Asia University
Machine learning (ML) has transformed numerous fields, but understanding its foundational research is crucial for its continued progress. This paper presents an overview of the significant classical ML algorithms and examines the state-of-the-art publications spanning twelve decades through an extensive bibliometric analysis study. We analyzed a dataset of highly cited papers from prominent ML conferences and journals, employing citation and keyword analyses to uncover critical insights. The study further identifies the most influential papers and authors, reveals the evolving collaborative networks within the ML community, and pinpoints prevailing research themes and emerging focus areas. Additionally, we examine the geographic distribution of highly cited publications, highlighting the leading countries in ML research. This study provides a comprehensive overview of the evolution of traditional learning algorithms and their impacts. It discusses challenges and opportunities for future development, focusing on the Global South. The findings from this paper offer valuable insights for both ML experts and the broader research community, enhancing understanding of the field's trajectory and its significant influence on recent advances in learning algorithms.
In medical imaging, accurate diagnosis heavily relies on effective image enhancement techniques, particularly for X-ray images. Existing methods often suffer from various challenges such as sacrificing global image characteristics over local image characteristics or vice versa. In this paper, we present a novel approach, called G-CLAHE (Global-Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization), which perfectly suits medical imaging with a focus on X-rays. This method adapts from Global Histogram Equalization (GHE) and Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE) to take both advantages and avoid weakness to preserve local and global characteristics. Experimental results show that it can significantly improve current state-of-the-art algorithms to effectively address their limitations and enhance the contrast and quality of X-ray images for diagnostic accuracy.
 University of CambridgeUniversidad de GranadaUniversity of TurkuDeakin UniversityK. N. Toosi University of TechnologyIslamic Azad University Science and Research BranchAsia UniversityNgee Ann PolytechnicSUSS UniversityIslamic Azad University Mashhad BranchEffat UniversityIslamic Azad University, Gonabad Branch
University of CambridgeUniversidad de GranadaUniversity of TurkuDeakin UniversityK. N. Toosi University of TechnologyIslamic Azad University Science and Research BranchAsia UniversityNgee Ann PolytechnicSUSS UniversityIslamic Azad University Mashhad BranchEffat UniversityIslamic Azad University, Gonabad BranchEpileptic seizures are one of the most crucial neurological disorders, and their early diagnosis will help the clinicians to provide accurate treatment for the patients. The electroencephalogram (EEG) signals are widely used for epileptic seizures detection, which provides specialists with substantial information about the functioning of the brain. In this paper, a novel diagnostic procedure using fuzzy theory and deep learning techniques is introduced. The proposed method is evaluated on the Bonn University dataset with six classification combinations and also on the Freiburg dataset. The tunable-Q wavelet transform (TQWT) is employed to decompose the EEG signals into different sub-bands. In the feature extraction step, 13 different fuzzy entropies are calculated from different sub-bands of TQWT, and their computational complexities are calculated to help researchers choose the best set for various tasks. In the following, an autoencoder (AE) with six layers is employed for dimensionality reduction. Finally, the standard adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS), and also its variants with grasshopper optimization algorithm (ANFIS-GOA), particle swarm optimization (ANFIS-PSO), and breeding swarm optimization (ANFIS-BS) methods are used for classification. Using our proposed method, ANFIS-BS method has obtained an accuracy of 99.74% in classifying into two classes and an accuracy of 99.46% in ternary classification on the Bonn dataset and 99.28% on the Freiburg dataset, reaching state-of-the-art performances on both of them.
08 Aug 2025
The Higgs mode is a key component in the spontaneous breaking of a continuous symmetry along with the Nambu-Goldstone mode, and has been studied extensively for homogeneous systems. We consider it for inhomogeneous systems, using the superfluid of harmonically trapped ultracold Fermi atomic gas. The Fermionic field operators are expanded in a complete set of wave functions corresponding to inhomogeneous situation. Within the Hatree-Fock approximation, we derive integral equations from the Bogoliubov-de Gennes equations, which lead to the frequencies of the collective modes, including the Higgs and Nambu-Goldstone modes. The results show that the frequency of the Higgs mode equals twice the absolute value of the order parameter at the center of trap. This feature is robust against variations in the interaction strength, trap potential, and temperature. These results are consistent with previous theoretical and experimental studies.
 National University of SingaporeDeakin UniversityUniversity of Texas at DallasIslamic Azad UniversityCairo UniversityDibrugarh UniversityUniversity of California San FranciscoFerdowsi University of MashhadK. N. Toosi University of TechnologySingapore University of Social SciencesAsia UniversityNgee Ann Polytechnic
National University of SingaporeDeakin UniversityUniversity of Texas at DallasIslamic Azad UniversityCairo UniversityDibrugarh UniversityUniversity of California San FranciscoFerdowsi University of MashhadK. N. Toosi University of TechnologySingapore University of Social SciencesAsia UniversityNgee Ann PolytechnicUnderstanding data and reaching valid conclusions are of paramount importance in the present era of big data. Machine learning and probability theory methods have widespread application for this purpose in different fields. One critically important yet less explored aspect is how data and model uncertainties are captured and analyzed. Proper quantification of uncertainty provides valuable information for optimal decision making. This paper reviewed related studies conducted in the last 30 years (from 1991 to 2020) in handling uncertainties in medical data using probability theory and machine learning techniques. Medical data is more prone to uncertainty due to the presence of noise in the data. So, it is very important to have clean medical data without any noise to get accurate diagnosis. The sources of noise in the medical data need to be known to address this issue. Based on the medical data obtained by the physician, diagnosis of disease, and treatment plan are prescribed. Hence, the uncertainty is growing in healthcare and there is limited knowledge to address these problems. We have little knowledge about the optimal treatment methods as there are many sources of uncertainty in medical science. Our findings indicate that there are few challenges to be addressed in handling the uncertainty in medical raw data and new models. In this work, we have summarized various methods employed to overcome this problem. Nowadays, application of novel deep learning techniques to deal such uncertainties have significantly increased.
Interpretation of electrocardiography (ECG) signals is required for diagnosing cardiac arrhythmia. Recently, machine learning techniques have been applied for automated computer-aided diagnosis. Machine learning tasks can be divided into regression and classification. Regression can be used for noise and artifacts removal as well as resolve issues of missing data from low sampling frequency. Classification task concerns the prediction of output diagnostic classes according to expert-labeled input classes. In this work, we propose a deep neural network model capable of solving regression and classification tasks. Moreover, we combined the two approaches, using unlabeled and labeled data, to train the model. We tested the model on the MIT-BIH Arrhythmia database. Our method showed high effectiveness in detecting cardiac arrhythmia based on modified Lead II ECG records, as well as achieved high quality of ECG signal approximation. For the former, our method attained overall accuracy of 87:33% and balanced accuracy of 80:54%, on par with reference approaches. For the latter, application of self-supervised learning allowed for training without the need for expert labels. The regression model yielded satisfactory performance with fairly accurate prediction of QRS complexes. Transferring knowledge from regression to the classification task, our method attained higher overall accuracy of 87:78%.
 University of CambridgeUniversidad de GranadaUniversity of TurkuDeakin UniversityK. N. Toosi University of TechnologyIslamic Azad University Science and Research BranchAsia UniversityNgee Ann PolytechnicSUSS UniversityIslamic Azad University Mashhad BranchEffat UniversityIslamic Azad University, Gonabad Branch
University of CambridgeUniversidad de GranadaUniversity of TurkuDeakin UniversityK. N. Toosi University of TechnologyIslamic Azad University Science and Research BranchAsia UniversityNgee Ann PolytechnicSUSS UniversityIslamic Azad University Mashhad BranchEffat UniversityIslamic Azad University, Gonabad BranchEpileptic seizures are one of the most crucial neurological disorders, and their early diagnosis will help the clinicians to provide accurate treatment for the patients. The electroencephalogram (EEG) signals are widely used for epileptic seizures detection, which provides specialists with substantial information about the functioning of the brain. In this paper, a novel diagnostic procedure using fuzzy theory and deep learning techniques is introduced. The proposed method is evaluated on the Bonn University dataset with six classification combinations and also on the Freiburg dataset. The tunable-Q wavelet transform (TQWT) is employed to decompose the EEG signals into different sub-bands. In the feature extraction step, 13 different fuzzy entropies are calculated from different sub-bands of TQWT, and their computational complexities are calculated to help researchers choose the best set for various tasks. In the following, an autoencoder (AE) with six layers is employed for dimensionality reduction. Finally, the standard adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS), and also its variants with grasshopper optimization algorithm (ANFIS-GOA), particle swarm optimization (ANFIS-PSO), and breeding swarm optimization (ANFIS-BS) methods are used for classification. Using our proposed method, ANFIS-BS method has obtained an accuracy of 99.74% in classifying into two classes and an accuracy of 99.46% in ternary classification on the Bonn dataset and 99.28% on the Freiburg dataset, reaching state-of-the-art performances on both of them.
Machine learning (ML) has emerged as a prominent field of research in
computer science and other related fields, thereby driving advancements in
other domains of interest. As the field continues to evolve, it is crucial to
understand the landscape of highly cited publications to identify key trends,
influential authors, and significant contributions made thus far. In this
paper, we present a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of highly cited ML
publications. We collected a dataset consisting of the top-cited papers from
reputable ML conferences and journals, covering a period of several years from
1959 to 2022. We employed various bibliometric techniques to analyze the data,
including citation analysis, co-authorship analysis, keyword analysis, and
publication trends. Our findings reveal the most influential papers, highly
cited authors, and collaborative networks within the machine learning
community. We identify popular research themes and uncover emerging topics that
have recently gained significant attention. Furthermore, we examine the
geographical distribution of highly cited publications, highlighting the
dominance of certain countries in ML research. By shedding light on the
landscape of highly cited ML publications, our study provides valuable insights
for researchers, policymakers, and practitioners seeking to understand the key
developments and trends in this rapidly evolving field.
A comprehensive pharmaceutical recommendation system was designed based on the patients and drugs features extracted from this http URL and this http URL. First, data from these databases were combined, and a dataset of patients and drug information was built. Secondly, the patients and drugs were clustered, and then the recommendation was performed using different ratings provided by patients, and importantly by the knowledge obtained from patients and drug specifications, and considering drug interactions. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first group to consider patients conditions and history in the proposed approach for selecting a specific medicine appropriate for that particular user. Our approach applies artificial intelligence (AI) models for the implementation. Sentiment analysis using natural language processing approaches is employed in pre-processing along with neural network-based methods and recommender system algorithms for modeling the system. In our work, patients conditions and drugs features are used for making two models based on matrix factorization. Then we used drug interaction to filter drugs with severe or mild interactions with other drugs. We developed a deep learning model for recommending drugs by using data from 2304 patients as a training set, and then we used data from 660 patients as our validation set. After that, we used knowledge from critical information about drugs and combined the outcome of the model into a knowledge-based system with the rules obtained from constraints on taking medicine.
We show that the five α cluster states recently observed in 20Ne,
slightly above the five α threshold energy, are Bose-Einstein
condensates of five α clusters. The states are described well using a
superfluid cluster model, where the order parameter is defined. We suggest that
the the five α states are fragmented. Theory predicts the emergence of a
five α rotational roton band characterized by a large moment of inertia.
This band is formed through roton excitations of the five α BEC vacuum
and possesses dual properties of superfluidity and crystallinity, a property of
supersolidity. The persistent existence of such a roton bandis discussed and
confirmed for the four α condensate above the four α threshold in
16O and the three α condensate above the three α threshold
in 12C.
29 Apr 2023
University of Technology SydneyBangladesh University of Engineering and TechnologyUniversity of Southern Queensland University of SydneyKumamoto UniversityUniversity of New EnglandSRM Institute of Science and TechnologyTaylor’s UniversityAsia UniversityKookmin UniversitySUSS UniversityAustralian International Institute of Higher EducationCogninet Australia
University of SydneyKumamoto UniversityUniversity of New EnglandSRM Institute of Science and TechnologyTaylor’s UniversityAsia UniversityKookmin UniversitySUSS UniversityAustralian International Institute of Higher EducationCogninet Australia
 University of SydneyKumamoto UniversityUniversity of New EnglandSRM Institute of Science and TechnologyTaylor’s UniversityAsia UniversityKookmin UniversitySUSS UniversityAustralian International Institute of Higher EducationCogninet Australia
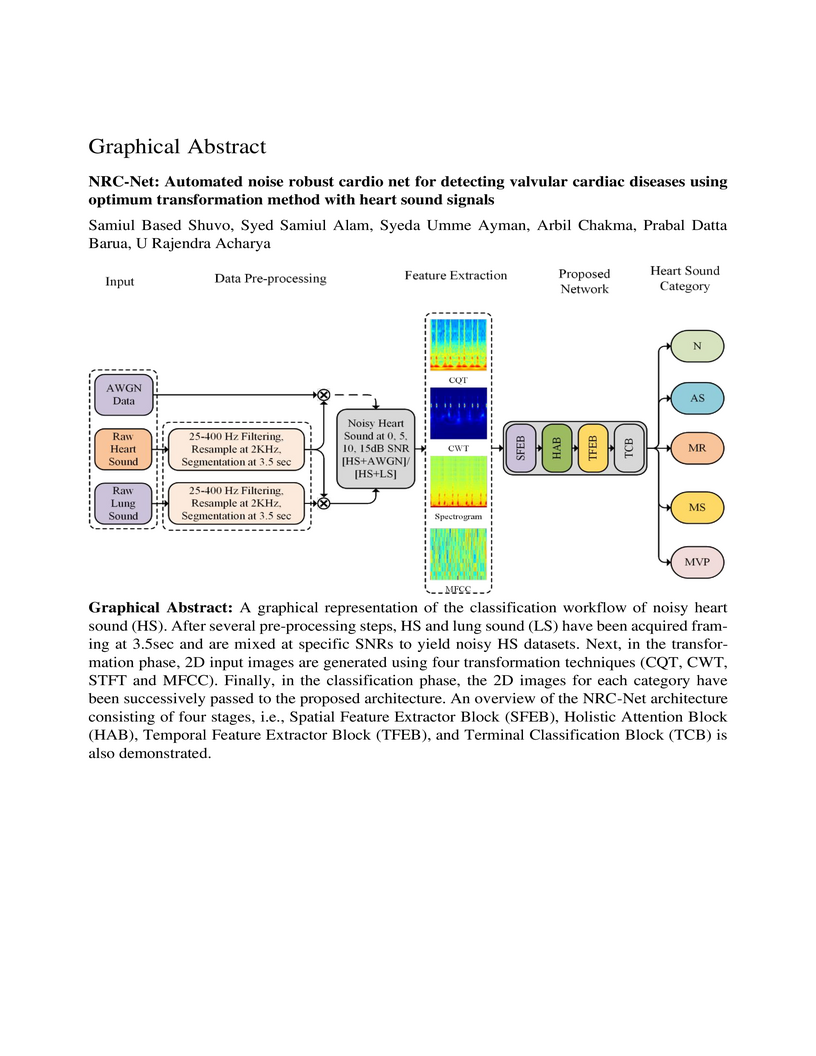
University of SydneyKumamoto UniversityUniversity of New EnglandSRM Institute of Science and TechnologyTaylor’s UniversityAsia UniversityKookmin UniversitySUSS UniversityAustralian International Institute of Higher EducationCogninet AustraliaCardiovascular diseases (CVDs) can be effectively treated when detected
early, reducing mortality rates significantly. Traditionally, phonocardiogram
(PCG) signals have been utilized for detecting cardiovascular disease due to
their cost-effectiveness and simplicity. Nevertheless, various environmental
and physiological noises frequently affect the PCG signals, compromising their
essential distinctive characteristics. The prevalence of this issue in
overcrowded and resource-constrained hospitals can compromise the accuracy of
medical diagnoses. Therefore, this study aims to discover the optimal
transformation method for detecting CVDs using noisy heart sound signals and
propose a noise robust network to improve the CVDs classification
performance.For the identification of the optimal transformation method for
noisy heart sound data mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCCs), short-time
Fourier transform (STFT), constant-Q nonstationary Gabor transform (CQT) and
continuous wavelet transform (CWT) has been used with VGG16. Furthermore, we
propose a novel convolutional recurrent neural network (CRNN) architecture
called noise robust cardio net (NRC-Net), which is a lightweight model to
classify mitral regurgitation, aortic stenosis, mitral stenosis, mitral valve
prolapse, and normal heart sounds using PCG signals contaminated with
respiratory and random noises. An attention block is included to extract
important temporal and spatial features from the noisy corrupted heart
sound.The results of this study indicate that,CWT is the optimal transformation
method for noisy heart sound signals. When evaluated on the GitHub heart sound
dataset, CWT demonstrates an accuracy of 95.69% for VGG16, which is 1.95%
better than the second-best CQT transformation technique. Moreover, our
proposed NRC-Net with CWT obtained an accuracy of 97.4%, which is 1.71% higher
than the VGG16.
09 Aug 2025
The rigged Hilbert space, a triplet extension of the Hilbert space, provides a mathematically rigorous foundation for quantum mechanics by extending the Hilbert space to accommodate generalized eigenstates. In this paper, we construct a triplet structure for the thermal space arising in Thermo Field Dynamics with the aid of the tensor product formulation of rigged Hilbert spaces, a formalism that reformulates thermal averages as pure-state expectation values in a doubled Hilbert space. We then induce the rigged Liouville space for Liouville space of density operators from the triplet structure for Thermo Field Dynamics; the rigged Liouville space corresponds isomorphically one-to-one with that of Thermo Field Dynamics. This correspondence offers a unified topological foundation for quantum statistical mechanics at finite temperature and establishes a framework for future generalizations to open and non-equilibrium quantum systems.
We formalise the notion of an \emph{anonymous public announcement} in the
tradition of public announcement logic. Such announcements can be seen as
in-between a public announcement from ``the outside" (an announcement of
ϕ) and a public announcement by one of the agents (an announcement of
Kaϕ): we get more information than just ϕ, but not (necessarily)
about exactly who made it. Even if such an announcement is prima facie
anonymous, depending on the background knowledge of the agents it might reveal
the identity of the announcer: if I post something on a message board, the
information might reveal who I am even if I don't sign my name. Furthermore,
like in the Russian Cards puzzle, if we assume that the announcer's intention
was to stay anonymous, that in fact might reveal more information. In this
paper we first look at the case when no assumption about intentions are made,
in which case the logic with an anonymous public announcement operator is
reducible to epistemic logic. We then look at the case when we assume common
knowledge of the intention to stay anonymous, which is both more complex and
more interesting: in several ways it boils down to the notion of a ``safe"
announcement (again, similarly to Russian Cards). Main results include formal
expressivity results and axiomatic completeness for key logical languages.
Accurate diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) followed by effective rehabilitation is essential for the management of this disorder. Artificial intelligence (AI) techniques can aid physicians to apply automatic diagnosis and rehabilitation procedures. AI techniques comprise traditional machine learning (ML) approaches and deep learning (DL) techniques. Conventional ML methods employ various feature extraction and classification techniques, but in DL, the process of feature extraction and classification is accomplished intelligently and integrally. DL methods for diagnosis of ASD have been focused on neuroimaging-based approaches. Neuroimaging techniques are non-invasive disease markers potentially useful for ASD diagnosis. Structural and functional neuroimaging techniques provide physicians substantial information about the structure (anatomy and structural connectivity) and function (activity and functional connectivity) of the brain. Due to the intricate structure and function of the brain, proposing optimum procedures for ASD diagnosis with neuroimaging data without exploiting powerful AI techniques like DL may be challenging. In this paper, studies conducted with the aid of DL networks to distinguish ASD are investigated. Rehabilitation tools provided for supporting ASD patients utilizing DL networks are also assessed. Finally, we will present important challenges in the automated detection and rehabilitation of ASD and propose some future works.
Intelligence Everywhere is predicated on the seamless integration of IoT networks transporting a vast amount of data streams through many computing resources across an edge-to-cloud continuum, relying on the orchestration of distributed machine learning models. The result is an interconnected and collective intelligent ecosystem where devices, systems, services, and users work together to support IoT applications. This paper discusses the state-of-the-art research and the principles of the Intelligence Everywhere framework for enhancing IoT applications in vertical sectors such as Digital Health, Infrastructure, and Transportation/Mobility in the context of intelligent society (Society 5.0). It also introduces a novel perspective for the development of horizontal IoT applications, capable of running across various IoT networks while fostering collective intelligence across diverse sectors. Finally, this paper provides comprehensive insights into the challenges and opportunities for harnessing collective knowledge from real-time insights, leading to optimised processes and better overall collaboration across different IoT sectors.
 National University of SingaporeDeakin UniversityIslamic Azad UniversitySemnan UniversityDibrugarh UniversityMashhad University of Medical SciencesFerdowsi University of MashhadK. N. Toosi University of TechnologyIran University of Medical SciencesSingapore University of Social SciencesAsia UniversityNgee Ann PolytechnicRajaie Cardiovascular Medical and Research Center
National University of SingaporeDeakin UniversityIslamic Azad UniversitySemnan UniversityDibrugarh UniversityMashhad University of Medical SciencesFerdowsi University of MashhadK. N. Toosi University of TechnologyIran University of Medical SciencesSingapore University of Social SciencesAsia UniversityNgee Ann PolytechnicRajaie Cardiovascular Medical and Research CenterCoronavirus, or COVID-19, is a hazardous disease that has endangered the health of many people around the world by directly affecting the lungs. COVID-19 is a medium-sized, coated virus with a single-stranded RNA, and also has one of the largest RNA genomes and is approximately 120 nm. The X-Ray and computed tomography (CT) imaging modalities are widely used to obtain a fast and accurate medical diagnosis. Identifying COVID-19 from these medical images is extremely challenging as it is time-consuming and prone to human errors. Hence, artificial intelligence (AI) methodologies can be used to obtain consistent high performance. Among the AI methods, deep learning (DL) networks have gained popularity recently compared to conventional machine learning (ML). Unlike ML, all stages of feature extraction, feature selection, and classification are accomplished automatically in DL models. In this paper, a complete survey of studies on the application of DL techniques for COVID-19 diagnostic and segmentation of lungs is discussed, concentrating on works that used X-Ray and CT images. Additionally, a review of papers on the forecasting of coronavirus prevalence in different parts of the world with DL is presented. Lastly, the challenges faced in the detection of COVID-19 using DL techniques and directions for future research are discussed.
Traditional ground wireless communication networks cannot provide high-quality services for artificial intelligence (AI) applications such as intelligent transportation systems (ITS) due to deployment, coverage and capacity issues. The space-air-ground integrated network (SAGIN) has become a research focus in the industry. Compared with traditional wireless communication networks, SAGIN is more flexible and reliable, and it has wider coverage and higher quality of seamless connection. However, due to its inherent heterogeneity, time-varying and self-organizing characteristics, the deployment and use of SAGIN still faces huge challenges, among which the orchestration of heterogeneous resources is a key issue. Based on virtual network architecture and deep reinforcement learning (DRL), we model SAGIN's heterogeneous resource orchestration as a multi-domain virtual network embedding (VNE) problem, and propose a SAGIN cross-domain VNE algorithm. We model the different network segments of SAGIN, and set the network attributes according to the actual situation of SAGIN and user needs. In DRL, the agent is acted by a five-layer policy network. We build a feature matrix based on network attributes extracted from SAGIN and use it as the agent training environment. Through training, the probability of each underlying node being embedded can be derived. In test phase, we complete the embedding process of virtual nodes and links in turn based on this probability. Finally, we verify the effectiveness of the algorithm from both training and testing.
Network virtualization (NV) is a technology with broad application prospects.
Virtual network embedding (VNE) is the core orientation of VN, which aims to
provide more flexible underlying physical resource allocation for user function
requests. The classical VNE problem is usually solved by heuristic method, but
this method often limits the flexibility of the algorithm and ignores the time
limit. In addition, the partition autonomy of physical domain and the dynamic
characteristics of virtual network request (VNR) also increase the difficulty
of VNE. This paper proposed a new type of VNE algorithm, which applied
reinforcement learning (RL) and graph neural network (GNN) theory to the
algorithm, especially the combination of graph convolutional neural network
(GCNN) and RL algorithm. Based on a self-defined fitness matrix and fitness
value, we set up the objective function of the algorithm implementation,
realized an efficient dynamic VNE algorithm, and effectively reduced the degree
of resource fragmentation. Finally, we used comparison algorithms to evaluate
the proposed method. Simulation experiments verified that the dynamic VNE
algorithm based on RL and GCNN has good basic VNE characteristics. By changing
the resource attributes of physical network and virtual network, it can be
proved that the algorithm has good flexibility.
In 1986 Victor Miller described an algorithm for computing the Weil pairing in his unpublished manuscript. This algorithm has then become the core of all pairing-based cryptosystems. Many improvements of the algorithm have been presented. Most of them involve a choice of elliptic curves of a \emph{special} forms to exploit a possible twist during Tate pairing computation. Other improvements involve a reduction of the number of iterations in the Miller's algorithm. For the generic case, Blake, Murty and Xu proposed three refinements to Miller's algorithm over Weierstrass curves. Though their refinements which only reduce the total number of vertical lines in Miller's algorithm, did not give an efficient computation as other optimizations, but they can be applied for computing \emph{both} of Weil and Tate pairings on \emph{all} pairing-friendly elliptic curves. In this paper we extend the Blake-Murty-Xu's method and show how to perform an elimination of all vertical lines in Miller's algorithm during Weil/Tate pairings computation on \emph{general} elliptic curves. Experimental results show that our algorithm is faster about 25% in comparison with the original Miller's algorithm.
Debiasing pipeline improves deep learning model generalization for X-ray based lung nodule detection
Debiasing pipeline improves deep learning model generalization for X-ray based lung nodule detection
University of Technology SydneyUniversity of Southern QueenslandCharles Sturt UniversityUniversiti Kebangsaan MalaysiaKing Abdulaziz UniversityKumamoto UniversityUniversity of New EnglandSingapore University of Social SciencesAsia UniversityWestmead HospitalNgee Ann PolytechnicCogninet AustraliaIBM Australia Limited
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death worldwide and a good prognosis depends on early diagnosis. Unfortunately, screening programs for the early diagnosis of lung cancer are uncommon. This is in-part due to the at-risk groups being located in rural areas far from medical facilities. Reaching these populations would require a scaled approach that combines mobility, low cost, speed, accuracy, and privacy. We can resolve these issues by combining the chest X-ray imaging mode with a federated deep-learning approach, provided that the federated model is trained on homogenous data to ensure that no single data source can adversely bias the model at any point in time. In this study we show that an image pre-processing pipeline that homogenizes and debiases chest X-ray images can improve both internal classification and external generalization, paving the way for a low-cost and accessible deep learning-based clinical system for lung cancer screening. An evolutionary pruning mechanism is used to train a nodule detection deep learning model on the most informative images from a publicly available lung nodule X-ray dataset. Histogram equalization is used to remove systematic differences in image brightness and contrast. Model training is performed using all combinations of lung field segmentation, close cropping, and rib suppression operators. We show that this pre-processing pipeline results in deep learning models that successfully generalize an independent lung nodule dataset using ablation studies to assess the contribution of each operator in this pipeline. In stripping chest X-ray images of known confounding variables by lung field segmentation, along with suppression of signal noise from the bone structure we can train a highly accurate deep learning lung nodule detection algorithm with outstanding generalization accuracy of 89% to nodule samples in unseen data.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.