LINE Corporation
This paper presents recent progress on integrating speech separation and enhancement (SSE) into the ESPnet toolkit. Compared with the previous ESPnet-SE work, numerous features have been added, including recent state-of-the-art speech enhancement models with their respective training and evaluation recipes. Importantly, a new interface has been designed to flexibly combine speech enhancement front-ends with other tasks, including automatic speech recognition (ASR), speech translation (ST), and spoken language understanding (SLU). To showcase such integration, we performed experiments on carefully designed synthetic datasets for noisy-reverberant multi-channel ST and SLU tasks, which can be used as benchmark corpora for future research. In addition to these new tasks, we also use CHiME-4 and WSJ0-2Mix to benchmark multi- and single-channel SE approaches. Results show that the integration of SE front-ends with back-end tasks is a promising research direction even for tasks besides ASR, especially in the multi-channel scenario. The code is available online at this https URL. The multi-channel ST and SLU datasets, which are another contribution of this work, are released on HuggingFace.
Preference-based reinforcement learning (PbRL) is an approach that enables RL agents to learn from preference, which is particularly useful when formulating a reward function is challenging. Existing PbRL methods generally involve a two-step procedure: they first learn a reward model based on given preference data and then employ off-the-shelf reinforcement learning algorithms using the learned reward model. However, obtaining an accurate reward model solely from preference information, especially when the preference is from human teachers, can be difficult. Instead, we propose a PbRL algorithm that directly learns from preference without requiring any reward modeling. To achieve this, we adopt a contrastive learning framework to design a novel policy scoring metric that assigns a high score to policies that align with the given preferences. We apply our algorithm to offline RL tasks with actual human preference labels and show that our algorithm outperforms or is on par with the existing PbRL methods. Notably, on high-dimensional control tasks, our algorithm surpasses offline RL methods that learn with ground-truth reward information. Finally, we show that our algorithm can be successfully applied to fine-tune large language models.
This paper investigates an end-to-end neural diarization (EEND) method for an unknown number of speakers. In contrast to the conventional cascaded approach to speaker diarization, EEND methods are better in terms of speaker overlap handling. However, EEND still has a disadvantage in that it cannot deal with a flexible number of speakers. To remedy this problem, we introduce encoder-decoder-based attractor calculation module (EDA) to EEND. Once frame-wise embeddings are obtained, EDA sequentially generates speaker-wise attractors on the basis of a sequence-to-sequence method using an LSTM encoder-decoder. The attractor generation continues until a stopping condition is satisfied; thus, the number of attractors can be flexible. Diarization results are then estimated as dot products of the attractors and embeddings. The embeddings from speaker overlaps result in larger dot product values with multiple attractors; thus, this method can deal with speaker overlaps. Because the maximum number of output speakers is still limited by the training set, we also propose an iterative inference method to remove this restriction. Further, we propose a method that aligns the estimated diarization results with the results of an external speech activity detector, which enables fair comparison against cascaded approaches. Extensive evaluations on simulated and real datasets show that EEND-EDA outperforms the conventional cascaded approach.
Dark patterns, which are user interface designs in online services, induce
users to take unintended actions. Recently, dark patterns have been raised as
an issue of privacy and fairness. Thus, a wide range of research on detecting
dark patterns is eagerly awaited. In this work, we constructed a dataset for
dark pattern detection and prepared its baseline detection performance with
state-of-the-art machine learning methods. The original dataset was obtained
from Mathur et al.'s study in 2019, which consists of 1,818 dark pattern texts
from shopping sites. Then, we added negative samples, i.e., non-dark pattern
texts, by retrieving texts from the same websites as Mathur et al.'s dataset.
We also applied state-of-the-art machine learning methods to show the automatic
detection accuracy as baselines, including BERT, RoBERTa, ALBERT, and XLNet. As
a result of 5-fold cross-validation, we achieved the highest accuracy of 0.975
with RoBERTa. The dataset and baseline source codes are available at
this https URL
Most text-to-speech (TTS) methods use high-quality speech corpora recorded in a well-designed environment, incurring a high cost for data collection. To solve this problem, existing noise-robust TTS methods are intended to use noisy speech corpora as training data. However, they only address either time-invariant or time-variant noises. We propose a degradation-robust TTS method, which can be trained on speech corpora that contain both additive noises and environmental distortions. It jointly represents the time-variant additive noises with a frame-level encoder and the time-invariant environmental distortions with an utterance-level encoder. We also propose a regularization method to attain clean environmental embedding that is disentangled from the utterance-dependent information such as linguistic contents and speaker characteristics. Evaluation results show that our method achieved significantly higher-quality synthetic speech than previous methods in the condition including both additive noise and reverberation.
End-to-end neural diarization (EEND) with encoder-decoder-based attractors
(EDA) is a promising method to handle the whole speaker diarization problem
simultaneously with a single neural network. While the EEND model can produce
all frame-level speaker labels simultaneously, it disregards output label
dependency. In this work, we propose a novel EEND model that introduces the
label dependency between frames. The proposed method generates
non-autoregressive intermediate attractors to produce speaker labels at the
lower layers and conditions the subsequent layers with these labels. While the
proposed model works in a non-autoregressive manner, the speaker labels are
refined by referring to the whole sequence of intermediate labels. The
experiments with the two-speaker CALLHOME dataset show that the intermediate
labels with the proposed non-autoregressive intermediate attractors boost the
diarization performance. The proposed method with the deeper network benefits
more from the intermediate labels, resulting in better performance and training
throughput than EEND-EDA.
We revisit the widely used bss eval metrics for source separation with an eye out for performance. We propose a fast algorithm fixing shortcomings of publicly available implementations. First, we show that the metrics are fully specified by the squared cosine of just two angles between estimate and reference subspaces. Second, large linear systems are involved. However, they are structured, and we apply a fast iterative method based on conjugate gradient descent. The complexity of this step is thus reduced by a factor quadratic in the distortion filter size used in bss eval, usually 512. In experiments, we assess speed and numerical accuracy. Not only is the loss of accuracy due to the approximate solver acceptable for most applications, but the speed-up is up to two orders of magnitude in some, not so extreme, cases. We confirm that our implementation can train neural networks, and find that longer distortion filters may be beneficial.
This paper proposes InterAug: a novel training method for CTC-based ASR using augmented intermediate representations for conditioning. The proposed method exploits the conditioning framework of self-conditioned CTC to train robust models by conditioning with "noisy" intermediate predictions. During the training, intermediate predictions are changed to incorrect intermediate predictions, and fed into the next layer for conditioning. The subsequent layers are trained to correct the incorrect intermediate predictions with the intermediate losses. By repeating the augmentation and the correction, iterative refinements, which generally require a special decoder, can be realized only with the audio encoder. To produce noisy intermediate predictions, we also introduce new augmentation: intermediate feature space augmentation and intermediate token space augmentation that are designed to simulate typical errors. The combination of the proposed InterAug framework with new augmentation allows explicit training of the robust audio encoders. In experiments using augmentations simulating deletion, insertion, and substitution error, we confirmed that the trained model acquires robustness to each error, boosting the speech recognition performance of the strong self-conditioned CTC baseline.
In this paper, we propose two mask-based beamforming methods using a deep neural network (DNN) trained by multichannel loss functions. Beamforming technique using time-frequency (TF)-masks estimated by a DNN have been applied to many applications where TF-masks are used for estimating spatial covariance matrices. To train a DNN for mask-based beamforming, loss functions designed for monaural speech enhancement/separation have been employed. Although such a training criterion is simple, it does not directly correspond to the performance of mask-based beamforming. To overcome this problem, we use multichannel loss functions which evaluate the estimated spatial covariance matrices based on the multichannel Itakura--Saito divergence. DNNs trained by the multichannel loss functions can be applied to construct several beamformers. Experimental results confirmed their effectiveness and robustness to microphone configurations.
Recently, it is shown that shuffling can amplify the central differential
privacy guarantees of data randomized with local differential privacy. Within
this setup, a centralized, trusted shuffler is responsible for shuffling by
keeping the identities of data anonymous, which subsequently leads to stronger
privacy guarantees for systems. However, introducing a centralized entity to
the originally local privacy model loses some appeals of not having any
centralized entity as in local differential privacy. Moreover, implementing a
shuffler in a reliable way is not trivial due to known security issues and/or
requirements of advanced hardware or secure computation technology.
Motivated by these practical considerations, we rethink the shuffle model to
relax the assumption of requiring a centralized, trusted shuffler. We introduce
network shuffling, a decentralized mechanism where users exchange data in a
random-walk fashion on a network/graph, as an alternative of achieving privacy
amplification via anonymity. We analyze the threat model under such a setting,
and propose distributed protocols of network shuffling that is straightforward
to implement in practice. Furthermore, we show that the privacy amplification
rate is similar to other privacy amplification techniques such as uniform
shuffling. To our best knowledge, among the recently studied intermediate trust
models that leverage privacy amplification techniques, our work is the first
that is not relying on any centralized entity to achieve privacy amplification.
Synthesizing and converting environmental sounds have the potential for many
applications such as supporting movie and game production, data augmentation
for sound event detection and scene classification. Conventional works on
synthesizing and converting environmental sounds are based on a physical
modeling or concatenative approach. However, there are a limited number of
works that have addressed environmental sound synthesis and conversion with
statistical generative models; thus, this research area is not yet well
organized. In this paper, we review problem definitions, applications, and
evaluation methods of environmental sound synthesis and conversion. We then
report on environmental sound synthesis using sound event labels, in which we
focus on the current performance of statistical environmental sound synthesis
and investigate how we should conduct subjective experiments on environmental
sound synthesis.
We propose to learn surrogate functions of universal speech priors for
determined blind speech separation. Deep speech priors are highly desirable due
to their high modelling power, but are not compatible with state-of-the-art
independent vector analysis based on majorization-minimization (AuxIVA), since
deriving the required surrogate function is not easy, nor always possible.
Instead, we do away with exact majorization and directly approximate the
surrogate. Taking advantage of iterative source steering (ISS) updates, we back
propagate the permutation invariant separation loss through multiple iterations
of AuxIVA. ISS lends itself well to this task due to its lower complexity and
lack of matrix inversion. Experiments show large improvements in terms of scale
invariant signal-to-distortion (SDR) ratio and word error rate compared to
baseline methods. Training is done on two speakers mixtures and we experiment
with two losses, SDR and coherence. We find that the learnt approximate
surrogate generalizes well on mixtures of three and four speakers without any
modification. We also demonstrate generalization to a different variation of
the AuxIVA update equations. The SDR loss leads to fastest convergence in
iterations, while coherence leads to the lowest word error rate (WER). We
obtain as much as 36 % reduction in WER.
We propose a self-supervised learning method using multiple sampling
strategies to obtain general-purpose audio representation. Multiple sampling
strategies are used in the proposed method to construct contrastive losses from
different perspectives and learn representations based on them. In this study,
in addition to the widely used clip-level sampling strategy, we introduce two
new strategies, a frame-level strategy and a task-specific strategy. The
proposed multiple strategies improve the performance of frame-level
classification and other tasks like pitch detection, which are not the focus of
the conventional single clip-level sampling strategy. We pre-trained the method
on a subset of Audioset and applied it to a downstream task with frozen
weights. The proposed method improved clip classification, sound event
detection, and pitch detection performance by 25%, 20%, and 3.6%.
Achieving high accuracy with low latency has always been a challenge in streaming end-to-end automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems. By attending to more future contexts, a streaming ASR model achieves higher accuracy but results in larger latency, which hurts the streaming performance. In the Mask-CTC framework, an encoder network is trained to learn the feature representation that anticipates long-term contexts, which is desirable for streaming ASR. Mask-CTC-based encoder pre-training has been shown beneficial in achieving low latency and high accuracy for triggered attention-based ASR. However, the effectiveness of this method has not been demonstrated for various model architectures, nor has it been verified that the encoder has the expected look-ahead capability to reduce latency. This study, therefore, examines the effectiveness of Mask-CTCbased pre-training for models with different architectures, such as Transformer-Transducer and contextual block streaming ASR. We also discuss the effect of the proposed pre-training method on obtaining accurate output spike timing.
We revisit the source image estimation problem from blind source separation
(BSS). We generalize the traditional minimum distortion principle to maximum
likelihood estimation with a model for the residual spectrograms. Because
residual spectrograms typically contain other sources, we propose to use a
mixed-norm model that lets us finely tune sparsity in time and frequency. We
propose to carry out the minimization of the mixed-norm via
majorization-minimization optimization, leading to an iteratively reweighted
least-squares algorithm. The algorithm balances well efficiency and ease of
implementation. We assess the performance of the proposed method as applied to
two well-known determined BSS and one joint BSS-dereverberation algorithms. We
find out that it is possible to tune the parameters to improve separation by up
to 2 dB, with no increase in distortion, and at little computational cost. The
method thus provides a cheap and easy way to boost the performance of blind
source separation.
Non-autoregressive (NAR) models simultaneously generate multiple outputs in a
sequence, which significantly reduces the inference speed at the cost of
accuracy drop compared to autoregressive baselines. Showing great potential for
real-time applications, an increasing number of NAR models have been explored
in different fields to mitigate the performance gap against AR models. In this
work, we conduct a comparative study of various NAR modeling methods for
end-to-end automatic speech recognition (ASR). Experiments are performed in the
state-of-the-art setting using ESPnet. The results on various tasks provide
interesting findings for developing an understanding of NAR ASR, such as the
accuracy-speed trade-off and robustness against long-form utterances. We also
show that the techniques can be combined for further improvement and applied to
NAR end-to-end speech translation. All the implementations are publicly
available to encourage further research in NAR speech processing.
This paper proposes a method for improved CTC inference with searched intermediates and multi-pass conditioning. The paper first formulates self-conditioned CTC as a probabilistic model with an intermediate prediction as a latent representation and provides a tractable conditioning framework. We then propose two new conditioning methods based on the new formulation: (1) Searched intermediate conditioning that refines intermediate predictions with beam-search, (2) Multi-pass conditioning that uses predictions of previous inference for conditioning the next inference. These new approaches enable better conditioning than the original self-conditioned CTC during inference and improve the final performance. Experiments with the LibriSpeech dataset show relative 3%/12% performance improvement at the maximum in test clean/other sets compared to the original self-conditioned CTC.
This paper proposes a method to relax the conditional independence assumption
of connectionist temporal classification (CTC)-based automatic speech
recognition (ASR) models. We train a CTC-based ASR model with auxiliary CTC
losses in intermediate layers in addition to the original CTC loss in the last
layer. During both training and inference, each generated prediction in the
intermediate layers is summed to the input of the next layer to condition the
prediction of the last layer on those intermediate predictions. Our method is
easy to implement and retains the merits of CTC-based ASR: a simple model
architecture and fast decoding speed. We conduct experiments on three different
ASR corpora. Our proposed method improves a standard CTC model significantly
(e.g., more than 20 % relative word error rate reduction on the WSJ corpus)
with a little computational overhead. Moreover, for the TEDLIUM2 corpus and the
AISHELL-1 corpus, it achieves a comparable performance to a strong
autoregressive model with beam search, but the decoding speed is at least 30
times faster.
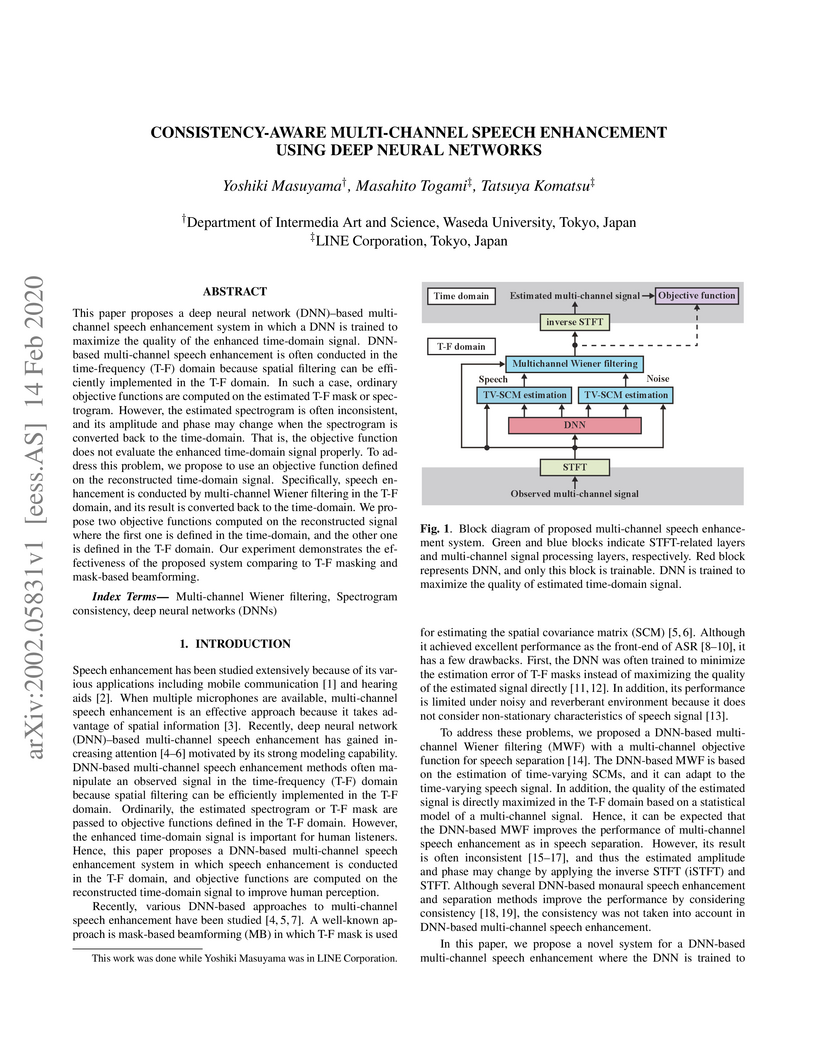
This paper proposes a deep neural network (DNN)-based multi-channel speech enhancement system in which a DNN is trained to maximize the quality of the enhanced time-domain signal. DNN-based multi-channel speech enhancement is often conducted in the time-frequency (T-F) domain because spatial filtering can be efficiently implemented in the T-F domain. In such a case, ordinary objective functions are computed on the estimated T-F mask or spectrogram. However, the estimated spectrogram is often inconsistent, and its amplitude and phase may change when the spectrogram is converted back to the time-domain. That is, the objective function does not evaluate the enhanced time-domain signal properly. To address this problem, we propose to use an objective function defined on the reconstructed time-domain signal. Specifically, speech enhancement is conducted by multi-channel Wiener filtering in the T-F domain, and its result is converted back to the time-domain. We propose two objective functions computed on the reconstructed signal where the first one is defined in the time-domain, and the other one is defined in the T-F domain. Our experiment demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed system comparing to T-F masking and mask-based beamforming.
We propose a new framework of synthesizing data using deep generative models in a differentially private manner. Within our framework, sensitive data are sanitized with rigorous privacy guarantees in a one-shot fashion, such that training deep generative models is possible without re-using the original data. Hence, no extra privacy costs or model constraints are incurred, in contrast to popular approaches such as Differentially Private Stochastic Gradient Descent (DP-SGD), which, among other issues, causes degradation in privacy guarantees as the training iteration increases. We demonstrate a realization of our framework by making use of the characteristic function and an adversarial re-weighting objective, which are of independent interest as well. Our proposal has theoretical guarantees of performance, and empirical evaluations on multiple datasets show that our approach outperforms other methods at reasonable levels of privacy.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.