The Education University of Hong Kong
Researchers introduce SGSimEval, a comprehensive and similarity-enhanced benchmark for evaluating automatic survey generation (ASG) systems. This framework assesses ASG outputs across outline, content, and reference quality, integrating both LLM-based scoring and novel human-preference aligned similarity metrics to provide a robust evaluation.
The CCoL framework jointly learns vision-language-action policies, utilizing continuous dynamics modeling and semantic-physical alignment to mitigate compounding errors and generate smoother, more coherent robot trajectories. It achieved an average 90.5% success rate on 'Cube Transfer' in simulation and reduced velocity fluctuations by 30.8% compared to a variant without continuous co-learning.
This research introduces Knowledge Graph-enhanced Retrieval-Augmented Generation (KG-RAG), an adaptive AI tutoring framework that addresses the limitations of large language models in educational settings. The system improves student learning outcomes by providing more coherent and accurate explanations, achieving a 35% increase in assessment scores in controlled experiments while also demonstrating economic feasibility.
The questionable responses caused by knowledge hallucination may lead to
LLMs' unstable ability in decision-making. However, it has never been
investigated whether the LLMs' hallucination is possibly usable to generate
negative reasoning for facilitating the detection of fake news. This study
proposes a novel supervised self-reinforced reasoning rectification approach -
SR3 that yields both common reasonable reasoning and wrong understandings
(negative reasoning) for news via LLMs reflection for semantic consistency
learning. Upon that, we construct a negative reasoning-based news learning
model called - \emph{NRFE}, which leverages positive or negative news-reasoning
pairs for learning the semantic consistency between them. To avoid the impact
of label-implicated reasoning, we deploy a student model - \emph{NRFE-D} that
only takes news content as input to inspect the performance of our method by
distilling the knowledge from \emph{NRFE}. The experimental results verified on
three popular fake news datasets demonstrate the superiority of our method
compared with three kinds of baselines including prompting on LLMs, fine-tuning
on pre-trained SLMs, and other representative fake news detection methods.
14 Jul 2025
Recent years have witnessed the remarkable success of recommendation systems (RSs) in alleviating the information overload problem. As a new paradigm of RSs, session-based recommendation (SR) specializes in users' short-term preference capture and aims to provide a more dynamic and timely recommendation based on the ongoing interacted actions. In this survey, we will give a comprehensive overview of the recent works on SR. First, we clarify the definitions of various SR tasks and introduce the characteristics of session-based recommendation against other recommendation tasks. Then, we summarize the existing methods in two categories: sequential neural network based methods and graph neural network (GNN) based methods. The standard frameworks and technical are also introduced. Finally, we discuss the challenges of SR and new research directions in this area.
06 Jul 2025
The ability of language models to comprehend and interact in diverse linguistic and cultural landscapes is crucial. The Cantonese language used in Hong Kong presents unique challenges for natural language processing due to its rich cultural nuances and lack of dedicated evaluation datasets. The HKCanto-Eval benchmark addresses this gap by evaluating the performance of large language models (LLMs) on Cantonese language understanding tasks, extending to English and Written Chinese for cross-lingual evaluation. HKCanto-Eval integrates cultural and linguistic nuances intrinsic to Hong Kong, providing a robust framework for assessing language models in realistic scenarios. Additionally, the benchmark includes questions designed to tap into the underlying linguistic metaknowledge of the models. Our findings indicate that while proprietary models generally outperform open-weight models, significant limitations remain in handling Cantonese-specific linguistic and cultural knowledge, highlighting the need for more targeted training data and evaluation methods. The code can be accessed at this https URL
01 Sep 2025
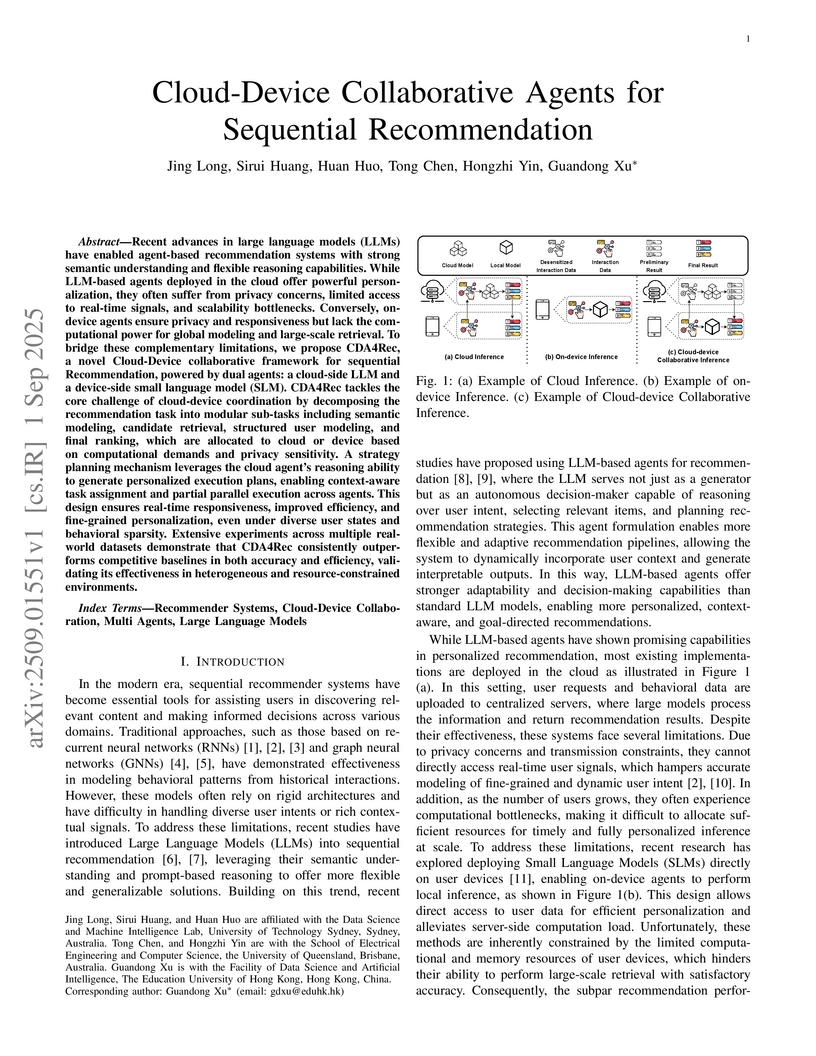
Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have enabled agent-based recommendation systems with strong semantic understanding and flexible reasoning capabilities. While LLM-based agents deployed in the cloud offer powerful personalization, they often suffer from privacy concerns, limited access to real-time signals, and scalability bottlenecks. Conversely, on-device agents ensure privacy and responsiveness but lack the computational power for global modeling and large-scale retrieval. To bridge these complementary limitations, we propose CDA4Rec, a novel Cloud-Device collaborative framework for sequential Recommendation, powered by dual agents: a cloud-side LLM and a device-side small language model (SLM). CDA4Rec tackles the core challenge of cloud-device coordination by decomposing the recommendation task into modular sub-tasks including semantic modeling, candidate retrieval, structured user modeling, and final ranking, which are allocated to cloud or device based on computational demands and privacy sensitivity. A strategy planning mechanism leverages the cloud agent's reasoning ability to generate personalized execution plans, enabling context-aware task assignment and partial parallel execution across agents. This design ensures real-time responsiveness, improved efficiency, and fine-grained personalization, even under diverse user states and behavioral sparsity. Extensive experiments across multiple real-world datasets demonstrate that CDA4Rec consistently outperforms competitive baselines in both accuracy and efficiency, validating its effectiveness in heterogeneous and resource-constrained environments.
Despite living in the era of the internet, phone-based scams remain one of
the most prevalent forms of scams. These scams aim to exploit victims for
financial gain, causing both monetary losses and psychological distress. While
governments, industries, and academia have actively introduced various
countermeasures, scammers also continue to evolve their tactics, making phone
scams a persistent threat. To combat these increasingly sophisticated scams,
detection technologies must also advance. In this work, we propose a framework
for modeling scam calls and introduce an LLM-based real-time detection
approach, which assesses fraudulent intent in conversations, further providing
immediate warnings to users to mitigate harm. Through experiments, we evaluate
the method's performance and analyze key factors influencing its effectiveness.
This analysis enables us to refine the method to improve precision while
exploring the trade-off between recall and timeliness, paving the way for
future directions in this critical area of research.
19 Aug 2025
Multi-modal recommender system focuses on utilizing rich modal information ( i.e., images and textual descriptions) of items to improve recommendation performance. The current methods have achieved remarkable success with the powerful structure modeling capability of graph neural networks. However, these methods are often hindered by sparse data in real-world scenarios. Although contrastive learning and homography ( i.e., homogeneous graphs) are employed to address the data sparsity challenge, existing methods still suffer two main limitations: 1) Simple multi-modal feature contrasts fail to produce effective representations, causing noisy modal-shared features and loss of valuable information in modal-unique features; 2) The lack of exploration of the homograph relations between user interests and item co-occurrence results in incomplete mining of user-item interplay.
To address the above limitations, we propose a novel framework for \textbf{R}\textbf{E}fining multi-mod\textbf{A}l cont\textbf{R}astive learning and ho\textbf{M}ography relations (\textbf{REARM}). Specifically, we complement multi-modal contrastive learning by employing meta-network and orthogonal constraint strategies, which filter out noise in modal-shared features and retain recommendation-relevant information in modal-unique features. To mine homogeneous relationships effectively, we integrate a newly constructed user interest graph and an item co-occurrence graph with the existing user co-occurrence and item semantic graphs for graph learning. The extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of REARM to various state-of-the-art baselines. Our visualization further shows an improvement made by REARM in distinguishing between modal-shared and modal-unique features. Code is available \href{this https URL}{here}.
Urban time series, such as mobility flows, energy consumption, and pollution records, encapsulate complex urban dynamics and structures. However, data collection in each city is impeded by technical challenges such as budget limitations and sensor failures, necessitating effective data imputation techniques that can enhance data quality and reliability. Existing imputation models, categorized into learning-based and analytics-based paradigms, grapple with the trade-off between capacity and generalizability. Collaborative learning to reconstruct data across multiple cities holds the promise of breaking this trade-off. Nevertheless, urban data's inherent irregularity and heterogeneity issues exacerbate challenges of knowledge sharing and collaboration across cities. To address these limitations, we propose a novel collaborative imputation paradigm leveraging meta-learned implicit neural representations (INRs). INRs offer a continuous mapping from domain coordinates to target values, integrating the strengths of both paradigms. By imposing embedding theory, we first employ continuous parameterization to handle irregularity and reconstruct the dynamical system. We then introduce a cross-city collaborative learning scheme through model-agnostic meta learning, incorporating hierarchical modulation and normalization techniques to accommodate multiscale representations and reduce variance in response to heterogeneity. Extensive experiments on a diverse urban dataset from 20 global cities demonstrate our model's superior imputation performance and generalizability, underscoring the effectiveness of collaborative imputation in resource-constrained settings.
10 Mar 2024
This study presents a framework for conducting psychological and linguistic
research through simulated conversations using large language models (LLMs).
The proposed methodology offers significant advantages, particularly for
simulating human interactions involving potential unethical language or
behaviors that would be impermissible in traditional experiments with human
participants. As a demonstration, we employed LLMs to simulate family
conversations across four parenting styles (authoritarian, authoritative,
permissive, and uninvolved). In general, we observed that the characteristics
of the four parenting styles were portrayed in the simulated conversations.
Several strategies could be used to improve the simulation quality, such as
including context awareness, employing a few-shot prompting approach or
fine-tuning models to cater to specific simulation requirements. Overall, this
study introduces a promising methodology for conducting psychological and
linguistic research through simulated conversations, while acknowledging the
current limitations and proposing potential solutions for future refinement and
improvement.
Researchers utilized spin glass theory to analyze the loss landscapes of single-hidden-layer ReLU networks, revealing their complex, rugged topography, the impact of permutation symmetry on solution separation, and a hierarchical clustering of trained solutions reminiscent of Replica Symmetry Breaking. The study empirically demonstrated that flatter loss minima, often found with smaller batch sizes, consistently lead to improved generalization performance.
Timely updating of Internet of Things data is crucial for achieving immersion in vehicular metaverse services. However, challenges such as latency caused by massive data transmissions, privacy risks associated with user data, and computational burdens on metaverse service providers (MSPs) hinder the continuous collection of high-quality data. To address these challenges, we propose an immersion-aware model trading framework that enables efficient and privacy-preserving data provisioning through federated learning (FL). Specifically, we first develop a novel multi-dimensional evaluation metric for the immersion of models (IoM). The metric considers the freshness and accuracy of the local model, and the amount and potential value of raw training data. Building on the IoM, we design an incentive mechanism to encourage metaverse users (MUs) to participate in FL by providing local updates to MSPs under resource constraints. The trading interactions between MSPs and MUs are modeled as an equilibrium problem with equilibrium constraints (EPEC) to analyze and balance their costs and gains, where MSPs as leaders determine rewards, while MUs as followers optimize resource allocation. To ensure privacy and adapt to dynamic network conditions, we develop a distributed dynamic reward algorithm based on deep reinforcement learning, without acquiring any private information from MUs and other MSPs. Experimental results show that the proposed framework outperforms state-of-the-art benchmarks, achieving improvements in IoM of 38.3% and 37.2%, and reductions in training time to reach the target accuracy of 43.5% and 49.8%, on average, for the MNIST and GTSRB datasets, respectively. These findings validate the effectiveness of our approach in incentivizing MUs to contribute high-value local models to MSPs, providing a flexible and adaptive scheme for data provisioning in vehicular metaverse services.
Large imbalance often exists between the foreground points (i.e., objects) and the background points in outdoor LiDAR point clouds. It hinders cutting-edge detectors from focusing on informative areas to produce accurate 3D object detection results. This paper proposes a novel object detection network by semantical point-voxel feature interaction, dubbed PV-RCNN++. Unlike most of existing methods, PV-RCNN++ explores the semantic information to enhance the quality of object detection. First, a semantic segmentation module is proposed to retain more discriminative foreground keypoints. Such a module will guide our PV-RCNN++ to integrate more object-related point-wise and voxel-wise features in the pivotal areas. Then, to make points and voxels interact efficiently, we utilize voxel query based on Manhattan distance to quickly sample voxel-wise features around keypoints. Such the voxel query will reduce the time complexity from O(N) to O(K), compared to the ball query. Further, to avoid being stuck in learning only local features, an attention-based residual PointNet module is designed to expand the receptive field to adaptively aggregate the neighboring voxel-wise features into keypoints. Extensive experiments on the KITTI dataset show that PV-RCNN++ achieves 81.60%, 40.18%, 68.21% 3D mAP on Car, Pedestrian, and Cyclist, achieving comparable or even better performance to the state-of-the-arts.
18 Oct 2024
The cold start problem in recommender systems remains a critical challenge. Current solutions often train hybrid models on auxiliary data for both cold and warm users/items, potentially degrading the experience for the latter. This drawback limits their viability in practical scenarios where the satisfaction of existing warm users/items is paramount. Although graph neural networks (GNNs) excel at warm recommendations by effective collaborative signal modeling, they haven't been effectively leveraged for the cold-start issue within a user-item graph, which is largely due to the lack of initial connections for cold user/item entities. Addressing this requires a GNN adept at cold-start recommendations without sacrificing performance for existing ones. To this end, we introduce Graph Neural Patching for Cold-Start Recommendations (GNP), a customized GNN framework with dual functionalities: GWarmer for modeling collaborative signal on existing warm users/items and Patching Networks for simulating and enhancing GWarmer's performance on cold-start recommendations. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets confirm GNP's superiority in recommending both warm and cold users/items.
With rapid advancements in large language models (LLMs), AI-generated content (AIGC) has emerged as a key driver of technological innovation and economic transformation. Personalizing AIGC services to meet individual user demands is essential but challenging for AIGC service providers (ASPs) due to the subjective and complex demands of mobile users (MUs), as well as the computational and communication resource constraints faced by ASPs. To tackle these challenges, we first develop a novel multi-dimensional quality-of-experience (QoE) metric. This metric comprehensively evaluates AIGC services by integrating accuracy, token count, and timeliness. We focus on a mobile edge computing (MEC)-enabled AIGC network, consisting of multiple ASPs deploying differentiated AIGC models on edge servers and multiple MUs with heterogeneous QoE requirements requesting AIGC services from ASPs. To incentivize ASPs to provide personalized AIGC services under MEC resource constraints, we propose a QoE-driven incentive mechanism. We formulate the problem as an equilibrium problem with equilibrium constraints (EPEC), where MUs as leaders determine rewards, while ASPs as followers optimize resource allocation. To solve this, we develop a dual-perturbation reward optimization algorithm, reducing the implementation complexity of adaptive pricing. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed mechanism achieves a reduction of approximately 64.9% in average computational and communication overhead, while the average service cost for MUs and the resource consumption of ASPs decrease by 66.5% and 76.8%, respectively, compared to state-of-the-art benchmarks.
06 May 2022
Affective brain-computer interfaces based on electroencephalography (EEG) is
an important branch in the field of affective computing. However, individual
differences and noisy labels seriously limit the effectiveness and
generalizability of EEG-based emotion recognition models. In this paper, we
propose a novel transfer learning framework with Prototypical Representation
based Pairwise Learning (PR-PL) to learn discriminative and generalized
prototypical representations for emotion revealing across individuals and
formulate emotion recognition as pairwise learning for alleviating the reliance
on precise label information. Extensive experiments are conducted on two
benchmark databases under four cross-validation evaluation protocols
(cross-subject cross-session, cross-subject within-session, within-subject
cross-session, and within-subject within-session). The experimental results
demonstrate the superiority of the proposed PR-PL against the state-of-the-arts
under all four evaluation protocols, which shows the effectiveness and
generalizability of PR-PL in dealing with the ambiguity of EEG responses in
affective studies. The source code is available at
this https URL
Recent measurements made by the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS) have detected accurate positron flux for energy range 1-1000 GeV. The energy spectrum can be best described by two source terms: the low-energy background diffusion term and an unknown high-energy source term. In this article, we discuss the possibility of the emission of positrons originating from dark matter annihilation in two nearby black hole X-ray binaries A0620-00 and XTE J1118+480. We show that the dark matter density spikes around these two black holes can best produce the observed AMS-02 high-energy positron flux due to dark matter annihilation with rest mass mDM≈8000 GeV via the W+W− annihilation channel. This initiates a new proposal to account for the unknown high-energy source term in the AMS-02 positron spectrum.
Recently, a tight correlation between the dynamical radial acceleration and the baryonic radial acceleration in galaxies - the radial acceleration relation - has been discovered. This has been claimed as an indirect support of the modified gravity theories. However, whether the radial acceleration relation could also be found in galaxy clusters is controversial. In this article, we derive and present an analytic radial acceleration relation for the central region of galaxy clusters. We examine the data of some large galaxy clusters and we find that the resulting radial acceleration relation has a very large scatter. Moreover, although the radial acceleration relation for galaxy clusters shows some agreement with the one discovered in galaxies for a certain range of baryonic radial acceleration, their functional forms are somewhat different from each other. This suggests that the radial acceleration relation may not be a universal relation in general.
Large language models (LLMs) have made remarkable progress in various natural
language processing tasks as a benefit of their capability to comprehend and
reason with factual knowledge. However, a significant amount of factual
knowledge is stored in structured data, which possesses unique characteristics
that differ from the unstructured texts used for pretraining. This difference
can introduce imperceptible inference parameter deviations, posing challenges
for LLMs in effectively utilizing and reasoning with structured data to
accurately infer factual knowledge. To this end, we propose a benchmark named
StructFact, to evaluate the structural reasoning capabilities of LLMs in
inferring factual knowledge. StructFact comprises 8,340 factual questions
encompassing various tasks, domains, timelines, and regions. This benchmark
allows us to investigate the capability of LLMs across five factual tasks
derived from the unique characteristics of structural facts. Extensive
experiments on a set of LLMs with different training strategies reveal the
limitations of current LLMs in inferring factual knowledge from structured
data. We present this benchmark as a compass to navigate the strengths and
weaknesses of LLMs in reasoning with structured data for knowledge-sensitive
tasks, and to encourage advancements in related real-world applications. Please
find our code at https://github.com/EganGu/StructFact.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.