Shanghai Innovation Institute
An open-source framework, AgentGym-RL, facilitates the training of large language model agents for long-horizon decision-making through multi-turn reinforcement learning and a progressive interaction scaling strategy called ScalingInter-RL. This approach enables a 7B parameter model to achieve an average success rate comparable to or exceeding larger proprietary models across diverse environments, highlighting the impact of RL training on agentic intelligence.
This research introduces "Thinking with Video," a new paradigm that leverages video generation for multimodal reasoning by enabling dynamic visualization and human-like imagination in problem-solving. It evaluates frontier video models like Sora-2 on a new, comprehensive benchmark, VideoThinkBench, showcasing their unexpected capabilities across vision and text-centric tasks.
SIM-CoT stabilizes and enhances implicit Chain-of-Thought reasoning in large language models by integrating fine-grained, step-level supervision for latent tokens during training. It addresses latent instability, achieves higher accuracy than explicit CoT in some settings while preserving inference efficiency, and offers unprecedented interpretability into the model's internal thought processes.
AgiBot World Colosseo presents a large-scale platform and dataset, AgiBot World, comprising over 1 million real-world robot manipulation trajectories spanning diverse tasks and environments. The work introduces GO-1, a generalist policy leveraging vision-language models and latent action representations, achieving an average 32% performance improvement over prior generalist policies on complex manipulation tasks.
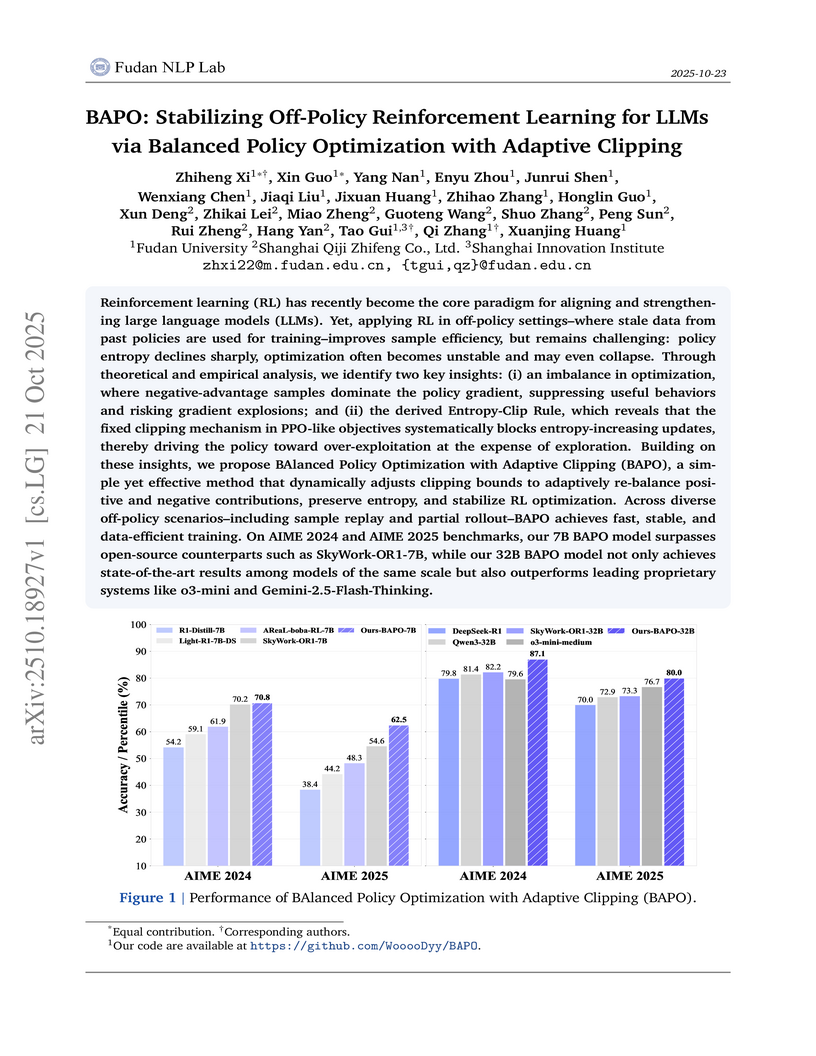
BAPO introduces an adaptive clipping mechanism for off-policy Reinforcement Learning in Large Language Models, which dynamically re-balances optimization signals and preserves policy entropy. This method achieves state-of-the-art performance on AIME reasoning benchmarks, outperforming comparable open-source models and demonstrating competitiveness with proprietary systems.
24 Oct 2025
Researchers introduced LIBERO-Plus, a diagnostic benchmark for vision-language-action (VLA) models, revealing that current models exhibit substantial fragility to environmental perturbations and frequently ignore linguistic instructions. Fine-tuning with a generalized dataset significantly enhances their robustness.
25 Aug 2025
Proximal Supervised Fine-Tuning (PSFT) introduces a PPO-inspired clipped objective to stabilize large language model fine-tuning, preventing entropy collapse and catastrophic forgetting. This approach yields a more robust and generalized base model, serving as a superior "cold start" for subsequent reinforcement learning from human feedback or direct preference optimization, which ultimately leads to enhanced performance across various tasks.
09 Oct 2025
MUSE, an agent framework from the Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory and collaborators, enables Large Language Models to learn continuously from experience and self-evolve for complex, long-horizon real-world tasks. It achieved a new state-of-the-art performance of 51.78% partial completion score on the challenging TheAgentCompany (TAC) benchmark, surpassing previous methods by nearly 20%.
PREF-GRPO introduces a novel training method for text-to-image (T2I) models that stabilizes reinforcement learning against reward hacking by utilizing pairwise preference rewards. The accompanying UNIGENBENCH offers a fine-grained, MLLM-powered framework for comprehensive and diagnostic evaluation of T2I models.
SRPO (Self-Referential Policy Optimization) enhances Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models for robotic manipulation by addressing reward sparsity, generating dense, progress-wise rewards using the model's own successful trajectories and latent world representations from V-JEPA 2. The method achieved a 99.2% success rate on the LIBERO benchmark, a 103% relative improvement over its one-shot SFT baseline, and demonstrated strong generalization on the LIBERO-Plus benchmark.
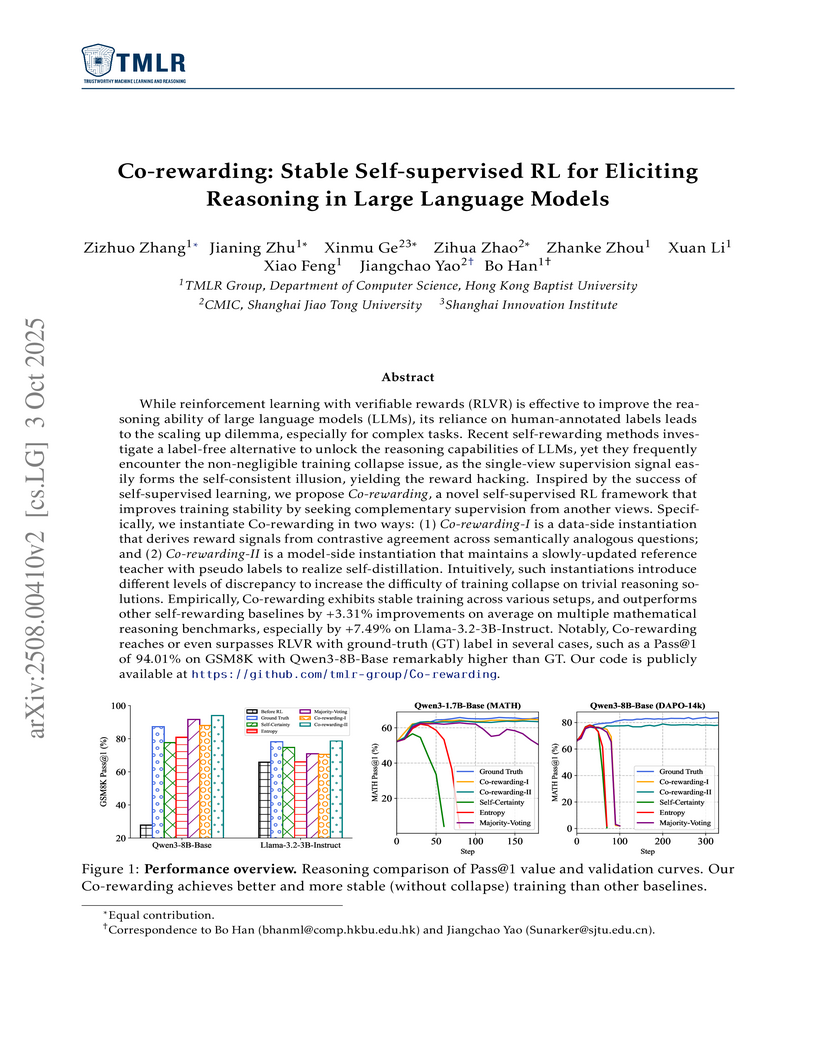
Co-rewarding establishes a stable self-supervised reinforcement learning framework for large language models, leveraging complementary supervision via data-side analogy-invariance and model-side temporal invariance. This effectively prevents training collapse and reward hacking, leading to enhanced reasoning capabilities that often surpass prior self-rewarding methods and sometimes rival ground-truth supervised approaches.
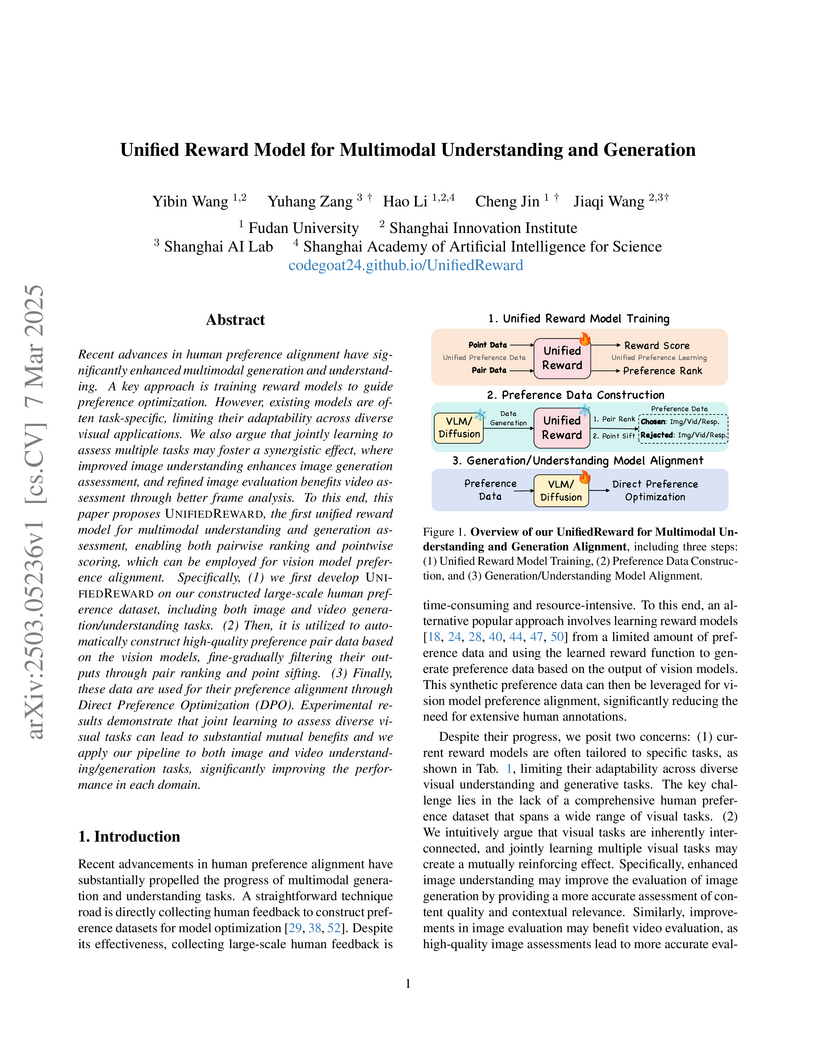
Researchers from Fudan University and Shanghai AI Lab introduce UNIFIEDREWARD, the first unified reward model for multimodal understanding and generation that achieves superior performance across both image and video tasks through innovative joint learning of multiple visual domains, demonstrating significant improvements in preference alignment while enabling efficient Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) through a novel combination of pairwise ranking and pointwise scoring.
Researchers developed UniMedVL, a unified medical foundation model capable of simultaneously performing both understanding and generation tasks within a single architecture, leveraging the UniMed-5M multimodal dataset and a progressive curriculum learning strategy. The model achieves superior performance across diverse medical visual understanding benchmarks and demonstrates high-fidelity generation and seamless execution of complex interleaved multimodal tasks.
11 Oct 2025
Researchers from Zhejiang University, Ant Group, and others introduced ENVIRONMENT TUNING, a training paradigm for Large Language Model (LLM) agents that focuses on modifying the learning environment itself. This method enables agents to achieve robust generalization and stability in complex, multi-turn tool-use tasks despite extreme data scarcity, significantly boosting performance on benchmarks like BFCL V3 by up to 18.50% and improving out-of-distribution generalization where supervised fine-tuning models collapse.
A new comprehensive video dataset named Sekai, curated by Shanghai AI Laboratory, supports advanced world exploration models with over 5,000 hours of videos from real-world and game sources, annotated with explicit camera trajectories and extensive metadata. This data effectively improved model performance in text-to-video, image-to-video, and camera-controlled video generation tasks.
Researchers from Shanghai AI Laboratory, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and The University of Hong Kong developed MM-Eureka, an open-source multimodal model utilizing rule-based reinforcement learning with novel online filtering and two-stage training strategies. This model achieves leading open-source performance in multimodal mathematical and multidisciplinary reasoning, scoring 74.8 on MathVista and 73.4 on WeMath, and is accompanied by the new MMK12 high-quality multimodal mathematical reasoning dataset.
Yume introduces an interactive world generation model that synthesizes dynamic, explorable virtual environments from images or text, featuring intuitive keyboard-driven camera control. The model produces high-fidelity real-world urban scenes, outperforming existing methods in visual quality and instruction following.
MOSS-Speech, developed by the SII OpenMOSS Team, Fudan University, and MOSI, introduces a model for direct speech-to-speech interaction that eliminates reliance on intermediate text. It achieves state-of-the-art results in speech modeling and spoken question answering, for instance, scoring 67.19 in MMLU and 69.53 in CMMLU, while preserving the linguistic capabilities of its underlying text LLM better than previous multimodal systems.
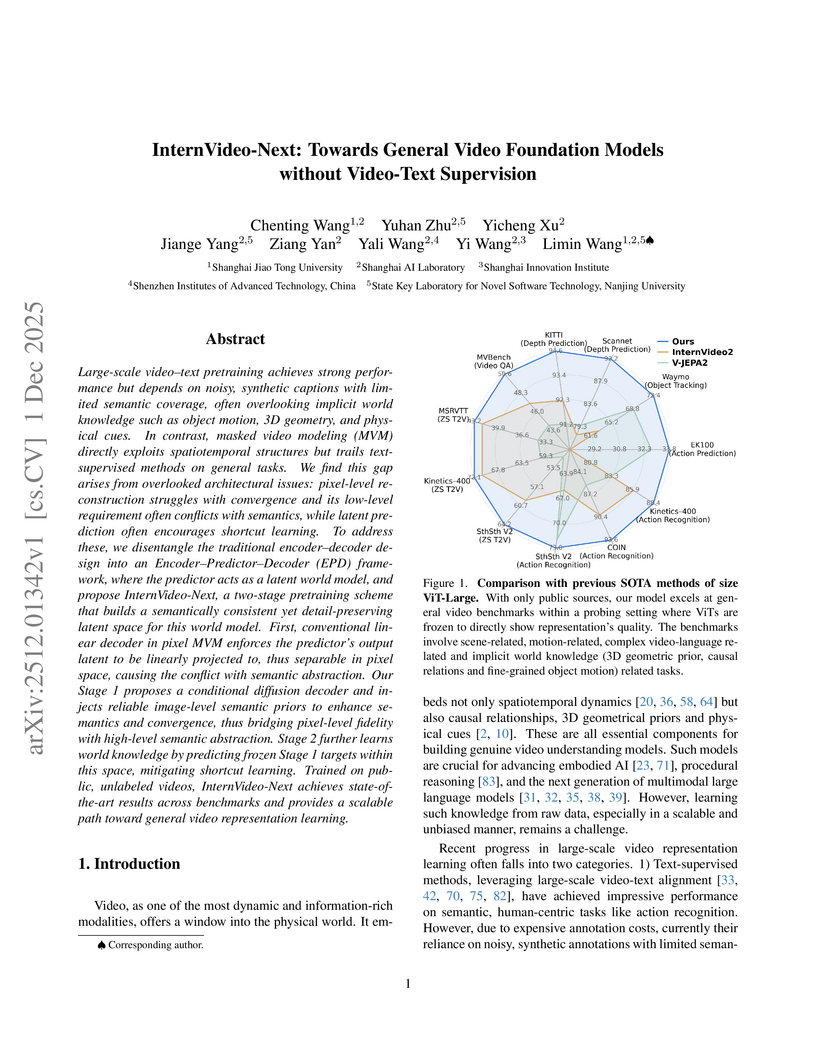
InternVideo-Next, a self-supervised framework developed by researchers including those from Shanghai AI Lab and Shanghai Jiao Tong University, establishes a new benchmark for general video understanding by achieving state-of-the-art performance across diverse tasks without requiring video-text supervision. It unifies pixel-level fidelity with semantic abstraction, outperforming text-supervised models on Kinetics-400 and Something-Something V2 while excelling in tasks like 3D depth estimation and object tracking.
RoboOmni, developed by Fudan University and NUS, introduces an end-to-end omni-modal framework for robots to proactively infer and verify user intentions from human speech, environmental sounds, and visual cues. The system achieved an 85.6% success rate on cross-modal contextual instructions, outperforming baselines like NORA (25.9%), and reduced inference latency by 0.49x compared to ASR-based approaches.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.