Technische Universität Kaiserslautern
30 Jun 2022
OpDiLib extends classical operator overloading Automatic Differentiation to OpenMP parallelized code, leveraging the OpenMP Tools (OMPT) API for fully automatic differentiation without requiring source code modifications. The library achieves robust performance and scaling for scientific simulations, while offering fine-grained control over adjoint variable updates for optimal efficiency.
Deep learning approaches to anomaly detection have recently improved the
state of the art in detection performance on complex datasets such as large
collections of images or text. These results have sparked a renewed interest in
the anomaly detection problem and led to the introduction of a great variety of
new methods. With the emergence of numerous such methods, including approaches
based on generative models, one-class classification, and reconstruction, there
is a growing need to bring methods of this field into a systematic and unified
perspective. In this review we aim to identify the common underlying principles
as well as the assumptions that are often made implicitly by various methods.
In particular, we draw connections between classic 'shallow' and novel deep
approaches and show how this relation might cross-fertilize or extend both
directions. We further provide an empirical assessment of major existing
methods that is enriched by the use of recent explainability techniques, and
present specific worked-through examples together with practical advice.
Finally, we outline critical open challenges and identify specific paths for
future research in anomaly detection.
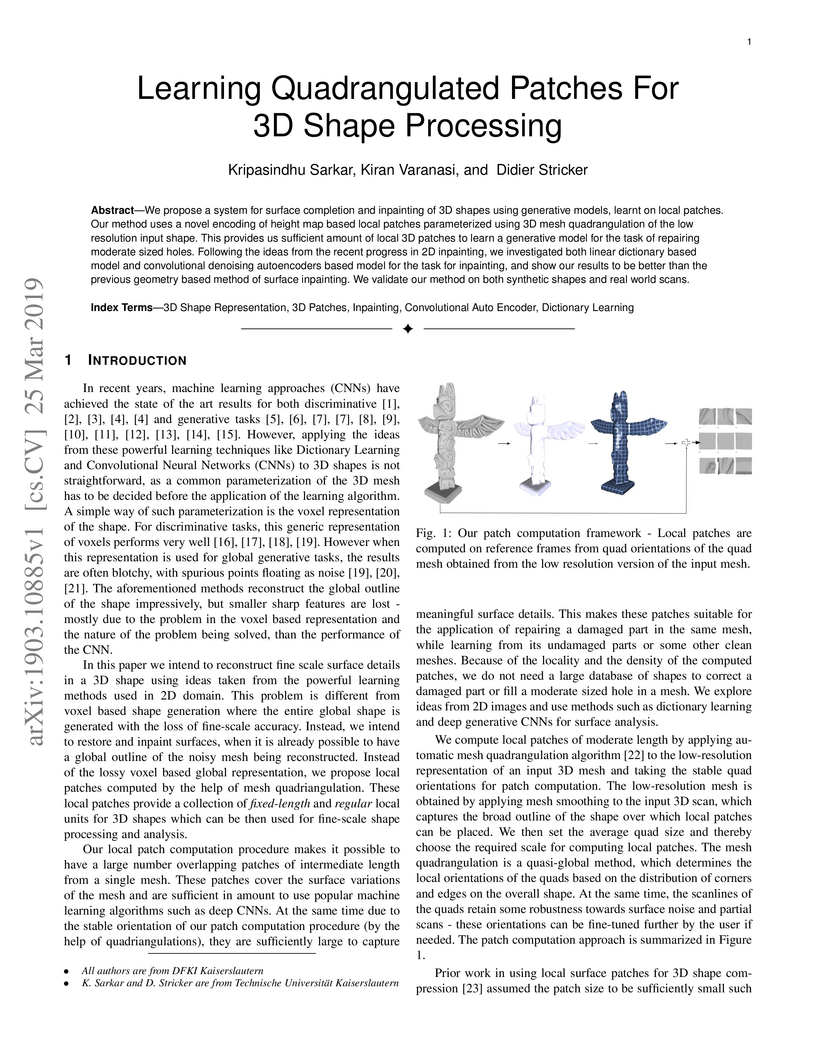
We propose a system for surface completion and inpainting of 3D shapes using generative models, learnt on local patches. Our method uses a novel encoding of height map based local patches parameterized using 3D mesh quadrangulation of the low resolution input shape. This provides us sufficient amount of local 3D patches to learn a generative model for the task of repairing moderate sized holes. Following the ideas from the recent progress in 2D inpainting, we investigated both linear dictionary based model and convolutional denoising autoencoders based model for the task for inpainting, and show our results to be better than the previous geometry based method of surface inpainting. We validate our method on both synthetic shapes and real world scans.
The evolution of wireless communications into 6G and beyond is expected to rely on new machine learning (ML)-based capabilities. These can enable proactive decisions and actions from wireless-network components to sustain quality-of-service (QoS) and user experience. Moreover, new use cases in the area of vehicular and industrial communications will emerge. Specifically in the area of vehicle communication, vehicle-to-everything (V2X) schemes will benefit strongly from such advances. With this in mind, we have conducted a detailed measurement campaign that paves the way to a plethora of diverse ML-based studies. The resulting datasets offer GPS-located wireless measurements across diverse urban environments for both cellular (with two different operators) and sidelink radio access technologies, thus enabling a variety of different studies towards V2X. The datasets are labeled and sampled with a high time resolution. Furthermore, we make the data publicly available with all the necessary information to support the onboarding of new researchers. We provide an initial analysis of the data showing some of the challenges that ML needs to overcome and the features that ML can leverage, as well as some hints at potential research studies.
Deep learning methods have shown great success in several domains as they process a large amount of data efficiently, capable of solving complex classification, forecast, segmentation, and other tasks. However, they come with the inherent drawback of inexplicability limiting their applicability and trustworthiness. Although there exists work addressing this perspective, most of the existing approaches are limited to the image modality due to the intuitive and prominent concepts. Conversely, the concepts in the time-series domain are more complex and non-comprehensive but these and an explanation for the network decision are pivotal in critical domains like medical, financial, or industry. Addressing the need for an explainable approach, we propose a novel interpretable network scheme, designed to inherently use an explainable reasoning process inspired by the human cognition without the need of additional post-hoc explainability methods. Therefore, class-specific patches are used as they cover local concepts relevant to the classification to reveal similarities with samples of the same class. In addition, we introduce a novel loss concerning interpretability and accuracy that constraints P2ExNet to provide viable explanations of the data including relevant patches, their position, class similarities, and comparison methods without compromising accuracy. Analysis of the results on eight publicly available time-series datasets reveals that P2ExNet reaches comparable performance when compared to its counterparts while inherently providing understandable and traceable decisions.
We present a novel adversarial penalized self-knowledge distillation method,
named adversarial learning and implicit regularization for self-knowledge
distillation (AI-KD), which regularizes the training procedure by adversarial
learning and implicit distillations. Our model not only distills the
deterministic and progressive knowledge which are from the pre-trained and
previous epoch predictive probabilities but also transfers the knowledge of the
deterministic predictive distributions using adversarial learning. The
motivation is that the self-knowledge distillation methods regularize the
predictive probabilities with soft targets, but the exact distributions may be
hard to predict. Our method deploys a discriminator to distinguish the
distributions between the pre-trained and student models while the student
model is trained to fool the discriminator in the trained procedure. Thus, the
student model not only can learn the pre-trained model's predictive
probabilities but also align the distributions between the pre-trained and
student models. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method with
network architectures on multiple datasets and show the proposed method
achieves better performance than state-of-the-art methods.
 CNRS
CNRS University of Amsterdam
University of Amsterdam UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley University of OxfordUniversity of Edinburgh
University of OxfordUniversity of Edinburgh Peking UniversityThe University of ManchesterThe University of Sydney
Peking UniversityThe University of ManchesterThe University of Sydney Sorbonne Université
Sorbonne Université Leiden UniversityMax Planck Institute for AstrophysicsUniversity of TwenteTallinn University of TechnologyObservatoire de ParisUniversity of HamburgUniversité Côte d’Azur
Leiden UniversityMax Planck Institute for AstrophysicsUniversity of TwenteTallinn University of TechnologyObservatoire de ParisUniversity of HamburgUniversité Côte d’Azur University of GroningenSwinburne University of TechnologyMax-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie
University of GroningenSwinburne University of TechnologyMax-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie Harvard-Smithsonian Center for AstrophysicsHelmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-RossendorfPSL Research UniversityLESIAObservatoire de la Côte d’AzurRhodes UniversityKavli Institute for Astronomy and AstrophysicsUniversität BielefeldThüringer Landessternwarte TautenburgRadboud University NijmegenVrije Universiteit AmsterdamLeibniz-Institut für Astrophysik PotsdamSRON Netherlands Institute for Space ResearchASTRON, Netherlands Institute for Radio AstronomyNetherlands eScience CenterTechnische Universität KaiserslauternCSIRO Astronomy and Space ScienceUniv Paris DiderotLebedev Physical Institute, Russian Academy of SciencesSKA South AfricaLaboratoire de Physique et Chimie de l’Environnement et de l’EspaceStation de radioastronomie de NançaySKA OrganisationSorbonne Paris Cit",Universit
de Lyon
Harvard-Smithsonian Center for AstrophysicsHelmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-RossendorfPSL Research UniversityLESIAObservatoire de la Côte d’AzurRhodes UniversityKavli Institute for Astronomy and AstrophysicsUniversität BielefeldThüringer Landessternwarte TautenburgRadboud University NijmegenVrije Universiteit AmsterdamLeibniz-Institut für Astrophysik PotsdamSRON Netherlands Institute for Space ResearchASTRON, Netherlands Institute for Radio AstronomyNetherlands eScience CenterTechnische Universität KaiserslauternCSIRO Astronomy and Space ScienceUniv Paris DiderotLebedev Physical Institute, Russian Academy of SciencesSKA South AfricaLaboratoire de Physique et Chimie de l’Environnement et de l’EspaceStation de radioastronomie de NançaySKA OrganisationSorbonne Paris Cit",Universit
de LyonWe have conducted two pilot surveys for radio pulsars and fast transients
with the Low-Frequency Array (LOFAR) around 140 MHz and here report on the
first low-frequency fast-radio burst limit and the discovery of two new
pulsars. The first survey, the LOFAR Pilot Pulsar Survey (LPPS), observed a
large fraction of the northern sky, ~1.4 x 10^4 sq. deg, with 1-hr dwell times.
Each observation covered ~75 sq. deg using 7 independent fields formed by
incoherently summing the high-band antenna fields. The second pilot survey, the
LOFAR Tied-Array Survey (LOTAS), spanned ~600 sq. deg, with roughly a 5-fold
increase in sensitivity compared with LPPS. Using a coherent sum of the 6 LOFAR
"Superterp" stations, we formed 19 tied-array beams, together covering 4 sq.
deg per pointing. From LPPS we derive a limit on the occurrence, at 142 MHz, of
dispersed radio bursts of < 150 /day/sky, for bursts brighter than S > 107 Jy
for the narrowest searched burst duration of 0.66 ms. In LPPS, we re-detected
65 previously known pulsars. LOTAS discovered two pulsars, the first with LOFAR
or any digital aperture array. LOTAS also re-detected 27 previously known
pulsars. These pilot studies show that LOFAR can efficiently carry out all-sky
surveys for pulsars and fast transients, and they set the stage for further
surveying efforts using LOFAR and the planned low-frequency component of the
Square Kilometer Array.
 University of Cambridge
University of Cambridge Imperial College London
Imperial College London University of WarwickLudwig-Maximilians-Universität MünchenJP Morgan AI ResearchTechnische Universität KaiserslauternChalmers Technical UniversityDeutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz (DFKI)Leibniz Institute for Prevention Research and Epidemiology – BIPS GmbH
University of WarwickLudwig-Maximilians-Universität MünchenJP Morgan AI ResearchTechnische Universität KaiserslauternChalmers Technical UniversityDeutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz (DFKI)Leibniz Institute for Prevention Research and Epidemiology – BIPS GmbHAlgorithmic fairness is an increasingly important field concerned with
detecting and mitigating biases in machine learning models. There has been a
wealth of literature for algorithmic fairness in regression and classification
however there has been little exploration of the field for survival analysis.
Survival analysis is the prediction task in which one attempts to predict the
probability of an event occurring over time. Survival predictions are
particularly important in sensitive settings such as when utilising machine
learning for diagnosis and prognosis of patients. In this paper we explore how
to utilise existing survival metrics to measure bias with group fairness
metrics. We explore this in an empirical experiment with 29 survival datasets
and 8 measures. We find that measures of discrimination are able to capture
bias well whereas there is less clarity with measures of calibration and
scoring rules. We suggest further areas for research including prediction-based
fairness metrics for distribution predictions.
We present an efficient method to shorten the analytic integration-by-parts
(IBP) reduction coefficients of multi-loop Feynman integrals. For our approach,
we develop an improved version of Leinartas' multivariate partial fraction
algorithm, and provide a modern implementation based on the computer algebra
system Singular. Furthermore, We observe that for an integral basis with
uniform transcendental (UT) weights, the denominators of IBP reduction
coefficients with respect to the UT basis are either symbol letters or
polynomials purely in the spacetime dimension D. With a UT basis, the partial
fraction algorithm is more efficient both with respect to its performance and
the size reduction. We show that in complicated examples with existence of a UT
basis, the IBP reduction coefficients size can be reduced by a factor of as
large as ∼100. We observe that our algorithm also works well for settings
without a UT basis.
30 Oct 2023
Phase transitions correspond to the singular behavior of physical systems in response to continuous control parameters like temperature or external fields. Near continuous phase transitions, associated with the divergence of a correlation length, universal power-law scaling behavior with critical exponents independent of microscopic system details is found. Recently, dynamical quantum phase transitions and universal scaling have been predicted and also observed in the non-equilibrium dynamics of isolated quantum systems after a quench, with time playing the role of the control parameter. However, signatures of such critical phenomena in time in open systems, whose dynamics is driven by the dissipative contact to an environment, were so far elusive. Here, we present results indicating that critical scaling with respect to time can also occur during the relaxation dynamics of an open quantum system described by mixed states. We experimentally measure the relaxation dynamics of the large atomic spin of individual Caesium atoms induced by the dissipative coupling via spin-exchange processes to an ultracold Bose gas of Rubidium atoms. For initial states far from equilibrium, the entropy of the spin state is found to peak in time, transiently approaching its maximum possible value, before eventually relaxing to its lower equilibrium value. Moreover, a finite-size scaling analysis based on numerical simulations shows that it corresponds to a critical point with respect to time of the dissipative system in the limit of large system sizes. It is signalled by the divergence of a characteristic length at a critical time, characterized by critical exponents that are found to be independent of system details.
Multivariate partial fractioning is a powerful tool for simplifying rational function coefficients in scattering amplitude computations. Since current research problems lead to large sets of complicated rational functions, performance of the partial fractioning as well as size of the obtained expressions are a prime concern. We develop a large scale parallel framework for multivariate partial fractioning, which implements and combines an improved version of Leinartas' algorithm and the {\sc MultivariateApart} algorithm. Our approach relies only on open source software. It combines parallelism over the different rational function coefficients with parallelism for individual expressions. The implementation is based on the \textsc{Singular}/\textsc{GPI-Space framework} for massively parallel computer algebra, which formulates parallel algorithms in terms of Petri nets. The modular nature of this approach allows for easy incorporation of future algorithmic developments into our package. We demonstrate the performance of our framework by simplifying expressions arising from current multiloop scattering amplitude problems.
19 May 2021
We present a new open source C library \texttt{msolve} dedicated to solving
multivariate polynomial systems of dimension zero through computer algebra
methods. The core algorithmic framework of \texttt{msolve} relies on Gr\''obner
bases and linear algebra based algorithms for polynomial system solving. It
relies on Gr\''obner basis computation w.r.t.\ the degree reverse
lexicographical order, Gr\''obner conversion to a lexicographical Gr\''obner
basis and real solving of univariate polynomials. We explain in detail how
these three main steps of the solving process are implemented, how we exploit
\texttt{AVX2} instruction processors and the more general implementation ideas
we put into practice to better exploit the computational capabilities of this
algorithmic framework. We compare the practical performances of \texttt{msolve}
with leading computer algebra systems such as \textsc{Magma}, \textsc{Maple},
\textsc{Singular} on a wide range of systems with finitely many complex
solutions, showing that \texttt{msolve} can tackle systems which were out of
reach by the computer algebra software state-of-the-art.
This paper provides the first comprehensive evaluation and analysis of modern (deep-learning) unsupervised anomaly detection methods for chemical process data. We focus on the Tennessee Eastman process dataset, which has been a standard litmus test to benchmark anomaly detection methods for nearly three decades. Our extensive study will facilitate choosing appropriate anomaly detection methods in industrial applications.
25 Apr 2022
We study the static and dynamic magnetic properties of epitaxially strained γ-Fe2O3 (maghemite) thin films grown via pulsed-laser deposition on MgO substrates by SQUID magnetometry and cryogenic broadband ferromagnetic resonance experiments. SQUID magnetometry measurements reveal hysteretic magnetization curves for magnetic fields applied both in- and out of the sample plane. From the magnetization dynamics of our thin films, we find a small negative effective magnetization in agreement with a strain induced perpendicular magnetic anisotropy. Moreover, we observe a non-linear evolution of the ferromagnetic resonance-linewidth as function of the microwave frequency and explain this finding with a model based on slowly relaxing impurities, the so-called slow relaxor model. By investigating the magnetization dynamics in our maghemite thin films as a function of frequency and temperature, we can isolate the temperature dependent contribution of the slowly relaxing impurities to the resonance linewidth and, in particular, observe a sign change in the effective magnetization. This finding provides evidence for a transition of the magnetic anisotropy from a perpendicular easy axis to an easy in-plane anisotropy for reduced temperatures.
01 Jul 2024
The extreme requirements for high reliability and low latency in the upcoming Sixth Generation (6G) wireless networks are challenging the design of multi-hop wireless transport networks. Inspired by the advent of the virtualization concept in the wireless networks design and openness paradigm as fostered by the O-RAN Alliance, we target a revolutionary resource allocation scheme to improve the overall transmission efficiency.
In this paper, we investigate the problem of multi-hop decode-and-forward (DF) relaying in the finite blocklength (FBL) regime, and propose a DMH-HARQ scheme, which maximizes the end-to-end (E2E) communication reliability in the wireless transport network. We also propose an integer dynamic programming (DP) algorithm to efficiently solve the optimal DMH-HARQ strategy. Constrained within a certain time frame to accomplish E2E transmission, our proposed approach is proven to outperform the conventional listening-based cooperative ARQ, as well as any static HARQ strategy, regarding the E2E reliability. It is applicable without dependence on special delay constraint, and is particularly competitive for long-distance transport network with many hops.
15 Jan 2020
The inertial effects of magnetic solitons play a crucial role in their
dynamics and stability. Yet governing their inertial effects is a challenge for
their use in real devices. Here, we show how to control the inertial effects of
magnetic droplet solitons. Magnetic droplets are strongly nonlinear and
localized autosolitons than can form in current-driven nanocontacts. Droplets
can be considered as dynamical particles with an effective mass. We show that
the dynamical droplet bears a second excitation under its own inertia. These
excitations comprise a chiral profile, and appear when the droplet resists the
force induced by the Oersted field of the current injected into the
nanocontact. We reveal the role of the spin torque on the excitation of these
chiral modes and we show how to control these modes using the current and the
field.
18 Feb 2014
In this paper we propose a model for a sewer network coupled to surface flow and investigate it numerically. In particular, we present a new model for the manholes in storm sewer systems. It is derived using the balance of the total energy in the complete network. The resulting system of equations contains, aside from hyperbolic conservation laws for the sewer network and algebraic relations for the coupling conditions, a system of ODEs governing the flow in the manholes. The manholes provide natural points for the interaction of the sewer system and the run off on the urban surface modelled by shallow water equations. Finally, a numerical method for the coupled system is presented. In several numerical tests we study the influence of the manhole model on the sewer system and the coupling with 2D surface flow.
12 Feb 2019
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a powerful standard tool for reducing
the dimensionality of data. Unfortunately, it is sensitive to outliers so that
various robust PCA variants were proposed in the literature. This paper
addresses the robust PCA by successively determining the directions of lines
having minimal Euclidean distances from the data points. The corresponding
energy functional is not differentiable at a finite number of directions which
we call anchor directions. We derive a Weiszfeld-like algorithm for minimizing
the energy functional which has several advantages over existing algorithms.
Special attention is paid to the careful handling of the anchor directions,
where we take the relation between local minima and one-sided derivatives of
Lipschitz continuous functions on submanifolds of Rd into account.
Using ideas for stabilizing the classical Weiszfeld algorithm at anchor points
and the Kurdyka-{\L}ojasiewicz property of the energy functional, we prove
global convergence of the whole sequence of iterates generated by the algorithm
to a critical point of the energy functional. Numerical examples demonstrate
the very good performance of our algorithm.
05 Sep 2019
The quantum dynamics of a damped and forced harmonic oscillator is
investigated in terms of a Lindblad master equation. Elementary algebraic
techniques are employed allowing for example to analyze the long time behavior,
i.e. the quantum limit cycle. The time evolution of various expectation values
is obtained in closed form as well as the entropy and the Husimi phase space
distribution. We also discuss the related description in terms of a
non-Hermitian Hamiltonian.
Deep learning based medical image classifiers have shown remarkable prowess
in various application areas like ophthalmology, dermatology, pathology, and
radiology. However, the acceptance of these Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD)
systems in real clinical setups is severely limited primarily because their
decision-making process remains largely obscure. This work aims at elucidating
a deep learning based medical image classifier by verifying that the model
learns and utilizes similar disease-related concepts as described and employed
by dermatologists. We used a well-trained and high performing neural network
developed by REasoning for COmplex Data (RECOD) Lab for classification of three
skin tumours, i.e. Melanocytic Naevi, Melanoma and Seborrheic Keratosis and
performed a detailed analysis on its latent space. Two well established and
publicly available skin disease datasets, PH2 and derm7pt, are used for
experimentation. Human understandable concepts are mapped to RECOD image
classification model with the help of Concept Activation Vectors (CAVs),
introducing a novel training and significance testing paradigm for CAVs. Our
results on an independent evaluation set clearly shows that the classifier
learns and encodes human understandable concepts in its latent representation.
Additionally, TCAV scores (Testing with CAVs) suggest that the neural network
indeed makes use of disease-related concepts in the correct way when making
predictions. We anticipate that this work can not only increase confidence of
medical practitioners on CAD but also serve as a stepping stone for further
development of CAV-based neural network interpretation methods.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.