semi-supervised-learning
Semi-supervised learning (SSL) has become a promising direction for medical image segmentation, enabling models to learn from limited labeled data alongside abundant unlabeled samples. However, existing SSL approaches for multi-modal medical imaging often struggle to exploit the complementary information between modalities due to semantic discrepancies and misalignment across MRI sequences. To address this, we propose a novel semi-supervised multi-modal framework that explicitly enhances modality-specific representations and facilitates adaptive cross-modal information fusion. Specifically, we introduce a Modality-specific Enhancing Module (MEM) to strengthen semantic cues unique to each modality via channel-wise attention, and a learnable Complementary Information Fusion (CIF) module to adaptively exchange complementary knowledge between modalities. The overall framework is optimized using a hybrid objective combining supervised segmentation loss and cross-modal consistency regularization on unlabeled data. Extensive experiments on the BraTS 2019 (HGG subset) demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms strong semi-supervised and multi-modal baselines under 1\%, 5\%, and 10\% labeled data settings, achieving significant improvements in both Dice and Sensitivity scores. Ablation studies further confirm the complementary effects of our proposed MEM and CIF in bridging cross-modality discrepancies and improving segmentation robustness under scarce supervision.
Liver fibrosis represents a significant global health burden, necessitating accurate staging for effective clinical management. This report introduces the LiQA (Liver Fibrosis Quantification and Analysis) dataset, established as part of the CARE 2024 challenge. Comprising 440 patients with multi-phase, multi-center MRI scans, the dataset is curated to benchmark algorithms for Liver Segmentation (LiSeg) and Liver Fibrosis Staging (LiFS) under complex real-world conditions, including domain shifts, missing modalities, and spatial misalignment. We further describe the challenge's top-performing methodology, which integrates a semi-supervised learning framework with external data for robust segmentation, and utilizes a multi-view consensus approach with Class Activation Map (CAM)-based regularization for staging. Evaluation of this baseline demonstrates that leveraging multi-source data and anatomical constraints significantly enhances model robustness in clinical settings.
09 Dec 2025
Ultracool dwarfs consist of lowest-mass stars and brown dwarfs. Their interior is fully convective, different from that of the partly-convective Sun-like stars. Magnetic field generation process beneath the surface of ultracool dwarfs is still poorly understood and controversial. To increase samples of active ultracool dwarfs significantly, we have identified 962 ultracool dwarfs in the latest LAMOST data release, DR11. We also simulate the Chinese Space Station Survey Telescope (CSST) low-resolution slitless spectra by degrading the LAMOST spectra. A semi-supervised machine learning approach with an autoencoder model is built to identify ultracool dwarfs with the simulated CSST spectra, which demonstrates the capability of the CSST all-sky slitless spectroscopic survey on the detection of ultracool dwarfs. Magnetic activity of the ultracool dwarfs is investigated by using the Hα line emission as a proxy. The rotational periods of 82 ultracool dwarfs are derived based on the Kepler/K2 light curves. We also derive the activity-rotation relation of the ultracool dwarfs, which is saturated around a Rossby number of 0.12.
The main objective of this study is to propose an optimal transport based semi-supervised approach to learn from scarce labelled image data using deep convolutional networks. The principle lies in implicit graph-based transductive semi-supervised learning where the similarity metric between image samples is the Wasserstein distance. This metric is used in the label propagation mechanism during learning. We apply and demonstrate the effectiveness of the method on a GNSS real life application. More specifically, we address the problem of multi-path interference detection. Experiments are conducted under various signal conditions. The results show that for specific choices of hyperparameters controlling the amount of semi-supervision and the level of sensitivity to the metric, the classification accuracy can be significantly improved over the fully supervised training method.
Despite the notable success of graph convolutional networks (GCNs) in skeleton-based action recognition, their performance often depends on large volumes of labeled data, which are frequently scarce in practical settings. To address this limitation, we propose a novel label-efficient GCN model. Our work makes two primary contributions. First, we develop a novel acquisition function that employs an adversarial strategy to identify a compact set of informative exemplars for labeling. This selection process balances representativeness, diversity, and uncertainty. Second, we introduce bidirectional and stable GCN architectures. These enhanced networks facilitate a more effective mapping between the ambient and latent data spaces, enabling a better understanding of the learned exemplar distribution. Extensive evaluations on two challenging skeleton-based action recognition benchmarks reveal significant improvements achieved by our label-efficient GCNs compared to prior work.
Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) and Intraoral Scanning (IOS) are essential for digital dentistry, but annotated data scarcity limits automated solutions for pulp canal segmentation and cross-modal registration. To benchmark semi-supervised learning (SSL) in this domain, we organized the STSR 2025 Challenge at MICCAI 2025, featuring two tasks: (1) semi-supervised segmentation of teeth and pulp canals in CBCT, and (2) semi-supervised rigid registration of CBCT and IOS. We provided 60 labeled and 640 unlabeled IOS samples, plus 30 labeled and 250 unlabeled CBCT scans with varying resolutions and fields of view. The challenge attracted strong community participation, with top teams submitting open-source deep learning-based SSL solutions. For segmentation, leading methods used nnU-Net and Mamba-like State Space Models with pseudo-labeling and consistency regularization, achieving a Dice score of 0.967 and Instance Affinity of 0.738 on the hidden test set. For registration, effective approaches combined PointNetLK with differentiable SVD and geometric augmentation to handle modality gaps; hybrid neural-classical refinement enabled accurate alignment despite limited labels. All data and code are publicly available at this https URL to ensure reproducibility.
AlignSAE enhances Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) for Large Language Model (LLM) interpretability by introducing a "pre-train, then post-train" curriculum, explicitly aligning latent features with human-defined concepts. This method creates a verifiable and controllable interface, achieving perfect one-to-one concept binding and enabling robust causal steering of factual knowledge within a frozen GPT-2 model.
AnyTalker presents a framework for scalable multi-person talking video generation, utilizing a two-stage training strategy that leverages approximately 1000 hours of single-person data and only 12 hours of authentic multi-person interaction. This approach achieves state-of-the-art interactivity and visual quality, demonstrating generalization to an arbitrary number of identities and diverse input types while significantly reducing data collection costs.
 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Shanghai Jiao Tong UniversityXidian UniversityHarbin Institute of TechnologyHangzhou Dianzi University
Shanghai Jiao Tong UniversityXidian UniversityHarbin Institute of TechnologyHangzhou Dianzi University The University of Hong KongShenzhen University
The University of Hong KongShenzhen University Shandong University
Shandong University Queen Mary University of LondonUniversity of LeicesterHangzhou Dental Hospital GroupHangzhou Geriatric Stomatology HospitalYunnan Provincial Stomatology HospitalShanghai MediWorks Precision Instruments Co., Ltd
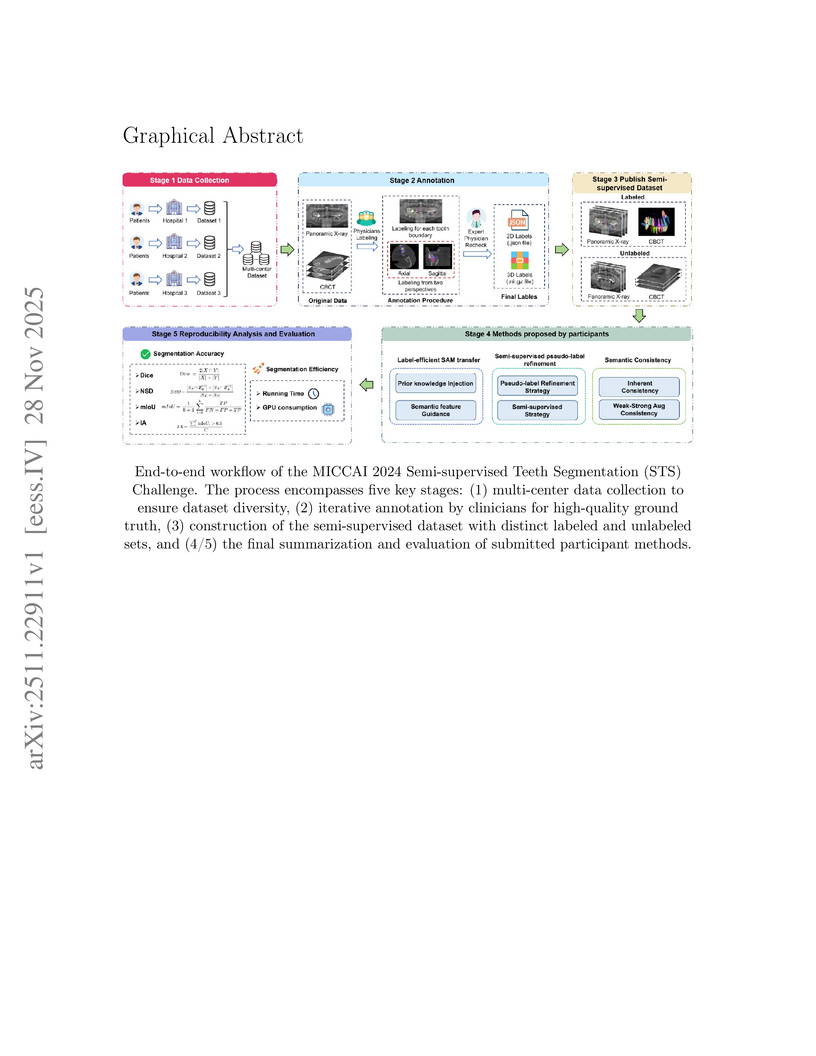
Queen Mary University of LondonUniversity of LeicesterHangzhou Dental Hospital GroupHangzhou Geriatric Stomatology HospitalYunnan Provincial Stomatology HospitalShanghai MediWorks Precision Instruments Co., LtdOrthopantomogram (OPGs) and Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) are vital for dentistry, but creating large datasets for automated tooth segmentation is hindered by the labor-intensive process of manual instance-level annotation. This research aimed to benchmark and advance semi-supervised learning (SSL) as a solution for this data scarcity problem. We organized the 2nd Semi-supervised Teeth Segmentation (STS 2024) Challenge at MICCAI 2024. We provided a large-scale dataset comprising over 90,000 2D images and 3D axial slices, which includes 2,380 OPG images and 330 CBCT scans, all featuring detailed instance-level FDI annotations on part of the data. The challenge attracted 114 (OPG) and 106 (CBCT) registered teams. To ensure algorithmic excellence and full transparency, we rigorously evaluated the valid, open-source submissions from the top 10 (OPG) and top 5 (CBCT) teams, respectively. All successful submissions were deep learning-based SSL methods. The winning semi-supervised models demonstrated impressive performance gains over a fully-supervised nnU-Net baseline trained only on the labeled data. For the 2D OPG track, the top method improved the Instance Affinity (IA) score by over 44 percentage points. For the 3D CBCT track, the winning approach boosted the Instance Dice score by 61 percentage points. This challenge confirms the substantial benefit of SSL for complex, instance-level medical image segmentation tasks where labeled data is scarce. The most effective approaches consistently leveraged hybrid semi-supervised frameworks that combined knowledge from foundational models like SAM with multi-stage, coarse-to-fine refinement pipelines. Both the challenge dataset and the participants' submitted code have been made publicly available on GitHub (this https URL), ensuring transparency and reproducibility.
In open-world scenarios, Generalized Category Discovery (GCD) requires identifying both known and novel categories within unlabeled data. However, existing methods often suffer from prototype confusion caused by shortcut learning, which undermines generalization and leads to forgetting of known classes. We propose ClearGCD, a framework designed to mitigate reliance on non-semantic cues through two complementary mechanisms. First, Semantic View Alignment (SVA) generates strong augmentations via cross-class patch replacement and enforces semantic consistency using weak augmentations. Second, Shortcut Suppression Regularization (SSR) maintains an adaptive prototype bank that aligns known classes while encouraging separation of potential novel ones. ClearGCD can be seamlessly integrated into parametric GCD approaches and consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods across multiple benchmarks.
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have demonstrated exceptional efficacy in relational learning tasks, including node classification and link prediction. However, their application raises significant fairness concerns, as GNNs can perpetuate and even amplify societal biases against protected groups defined by sensitive attributes such as race or gender. These biases are often inherent in the node features, structural topology, and message-passing mechanisms of the graph itself. A critical limitation of existing fairness-aware GNN methods is their reliance on the strong assumption that sensitive attributes are fully available for all nodes during training--a condition that poses a practical impediment due to privacy concerns and data collection constraints. To address this gap, we propose a novel, model-agnostic fairness regularization framework designed for the realistic scenario where sensitive attributes are only partially available. Our approach formalizes a fairness-aware objective function that integrates both equal opportunity and statistical parity as differentiable regularization terms. Through a comprehensive empirical evaluation across five real-world benchmark datasets, we demonstrate that the proposed method significantly mitigates bias across key fairness metrics while maintaining competitive node classification performance. Results show that our framework consistently outperforms baseline models in achieving a favorable fairness-accuracy trade-off, with minimal degradation in predictive accuracy. The datasets and source code will be publicly released at this https URL.
Dataset distillation creates a small distilled set that enables efficient training by capturing key information from the full dataset. While existing dataset distillation methods perform well on balanced datasets, they struggle under long-tailed distributions, where imbalanced class frequencies induce biased model representations and corrupt statistical estimates such as Batch Normalization (BN) statistics. In this paper, we rethink long-tailed dataset distillation by revisiting the limitations of trajectory-based methods, and instead adopt the statistical alignment perspective to jointly mitigate model bias and restore fair supervision. To this end, we introduce three dedicated components that enable unbiased recovery of distilled images and soft relabeling: (1) enhancing expert models (an observer model for recovery and a teacher model for relabeling) to enable reliable statistics estimation and soft-label generation; (2) recalibrating BN statistics via a full forward pass with dynamically adjusted momentum to reduce representation skew; (3) initializing synthetic images by incrementally selecting high-confidence and diverse augmentations via a multi-round mechanism that promotes coverage and diversity. Extensive experiments on four long-tailed benchmarks show consistent improvements over state-of-the-art methods across varying degrees of class this http URL, our approach improves top-1 accuracy by 15.6% on CIFAR-100-LT and 11.8% on Tiny-ImageNet-LT under IPC=10 and IF=10.
Self-supervised learning (SSL) offers a promising approach for learning electroencephalography (EEG) representations from unlabeled data, reducing the need for expensive annotations for clinical applications like sleep staging and seizure detection. While current EEG SSL methods predominantly use masked reconstruction strategies like masked autoencoders (MAE) that capture local temporal patterns, position prediction pretraining remains underexplored despite its potential to learn long-range dependencies in neural signals. We introduce PAirwise Relative Shift or PARS pretraining, a novel pretext task that predicts relative temporal shifts between randomly sampled EEG window pairs. Unlike reconstruction-based methods that focus on local pattern recovery, PARS encourages encoders to capture relative temporal composition and long-range dependencies inherent in neural signals. Through comprehensive evaluation on various EEG decoding tasks, we demonstrate that PARS-pretrained transformers consistently outperform existing pretraining strategies in label-efficient and transfer learning settings, establishing a new paradigm for self-supervised EEG representation learning.
Skeleton-based human action recognition aims to classify human skeletal sequences, which are spatiotemporal representations of actions, into predefined categories. To reduce the reliance on costly annotations of skeletal sequences while maintaining competitive recognition accuracy, the task of 3D Action Recognition with Limited Training Samples, also known as semi-supervised 3D Action Recognition, has been proposed. In addition, active learning, which aims to proactively select the most informative unlabeled samples for annotation, has been explored in semi-supervised 3D Action Recognition for training sample selection. Specifically, researchers adopt an encoder-decoder framework to embed skeleton sequences into a latent space, where clustering information, combined with a margin-based selection strategy using a multi-head mechanism, is utilized to identify the most informative sequences in the unlabeled set for annotation. However, the most representative skeleton sequences may not necessarily be the most informative for the action recognizer, as the model may have already acquired similar knowledge from previously seen skeleton samples. To solve it, we reformulate Semi-supervised 3D action recognition via active learning from a novel perspective by casting it as a Markov Decision Process (MDP). Built upon the MDP framework and its training paradigm, we train an informative sample selection model to intelligently guide the selection of skeleton sequences for annotation. To enhance the representational capacity of the factors in the state-action pairs within our method, we project them from Euclidean space to hyperbolic space. Furthermore, we introduce a meta tuning strategy to accelerate the deployment of our method in real-world scenarios. Extensive experiments on three 3D action recognition benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
Researchers at Guangdong University of Technology developed ADGNN, an active diffusion Graph Neural Network that integrates three external information sources to enable infinite diffusion on graphs. The model achieves state-of-the-art node classification accuracy on both homophilic and heterophilic graphs, including up to 92.2% on the Wisconsin dataset, while effectively preventing over-smoothing.
We introduce Time-Conditioned Contraction Matching (TCCM), a novel method for semi-supervised anomaly detection in tabular data. TCCM is inspired by flow matching, a recent generative modeling framework that learns velocity fields between probability distributions and has shown strong performance compared to diffusion models and generative adversarial networks. Instead of directly applying flow matching as originally formulated, TCCM builds on its core idea -- learning velocity fields between distributions -- but simplifies the framework by predicting a time-conditioned contraction vector toward a fixed target (the origin) at each sampled time step. This design offers three key advantages: (1) a lightweight and scalable training objective that removes the need for solving ordinary differential equations during training and inference; (2) an efficient scoring strategy called one time-step deviation, which quantifies deviation from expected contraction behavior in a single forward pass, addressing the inference bottleneck of existing continuous-time models such as DTE (a diffusion-based model with leading anomaly detection accuracy but heavy inference cost); and (3) explainability and provable robustness, as the learned velocity field operates directly in input space, making the anomaly score inherently feature-wise attributable; moreover, the score function is Lipschitz-continuous with respect to the input, providing theoretical guarantees under small perturbations. Extensive experiments on the ADBench benchmark show that TCCM strikes a favorable balance between detection accuracy and inference cost, outperforming state-of-the-art methods -- especially on high-dimensional and large-scale datasets. The source code is available at our GitHub repository.
Modern machine learning solutions require extensive data collection where labeling remains costly. To reduce this burden, open set active learning approaches aim to select informative samples from a large pool of unlabeled data that includes irrelevant or unknown classes. In this context, we propose Sharpness Aware Minimization for Open Set Active Learning (SAMOSA) as an effective querying algorithm. Building on theoretical findings concerning the impact of data typicality on the generalization properties of traditional stochastic gradient descent (SGD) and sharpness-aware minimization (SAM), SAMOSA actively queries samples based on their typicality. SAMOSA effectively identifies atypical samples that belong to regions of the embedding manifold close to the model decision boundaries. Therefore, SAMOSA prioritizes the samples that are (i) highly informative for the targeted classes, and (ii) useful for distinguishing between targeted and unwanted classes. Extensive experiments show that SAMOSA achieves up to 3% accuracy improvement over the state of the art across several datasets, while not introducing computational overhead. The source code of our experiments is available at: this https URL
The FRANCK framework enables Source-Free Object Detection (SFOD) for Detection Transformer (DETR) models by introducing a query-centric adaptation approach, achieving state-of-the-art performance across various domain shift scenarios. It integrates novel modules for sample reweighting, contrastive learning, and feature distillation to enhance detection accuracy when source data is unavailable.
LLM-powered agents are both a promising new technology and a source of complexity, where choices about models, tools, and prompting can affect their usefulness. While numerous benchmarks measure agent accuracy across domains, they mostly assume full automation, failing to represent the collaborative nature of real-world use cases. In this paper, we make two major steps towards the rigorous assessment of human-agent interactions. First, we propose PULSE, a framework for more efficient human-centric evaluation of agent designs, which comprises collecting user feedback, training an ML model to predict user satisfaction, and computing results by combining human satisfaction ratings with model-generated pseudo-labels. Second, we deploy the framework on a large-scale web platform built around the open-source software agent OpenHands, collecting in-the-wild usage data across over 15k users. We conduct case studies around how three agent design decisions -- choice of LLM backbone, planning strategy, and memory mechanisms -- impact developer satisfaction rates, yielding practical insights for software agent design. We also show how our framework can lead to more robust conclusions about agent design, reducing confidence intervals by 40% compared to a standard A/B test. Finally, we find substantial discrepancies between in-the-wild results and benchmark performance (e.g., the anti-correlation between results comparing claude-sonnet-4 and gpt-5), underscoring the limitations of benchmark-driven evaluation. Our findings provide guidance for evaluations of LLM agents with humans and identify opportunities for better agent designs.
Active Learning (AL) promises to reduce annotation cost by prioritizing informative samples, yet its reliability is undermined when labels are noisy or when the data distribution shifts. In practice, annotators make mistakes, rare categories are ambiguous, and conventional AL heuristics (uncertainty, diversity) often amplify such errors by repeatedly selecting mislabeled or redundant samples. We propose Reliable Active Learning via Neural Collapse Geometry (NCAL-R), a framework that leverages the emergent geometric regularities of deep networks to counteract unreliable supervision. Our method introduces two complementary signals: (i) a Class-Mean Alignment Perturbation score, which quantifies how candidate samples structurally stabilize or distort inter-class geometry, and (ii) a Feature Fluctuation score, which captures temporal instability of representations across training checkpoints. By combining these signals, NCAL-R prioritizes samples that both preserve class separation and highlight ambiguous regions, mitigating the effect of noisy or redundant labels. Experiments on ImageNet-100 and CIFAR100 show that NCAL-R consistently outperforms standard AL baselines, achieving higher accuracy with fewer labels, improved robustness under synthetic label noise, and stronger generalization to out-of-distribution data. These results suggest that incorporating geometric reliability criteria into acquisition decisions can make Active Learning less brittle to annotation errors and distribution shifts, a key step toward trustworthy deployment in real-world labeling pipelines. Our code is available at this https URL.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.