Southwest University of Science and Technology
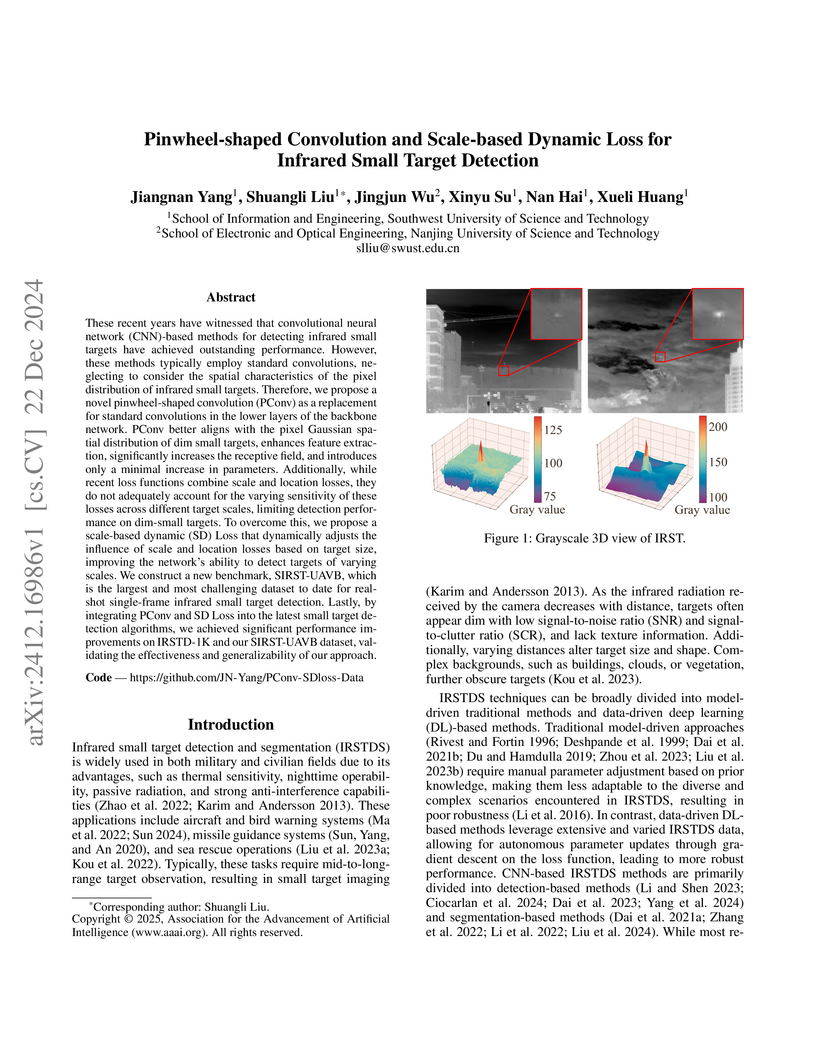
Researchers developed a Pinwheel-shaped Convolution (PConv) to enhance feature extraction by aligning with infrared small target characteristics and introduced a Scale-based Dynamic (SD) Loss to stabilize training by adaptively weighting loss components. These contributions, alongside the release of the SIRST-UAVB dataset, consistently improved infrared small target detection across multiple models.
18 Sep 2025
We report a feasibility study of the semileptonic decay Λ→pe−νˉe by using a fast simulation software package at STCF. With an anticipated integrated luminosity of 3.4 trillion J/ψ per year at a center-of-mass energy at 3.097 GeV, the statistical sensitivity of the branching fraction is determined to be 0.15\%. The statistical sensitivities of form factors gav and gw are determined to be 0.4\% and 2.15\%, respectively. Combining this result with g1(0) from Lattice QCD, we can obtain the projected sensitivity of ∣Vus∣, to be 0.9\%, which is comparable to the precision obtained through meson decay measurements. The precise measurement to be obtained at STCF will provide a rigorous test of Standard Model.
Researchers at Xidian University and Southwest University of Science and Technology introduce PGTFormer, an end-to-end framework for blind video face restoration that directly handles unaligned faces and diverse poses without requiring pre-alignment. The approach generates high-fidelity, temporally coherent video faces, demonstrating superior performance on various quality and temporal consistency metrics compared to prior methods while achieving faster inference.
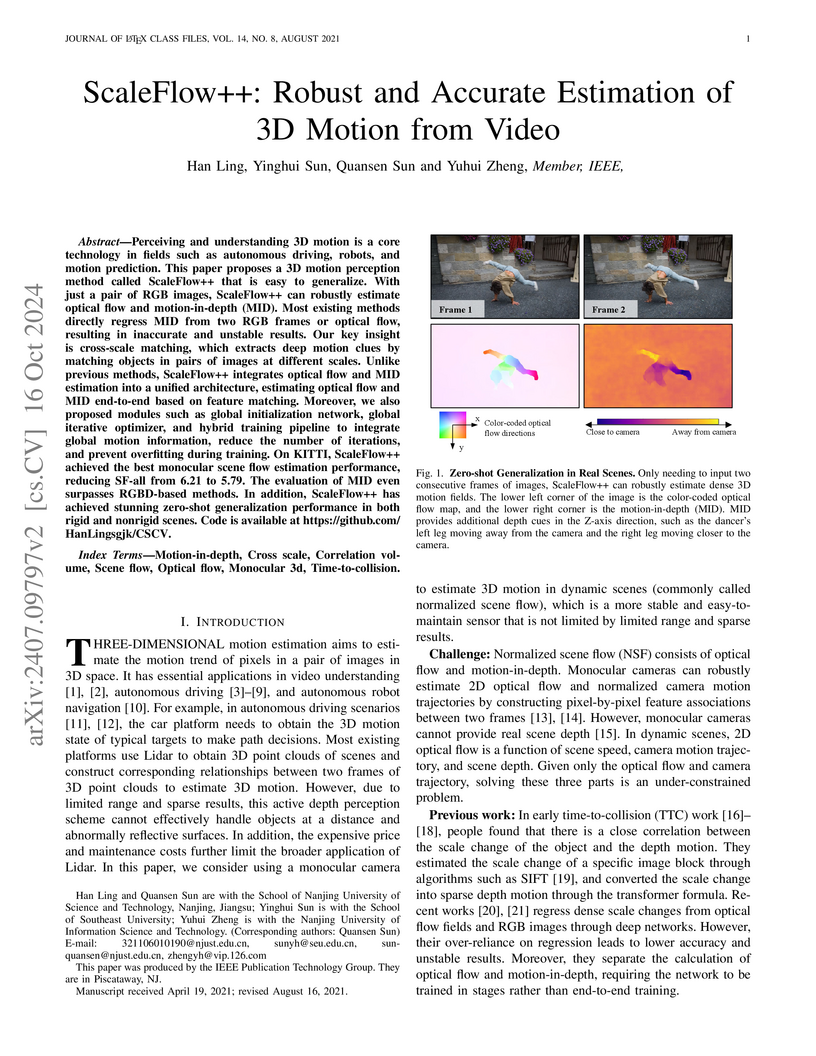
ScaleFlow++ accurately estimates dense 3D motion, including optical flow and motion-in-depth, from a single monocular video by employing a cross-scale correlation volume for explicit scale matching. The method achieved a new best monocular scene flow performance on KITTI, reducing the MID error to 38.44 and demonstrating robust zero-shot generalization.
The rise of HDR-WCG display devices has highlighted the need to convert SDRTV to HDRTV, as most video sources are still in SDR. Existing methods primarily focus on designing neural networks to learn a single-style mapping from SDRTV to HDRTV. However, the limited information in SDRTV and the diversity of styles in real-world conversions render this process an ill-posed problem, thereby constraining the performance and generalization of these methods. Inspired by generative approaches, we propose a novel method for SDRTV to HDRTV conversion guided by real HDRTV priors. Despite the limited information in SDRTV, introducing real HDRTV as reference priors significantly constrains the solution space of the originally high-dimensional ill-posed problem. This shift transforms the task from solving an unreferenced prediction problem to making a referenced selection, thereby markedly enhancing the accuracy and reliability of the conversion process. Specifically, our approach comprises two stages: the first stage employs a Vector Quantized Generative Adversarial Network to capture HDRTV priors, while the second stage matches these priors to the input SDRTV content to recover realistic HDRTV outputs. We evaluate our method on public datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness with significant improvements in both objective and subjective metrics across real and synthetic datasets.
Researchers from Sichuan University introduced Robust Self-paced Hashing with Noisy Labels (RSHNL), an AI-driven method that significantly improves cross-modal retrieval by identifying and mitigating the impact of noisy labels. It consistently outperforms 11 state-of-the-art baselines across various noise rates and hash bit lengths on multiple datasets, demonstrating enhanced robustness.
This systematic literature review surveys serverless edge computing, proposing a comprehensive taxonomy to classify research efforts. It identifies current trends, analyzes existing frameworks and platforms, and highlights open research challenges and future directions in this evolving domain.
Low-Light Image Enhancement by Learning Contrastive Representations in Spatial and Frequency Domains
Low-Light Image Enhancement by Learning Contrastive Representations in Spatial and Frequency Domains
Images taken under low-light conditions tend to suffer from poor visibility, which can decrease image quality and even reduce the performance of the downstream tasks. It is hard for a CNN-based method to learn generalized features that can recover normal images from the ones under various unknow low-light conditions. In this paper, we propose to incorporate the contrastive learning into an illumination correction network to learn abstract representations to distinguish various low-light conditions in the representation space, with the purpose of enhancing the generalizability of the network. Considering that light conditions can change the frequency components of the images, the representations are learned and compared in both spatial and frequency domains to make full advantage of the contrastive learning. The proposed method is evaluated on LOL and LOL-V2 datasets, the results show that the proposed method achieves better qualitative and quantitative results compared with other state-of-the-arts.
10 Jun 2025
For loops with UV divergences, assuming that the physical contributions of
loops from UV regions are insignificant, a method of UV-free scheme described
by an equation is introduced to derive loop results without UV divergences in
calculations, i.e., a route of the analytic continuation
TF→TP besides the traditional
route ∞−∞ in mathematical structure. This scheme provides a new
perspective to an open question of the hierarchy problem of Higgs mass, i.e.,
an alternative interpretation without fine-tuning within the standard model.
Adversarial examples' (AE) transferability refers to the phenomenon that AEs crafted with one surrogate model can also fool other models. Notwithstanding remarkable progress in untargeted transferability, its targeted counterpart remains challenging. This paper proposes an everywhere scheme to boost targeted transferability. Our idea is to attack a victim image both globally and locally. We aim to optimize 'an army of targets' in every local image region instead of the previous works that optimize a high-confidence target in the image. Specifically, we split a victim image into non-overlap blocks and jointly mount a targeted attack on each block. Such a strategy mitigates transfer failures caused by attention inconsistency between surrogate and victim models and thus results in stronger transferability. Our approach is method-agnostic, which means it can be easily combined with existing transferable attacks for even higher transferability. Extensive experiments on ImageNet demonstrate that the proposed approach universally improves the state-of-the-art targeted attacks by a clear margin, e.g., the transferability of the widely adopted Logit attack can be improved by 28.8%-300%.We also evaluate the crafted AEs on a real-world platform: Google Cloud Vision. Results further support the superiority of the proposed method.
The robustness of neural network classifiers is important in the
safety-critical domain and can be quantified by robustness verification. At
present, efficient and scalable verification techniques are always sound but
incomplete, and thus, the improvement of verified robustness results is the key
criterion to evaluate the performance of incomplete verification approaches.
The multi-variate function MaxPool is widely adopted yet challenging to verify.
In this paper, we present Ti-Lin, a robustness verifier for MaxPool-based CNNs
with Tight Linear Approximation. Following the sequel of minimizing the
over-approximation zone of the non-linear function of CNNs, we are the first to
propose the provably neuron-wise tightest linear bounds for the MaxPool
function. By our proposed linear bounds, we can certify larger robustness
results for CNNs. We evaluate the effectiveness of Ti-Lin on different
verification frameworks with open-sourced benchmarks, including LeNet,
PointNet, and networks trained on the MNIST, CIFAR-10, Tiny ImageNet and
ModelNet40 datasets. Experimental results show that Ti-Lin significantly
outperforms the state-of-the-art methods across all networks with up to 78.6%
improvement in terms of the certified accuracy with almost the same time
consumption as the fastest tool. Our code is available at
this https URL
This paper presents a lightweight image fusion algorithm specifically designed for merging visible light and infrared images, with an emphasis on balancing performance and efficiency. The proposed method enhances the generator in a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) by integrating the Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) to improve feature focus and utilizing Depthwise Separable Convolution (DSConv) for more efficient computations. These innovations significantly reduce the model's computational cost, including the number of parameters and inference latency, while maintaining or even enhancing the quality of the fused images. Comparative experiments using the M3FD dataset demonstrate that the proposed algorithm not only outperforms similar image fusion methods in terms of fusion quality but also offers a more resource-efficient solution suitable for deployment on embedded devices. The effectiveness of the lightweight design is validated through extensive ablation studies, confirming its potential for real-time applications in complex environments.
Adversarial examples (AEs) have been extensively studied due to their potential for privacy protection and inspiring robust neural networks. Yet, making a targeted AE transferable across unknown models remains challenging. In this paper, to alleviate the overfitting dilemma common in an AE crafted by existing simple iterative attacks, we propose fine-tuning it in the feature space. Specifically, starting with an AE generated by a baseline attack, we encourage the features conducive to the target class and discourage the features to the original class in a middle layer of the source model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that only a few iterations of fine-tuning can boost existing attacks' targeted transferability nontrivially and universally. Our results also verify that the simple iterative attacks can yield comparable or even better transferability than the resource-intensive methods, which rest on training target-specific classifiers or generators with additional data. The code is available at: this http URL.
Researchers at Xidian University and Novastar Tech developed RealCamNet, an end-to-end deep neural network that unifies camera image signal processing and compression from raw sensor data to a display-ready RGB image. This system demonstrates superior rate-distortion performance and faster inference speeds compared to existing multi-stage pipelines.
Semi-supervised medical image segmentation (SSMIS) has been demonstrated the potential to mitigate the issue of limited medical labeled data. However, confirmation and cognitive biases may affect the prevalent teacher-student based SSMIS methods due to erroneous pseudo-labels. To tackle this challenge, we improve the mean teacher approach and propose the Students Discrepancy-Informed Correction Learning (SDCL) framework that includes two students and one non-trainable teacher, which utilizes the segmentation difference between the two students to guide the self-correcting learning. The essence of SDCL is to identify the areas of segmentation discrepancy as the potential bias areas, and then encourage the model to review the correct cognition and rectify their own biases in these areas. To facilitate the bias correction learning with continuous review and rectification, two correction loss functions are employed to minimize the correct segmentation voxel distance and maximize the erroneous segmentation voxel entropy. We conducted experiments on three public medical image datasets: two 3D datasets (CT and MRI) and one 2D dataset (MRI). The results show that our SDCL surpasses the current State-of-the-Art (SOTA) methods by 2.57\%, 3.04\%, and 2.34\% in the Dice score on the Pancreas, LA, and ACDC datasets, respectively. In addition, the accuracy of our method is very close to the fully supervised method on the ACDC dataset, and even exceeds the fully supervised method on the Pancreas and LA dataset. (Code available at \url{this https URL}).
Steady-state visual evoked potential (SSVEP) is one of the most commonly used
control signal in the brain-computer interface (BCI) systems. However, the
conventional spatial filtering methods for SSVEP classification highly depend
on the subject-specific calibration data. The need for the methods that can
alleviate the demand for the calibration data become urgent. In recent years,
developing the methods that can work in inter-subject classification scenario
has become a promising new direction. As the popular deep learning model
nowadays, Transformer has excellent performance and has been used in EEG signal
classification tasks. Therefore, in this study, we propose a deep learning
model for SSVEP classification based on Transformer structure in inter-subject
classification scenario, termed as SSVEPformer, which is the first application
of the transformer to the classification of SSVEP. Inspired by previous
studies, the model adopts the frequency spectrum of SSVEP data as input, and
explores the spectral and spatial domain information for classification.
Furthermore, to fully utilize the harmonic information, an extended SSVEPformer
based on the filter bank technology (FB-SSVEPformer) is proposed to further
improve the classification performance. Experiments were conducted using two
open datasets (Dataset 1: 10 subjects, 12-class task; Dataset 2: 35 subjects,
40-class task) in the inter-subject classification scenario. The experimental
results show that the proposed models could achieve better results in terms of
classification accuracy and information transfer rate, compared with other
baseline methods. The proposed model validates the feasibility of deep learning
models based on Transformer structure for SSVEP classification task, and could
serve as a potential model to alleviate the calibration procedure in the
practical application of SSVEP-based BCI systems.
Recent advances in face super-resolution research have utilized the
Transformer architecture. This method processes the input image into a series
of small patches. However, because of the strong correlation between different
facial components in facial images. When it comes to super-resolution of
low-resolution images, existing algorithms cannot handle the relationships
between patches well, resulting in distorted facial components in the
super-resolution results. To solve the problem, we propose a transformer
architecture based on graph neural networks called graph vision transformer
network. We treat each patch as a graph node and establish an adjacency matrix
based on the information between patches. In this way, the patch only interacts
between neighboring patches, further processing the relationship of facial
components. Quantitative and visualization experiments have underscored the
superiority of our algorithm over state-of-the-art techniques. Through detailed
comparisons, we have demonstrated that our algorithm possesses more advanced
super-resolution capabilities, particularly in enhancing facial components. The
PyTorch code is available at this https URL
Accurate power load forecasting is crucial for improving energy efficiency and ensuring power supply quality. Considering the power load forecasting problem involves not only dynamic factors like historical load variations but also static factors such as climate conditions that remain constant over specific periods. From the model-agnostic perspective, this paper proposes a parallel structure network to extract important information from both dynamic and static data. Firstly, based on complexity learning theory, it is demonstrated that models integrated through parallel structures exhibit superior generalization abilities compared to individual base learners. Additionally, the higher the independence between base learners, the stronger the generalization ability of the parallel structure model. This suggests that the structure of machine learning models inherently contains significant information. Building on this theoretical foundation, a parallel convolutional neural network (CNN)-gate recurrent unit (GRU) attention model (PCGA) is employed to address the power load forecasting issue, aiming to effectively integrate the influences of dynamic and static features. The CNN module is responsible for capturing spatial characteristics from static data, while the GRU module captures long-term dependencies in dynamic time series data. The attention layer is designed to focus on key information from the spatial-temporal features extracted by the parallel CNN-GRU. To substantiate the advantages of the parallel structure model in extracting and integrating multi-source information, a series of experiments are conducted.
One of the most important subconscious reactions, micro-expression (ME), is a spontaneous, subtle, and transient facial expression that reveals human beings' genuine emotion. Therefore, automatically recognizing ME (MER) is becoming increasingly crucial in the field of affective computing, providing essential technical support for lie detection, clinical psychological diagnosis, and public safety. However, the ME data scarcity has severely hindered the development of advanced data-driven MER models. Despite the recent efforts by several spontaneous ME databases to alleviate this problem, there is still a lack of sufficient data. Hence, in this paper, we overcome the ME data scarcity problem by collecting and annotating a dynamic spontaneous ME database with the largest current ME data scale called DFME (Dynamic Facial Micro-expressions). Specifically, the DFME database contains 7,526 well-labeled ME videos spanning multiple high frame rates, elicited by 671 participants and annotated by more than 20 professional annotators over three years. Furthermore, we comprehensively verify the created DFME, including using influential spatiotemporal video feature learning models and MER models as baselines, and conduct emotion classification and ME action unit classification experiments. The experimental results demonstrate that the DFME database can facilitate research in automatic MER, and provide a new benchmark for this field. DFME will be published via this https URL.
Performance of the sensor-based camera identification (SCI) method heavily
relies on the denoising filter in estimating Photo-Response Non-Uniformity
(PRNU). Given various attempts on enhancing the quality of the extracted PRNU,
it still suffers from unsatisfactory performance in low-resolution images and
high computational demand. Leveraging the similarity of PRNU estimation and
image denoising, we take advantage of the latest achievements of Convolutional
Neural Network (CNN)-based denoisers for PRNU extraction. In this paper, a
comparative evaluation of such CNN denoisers on SCI performance is carried out
on the public "Dresden Image Database". Our findings are two-fold. From one
aspect, both the PRNU extraction and image denoising separate noise from the
image content. Hence, SCI can benefit from the recent CNN denoisers if
carefully trained. From another aspect, the goals and the scenarios of PRNU
extraction and image denoising are different since one optimizes the quality of
noise and the other optimizes the image quality. A carefully tailored training
is needed when CNN denoisers are used for PRNU estimation. Alternative
strategies of training data preparation and loss function design are analyzed
theoretically and evaluated experimentally. We point out that feeding the CNNs
with image-PRNU pairs and training them with correlation-based loss function
result in the best PRNU estimation performance. To facilitate further studies
of SCI, we also propose a minimum-loss camera fingerprint quantization scheme
using which we save the fingerprints as image files in PNG format. Furthermore,
we make the quantized fingerprints of the cameras from the "Dresden Image
Database" publicly available.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.