics analytically and numerically. Finally, we apply the (k,q)-core decomposition to a real coauthorship dataset and recognize the leading groups at an early stage.
14 Nov 2024
Numerical simulation is a predominant tool for studying the dynamics in complex systems, but large-scale simulations are often intractable due to computational limitations. Here, we introduce the Neural Graph Simulator (NGS) for simulating time-invariant autonomous systems on graphs. Utilizing a graph neural network, the NGS provides a unified framework to simulate diverse dynamical systems with varying topologies and sizes without constraints on evaluation times through its non-uniform time step and autoregressive approach. The NGS offers significant advantages over numerical solvers by not requiring prior knowledge of governing equations and effectively handling noisy or missing data with a robust training scheme. It demonstrates superior computational efficiency over conventional methods, improving performance by over 105 times in stiff problems. Furthermore, it is applied to real traffic data, forecasting traffic flow with state-of-the-art accuracy. The versatility of the NGS extends beyond the presented cases, offering numerous potential avenues for enhancement.
Message-passing Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), which collect information from adjacent nodes achieve dismal performance on heterophilic graphs. Various schemes have been proposed to solve this problem, and propagating signed information on heterophilic edges has gained great attention. Recently, some works provided theoretical analysis that signed propagation always leads to performance improvement under a binary class scenario. However, we notice that prior analyses do not align well with multi-class benchmark datasets. This paper provides a new understanding of signed propagation for multi-class scenarios and points out two drawbacks in terms of message-passing and parameter update: (1) Message-passing: if two nodes belong to different classes but have a high similarity, signed propagation can decrease the separability. (2) Parameter update: the prediction uncertainty (e.g., conflict evidence) of signed neighbors increases during training, which can impede the stability of the algorithm. Based on the observation, we introduce two novel strategies for improving signed propagation under multi-class graphs. The proposed scheme combines calibration to secure robustness while reducing uncertainty. We show the efficacy of our theorem through extensive experiments on six benchmark graph datasets.
A complex system with many interacting individuals can be represented by a network consisting of nodes and links representing individuals and pairwise interactions, respectively. However, real-world systems grow with time and include many higher-order interactions. Such systems with higher-order interactions can be well described by a simplicial complex (SC), which is a type of hypergraph, consisting of simplexes representing sets of multiple interacting nodes. Here, capturing the properties of growing real-world systems, we propose a growing random SC (GRSC) model where a node is added and a higher dimensional simplex is established among nodes at each time step. We then rigorously derive various percolation properties in the GRSC. Finally, we confirm that the system exhibits an infinite-order phase transition as higher-order interactions accelerate the growth of the system and result in the advanced emergence of a giant cluster. This work can pave the way for interpreting growing complex systems with higher-order interactions such as social, biological, brain, and technological systems.
09 Mar 2025
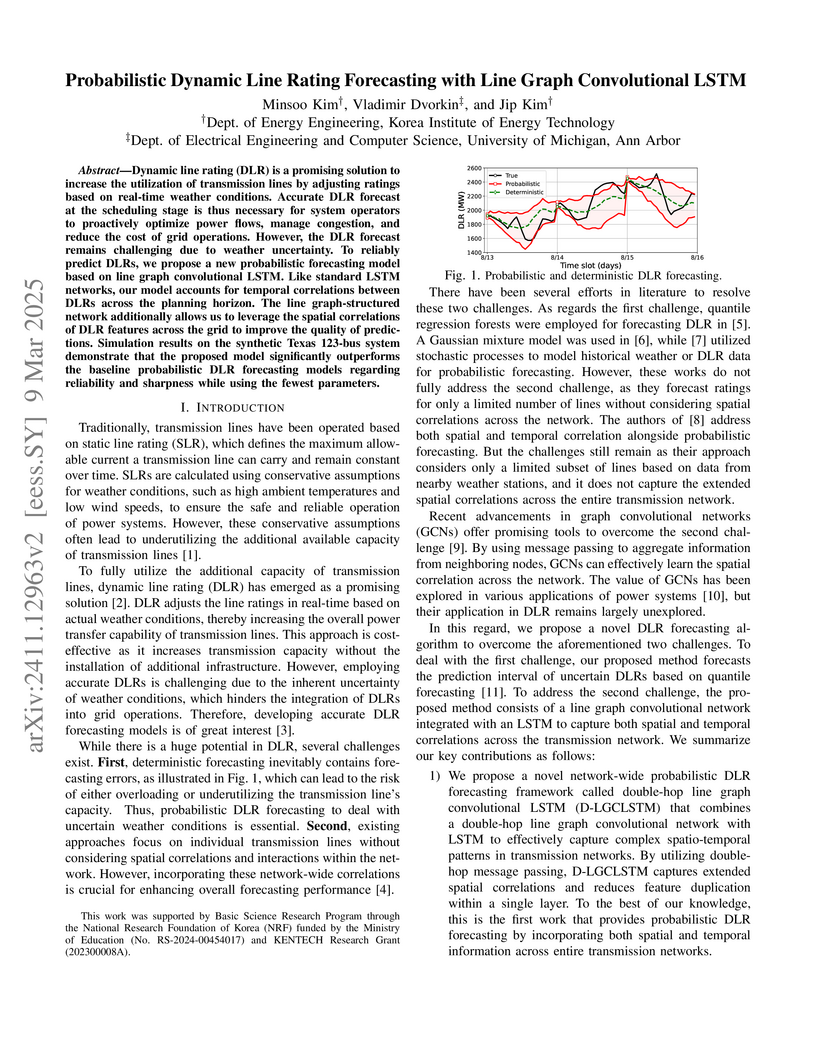
Dynamic line rating (DLR) is a promising solution to increase the utilization
of transmission lines by adjusting ratings based on real-time weather
conditions. Accurate DLR forecast at the scheduling stage is thus necessary for
system operators to proactively optimize power flows, manage congestion, and
reduce the cost of grid operations. However, the DLR forecast remains
challenging due to weather uncertainty. To reliably predict DLRs, we propose a
new probabilistic forecasting model based on line graph convolutional LSTM.
Like standard LSTM networks, our model accounts for temporal correlations
between DLRs across the planning horizon. The line graph-structured network
additionally allows us to leverage the spatial correlations of DLR features
across the grid to improve the quality of predictions. Simulation results on
the synthetic Texas 123-bus system demonstrate that the proposed model
significantly outperforms the baseline probabilistic DLR forecasting models
regarding reliability and sharpness while using the fewest parameters.
04 Feb 2025
This paper introduces the 193 bus synthetic Korean power grid (KPG 193),
developed using open data sources to address recent challenges of the Korean
power system. The KPG 193 test system serves as a valuable platform for
decarbonization research, capturing Korean low renewable energy penetration,
concentrated urban energy demand, and isolated grid structure. Clustering
techniques were applied to preserve key system characteristics while
maintaining computational tractability and representativeness. The system
includes 193 buses, 123 generators, 407 transmission lines, and incorporates
temporal weather datasets. Its feasibility was validated through Unit
Commitment (UC) and AC Optimal Power Flow (ACOPF) simulations using 2022 demand
and renewable generation data. This test system aims to provide a foundational
framework for modeling and analyzing the Korean power grid.
07 Mar 2025
This paper presents a risk-aware bi-level bidding strategy for Virtual Power
Plant (VPP) that integrates Power-to-Hydrogen (P2H) system, addressing the
challenges posed by renewable energy variability and market volatility. By
incorporating Conditional Value at Risk (CVaR) within the bi-level optimization
framework, the proposed strategy enables VPPs to mitigate financial risks
associated with uncertain market conditions. The upper-level problem seeks to
maximize revenue through optimal bidding, while the lower-level problem ensures
market-clearing compliance. The integration of the P2H system allows surplus
renewable energy to be stored as hydrogen, which is utilized as an energy
carrier, thereby increasing market profitability and enhancing resilience
against financial risks. The effectiveness of the proposed strategy is
validated through a modified IEEE 14 bus system, demonstrating that the
inclusion of the P2H system and CVaR-based risk aversion enhances both revenue
and financial hedging capability under volatile market conditions.This paper
underscores the strategic role of hydrogen storage in VPP operations,
contributing to supporting improved profitability and the efficacy of a
risk-aware bidding strategy.
Diffusion over networks has recently been used to define spatiotemporal scales and extend Kadanoff block spins of Euclidean space to supernodes of networks in the Laplacian renormalization group (LRG). Yet, its ad hoc coarse-graining procedure remains underdeveloped and unvalidated, limiting its broader applicability. Here we rigorously formulate an LRG preserving the equilibrium state, offering a principled coarse-graining procedure. We construct the renormalized Laplacian matrix preserving dominant spectral properties using a proper, quasi-complete basis transformation and the renormalized adjacency matrix preserving mean connectivity from equilibrium-state flows among supernodes. Applying recursively this equilibrium-preserving LRG to various hypergraphs, we find that in hypertrees with low spectral dimensions vertex degree and hyperedge cardinality distributions flow toward Poissonian forms, while in hypergraphs lacking a finite spectral dimension they broaden toward power-law forms when starting from Poissonian ones, revealing how informational, structural, and dynamical scale-invariances are interrelated.
22 Jul 2025
Scale-free networks -- from the Internet to biological systems -- exhibit hierarchical organization that resists conventional renormalization group (RG) analysis. Their combination of scale invariance and small-world connectivity challenges standard RG methods, which rely on well-defined length scales. We resolve this challenge by formulating a spectral-space RG framework that captures both structural and dynamical scaling in complex networks. Leveraging the Laplacian eigenspectrum, we implement coarse-graining transformations unconstrained by geometry. This yields universal scaling relations connecting fractal dimensions, spectral dimensions, and degree exponents, establishing the first systematic foundation for network renormalization. A novel meta-graph reconstruction algorithm enables direct extraction of renormalized topologies from spectral data. We validate our predictions across diverse real-world networks and uncover new phenomena: evolving networks display multi-scaling behavior indicative of structural transitions, and spectral non-recursiveness reveals hidden dynamical correlations invisible in static topology. Applied to the European power grid, our method identifies latent connections between distant regions, consistent with observed fault propagation. Our results position spectral-space renormalization as a unified framework for analyzing scale-invariant networks, with broad implications for network science, infrastructure resilience, and statistical physics.
10 Oct 2025
Ensuring both feasibility and efficiency in optimal power flow (OPF) operations has become increasingly important in modern power systems with high penetrations of renewable energy and energy storage. While deep neural networks (DNNs) have emerged as promising fast surrogates for OPF solvers, they often fail to satisfy critical operational constraints, especially those involving inter-temporal coupling, such as generator ramping limits and energy storage operations. To deal with these issues, we propose a Multi-Period Projection-Aware Deep Neural Network (MPA-DNN) that incorporates a projection layer for multi-period dispatch into the network. By doing so, our model enforces physical feasibility through the projection, enabling end-to-end learning of constraint-compliant dispatch trajectories without relying on labeled data. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves near-optimal performance while strictly satisfying all constraints in varying load conditions.
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have proven to be powerful in many graph-based applications. However, they fail to generalize well under heterophilic setups, where neighbor nodes have different labels. To address this challenge, we employ a confidence ratio as a hyper-parameter, assuming that some of the edges are disassortative (heterophilic). Here, we propose a two-phased algorithm. Firstly, we determine edge coefficients through subgraph matching using a supplementary module. Then, we apply GNNs with a modified label propagation mechanism to utilize the edge coefficients effectively. Specifically, our supplementary module identifies a certain proportion of task-irrelevant edges based on a given confidence ratio. Using the remaining edges, we employ the widely used optimal transport to measure the similarity between two nodes with their subgraphs. Finally, using the coefficients as supplementary information on GNNs, we improve the label propagation mechanism which can prevent two nodes with smaller weights from being closer. The experiments on benchmark datasets show that our model alleviates over-smoothing and improves performance.
Complex network analyses have provided clues to improve power-grid stability
with the help of numerical models. The high computational cost of numerical
simulations, however, has inhibited the approach, especially when it deals with
the dynamic properties of power grids such as frequency synchronization. In
this study, we investigate machine learning techniques to estimate the
stability of power-grid synchronization. We test three different machine
learning algorithms -- random forest, support vector machine, and artificial
neural network -- training them with two different types of synthetic power
grids consisting of homogeneous and heterogeneous input-power distribution,
respectively. We find that the three machine learning models better predict the
synchronization stability of power-grid nodes when they are trained with the
heterogeneous input-power distribution than the homogeneous one. With the
real-world power grids of Great Britain, Spain, France, and Germany, we also
demonstrate that the machine learning algorithms trained on synthetic power
grids are transferable to the stability prediction of the real-world power
grids, which implies the prospective applicability of machine learning
techniques on power-grid studies.
Graph neural networks (GNNs) are commonly used in semi-supervised settings.
Previous research has primarily focused on finding appropriate graph filters
(e.g. aggregation methods) to perform well on both homophilic and heterophilic
graphs. While these methods are effective, they can still suffer from the
sparsity of node features, where the initial data contain few non-zero
elements. This can lead to overfitting in certain dimensions in the first
projection matrix, as training samples may not cover the entire range of graph
filters (hyperplanes). To address this, we propose a novel data augmentation
strategy. Specifically, by flipping both the initial features and hyperplane,
we create additional space for training, which leads to more precise updates of
the learnable parameters and improved robustness for unseen features during
inference. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to mitigate
the overfitting caused by the initial features. Extensive experiments on
real-world datasets show that our proposed technique increases node
classification accuracy by up to 46.5% relatively.
We present VWAttacker, the first systematic testing framework for analyzing the security of Voice over WiFi (VoWiFi) User Equipment (UE) implementations. VWAttacker includes a complete VoWiFi network testbed that communicates with Commercial-Off-The-Shelf (COTS) UEs based on a simple interface to test the behavior of diverse VoWiFi UE implementations; uses property-guided adversarial testing to uncover security issues in different UEs systematically. To reduce manual effort in extracting and testing properties, we introduce an LLM-based, semi-automatic, and scalable approach for property extraction and testcase (TC) generation. These TCs are systematically mutated by two domain-specific transformations. Furthermore, we introduce two deterministic oracles to detect property violations automatically. Coupled with these techniques, VWAttacker extracts 63 properties from 11 specifications, evaluates 1,116 testcases, and detects 13 issues in 21 UEs. The issues range from enforcing a DH shared secret to 0 to supporting weak algorithms. These issues result in attacks that expose the victim UE's identity or establish weak channels, thus severely hampering the security of cellular networks. We responsibly disclose the findings to all the related vendors. At the time of writing, one of the vulnerabilities has been acknowledged by MediaTek with high severity.
04 Jul 2025
The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources has significantly reduced the inertia in the modernized power grid, making the system more vulnerable. One way to stabilize the grid is to add extra inertia from unused turbines, called the fast frequency response (FFR), to the existing grid. However, reinforcing inertia can cause unintended consequences, such as more significant avalanche failures. This phenomenon is known as the Braess paradox. Here, we propose a method to find the optimal position of FFR. This method is applied to the second-order Kuramoto model to find an effective position to mitigate cascading failures. To address this, we propose a method to evaluate a ratio between the positive effects of mitigation and the negative consequences. Through this analysis, we find that the peripheral area of the network is a seemingly effective location for inertia reinforcement across various reinforcement scales. This strategy provides essential insights for enhancing the stability of power grids in a time of widespread renewable energy usage.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.