Research Institutes of Sweden
The recent development of Foundation Models (FMs), represented by large
language models, vision transformers, and multimodal models, has been making a
significant impact on both academia and industry. Compared with small-scale
models, FMs have a much stronger demand for high-volume data during the
pre-training phase. Although general FMs can be pre-trained on data collected
from open sources such as the Internet, domain-specific FMs need proprietary
data, posing a practical challenge regarding the amount of data available due
to privacy concerns. Federated Learning (FL) is a collaborative learning
paradigm that breaks the barrier of data availability from different
participants. Therefore, it provides a promising solution to customize and
adapt FMs to a wide range of domain-specific tasks using distributed datasets
whilst preserving privacy. This survey paper discusses the potentials and
challenges of synergizing FL and FMs and summarizes core techniques, future
directions, and applications. A periodically updated paper collection on FM-FL
is available at https://github.com/lishenghui/awesome-fm-fl.
This two-part comprehensive survey is devoted to a computing framework most
commonly known under the names Hyperdimensional Computing and Vector Symbolic
Architectures (HDC/VSA). Both names refer to a family of computational models
that use high-dimensional distributed representations and rely on the algebraic
properties of their key operations to incorporate the advantages of structured
symbolic representations and vector distributed representations. Notable models
in the HDC/VSA family are Tensor Product Representations, Holographic Reduced
Representations, Multiply-Add-Permute, Binary Spatter Codes, and Sparse Binary
Distributed Representations but there are other models too. HDC/VSA is a highly
interdisciplinary field with connections to computer science, electrical
engineering, artificial intelligence, mathematics, and cognitive science. This
fact makes it challenging to create a thorough overview of the field. However,
due to a surge of new researchers joining the field in recent years, the
necessity for a comprehensive survey of the field has become extremely
important. Therefore, amongst other aspects of the field, this Part I surveys
important aspects such as: known computational models of HDC/VSA and
transformations of various input data types to high-dimensional distributed
representations. Part II of this survey is devoted to applications, cognitive
computing and architectures, as well as directions for future work. The survey
is written to be useful for both newcomers and practitioners.
Federated Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (FedPEFT) has emerged as a
promising paradigm for privacy-preserving and efficient adaptation of
Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs) in Federated Learning (FL) settings. It
preserves data privacy by keeping the data decentralized and training the model
on local devices, ensuring that raw data never leaves the user's device.
Moreover, the integration of PEFT methods such as LoRA significantly reduces
the number of trainable parameters compared to fine-tuning the entire model,
thereby minimizing communication costs and computational overhead. Despite its
potential, the security implications of FedPEFT remain underexplored. This
paper introduces a novel security threat to FedPEFT, termed PEFT-as-an-Attack
(PaaA), which exposes how PEFT can be exploited as an attack vector to
circumvent PLMs' safety alignment and generate harmful content in response to
malicious prompts. Our evaluation of PaaA reveals that with less than 1% of the
model's parameters set as trainable, and a small subset of clients acting
maliciously, the attack achieves an approximate 80% attack success rate using
representative PEFT methods such as LoRA. To mitigate this threat, we further
investigate potential defense strategies, including Robust Aggregation Schemes
(RASs) and Post-PEFT Safety Alignment (PPSA). However, our empirical analysis
highlights the limitations of these defenses, i.e., even the most advanced
RASs, such as DnC and ClippedClustering, struggle to defend against PaaA in
scenarios with highly heterogeneous data distributions. Similarly, while PPSA
can reduce attack success rates to below 10%, it severely degrades the model's
accuracy on the target task. Our results underscore the urgent need for more
effective defense mechanisms that simultaneously ensure security and maintain
the performance of the FedPEFT paradigm.
Vector space models for symbolic processing that encode symbols by random vectors have been proposed in cognitive science and connectionist communities under the names Vector Symbolic Architecture (VSA), and, synonymously, Hyperdimensional (HD) computing. In this paper, we generalize VSAs to function spaces by mapping continuous-valued data into a vector space such that the inner product between the representations of any two data points represents a similarity kernel. By analogy to VSA, we call this new function encoding and computing framework Vector Function Architecture (VFA). In VFAs, vectors can represent individual data points as well as elements of a function space (a reproducing kernel Hilbert space). The algebraic vector operations, inherited from VSA, correspond to well-defined operations in function space. Furthermore, we study a previously proposed method for encoding continuous data, fractional power encoding (FPE), which uses exponentiation of a random base vector to produce randomized representations of data points and fulfills the kernel properties for inducing a VFA. We show that the distribution from which elements of the base vector are sampled determines the shape of the FPE kernel, which in turn induces a VFA for computing with band-limited functions. In particular, VFAs provide an algebraic framework for implementing large-scale kernel machines with random features, extending Rahimi and Recht, 2007. Finally, we demonstrate several applications of VFA models to problems in image recognition, density estimation and nonlinear regression. Our analyses and results suggest that VFAs constitute a powerful new framework for representing and manipulating functions in distributed neural systems, with myriad applications in artificial intelligence.
29 Sep 2022
Motivated by recent innovations in biologically-inspired neuromorphic hardware, this article presents a novel unsupervised machine learning algorithm named Hyperseed that draws on the principles of Vector Symbolic Architectures (VSA) for fast learning of a topology preserving feature map of unlabelled data. It relies on two major operations of VSA, binding and bundling. The algorithmic part of Hyperseed is expressed within Fourier Holographic Reduced Representations model, which is specifically suited for implementation on spiking neuromorphic hardware. The two primary contributions of the Hyperseed algorithm are, few-shot learning and a learning rule based on single vector operation. These properties are empirically evaluated on synthetic datasets as well as on illustrative benchmark use-cases, IRIS classification, and a language identification task using n-gram statistics. The results of these experiments confirm the capabilities of Hyperseed and its applications in neuromorphic hardware.
Expand & Sparsify is a principle that is observed in anatomically similar neural circuits found in the mushroom body (insects) and the cerebellum (mammals). Sensory data are projected randomly to much higher-dimensionality (expand part) where only few the most strongly excited neurons are activated (sparsify part). This principle has been leveraged to design a FlyHash algorithm that forms similarity-preserving sparse embeddings, which have been found useful for such tasks as novelty detection, pattern recognition, and similarity search. Despite its simplicity, FlyHash has a number of design choices to be set such as preprocessing of the input data, choice of sparsifying activation function, and formation of the random projection matrix. In this paper, we explore the effect of these choices on the performance of similarity search with FlyHash embeddings. We find that the right combination of design choices can lead to drastic difference in the search performance.
Hyperdimensional computing (HDC), also known as vector symbolic architectures (VSA), is a computing framework used within artificial intelligence and cognitive computing that operates with distributed vector representations of large fixed dimensionality. A critical step for designing the HDC/VSA solutions is to obtain such representations from the input data. Here, we focus on sequences and propose their transformation to distributed representations that both preserve the similarity of identical sequence elements at nearby positions and are equivariant to the sequence shift. These properties are enabled by forming representations of sequence positions using recursive binding and superposition operations. The proposed transformation was experimentally investigated with symbolic strings used for modeling human perception of word similarity. The obtained results are on a par with more sophisticated approaches from the literature. The proposed transformation was designed for the HDC/VSA model known as Fourier Holographic Reduced Representations. However, it can be adapted to some other HDC/VSA models.
In the optimization of dynamic systems, the variables typically have
constraints. Such problems can be modeled as a Constrained Markov Decision
Process (CMDP). This paper considers the peak Constrained Markov Decision
Process (PCMDP), where the agent chooses the policy to maximize total reward in
the finite horizon as well as satisfy constraints at each epoch with
probability 1. We propose a model-free algorithm that converts PCMDP problem to
an unconstrained problem and a Q-learning based approach is applied. We define
the concept of probably approximately correct (PAC) to the proposed PCMDP
problem. The proposed algorithm is proved to achieve an (ϵ,p)-PAC
policy when the episode K≥Ω(ϵ2I2H6SAℓ), where
S and A are the number of states and actions, respectively. H is the
number of epochs per episode. I is the number of constraint functions, and
ℓ=log(pSAT). We note that this is the first result on PAC kind
of analysis for PCMDP with peak constraints, where the transition dynamics are
not known apriori. We demonstrate the proposed algorithm on an energy
harvesting problem and a single machine scheduling problem, where it performs
close to the theoretical upper bound of the studied optimization problem.
We investigate the task of retrieving information from compositional
distributed representations formed by Hyperdimensional Computing/Vector
Symbolic Architectures and present novel techniques which achieve new
information rate bounds. First, we provide an overview of the decoding
techniques that can be used to approach the retrieval task. The techniques are
categorized into four groups. We then evaluate the considered techniques in
several settings that involve, e.g., inclusion of external noise and storage
elements with reduced precision. In particular, we find that the decoding
techniques from the sparse coding and compressed sensing literature (rarely
used for Hyperdimensional Computing/Vector Symbolic Architectures) are also
well-suited for decoding information from the compositional distributed
representations. Combining these decoding techniques with interference
cancellation ideas from communications improves previously reported bounds
(Hersche et al., 2021) of the information rate of the distributed
representations from 1.20 to 1.40 bits per dimension for smaller codebooks and
from 0.60 to 1.26 bits per dimension for larger codebooks.
Memory-augmented neural networks enhance a neural network with an external
key-value memory whose complexity is typically dominated by the number of
support vectors in the key memory. We propose a generalized key-value memory
that decouples its dimension from the number of support vectors by introducing
a free parameter that can arbitrarily add or remove redundancy to the key
memory representation. In effect, it provides an additional degree of freedom
to flexibly control the trade-off between robustness and the resources required
to store and compute the generalized key-value memory. This is particularly
useful for realizing the key memory on in-memory computing hardware where it
exploits nonideal, but extremely efficient non-volatile memory devices for
dense storage and computation. Experimental results show that adapting this
parameter on demand effectively mitigates up to 44% nonidealities, at equal
accuracy and number of devices, without any need for neural network retraining.
A prominent approach to solving combinatorial optimization problems on parallel hardware is Ising machines, i.e., hardware implementations of networks of interacting binary spin variables. Most Ising machines leverage second-order interactions although important classes of optimization problems, such as satisfiability problems, map more seamlessly to Ising networks with higher-order interactions. Here, we demonstrate that higher-order Ising machines can solve satisfiability problems more resource-efficiently in terms of the number of spin variables and their connections when compared to traditional second-order Ising machines. Further, our results show on a benchmark dataset of Boolean \textit{k}-satisfiability problems that higher-order Ising machines implemented with coupled oscillators rapidly find solutions that are better than second-order Ising machines, thus, improving the current state-of-the-art for Ising machines.
Riemannian geometry provides us with powerful tools to explore the latent
space of generative models while preserving the underlying structure of the
data. The latent space can be equipped it with a Riemannian metric, pulled back
from the data manifold. With this metric, we can systematically navigate the
space relying on geodesics defined as the shortest curves between two points.
Generative models are often stochastic, causing the data space, the Riemannian
metric, and the geodesics, to be stochastic as well. Stochastic objects are at
best impractical, and at worst impossible, to manipulate. A common solution is
to approximate the stochastic pullback metric by its expectation. But the
geodesics derived from this expected Riemannian metric do not correspond to the
expected length-minimising curves. In this work, we propose another metric
whose geodesics explicitly minimise the expected length of the pullback metric.
We show this metric defines a Finsler metric, and we compare it with the
expected Riemannian metric. In high dimensions, we prove that both metrics
converge to each other at a rate of O(D1). This
convergence implies that the established expected Riemannian metric is an
accurate approximation of the theoretically more grounded Finsler metric. This
provides justification for using the expected Riemannian metric for practical
implementations.
Multilayer neural networks set the current state of the art for many technical classification problems. But, these networks are still, essentially, black boxes in terms of analyzing them and predicting their performance. Here, we develop a statistical theory for the one-layer perceptron and show that it can predict performances of a surprisingly large variety of neural networks with different architectures. A general theory of classification with perceptrons is developed by generalizing an existing theory for analyzing reservoir computing models and connectionist models for symbolic reasoning known as vector symbolic architectures. Our statistical theory offers three formulas leveraging the signal statistics with increasing detail. The formulas are analytically intractable, but can be evaluated numerically. The description level that captures maximum details requires stochastic sampling methods. Depending on the network model, the simpler formulas already yield high prediction accuracy. The quality of the theory predictions is assessed in three experimental settings, a memorization task for echo state networks (ESNs) from reservoir computing literature, a collection of classification datasets for shallow randomly connected networks, and the ImageNet dataset for deep convolutional neural networks. We find that the second description level of the perceptron theory can predict the performance of types of ESNs, which could not be described previously. The theory can predict deep multilayer neural networks by being applied to their output layer. While other methods for prediction of neural networks performance commonly require to train an estimator model, the proposed theory requires only the first two moments of the distribution of the postsynaptic sums in the output neurons. The perceptron theory compares favorably to other methods that do not rely on training an estimator model.
26 Aug 2024
We propose an adaptive change point detection method (A-CPD) for machine
guided weak label annotation of audio recording segments. The goal is to
maximize the amount of information gained about the temporal activations of the
target sounds. For each unlabeled audio recording, we use a prediction model to
derive a probability curve used to guide annotation. The prediction model is
initially pre-trained on available annotated sound event data with classes that
are disjoint from the classes in the unlabeled dataset. The prediction model
then gradually adapts to the annotations provided by the annotator in an active
learning loop. We derive query segments to guide the weak label annotator
towards strong labels, using change point detection on these probabilities. We
show that it is possible to derive strong labels of high quality with a limited
annotation budget, and show favorable results for A-CPD when compared to two
baseline query segment strategies.
 CNRSNational Astronomical Observatory of Japan
CNRSNational Astronomical Observatory of Japan Sorbonne UniversitéNational Institute of Standards and TechnologyKorea Research Institute of Standards and ScienceNational Physical LaboratoryUniversité de NeuchâtelNational Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and TechnologyObservatoire de ParisUniversité Côte d’AzurNational Research CouncilResearch Institutes of SwedenObservatoire de la Côte d’AzurNational Institute of MetrologyInstitut d'Astrophysique de ParisNational Institute of Information and Communications TechnologyRoyal Observatory of BelgiumIstituto Nazionale di Ricerca MetrologicaPhysikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB)National Metrology Institute of JapanBureau International des Poids et MesuresNational Measurement InstituteLNE–SYRTEUnited States Naval Observatory (USNO)FSUE VNIIFTRIEmirates Metrology Institute (QCC EMI)Universit PSL
Sorbonne UniversitéNational Institute of Standards and TechnologyKorea Research Institute of Standards and ScienceNational Physical LaboratoryUniversité de NeuchâtelNational Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and TechnologyObservatoire de ParisUniversité Côte d’AzurNational Research CouncilResearch Institutes of SwedenObservatoire de la Côte d’AzurNational Institute of MetrologyInstitut d'Astrophysique de ParisNational Institute of Information and Communications TechnologyRoyal Observatory of BelgiumIstituto Nazionale di Ricerca MetrologicaPhysikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB)National Metrology Institute of JapanBureau International des Poids et MesuresNational Measurement InstituteLNE–SYRTEUnited States Naval Observatory (USNO)FSUE VNIIFTRIEmirates Metrology Institute (QCC EMI)Universit PSLThis paper outlines the roadmap towards the redefinition of the second, which was recently updated by the CCTF Task Force created by the CCTF in 2020. The main achievements and the open challenges related to the status of the optical frequency standards, their contribution to time scales and UTC, the possibility of their comparison and the knowledge of the Earth's gravitational potential at the necessary level of uncertainty are discussed. In addition, the mandatory criteria to be achieved before redefinition and their current fulfilment level, together with the redefinition options based on a single or on a set of transitions are described.
In this paper, we present an approach to integer factorization using distributed representations formed with Vector Symbolic Architectures. The approach formulates integer factorization in a manner such that it can be solved using neural networks and potentially implemented on parallel neuromorphic hardware. We introduce a method for encoding numbers in distributed vector spaces and explain how the resonator network can solve the integer factorization problem. We evaluate the approach on factorization of semiprimes by measuring the factorization accuracy versus the scale of the problem. We also demonstrate how the proposed approach generalizes beyond the factorization of semiprimes; in principle, it can be used for factorization of any composite number. This work demonstrates how a well-known combinatorial search problem may be formulated and solved within the framework of Vector Symbolic Architectures, and it opens the door to solving similarly difficult problems in other domains.
07 Feb 2024
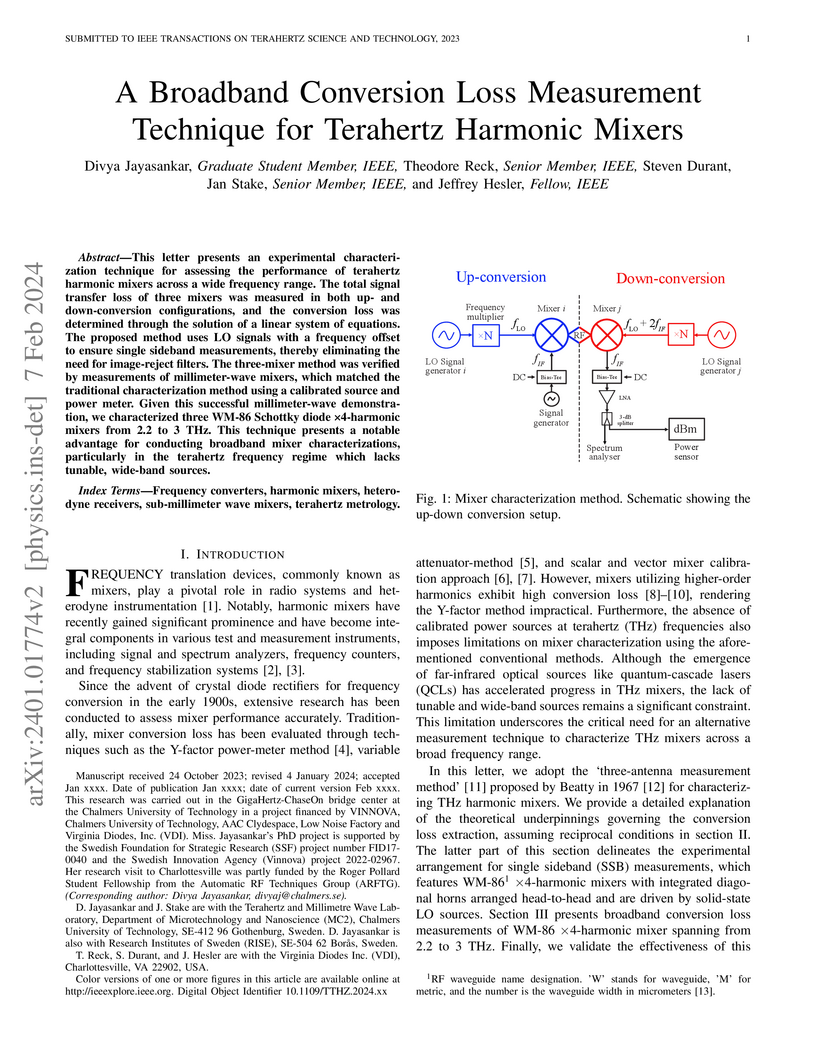
This letter presents an experimental characterization technique for assessing
the performance of terahertz harmonic mixers across a wide frequency range. The
total signal transfer loss of three mixers was measured in both up- and
down-conversion configurations, and the conversion loss was determined through
the solution of a linear system of equations. The proposed method uses LO
signals with a frequency offset to ensure single sideband measurements, thereby
eliminating the need for image-reject filters. The three-mixer method was
verified by measurements of millimeter-wave mixers, which matched the
traditional characterization method using a calibrated source and power meter.
Given this successful millimeter-wave demonstration, we characterized three
WM-86 Schottky diode x4-harmonic mixers from 2.2 to 3 THz. This technique
presents a notable advantage for conducting broadband mixer characterizations,
particularly in the terahertz frequency regime which lacks tunable, wide-band
sources.
29 Aug 2019
 ETH Zurich
ETH Zurich Delft University of Technology
Delft University of Technology Aalto UniversityNational Physical LaboratoryPolitecnico di TorinoCentraleSupélecResearch Institutes of SwedenPhysikalisch-Technische BundesanstaltUniversitá degli Studi di Cassino e del Lazio MeridionaleIstituto Nazionale di Ricerca MetrologicaFundación CIRCEIT'IS FoundationUniversit
degli Studi di Salerno
Aalto UniversityNational Physical LaboratoryPolitecnico di TorinoCentraleSupélecResearch Institutes of SwedenPhysikalisch-Technische BundesanstaltUniversitá degli Studi di Cassino e del Lazio MeridionaleIstituto Nazionale di Ricerca MetrologicaFundación CIRCEIT'IS FoundationUniversit
degli Studi di SalernoThe European Union funded project MICEV aims at improving the traceability of electrical and magnetic measurement at charging stations and to better assess the safety of this technology with respect to human exposure. The paper describes some limits of the instrumentation used for electrical measurements in the charging stations, and briefly presents two new calibration facilities for magnetic field meters and electric power meters. Modeling approaches for the efficiency and human exposure assessment are proposed. In the latter case, electromagnetic computational codes have been combined with dosimetric computational codes making use of highly detailed human anatomical phantoms in order to establish human exposure modeling real charging stations. Detailed results are presented for light vehicles where, according to our calculations, the concern towards human exposure is limited. Currently, the project has reached half way point (about 18 months) and will end in August 2020.
Compositional Factorization of Visual Scenes with Convolutional Sparse Coding and Resonator Networks
Compositional Factorization of Visual Scenes with Convolutional Sparse Coding and Resonator Networks
We propose a system for visual scene analysis and recognition based on encoding the sparse, latent feature-representation of an image into a high-dimensional vector that is subsequently factorized to parse scene content. The sparse feature representation is learned from image statistics via convolutional sparse coding, while scene parsing is performed by a resonator network. The integration of sparse coding with the resonator network increases the capacity of distributed representations and reduces collisions in the combinatorial search space during factorization. We find that for this problem the resonator network is capable of fast and accurate vector factorization, and we develop a confidence-based metric that assists in tracking the convergence of the resonator network.
08 Aug 2024
A key challenge in developing terahertz front-ends is achieving high coupling
efficiency between the waveguide feed horn and the optical beam. In this paper,
we have quantified the alignment requirements for the widely used E-plane split
diagonal horn antenna through theoretical analysis, electromagnetic simulation,
and experimental validation within the 325-500 GHz frequency range. The results
from our analytical models, simulations, and measurements are consistent and
shows good agreement. They reveal that even minor geometric asymmetries can
cause significant increases in fractional power radiated to the cross-polar
component due to amplitude and phase imbalances in the TE10 and TE01 modes.
Furthermore, a misalignment of approximately 8% of the wavelength was observed
to result in a 3-dB degradation in the optical coupling to a Gaussian beam
(Gaussicity) in middle of the waveguide band. These findings highlight the
critical importance of precise alignment and feed horn machining for the
successful implementation of terahertz front-end systems.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.