25 Sep 2025
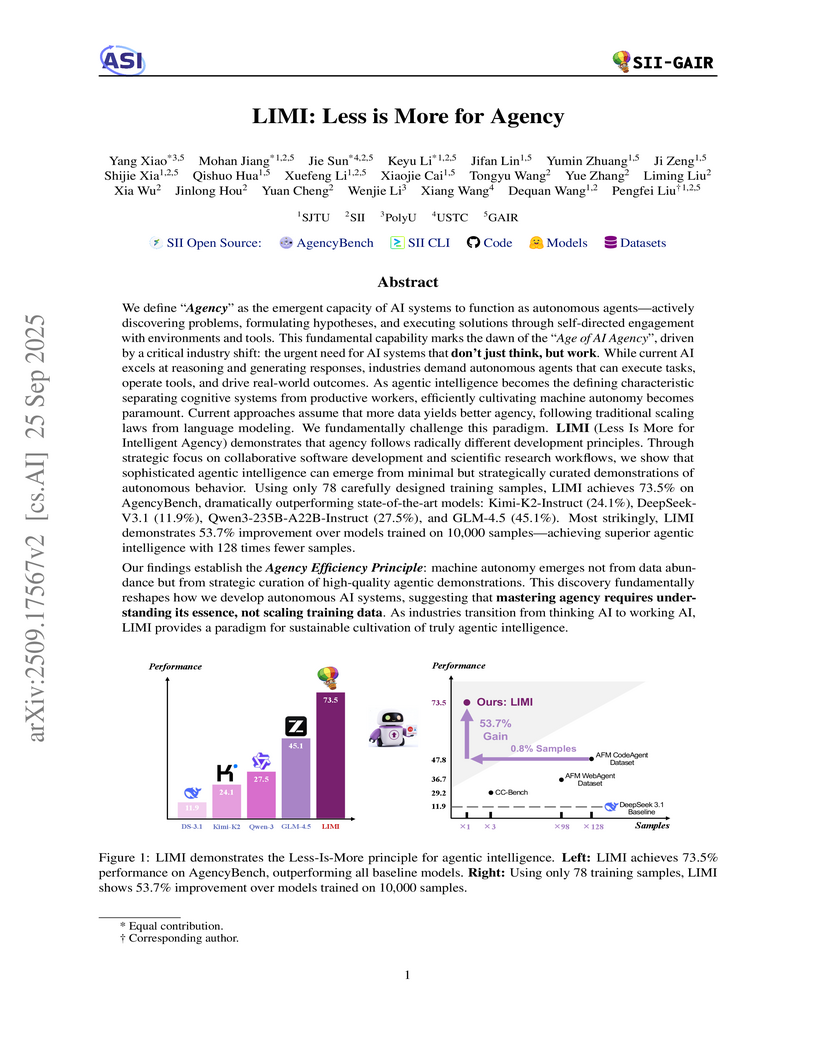
LIMI introduces an approach that cultivates advanced AI agency using a small, carefully chosen dataset, achieving an average 73.5% on AgencyBench. This method demonstrates a 53.7% performance improvement over models trained on 128 times more data, highlighting the efficacy of strategic data curation over data scale.
pi3 presents a permutation-equivariant architecture for visual geometry learning that completely removes the reliance on a fixed reference view. The model achieves state-of-the-art performance across camera pose, depth, and point map estimation, demonstrating superior robustness to input image order and efficiency.
13 Oct 2025
SR-Scientist transforms large language models into autonomous AI scientists for symbolic regression by enabling tool-use and long-horizon optimization, achieving superior precision and robustness in scientific equation discovery across multiple disciplines. Developed by researchers at Shanghai Jiao Tong University, this framework also incorporates reinforcement learning for agent self-improvement.
30 Mar 2025
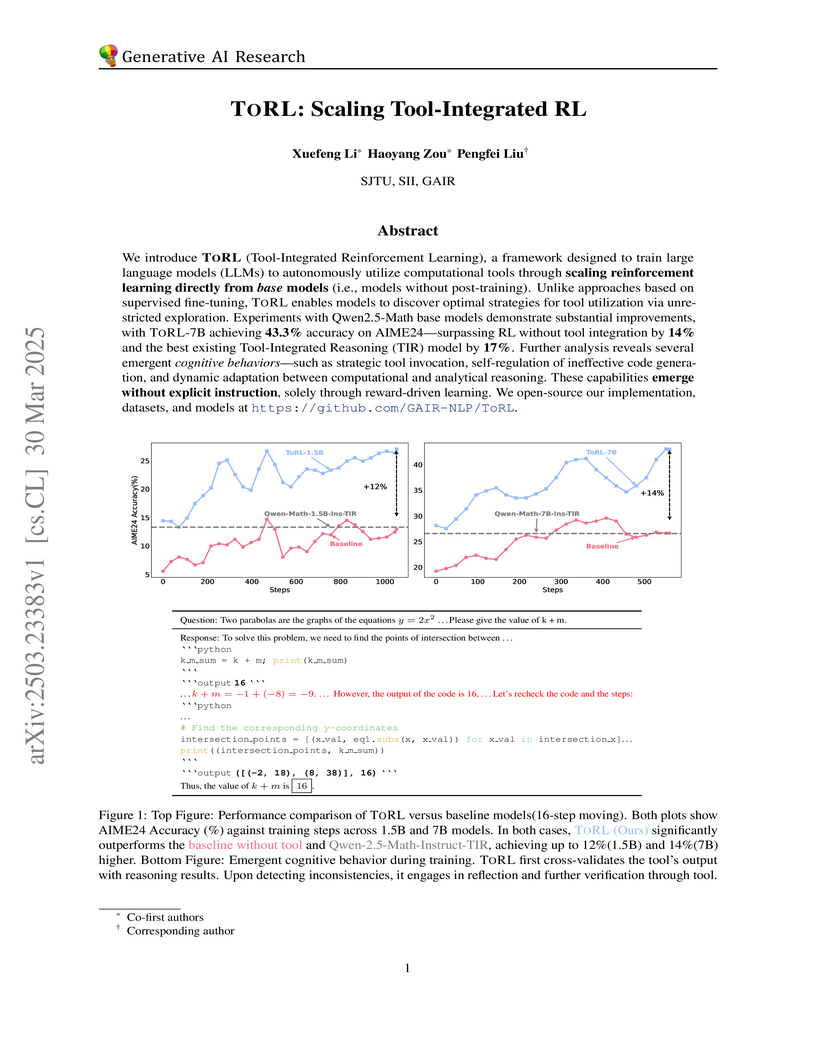
The paper "TORL: Scaling Tool-Integrated RL" introduces a framework for training large language models (LLMs) to autonomously use computational tools by scaling reinforcement learning directly from base models. The TORL framework consistently improves mathematical reasoning across benchmarks, achieving up to a 14.7% absolute accuracy gain for a 7B model compared to SFT-based baselines, and enables emergent behaviors like self-correction and reflection.
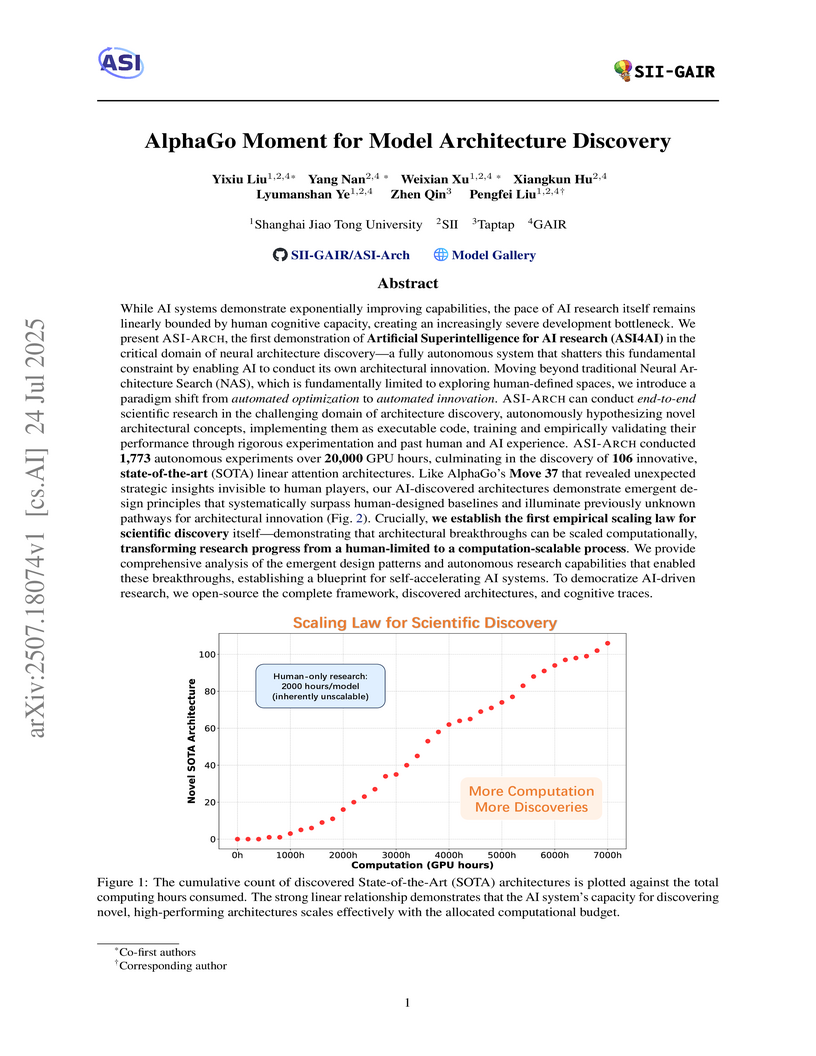
ASI-ARCH, developed by Shanghai Jiao Tong University and collaborators, is an autonomous system that discovers novel neural architectures by leveraging large language models for design, implementation, and analysis. It successfully identified 106 state-of-the-art linear attention architectures that outperform human-designed baselines and demonstrated the first empirical scaling law for scientific discovery, showing that architectural breakthroughs can be scaled computationally.
Research from Shanghai Jiao Tong University explores "mid-training" as a critical intermediate stage for enhancing reinforcement learning scalability in large language models, specifically Llama, for mathematical reasoning. It shows that strategic mid-training with a new 70+ billion token mathematical corpus and a two-stage process allows Llama models to achieve mathematical reasoning performance comparable to Qwen models after RL.
17 Apr 2025
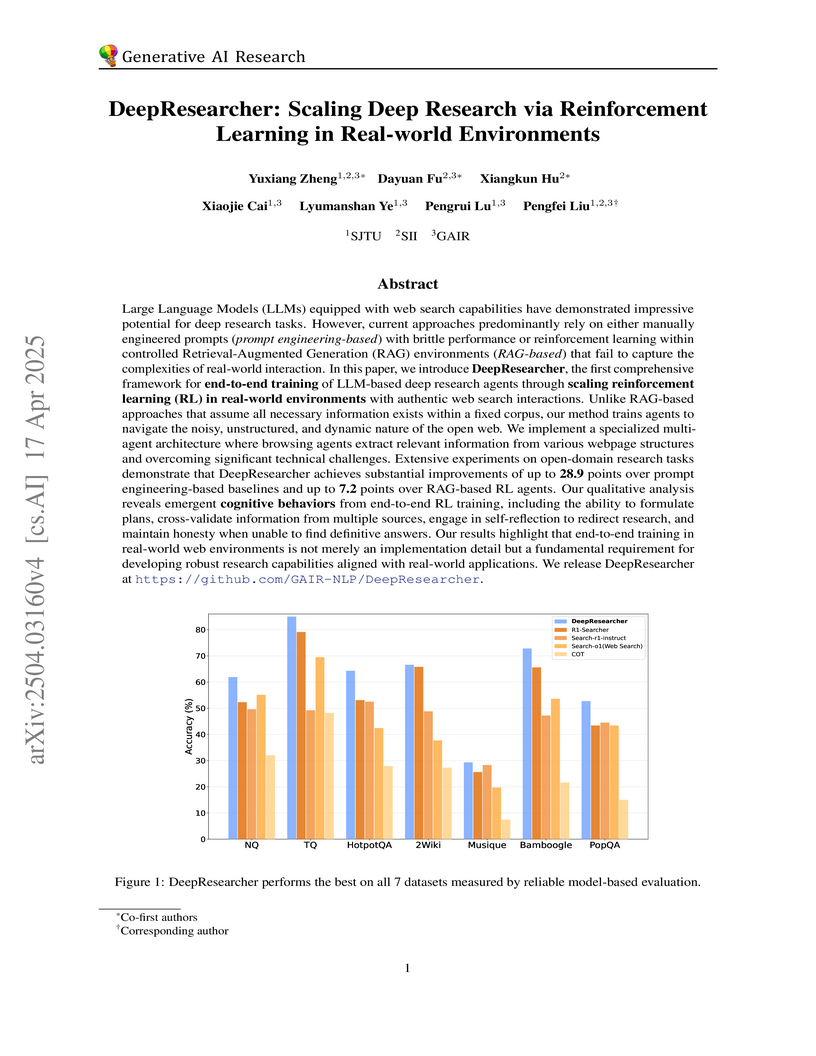
DeepResearcher introduces a comprehensive reinforcement learning framework to train Large Language Models for deep research tasks by directly interacting with the open web. The system achieves superior performance on diverse QA benchmarks, demonstrating the ability to generalize to novel domains, and exhibits emergent cognitive behaviors like planning and cross-validation through real-world web exposure.
Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have emerged as a powerful framework that unifies perception, language, and control, enabling robots to perform diverse tasks through multimodal understanding. However, current VLA models typically contain massive parameters and rely heavily on large-scale robot data pretraining, leading to high computational costs during training, as well as limited deployability for real-time inference. Moreover, most training paradigms often degrade the perceptual representations of the vision-language backbone, resulting in overfitting and poor generalization to downstream tasks. In this work, we present Evo-1, a lightweight VLA model that reduces computation and improves deployment efficiency, while maintaining strong performance without pretraining on robot data. Evo-1 builds on a native multimodal Vision-Language model (VLM), incorporating a novel cross-modulated diffusion transformer along with an optimized integration module, together forming an effective architecture. We further introduce a two-stage training paradigm that progressively aligns action with perception, preserving the representations of the VLM. Notably, with only 0.77 billion parameters, Evo-1 achieves state-of-the-art results on the Meta-World and RoboTwin suite, surpassing the previous best models by 12.4% and 6.9%, respectively, and also attains a competitive result of 94.8% on LIBERO. In real-world evaluations, Evo-1 attains a 78% success rate with high inference frequency and low memory overhead, outperforming all baseline methods. We release code, data, and model weights to facilitate future research on lightweight and efficient VLA models.
Shanghai Jiao Tong University and collaborating researchers develop "Thinking with Generated Images" (TwGI), a paradigm enabling large multimodal models to spontaneously generate intermediate visual steps during reasoning through native long-multimodal thought processes, achieving up to 50% relative improvement on complex multi-object vision generation tasks by implementing two complementary mechanisms—decomposing visual tasks into progressive subgoals and self-critiquing generated images for iterative refinement—while demonstrating substantial performance gains on GenEval and DPG-Bench benchmarks compared to baseline Anole models that rely solely on text-based chain-of-thought reasoning.
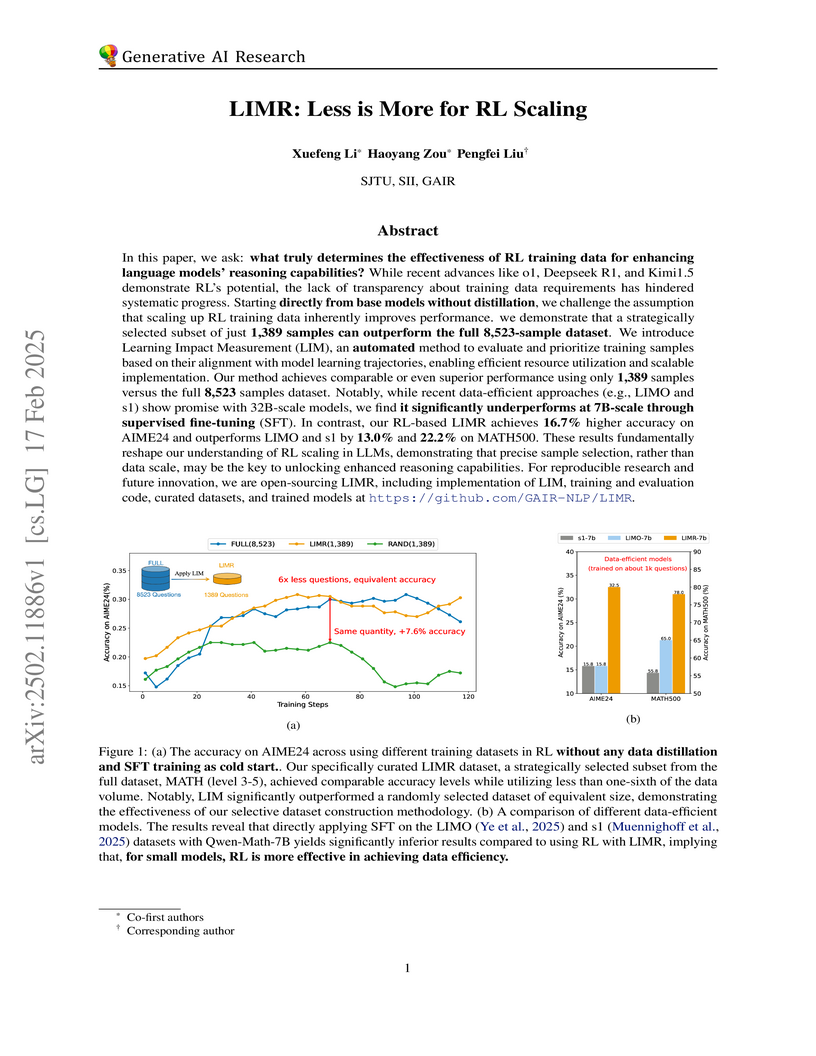
Shanghai Jiao Tong University researchers overturn conventional wisdom about RL training data requirements, demonstrating that just 1,389 strategically selected samples can outperform training on 8,523 samples through their novel Learning Impact Measurement (LIM) framework, achieving 16.7% higher accuracy on mathematical reasoning tasks while dramatically reducing computational costs.
Researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University developed AgentNet, a decentralized evolutionary framework for LLM-based multi-agent systems that eliminates central orchestration. This system dynamically adapts agent networks and refines expertise through RAG-based memory, achieving competitive or superior performance across mathematics, logical QA, and function-calling tasks, and demonstrating improved scalability and privacy-preserving collaboration.
Researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University and Shanghai AI Laboratory developed MesaTask, a framework that utilizes large language models and a Spatial Reasoning Chain to generate task-driven, realistic 3D tabletop scenes directly from high-level instructions. Complementing this, they introduced MesaTask-10K, a human-refined dataset of over 10,700 scenes, enabling the framework to achieve a Fréchet Inception Distance (FID) of 40.3 and a 99.1% success rate, outperforming existing baselines.
Mantis, a Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model from SJTU and collaborators, introduces Disentangled Visual Foresight (DVF) and a progressive training strategy to enhance robotic control. The model achieved a 96.7% average success rate on the LIBERO benchmark and demonstrated improved real-world instruction following and generalization, while its Adaptive Temporal Ensemble enabled nearly 50% faster inference.
Feature caching has recently emerged as a promising method for diffusion model acceleration. It effectively alleviates the inefficiency problem caused by high computational requirements by caching similar features in the inference process of the diffusion model. In this paper, we analyze existing feature caching methods from the perspective of information utilization, and point out that relying solely on historical information will lead to constrained accuracy and speed performance. And we propose a novel paradigm that introduces future information via self-speculation based on the information similarity at the same time step across different iteration times. Based on this paradigm, we present \textit{SpecDiff}, a training-free multi-level feature caching strategy including a cached feature selection algorithm and a multi-level feature classification algorithm. (1) Feature selection algorithm based on self-speculative information. \textit{SpecDiff} determines a dynamic importance score for each token based on self-speculative information and historical information, and performs cached feature selection through the importance score. (2) Multi-level feature classification algorithm based on feature importance scores. \textit{SpecDiff} classifies tokens by leveraging the differences in feature importance scores and introduces a multi-level feature calculation strategy. Extensive experiments show that \textit{SpecDiff} achieves average 2.80 \times, 2.74 \times , and 3.17\times speedup with negligible quality loss in Stable Diffusion 3, 3.5, and FLUX compared to RFlow on NVIDIA A800-80GB GPU. By merging speculative and historical information, \textit{SpecDiff} overcomes the speedup-accuracy trade-off bottleneck, pushing the Pareto frontier of speedup and accuracy in the efficient diffusion model inference.
20 May 2025
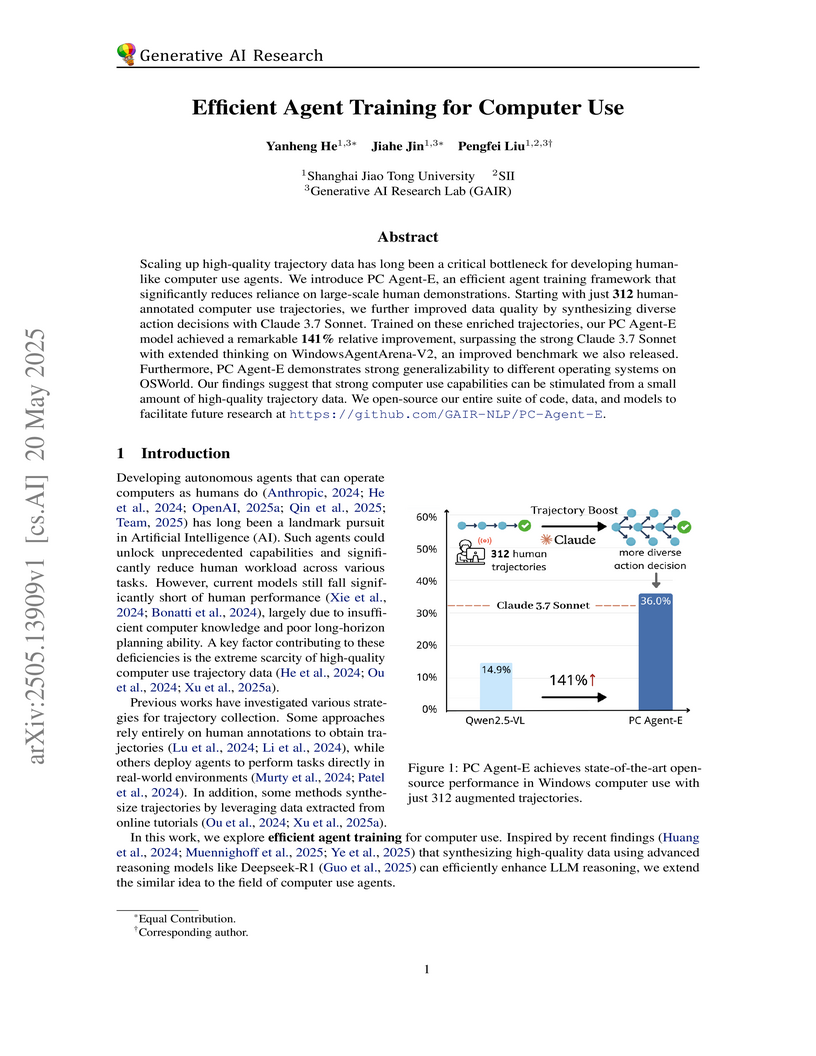
PC Agent-E offers an efficient training framework for computer use agents by leveraging a small dataset of 312 human trajectories augmented via AI-driven data synthesis. This approach enables the model to achieve state-of-the-art open-source performance on Windows and demonstrates strong cross-platform generalization.
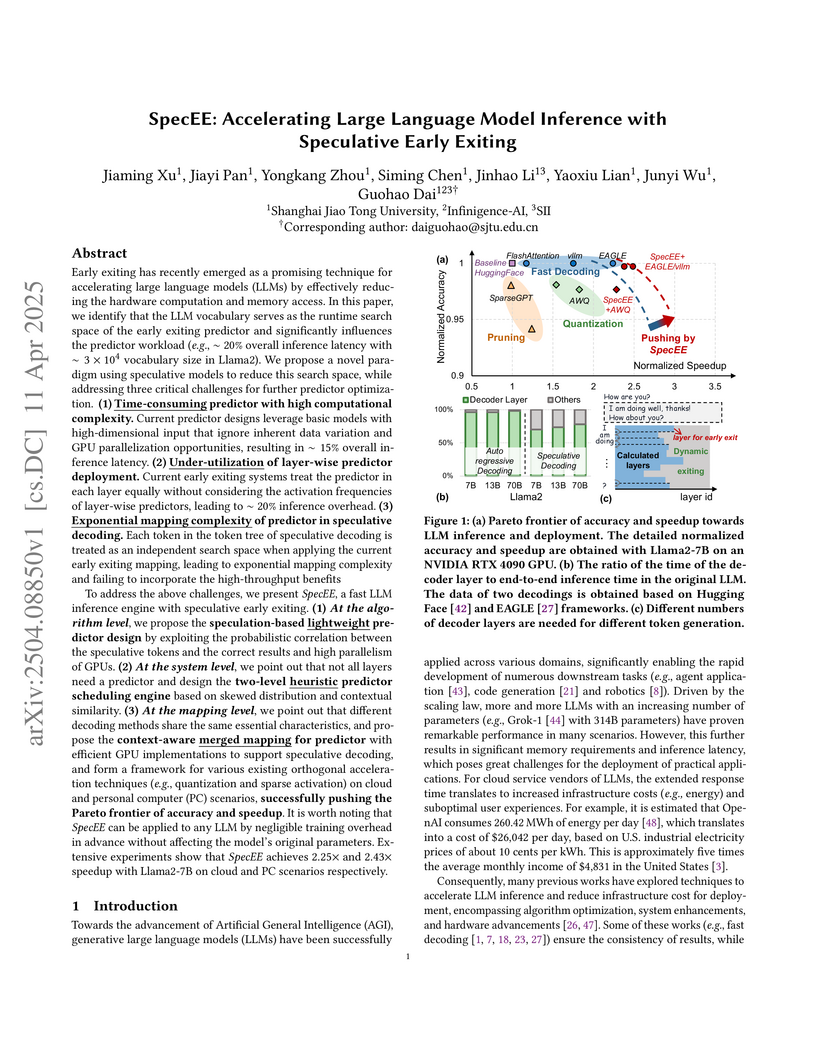
SpecEE accelerates Large Language Model inference by integrating speculative decoding with a refined early exiting framework, achieving up to 2.43x speedup on PC and 2.25x on cloud scenarios with minimal accuracy reduction. The method uses lightweight, speculation-guided predictors and a two-level scheduling mechanism to optimize computational efficiency.
22 Jul 2025
ResearcherBench introduces the first benchmark designed to evaluate Deep AI Research Systems (DARS) on frontier scientific questions. The benchmark reveals that leading DARS excel at providing insights for open-ended problems, while also highlighting a consistent pattern of high citation faithfulness but low overall groundedness in their generated content.
The emergence of groundbreaking large language models capable of performing
complex reasoning tasks holds significant promise for addressing various
scientific challenges, including those arising in complex clinical scenarios.
To enable their safe and effective deployment in real-world healthcare
settings, it is urgently necessary to benchmark the diagnostic capabilities of
current models systematically. Given the limitations of existing medical
benchmarks in evaluating advanced diagnostic reasoning, we present
DiagnosisArena, a comprehensive and challenging benchmark designed to
rigorously assess professional-level diagnostic competence. DiagnosisArena
consists of 1,113 pairs of segmented patient cases and corresponding diagnoses,
spanning 28 medical specialties, deriving from clinical case reports published
in 10 top-tier medical journals. The benchmark is developed through a
meticulous construction pipeline, involving multiple rounds of screening and
review by both AI systems and human experts, with thorough checks conducted to
prevent data leakage. Our study reveals that even the most advanced reasoning
models, o3, o1, and DeepSeek-R1, achieve only 51.12%, 31.09%, and 17.79%
accuracy, respectively. This finding highlights a significant generalization
bottleneck in current large language models when faced with clinical diagnostic
reasoning challenges. Through DiagnosisArena, we aim to drive further
advancements in AI's diagnostic reasoning capabilities, enabling more effective
solutions for real-world clinical diagnostic challenges. We provide the
benchmark and evaluation tools for further research and development
this https URL
The rapid advancement of large language models has fundamentally shifted the bottleneck in AI development from computational power to data availability-with countless valuable datasets remaining hidden across specialized repositories, research appendices, and domain platforms. As reasoning capabilities and deep research methodologies continue to evolve, a critical question emerges: can AI agents transcend conventional search to systematically discover any dataset that meets specific user requirements, enabling truly autonomous demand-driven data curation? We introduce DatasetResearch, the first comprehensive benchmark evaluating AI agents' ability to discover and synthesize datasets from 208 real-world demands across knowledge-intensive and reasoning-intensive tasks. Our tri-dimensional evaluation framework reveals a stark reality: even advanced deep research systems achieve only 22% score on our challenging DatasetResearch-pro subset, exposing the vast gap between current capabilities and perfect dataset discovery. Our analysis uncovers a fundamental dichotomy-search agents excel at knowledge tasks through retrieval breadth, while synthesis agents dominate reasoning challenges via structured generation-yet both catastrophically fail on "corner cases" outside existing distributions. These findings establish the first rigorous baseline for dataset discovery agents and illuminate the path toward AI systems capable of finding any dataset in the digital universe. Our benchmark and comprehensive analysis provide the foundation for the next generation of self-improving AI systems and are publicly available at this https URL.
28 Apr 2025
Researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University, SII, and the Generative AI Research Lab delineate "Cognition Engineering" as the new paradigm for generative AI's "Act II," emphasizing test-time scaling methods to advance Large Language Models beyond knowledge retrieval towards deep reasoning. The work introduces a framework for understanding and implementing techniques such as parallel sampling, tree search, multi-turn correction, and long Chain-of-Thought, demonstrating their role in cultivating AI's cognitive abilities, particularly when enhanced by reinforcement learning.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.