Northwest Institute of Nuclear Technology
04 Jan 2025
In non-geostationary orbit (NGSO) satellite communication systems, effectively utilizing beam hopping (BH) technology is crucial for addressing uneven traffic demands. However, optimizing beam scheduling and resource allocation in multi-NGSO BH scenarios remains a significant challenge. This paper proposes a multi-NGSO BH algorithm based on deep reinforcement learning (DRL) to optimize beam illumination patterns and power allocation. By leveraging three degrees of freedom (i.e., time, space, and power), the algorithm aims to optimize the long-term throughput and the long-term cumulative average delay (LTCAD). The solution is based on proximal policy optimization (PPO) with a hybrid action space combining discrete and continuous actions. Using two policy networks with a shared base layer, the proposed algorithm jointly optimizes beam scheduling and power allocation. One network selects beam illumination patterns in the discrete action space, while the other manages power allocation in the continuous space. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm significantly reduces LTCAD while maintaining high throughput in time-varying traffic scenarios. Compared to the four benchmark methods, it improves network throughput by up to 8.9% and reduces LTCAD by up to 69.2%
Infrared-visible object detection (IVOD) seeks to harness the complementary information in infrared and visible images, thereby enhancing the performance of detectors in complex environments. However, existing methods often neglect the frequency characteristics of complementary information, such as the abundant high-frequency details in visible images and the valuable low-frequency thermal information in infrared images, thus constraining detection performance. To solve this problem, we introduce a novel Frequency-Driven Feature Decomposition Network for IVOD, called FD2-Net, which effectively captures the unique frequency representations of complementary information across multimodal visual spaces. Specifically, we propose a feature decomposition encoder, wherein the high-frequency unit (HFU) utilizes discrete cosine transform to capture representative high-frequency features, while the low-frequency unit (LFU) employs dynamic receptive fields to model the multi-scale context of diverse objects. Next, we adopt a parameter-free complementary strengths strategy to enhance multimodal features through seamless inter-frequency recoupling. Furthermore, we innovatively design a multimodal reconstruction mechanism that recovers image details lost during feature extraction, further leveraging the complementary information from infrared and visible images to enhance overall representational capacity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FD2-Net outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) models across various IVOD benchmarks, i.e. LLVIP (96.2% mAP), FLIR (82.9% mAP), and M3FD (83.5% mAP).
In this study, we explore the inherent trade-off between accuracy and robustness in neural networks, drawing an analogy to the uncertainty principle in quantum mechanics. We propose that neural networks are subject to an uncertainty relation, which manifests as a fundamental limitation in their ability to simultaneously achieve high accuracy and robustness against adversarial attacks. Through mathematical proofs and empirical evidence, we demonstrate that this trade-off is a natural consequence of the sharp boundaries formed between different class concepts during training. Our findings reveal that the complementarity principle, a cornerstone of quantum physics, applies to neural networks, imposing fundamental limits on their capabilities in simultaneous learning of conjugate features. Meanwhile, our work suggests that achieving human-level intelligence through a single network architecture or massive datasets alone may be inherently limited. Our work provides new insights into the theoretical foundations of neural network vulnerability and opens up avenues for designing more robust neural network architectures.
Researchers from Beijing Institute of Technology and Northwest Institute of Nuclear Technology developed JefiGPU, a GPU-accelerated implementation of Jefimenko's equations for calculating electromagnetic fields. This system achieves an approximate 1000-fold speed-up over a single-core CPU implementation for certain configurations and provides field calculations with deviations around 3-14% from theoretical results, offering an efficient tool for applications like heavy-ion collision simulations.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), due to their low cost and high flexibility, have been widely used in various scenarios to enhance network performance. However, the optimization of UAV trajectories in unknown areas or areas without sufficient prior information, still faces challenges related to poor planning performance and low distributed execution. These challenges arise when UAVs rely solely on their own observation information and the information from other UAVs within their communicable range, without access to global information. To address these challenges, this paper proposes the Qedgix framework, which combines graph neural networks (GNNs) and the QMIX algorithm to achieve distributed optimization of the Age of Information (AoI) for users in unknown scenarios. The framework utilizes GNNs to extract information from UAVs, users within the observable range, and other UAVs within the communicable range, thereby enabling effective UAV trajectory planning. Due to the discretization and temporal features of AoI indicators, the Qedgix framework employs QMIX to optimize distributed partially observable Markov decision processes (Dec-POMDP) based on centralized training and distributed execution (CTDE) with respect to mean AoI values of users. By modeling the UAV network optimization problem in terms of AoI and applying the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem, the Qedgix framework achieves efficient neural network training through parameter sharing based on permutation invariance. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm significantly improves convergence speed while reducing the mean AoI values of users. The code is available at this https URL.
Understanding the mechanisms behind neural network optimization is crucial for improving network design and performance. While various optimization techniques have been developed, a comprehensive understanding of the underlying principles that govern these techniques remains elusive. Specifically, the role of symmetry breaking, a fundamental concept in physics, has not been fully explored in neural network optimization. This gap in knowledge limits our ability to design networks that are both efficient and effective. Here, we propose the symmetry breaking hypothesis to elucidate the significance of symmetry breaking in enhancing neural network optimization. We demonstrate that a simple input expansion can significantly improve network performance across various tasks, and we show that this improvement can be attributed to the underlying symmetry breaking mechanism. We further develop a metric to quantify the degree of symmetry breaking in neural networks, providing a practical approach to evaluate and guide network design. Our findings confirm that symmetry breaking is a fundamental principle that underpins various optimization techniques, including dropout, batch normalization, and equivariance. By quantifying the degree of symmetry breaking, our work offers a practical technique for performance enhancement and a metric to guide network design without the need for complete datasets and extensive training processes.
Neural networks demonstrate inherent vulnerability to small, non-random perturbations, emerging as adversarial attacks. Such attacks, born from the gradient of the loss function relative to the input, are discerned as input conjugates, revealing a systemic fragility within the network structure. Intriguingly, a mathematical congruence manifests between this mechanism and the quantum physics' uncertainty principle, casting light on a hitherto unanticipated interdisciplinarity. This inherent susceptibility within neural network systems is generally intrinsic, highlighting not only the innate vulnerability of these networks but also suggesting potential advancements in the interdisciplinary area for understanding these black-box networks.
08 Mar 2024
The effects of chlorine (Cl) and zinc (Zn) co-doping on the electronic structure and optical properties of the zinc blende ({\gamma}) phase of copper iodide ({\gamma}-CuI) scintillator material are investigated by using first-principles density functional theory calculations. The band structure, density of states, dielectric function, absorption coefficients, and reflectivity were analyzed before and after doping. Results show co-doping significantly modifies the band structure, reduces the band gap, and generates impurity energy levels. Cl doping enhances absorption in the high energy region while reducing visible light absorption. Zn doping induces a redshift in absorption and n-type conductivity at high concentrations. With suitable co-doping ratios, the absorption coefficient and reflectivity of {\gamma}-CuI can be optimized in the visible range to improve scintillation light yield. The calculations provide guidance for co-doping {\gamma}-CuI scintillators to achieve superior detection performance. The n-type conductivity also makes doped {\gamma}-CuI promising for optoelectronic applications.
Northwestern Polytechnical UniversityShaanxi Normal UniversityXidian University Peking UniversityCentral China Normal UniversityInstitute of Science TokyoXian Jiaotong UniversityNorthwest Institute of Nuclear TechnologyDP TechnologyAI for Science InstituteNational Meteorological Information CenterGuangzhou Institute of Geography, Academy of Sciences
Peking UniversityCentral China Normal UniversityInstitute of Science TokyoXian Jiaotong UniversityNorthwest Institute of Nuclear TechnologyDP TechnologyAI for Science InstituteNational Meteorological Information CenterGuangzhou Institute of Geography, Academy of Sciences
 Peking UniversityCentral China Normal UniversityInstitute of Science TokyoXian Jiaotong UniversityNorthwest Institute of Nuclear TechnologyDP TechnologyAI for Science InstituteNational Meteorological Information CenterGuangzhou Institute of Geography, Academy of Sciences
Peking UniversityCentral China Normal UniversityInstitute of Science TokyoXian Jiaotong UniversityNorthwest Institute of Nuclear TechnologyDP TechnologyAI for Science InstituteNational Meteorological Information CenterGuangzhou Institute of Geography, Academy of SciencesWe uncover a phenomenon largely overlooked by the scientific community utilizing AI: neural networks exhibit high susceptibility to minute perturbations, resulting in significant deviations in their outputs. Through an analysis of five diverse application areas -- weather forecasting, chemical energy and force calculations, fluid dynamics, quantum chromodynamics, and wireless communication -- we demonstrate that this vulnerability is a broad and general characteristic of AI systems. This revelation exposes a hidden risk in relying on neural networks for essential scientific computations, calling further studies on their reliability and security.
11 Aug 2025
In this paper, a physics-informed multiresolution wavelet neural network (PIMWNN) method is proposed for solving partial differential equations (PDEs). This method uses the multiresolution wavelet neural network (MWNN) to approximate unknown functions, then substituting the MWNN into PDEs and training the MWNN by least-squares algorithm. We apply the proposed method to various problems, including stationary/nonstationary advection, diffusion and advection-diffusion problems, and linear/nonlinear time-dependent problems. Numerical experiments show that the PIMWNN method can achieve higher accuracy and faster speed than Physics Informed Neural Networks (PINNs). Moreover, the PIMWNN method, being mesh-free, can handle different boundary conditions easily and solve the time-dependent problems efficiently. The proposed method is expected to solve the spectral bias problem in network training. These characteristics show the great potential of the PIMWNN method used in the field of numerical solving methods for PDEs.
02 Dec 2025
Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imaging plays a critical role in all-weather, day-and-night remote sensing, yet reconstruction is often challenged by noise, undersampling, and complex scattering scenarios. Conventional methods, including matched filtering and sparsity-based compressed sensing, are limited in capturing intricate scene structures and frequently suffer from artifacts, elevated sidelobes, and loss of fine details. Recent diffusion models have demonstrated superior capability in representing high-order priors; however, existing diffusion-based SAR methods still yield degraded reconstructions due to oversimplified likelihood approximations in guided sampling. In this work, we propose a diffusion-driven split Gibbs sampling framework for SAR reconstruction, rigorously integrating measurement fidelity with learned diffusion priors. By alternately performing likelihood- and prior-driven updates via proximal sampling, this method ensures progressive convergence toward the true posterior while fully leveraging the expressive power of diffusion priors. Extensive experiments on simulated and Sentinel-1A datasets demonstrate substantial performance improvements: over 7 dB average PSNR gain in simulations, along with significant sidelobe suppression (MPLSR +2.96 dB, MISLR +11.5 dB) with respect to the best baseline result. On real-world Sentinel-1A data, the method achieves an average PSNR gain of 1.6 dB while effectively reducing artifacts and preserving scene details, including ridges, edges, and fine textures. These results underscore the potential of the adapted framework as a robust and generalizable solution for high-fidelity SAR imaging across diverse sensing scenarios.
05 Apr 2024
We present a novel one-fluid cavitation model of a specific Mie-Gr\"uneisen
equation of state(EOS), named polynomial EOS, based on an artificial neural
network. Not only the physics-informed equation but also the experimental data
are embedded into the proposed model by an optimization problem. The
physics-informed data-driven model provides the concerned pressure within the
cavitation region, where the density tends to zero when the pressure falls
below the saturated pressure. The present model is then applied to computing
the challenging compressible multi-phase flow simulation, such as nuclear and
underwater explosions. Numerical simulations show that our model in application
agrees well with the corresponding experimental data, ranging from one
dimension to three dimensions with the h−adaptive mesh refinement algorithm
and load balance techniques in the structured and unstructured grid.
11 Feb 2025
We are currently in an era of escalating technological complexity and
profound societal transformations, where artificial intelligence (AI)
technologies exemplified by large language models (LLMs) have reignited
discussions on the 'Technological Singularity'. 'Technological Singularity' is
a philosophical concept referring to an irreversible and profound
transformation that occurs when AI capabilities surpass those of humans
comprehensively. However, quantitative modeling and analysis of the historical
evolution and future trends of AI technologies remain scarce, failing to
substantiate the singularity hypothesis adequately. This paper hypothesizes
that the development of AI technologies could be characterized by the
superposition of multiple logistic growth processes. To explore this
hypothesis, we propose a multi-logistic growth process model and validate it
using two real-world datasets: AI Historical Statistics and Arxiv AI Papers.
Our analysis of the AI Historical Statistics dataset assesses the effectiveness
of the multi-logistic model and evaluates the current and future trends in AI
technology development. Additionally, cross-validation experiments on the Arxiv
AI Paper, GPU Transistor and Internet User dataset enhance the robustness of
our conclusions derived from the AI Historical Statistics dataset. The
experimental results reveal that around 2024 marks the fastest point of the
current AI wave, and the deep learning-based AI technologies are projected to
decline around 2035-2040 if no fundamental technological innovation emerges.
Consequently, the technological singularity appears unlikely to arrive in the
foreseeable future.
30 Sep 2025
The production of high-yield, longitudinally polarized positron beams represents an outstanding challenge in advanced accelerator science. Laser-driven schemes offer a compact alternative but typically yield only transverse polarization, or require pre-polarized electron beams, and struggle to efficiently accelerate positrons to high energies. Here, we introduce an all-optical scheme that overcomes these limitations by integrating positron generation, acceleration, and spin manipulation in a unified framework. Through a head-on collision between an ultraintense, circularly polarized laser pulse and a counterpropagating unpolarized electron beam, we drive a robust QED cascade. The nonlinear Breit-Wheeler process within the cascade produces positrons that are born directly within the strong laser field. Crucially, these positrons are instantaneously captured and accelerated to multi-GeV energies (up to ∼9 GeV) via a direct laser acceleration mechanism, while their spins are simultaneously rotated to longitudinal alignment by the field dynamics. Our Monte-Carlo simulations confirm the simultaneous achievement of a high positron yield (∼20 e+/e−), a high average longitudinal polarization (∼50\%), and GeV-scale energies. This all-optical source, feasible at upcoming ultraintense laser facilities, presents a compact and efficient solution for applications in collider physics and fundamental high-energy experiments.
The development of Digital Twins (DTs) represents a transformative advance
for simulating and optimizing complex systems in a controlled digital space.
Despite their potential, the challenge of constructing DTs that accurately
replicate and predict the dynamics of real-world systems remains substantial.
This paper introduces an intelligent framework for the construction and
evaluation of DTs, specifically designed to enhance the accuracy and utility of
DTs in testing algorithmic performance. We propose a novel construction
methodology that integrates deep learning-based policy gradient techniques to
dynamically tune the DT parameters, ensuring high fidelity in the digital
replication of physical systems. Moreover, the Mean STate Error (MSTE) is
proposed as a robust metric for evaluating the performance of algorithms within
these digital space. The efficacy of our framework is demonstrated through
extensive simulations that show our DT not only accurately mirrors the physical
reality but also provides a reliable platform for algorithm evaluation. This
work lays a foundation for future research into DT technologies, highlighting
pathways for both theoretical enhancements and practical implementations in
various industries.
08 Jun 2024
Giant resonances (GRs) provide crucial insights into nuclear physics and astrophysics. Exciting GRs using particles like electrons is effective, yet the angular momentum (AM) transfer of electrons, including both intrinsic spin and orbital degrees of freedom in inelastic scattering, has never been studied. Here, we investigate AM transfer in GRs excited by plane-wave and vortex electrons, developing a comprehensive AM-resolved inelastic electron scattering theory. We find that even plane-wave electrons can model-independently extract transition strengths of higher multipolarity by selecting specific AM states of scattered electrons. Additionally, relativistic vortex electrons with orbital angular momentum (OAM) ±1 can be efficiently generated. Vortex electrons can also be used to extract GR transition strength as in the plane-wave case, regardless of the position of nucleus relative to the beam axis. Furthermore, relativistic vortex electrons with larger OAM can be generated for on-axis nuclei due to AM conservation. Our method offers new perspectives for nuclear structure research and paves the way for generating vortex particles.
Classification-regression prediction networks have realized impressive
success in several modern deep trackers. However, there is an inherent
difference between classification and regression tasks, so they have diverse
even opposite demands for feature matching. Existed models always ignore the
key issue and only employ a unified matching block in two task branches,
decaying the decision quality. Besides, these models also struggle with
decision misalignment situation. In this paper, we propose a multi-attention
associate prediction network (MAPNet) to tackle the above problems. Concretely,
two novel matchers, i.e., category-aware matcher and spatial-aware matcher, are
first designed for feature comparison by integrating self, cross, channel or
spatial attentions organically. They are capable of fully capturing the
category-related semantics for classification and the local spatial contexts
for regression, respectively. Then, we present a dual alignment module to
enhance the correspondences between two branches, which is useful to find the
optimal tracking solution. Finally, we describe a Siamese tracker built upon
the proposed prediction network, which achieves the leading performance on five
tracking benchmarks, consisting of LaSOT, TrackingNet, GOT-10k, TNL2k and
UAV123, and surpasses other state-of-the-art approaches.
15 Jun 2020
Impacts of quantum stochasticity on the dynamics of an ultra-relativistic
electron beam head-on colliding with a linearly polarized ultra-intense laser
pulse are theoretically investigated in a quasi-classical regime. Generally,
the angular distribution of the electron beam keeps symmetrically in transverse
directions in this regime, even under the ponderomotive force of the laser
pulse. Here we show that when the initial angular divergence $\Delta \theta_i
\lesssim 10^{-6} a_0^2witha_0$ being the normalized laser field amplitude,
an asymmetric angular distribution of the electron beam arises due to the
quantum stochasticity effect, via simulations employing Landau-Lifshitz,
quantum-modified Landau-Lifshitz equations, and quantum stochastic radiation
reaction form to describe the radiative electron dynamics respectively. The
asymmetry is robust against a variety of laser and electron parameters,
providing an experimentally detectable signature for the nature of quantum
stochasticity of photon emission with laser and electron beams currently
available.
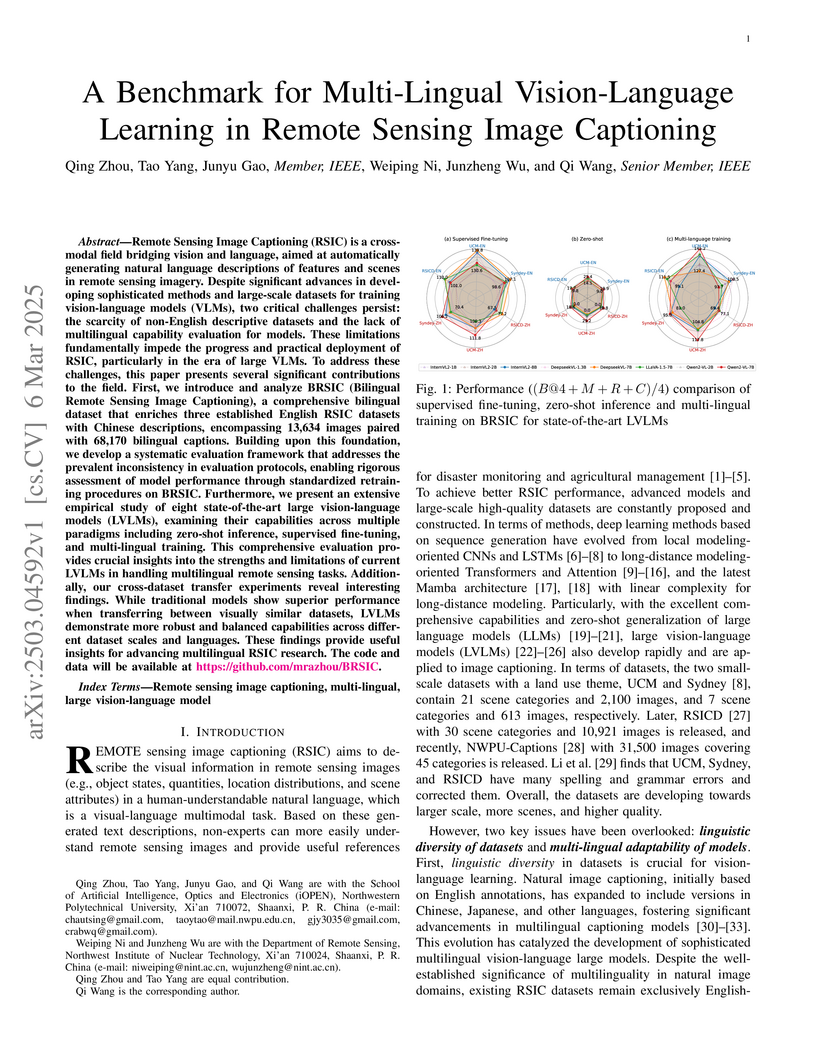
Remote Sensing Image Captioning (RSIC) is a cross-modal field bridging vision
and language, aimed at automatically generating natural language descriptions
of features and scenes in remote sensing imagery. Despite significant advances
in developing sophisticated methods and large-scale datasets for training
vision-language models (VLMs), two critical challenges persist: the scarcity of
non-English descriptive datasets and the lack of multilingual capability
evaluation for models. These limitations fundamentally impede the progress and
practical deployment of RSIC, particularly in the era of large VLMs. To address
these challenges, this paper presents several significant contributions to the
field. First, we introduce and analyze BRSIC (Bilingual Remote Sensing Image
Captioning), a comprehensive bilingual dataset that enriches three established
English RSIC datasets with Chinese descriptions, encompassing 13,634 images
paired with 68,170 bilingual captions. Building upon this foundation, we
develop a systematic evaluation framework that addresses the prevalent
inconsistency in evaluation protocols, enabling rigorous assessment of model
performance through standardized retraining procedures on BRSIC. Furthermore,
we present an extensive empirical study of eight state-of-the-art large
vision-language models (LVLMs), examining their capabilities across multiple
paradigms including zero-shot inference, supervised fine-tuning, and
multi-lingual training. This comprehensive evaluation provides crucial insights
into the strengths and limitations of current LVLMs in handling multilingual
remote sensing tasks. Additionally, our cross-dataset transfer experiments
reveal interesting findings. The code and data will be available at
this https URL
07 Mar 2025
GaAs-based light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are commonly employed in a variety of
applications, including medical imaging, biosensing, optical communications,
and night vision. In this paper, we present an alternative application of
GaAs-based LED with SI-GaAs substrate for X-ray detection and imaging. The
mechanism relies on the semiconductor frequency down-conversion process, where
the SI-GaAs substrate acts as a photodetector (PD). Upon X-ray irradiation, the
generated photocurrent by the SI-GaAs substrate drives the LED to emit NIR
photons which can be detect by a low-cost CCD. We demonstrate direct X-ray
detection and present preliminary imaging results, providing another example of
the applicability of the PD-LED design for optical frequency conversion. The
proposed LED X-ray detector leverages mature materials and fabrication
processes. The application of the frequency down-conversion concept makes it
possible for pixel-less imaging using a large single imaging unit, eliminating
the need for readout circuits. This PD-LED architecture offers an alternative
approach to direct X-ray detection and imaging, characterized by higher
absorption, improved image resolution, and enhanced material stability.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.