Leti
Recent studies using Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy (THz-TDS) with spintronic emitters as a source have revealed distinct signatures of the Rashba effect. This effect, which arises from the breaking of inversion symmetry in low-dimensional materials, has been recently investigated in CoFeB/PtSe2/MoSe2/LiNbO3-based heterostructures [S. Massabeau et al., APL Mater. 13, 041102, 2025 ]. The observed phenomena are at the source of the generated THz far-field emission, typically through mechanisms such as spin-to-charge conversion triggered by the absorption of ultrafast optical pulses. In this work, we employ first-principles simulations to quantify the Rashba effect at PtSe2/MoSe2/LiNbO3 interfaces, expanding the traditional understanding of spin transport by incorporating the orbital degree of freedom. Moreover, we quantify the degree of control on the THz emission depending on the polarization direction of LiNbO3. In order to achieve this, we analyze the accumulation of both spin and orbital components using linear response theory, revealing distinct behaviors. These findings are crucial for a deeper understanding of the physical processes governing angular momentum-to-charge conversion and THz emission. Moreover, they may provide broader insights into various experimental outcomes, including those related to spin-orbit torque.
01 Sep 2022
We propose and demonstrate complete spin state readout of a two-electron system in a double quantum dot probed by an electrometer. The protocol is based on repetitive single shot measurements using Pauli spin blockade and our ability to tune on fast timescales the detuning and the interdot tunnel coupling between the GHz and sub-Hz regime. A sequence of three distinct manipulations and measurements allows establishing if the spins are in S, Tzero, Tplus or Tminus state. This work points at a procedure to reduce the overhead for spin readout, an important challenge for scaling up spin qubit platforms.
16 Jan 2025
 CNRS
CNRS Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University University of Southern CaliforniaGhent University
University of Southern CaliforniaGhent University Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University Stanford University
Stanford University Université Paris-Saclay
Université Paris-Saclay CEA
CEA Princeton UniversityNational Institute of Standards and TechnologyThe University of British ColumbiaNorth Carolina State UniversityUniversity of TrentoIMECÉcole Polytechnique Fédérale de LausanneNational Research CouncilNTT CorporationLeibniz-Institute of Photonic TechnologyLetiHewlett Packard LabsHewlett Packard EnterpriseSapienza UniversityInstitut FEMTO-STInstitut National de la Recherche Scientifique-Énergie Matériaux Télécommunications (IN)Université Franche Comte CNRSUniversit
Grenoble AlpesEnrico Fermi” Research CenterQueens
’ University
Princeton UniversityNational Institute of Standards and TechnologyThe University of British ColumbiaNorth Carolina State UniversityUniversity of TrentoIMECÉcole Polytechnique Fédérale de LausanneNational Research CouncilNTT CorporationLeibniz-Institute of Photonic TechnologyLetiHewlett Packard LabsHewlett Packard EnterpriseSapienza UniversityInstitut FEMTO-STInstitut National de la Recherche Scientifique-Énergie Matériaux Télécommunications (IN)Université Franche Comte CNRSUniversit
Grenoble AlpesEnrico Fermi” Research CenterQueens
’ UniversityThis roadmap consolidates recent advances while exploring emerging applications, reflecting the remarkable diversity of hardware platforms, neuromorphic concepts, and implementation philosophies reported in the field. It emphasizes the critical role of cross-disciplinary collaboration in this rapidly evolving field.
20 Jun 2024
We report local time-resolved thermometry in a silicon nanowire quantum dot
device designed to host a linear array of spin qubits. Using two alternative
measurement schemes based on rf reflectometry, we are able to probe either
local electron or phonon temperatures with μs-scale time resolution and a
noise equivalent temperature of 3 mK/Hz. Following the
application of short microwave pulses, causing local periodic heating,
time-dependent thermometry can track the dynamics of thermal excitation and
relaxation, revealing clearly different characteristic time scales. This work
opens important prospects to investigate the out-of-equilibrium thermal
properties of semiconductor quantum electronic devices operating at very low
temperature. In particular, it may provide a powerful handle to understand
heating effects recently observed in semiconductor spin-qubit systems.
31 Jul 2022
The synthesis of single-cycle, compressed optical and microwave pulses sparked novel areas of fundamental research. In the field of acoustics, however, such a generation has not been introduced yet. For numerous applications, the large spatial extent of surface acoustic waves (SAW) causes unwanted perturbations and limits the accuracy of physical manipulations. Particularly, this restriction applies to SAW-driven quantum experiments with single flying electrons, where extra modulation renders the exact position of the transported electron ambiguous and leads to undesired spin mixing. Here, we address this challenge by demonstrating single-shot chirp synthesis of a strongly compressed acoustic pulse. Employing this solitary SAW pulse to transport a single electron between distant quantum dots with an efficiency exceeding 99%, we show that chirp synthesis is competitive with regular transduction approaches. Performing a time-resolved investigation of the SAW-driven sending process, we outline the potential of the chirped SAW pulse to synchronize single-electron transport from many quantum-dot sources. By superimposing multiple pulses, we further point out the capability of chirp synthesis to generate arbitrary acoustic waveforms tailorable to a variety of (opto)nanomechanical applications. Our results shift the paradigm of compressed pulses to the field of acoustic phonons and pave the way for a SAW-driven platform of single-electron transport that is precise, synchronized, and scalable.
22 May 2023
Memristor-based neural networks provide an exceptional energy-efficient
platform for artificial intelligence (AI), presenting the possibility of
self-powered operation when paired with energy harvesters. However, most
memristor-based networks rely on analog in-memory computing, necessitating a
stable and precise power supply, which is incompatible with the inherently
unstable and unreliable energy harvesters. In this work, we fabricated a robust
binarized neural network comprising 32,768 memristors, powered by a miniature
wide-bandgap solar cell optimized for edge applications. Our circuit employs a
resilient digital near-memory computing approach, featuring complementarily
programmed memristors and logic-in-sense-amplifier. This design eliminates the
need for compensation or calibration, operating effectively under diverse
conditions. Under high illumination, the circuit achieves inference performance
comparable to that of a lab bench power supply. In low illumination scenarios,
it remains functional with slightly reduced accuracy, seamlessly transitioning
to an approximate computing mode. Through image classification neural network
simulations, we demonstrate that misclassified images under low illumination
are primarily difficult-to-classify cases. Our approach lays the groundwork for
self-powered AI and the creation of intelligent sensors for various
applications in health, safety, and environment monitoring.
25 Sep 2022
Semiconductor spin qubits based on spin-orbit states are responsive to electric field excitation allowing for practical, fast and potentially scalable qubit control. Spin-electric susceptibility, however, renders these qubits generally vulnerable to electrical noise, which limits their coherence time. Here we report on a spin-orbit qubit consisting of a single hole electrostatically confined in a natural silicon metal-oxide-semiconductor device. By varying the magnetic field orientation, we reveal the existence of operation sweet spots where the impact of charge noise is minimized while preserving an efficient electric-dipole spin control. We correspondingly observe an extension of the Hahn-echo coherence time up to 88 μs, exceeding by an order of magnitude the best reported values for hole-spin qubits, and approaching the state-of-the-art for electron spin qubits with synthetic spin-orbit coupling in isotopically-purified silicon. This finding largely enhances the prospects of silicon-based hole spin qubits for scalable quantum information processing.
We show that up to 90% reflectivity can be achieved by using guided plasmonic
resonances in a one-dimensional periodic array of plasmonic nanoribbon. In
general, to achieve strong reflection from a guided resonance system requires
one to operate in the strongly over-coupled regime where the radiative decay
rate dominates over the intrinsic loss rate of the resonances. Using an
argument similar to what has been previous used to derive the Chu-Harrington
limit for antennas, we show theoretically that there is no intrinsic limit for
the radiative decay rate even when the system has an atomic scale thickness, in
contrast to the existence of such limits on antennas. We also show that the
current distribution due to plasmonic resonance can be designed to achieve very
high external radiative rate. Our results show that high reflectivity can be
achieved in an atomically-thin graphene layer, pointing to a new opportunity
for creating atomically-thin optical devices.
05 Feb 2025
We simulate the electronic and transport properties of metal/two-dimensional
material/metal vertical heterostructures, with a focus on graphene, hexagonal
boron nitride and two phases of molybdenum diselenide. Using density functional
theory and non-equilibrium Green's function, we assess how stacking
configurations and material thickness impact important properties, such as
density of states, potential barriers and conductivity. For monolayers, strong
orbital hybridization with the metallic electrodes significantly alters the
electronic characteristics, with the formation of states within the gap of the
semiconducting 2D materials. Trilayers reveal the critical role of interlayer
coupling, where the middle layer retains its intrinsic properties, thus
influencing the overall conductivity. Our findings highlight the potential for
customized multilayer designs to optimize electronic device performance based
on two-dimensional materials.
13 Mar 2025
We present an optomechanical device platform for characterization of optical,
thermal, and rheological properties of fluids on the micron scale. A suspended
silicon microdisk resonator with a vibrating mass of 100 fg and an effective
measurement volume of less than a pL is used to monitor properties of different
fluids at rest. By employing analytical models for thermo-optical effects,
thermal diffusion and fluid-structure interactions, our platform determines the
refractive index, thermal conductivity, viscosity, density and compressibility
of the fluid, in a compact measurement setup. A single measurement takes as
short as 70 microseconds, and the employed power can be less than 100
microwatts, guaranteeing measurement at rest and in thermal equilibrium.
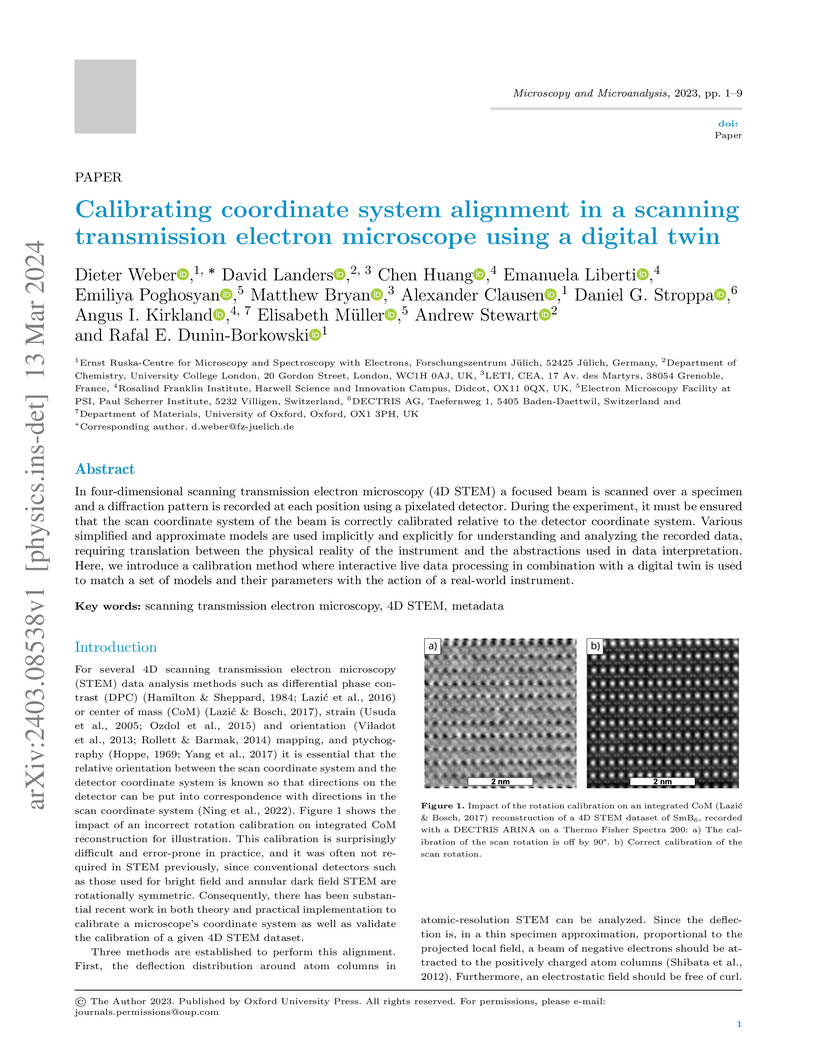
In four-dimensional scanning transmission electron microscopy (4D STEM) a focused beam is scanned over a specimen and a diffraction pattern is recorded at each position using a pixelated detector. During the experiment, it must be ensured that the scan coordinate system of the beam is correctly calibrated relative to the detector coordinate system. Various simplified and approximate models are used implicitly and explicitly for understanding and analyzing the recorded data, requiring translation between the physical reality of the instrument and the abstractions used in data interpretation. Here, we introduce a calibration method where interactive live data processing in combination with a digital twin is used to match a set of models and their parameters with the action of a real-world instrument.
08 May 2025
Open-source RISC-V cores are increasingly adopted in high-end embedded
domains such as automotive, where maximizing instructions per cycle (IPC) is
becoming critical. Building on the industry-supported open-source CVA6 core and
its superscalar variant, CVA6S, we introduce CVA6S+, an enhanced version
incorporating improved branch prediction, register renaming and enhanced
operand forwarding. These optimizations enable CVA6S+ to achieve a 43.5%
performance improvement over the scalar configuration and 10.9% over CVA6S,
with an area overhead of just 9.30% over the scalar core (CVA6). Furthermore,
we integrate CVA6S+ with the OpenHW Core-V High-Performance L1 Dcache
(HPDCache) and report a 74.1% bandwidth improvement over the legacy CVA6 cache
subsystem.
Hybrid superconductor-semiconductor Josephson field-effect transistors
(JoFETs) function as Josephson junctions with a gate-tunable critical current.
Additionally, they can feature a non-sinusoidal current-phase relation (CPR)
containing multiple harmonics of the superconducting phase difference, a so-far
underutilized property. In this work, we exploit this multi-harmonicity to
create a Josephson circuit element with an almost perfectly π-periodic CPR,
indicative of a largely dominant charge-4e supercurrent transport. Such a
Josephson element was recently proposed as the basic building block of a
protected superconducting qubit. Here, it is realized using a superconducting
quantum interference device (SQUID) with low-inductance aluminum arms and two
nominally identical JoFETs. The latter are fabricated from a SiGe/Ge/SiGe
quantum-well heterostructure embedding a high-mobility two-dimensional hole
gas. By carefully adjusting the JoFET gate voltages and finely tuning the
magnetic flux through the SQUID close to half a flux quantum, we achieve a
regime where the sin(2φ) component accounts for more than
\SI{95}{\percent} of the total supercurrent. This result demonstrates a new
promising route for the realization of superconducting qubits with enhanced
coherence properties.
29 Apr 2025
Spin qubits based on semiconductor quantum dots are a promising prospect for
quantum computation because of their high coherence times and gate fidelities.
However, scaling up those structures to the numbers required by fault-tolerant
quantum computing is currently hampered by a number of issues. One of the main
issues is the need for single-shot low-footprint qubit readout. Here, we
demonstrate the single-shot in situ measurement of a compact qubit unit-cell.
The unit cell is composed of two electron spins with a controllable exchange
interaction. We report initialization, single-shot readout and two-electron
entangling gate. The unit cell was successfully operated at up to 1 K, with
state-of-the-art charge noise levels extracted using free induction decay. With
its integrated readout and high stability, this foundry fabricated qubit unit
cell demonstrates strong potential for scalable quantum computing
architectures.
Model extraction emerges as a critical security threat with attack vectors
exploiting both algorithmic and implementation-based approaches. The main goal
of an attacker is to steal as much information as possible about a protected
victim model, so that he can mimic it with a substitute model, even with a
limited access to similar training data. Recently, physical attacks such as
fault injection have shown worrying efficiency against the integrity and
confidentiality of embedded models. We focus on embedded deep neural network
models on 32-bit microcontrollers, a widespread family of hardware platforms in
IoT, and the use of a standard fault injection strategy - Safe Error Attack
(SEA) - to perform a model extraction attack with an adversary having a limited
access to training data. Since the attack strongly depends on the input
queries, we propose a black-box approach to craft a successful attack set. For
a classical convolutional neural network, we successfully recover at least 90%
of the most significant bits with about 1500 crafted inputs. These information
enable to efficiently train a substitute model, with only 8% of the training
dataset, that reaches high fidelity and near identical accuracy level than the
victim model.
14 Sep 2021
Aluminium based platforms have allowed to reach major milestones for superconducting quantum circuits. For the next generation of devices, materials that are able to maintain low microwave losses while providing new functionalities, such as large kinetic inductance or compatibility with CMOS platform are sought for. Here we report on a combined direct current (DC) and microwave investigation of titanium nitride lms of dierent thicknesses grown using CMOS compatible methods. For microwave resonators made of TiN lm of thickness ∼3 nm, we measured large kinetic inductance LK ∼ 240 pH/sq, high mode impedance of ∼ 4.2 kΩ while maintaining microwave quality factor ∼ 10^5 in the single photon limit. We present an in-depth study of the microwave loss mechanisms in these devices that indicates the importance of quasiparticles and provide insights for further improvement.
The morphology of block copolymers (BCPs) critically influences material properties and applications. This work introduces a machine learning (ML)-enabled, high-throughput framework for analyzing grazing incidence small-angle X-ray scattering (GISAXS) data and atomic force microscopy (AFM) images to characterize BCP thin film morphology. A convolutional neural network was trained to classify AFM images by morphology type, achieving 97% testing accuracy. Classified images were then analyzed to extract 2D grain size measurements from the samples in a high-throughput manner. ML models were developed to predict morphological features based on processing parameters such as solvent ratio, additive type, and additive ratio. GISAXS-based properties were predicted with strong performances (R2 > 0.75), while AFM-based property predictions were less accurate (R2 < 0.60), likely due to the localized nature of AFM measurements compared to the bulk information captured by GISAXS. Beyond model performance, interpretability was addressed using Shapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP). SHAP analysis revealed that the additive ratio had the largest impact on morphological predictions, where additive provides the BCP chains with increased volume to rearrange into thermodynamically favorable morphologies. This interpretability helps validate model predictions and offers insight into parameter importance. Altogether, the presented framework combining high-throughput characterization and interpretable ML offers an approach to exploring and optimizing BCP thin film morphology across a broad processing landscape.
For the upcoming 6G wireless networks, reconfigurable intelligent surfaces
are an essential technology, enabling dynamic beamforming and signal
manipulation in both reflective and transmissive modes. It is expected to
utilize frequency bands in the millimeter-wave and THz, which presents unique
opportunities but also significant challenges. The selection of switching
technologies that can support high-frequency operation with minimal loss and
high efficiency is particularly complex. In this work, we demonstrate the
potential of advanced components such as Schottky diodes, memristor switches,
liquid metal-based switches, phase change materials, and RF-SOI technology in
RIS designs as an alternative to overcome limitations inherent in traditional
technologies in D-band (110-170 GHz).
14 Aug 2025
The Edelstein effect is a promising mechanism for generating spin and orbital polarization from charge currents in systems without inversion symmetry. In ferroelectric materials, such as Germanium Telluride (GeTe), the combination of bulk Rashba splitting and voltage-controlled ferroelectric polarization provides a pathway for electrical control of the sign of the charge-spin conversion. In this work, we investigate current-induced spin and orbital magnetization in bulk GeTe using Wannier-based tight-binding models derived from \textit{ab initio} calculations and semiclassical Boltzmann theory. Employing the modern theory of orbital magnetization, we demonstrate that the orbital Edelstein effect entirely dominates its spin counterpart. This difference is visualized through the spin and orbital textures at the Fermi surfaces, where the orbital moment surpasses the spin moment by one order of magnitude. Moreover, the orbital Edelstein effect remains largely unaffected in the absence of spin-orbit coupling, highlighting its distinct physical origin compared to the spin Edelstein effect.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) measures electron removal energies, providing direct access to core and valence electron binding energies, hence probing the electronic structure. In this work, we benchmark for the first time the ab initio many-body GW approximation on the complete electron binding energies of noble gas atoms (He-Rn), which spans 100~keV. Our results demonstrate that GW achieves an accuracy within 1.2% in XPS binding energies, by systematically restoring the underestimation from density-functional theory (DFT, error of 14%) or the overestimation from Hartree-Fock (HF, error of 4.7%). Such results also imply the correlations of d electrons are very well described by GW.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.