Ask or search anything...
 Tencent
TencentResearchers from Tencent Youtu Lab developed Training-Free Group Relative Policy Optimization, a method that enhances LLM agent performance in specialized tasks by learning and integrating experiential knowledge as a token prior without modifying model parameters. This approach achieved substantial performance gains on mathematical reasoning and web searching benchmarks with significantly reduced data and computational costs, leveraging the full capabilities of frozen large LLMs.
View blogTencent's LLM Department, HunYuan Infra Team, and CUHK developed Reinforcement Learning on Pre-Training data (RLPT), a framework applying reinforcement learning directly to unlabeled pre-training data. This approach addresses data scarcity and fosters deeper reasoning skills, showing absolute improvements of 3.0 on MMLU and 8.1 on GPQA-Diamond for Qwen3-4B-Base models.
View blogFlashSloth, developed by researchers from Xiamen University, Tencent Youtu Lab, and Shanghai AI Laboratory, introduces a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) architecture that significantly improves efficiency through embedded visual compression. The approach reduces visual tokens by 80-89% and achieves 2-5 times faster response times, while maintaining highly competitive performance across various vision-language benchmarks.
View blogSingle-stream Policy Optimization (SPO) introduces a group-free approach for enhancing Large Language Model (LLM) reasoning, overcoming inefficiencies in existing group-based reinforcement learning methods. The Tencent-authored work demonstrates superior performance, achieving a +3.4 percentage point improvement in `maj@32` score and a 4.35x speedup in agentic training throughput compared to GRPO, alongside more stable learning signals.
View blogA comprehensive synthesis of Large Language Models for automated software development covers the entire model lifecycle, from data curation to autonomous agents, and offers practical guidance derived from empirical experiments on pre-training, fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning, alongside a detailed analysis of challenges and future directions.
View blogThis survey provides a comprehensive synthesis of the rapidly evolving field of Multimodal Large Language Models, detailing their common architectures, multi-stage training paradigms, and diverse evaluation methodologies. It highlights the importance of data quality for instruction tuning and addresses key challenges, including the pervasive issue of multimodal hallucination.
View blogTencent's Hunyuan Foundation Model Team developed HunyuanVideo, an open-source framework for large video generative models that achieves performance comparable to leading closed-source solutions. The 13-billion-parameter model excels in human evaluations for motion dynamics and visual quality, supported by a systematic framework for data, architecture, and efficient training.
View blogThis research from Tencent and Tsinghua University provides the first formal proof that integrating external tools strictly expands a Large Language Model's problem-solving capabilities, overcoming the limitations of pure-text reasoning within practical token budgets. It also introduces an algorithm, ASPO, that stably guides LLMs to proactively leverage tools, demonstrating emergent cognitive patterns for complex tasks.
View blogProximal Supervised Fine-Tuning (PSFT) introduces a PPO-inspired clipped objective to stabilize large language model fine-tuning, preventing entropy collapse and catastrophic forgetting. This approach yields a more robust and generalized base model, serving as a superior "cold start" for subsequent reinforcement learning from human feedback or direct preference optimization, which ultimately leads to enhanced performance across various tasks.
View blogThis paper introduces "Diffusion of Thought (DoT)", a method for integrating Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning into diffusion language models. The approach demonstrates high accuracy and significant efficiency gains on reasoning tasks, outperforming autoregressive counterparts while offering a flexible computation-accuracy trade-off.
View blogPREF-GRPO introduces a novel training method for text-to-image (T2I) models that stabilizes reinforcement learning against reward hacking by utilizing pairwise preference rewards. The accompanying UNIGENBENCH offers a fine-grained, MLLM-powered framework for comprehensive and diagnostic evaluation of T2I models.
View blogTencent's Hunyuan3D 2.0 system introduces an open-source, large-scale foundational model for generating high-resolution textured 3D assets from images. The system leverages a two-stage diffusion pipeline, including a novel shape encoder and a multi-view consistent texture synthesis module, demonstrating superior performance in geometry detail, texture quality, and condition alignment compared to previous methods.
View blogThis survey paper defines and applies a 'full-stack' safety concept for Large Language Models (LLMs), systematically analyzing safety concerns across their entire lifecycle from data to deployment and commercialization. The collaboration synthesizes findings from over 900 papers, providing a unified taxonomy of attacks and defenses while identifying key insights and future research directions for LLM and LLM-agent safety.
View blogFlashWorld enables high-quality 3D scene generation from a single image or text prompt within seconds, achieving a 10-100x speedup over previous methods while delivering superior visual fidelity and consistent 3D structures. The model recovers intricate details and produces realistic backgrounds even for complex scenes, demonstrating strong performance across image-to-3D and text-to-3D tasks.
View blogThe 'Yan' framework provides a unified approach for interactive video generation, achieving real-time 1080P/60FPS AAA-level simulations with accurate physics. It supports multi-modal content generation guided by prompts and enables dynamic, multi-granularity editing of both structure and style during interaction.
View blogTencent Hunyuan3D developed Hunyuan3D Studio, an end-to-end AI pipeline that automates the generation of game-ready 3D assets from text or image prompts. This system integrates multiple AI modules to produce high-fidelity models with optimized geometry, PBR textures, and animatable rigs, drastically reducing production time and complexity.
View blogThe LaSeR framework enables Large Language Models to efficiently perform self-verification and enhance their reasoning capabilities by deriving a 'last-token self-rewarding score' directly from the final predicted token's probability distribution. This approach integrates self-assessment at nearly zero additional inference cost, improving reasoning performance while achieving high F1 scores for distinguishing correct from incorrect solutions.
View blog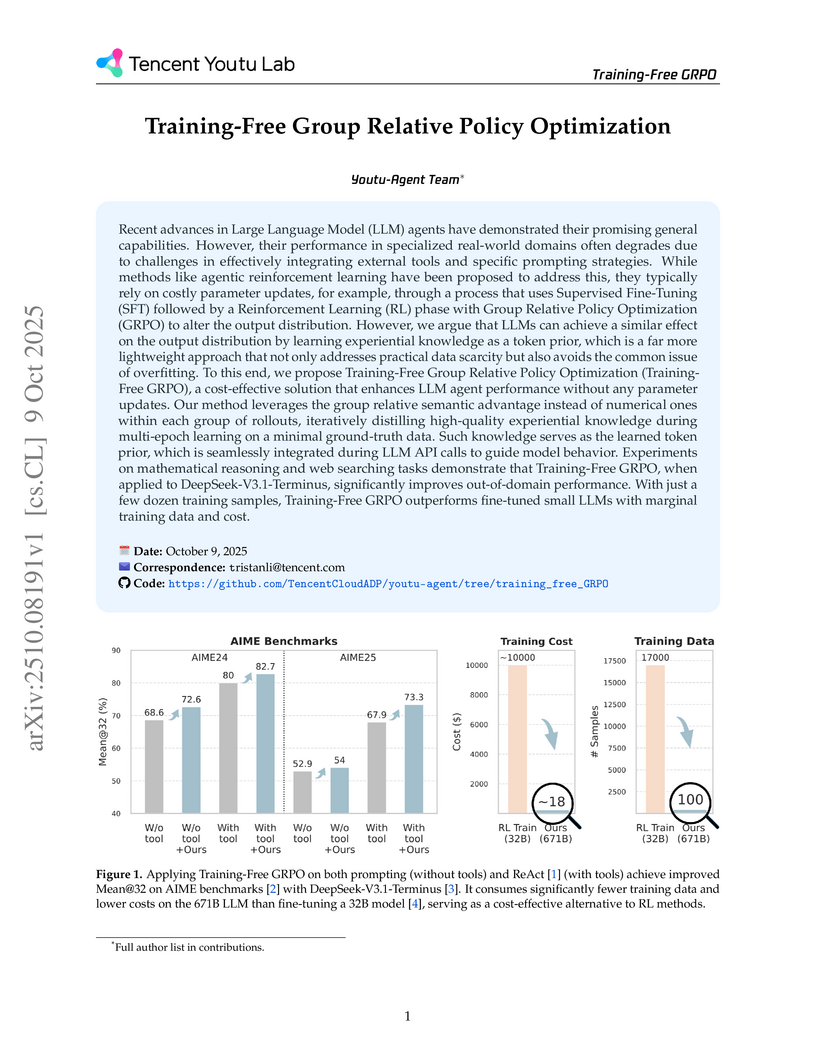
 The Chinese University of Hong Kong
The Chinese University of Hong Kong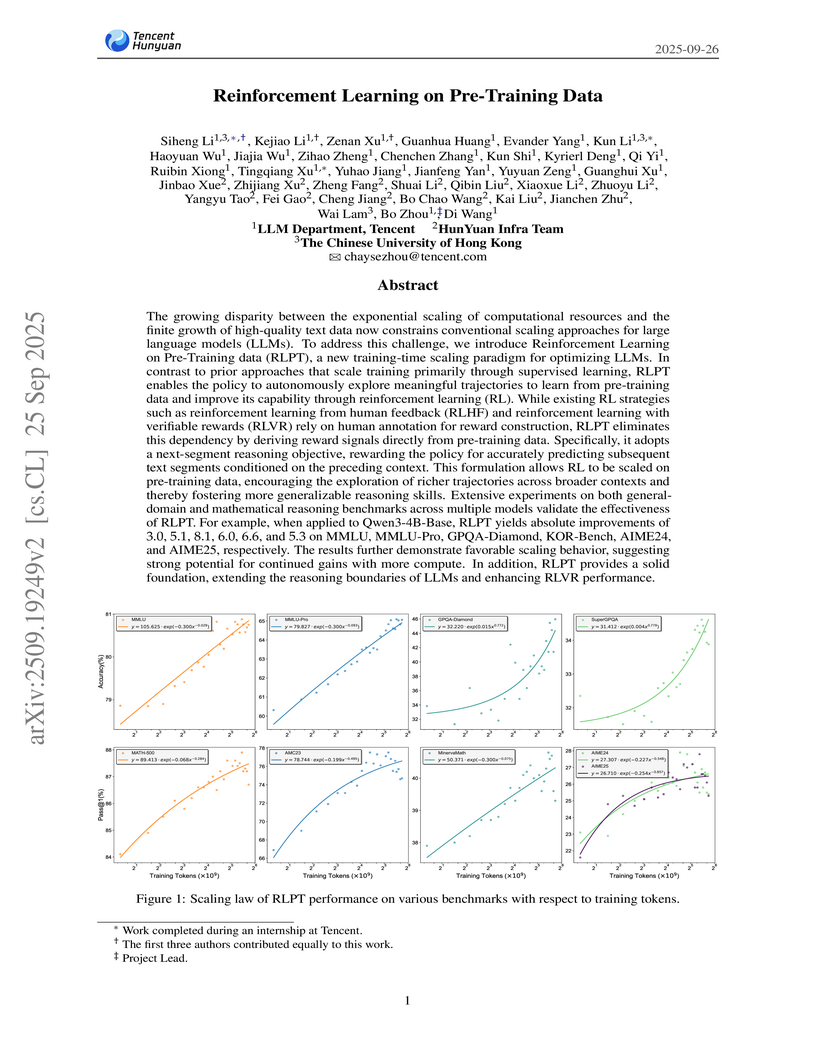


 Monash University
Monash University
 Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University
 University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China


 Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University

 ByteDance
ByteDance
 Huawei
Huawei The University of Hong Kong
The University of Hong Kong
 Fudan University
Fudan University

 University of Washington
University of Washington



 Renmin University of China
Renmin University of China