BNU-HKBU United International College
This comprehensive survey introduces "Cognitive Edge Computing," enabling advanced AI agents and large language models to perform complex reasoning tasks directly on resource-constrained edge devices. It systematically reviews optimization techniques across data, model, and system layers, proposing a unified framework and a standardized evaluation protocol to address the fundamental mismatch between model requirements and edge capabilities.
This paper offers a comprehensive survey of on-device AI models, systematically mapping their diverse applications, identifying persistent technical challenges, and detailing effective optimization and implementation methods. The work synthesizes advancements in data, model, and system design to enhance AI performance on resource-constrained edge devices, while also forecasting future trends and ethical considerations.
A comprehensive review synthesizes existing prompt engineering techniques for Large Language Models and Vision-Language Models, detailing methods from foundational to advanced, addressing applications, evaluation, and security implications. It provides a structured overview of how effective prompting enhances model performance, mitigates issues like hallucinations, and impacts AI security.
Researchers from Beijing Normal-Hong Kong Baptist University and collaborators introduced Quantformer, a deep learning architecture that adapts the Transformer model for quantitative financial trading using numerical time series. This model consistently outperformed 100 traditional price-volume factors and the CSI 300 benchmark, achieving a 17.35% Annual Return and 0.915 Sharpe Ratio for its best monthly strategy, with returns reaching 24.71% when selecting the top 1% of stocks.
A new hybrid method combines the time Finite Element Method with Physics-Informed Neural Networks to solve time-dependent partial differential equations, effectively mitigating statistical errors and causality issues often found in pure PINNs. This approach, enhanced with deep adaptive sampling, demonstrated up to 100 times faster computation for convection and 40 times faster for Allen-Cahn equations compared to Causal PINNs, while achieving comparable or higher accuracy, particularly for high-dimensional and low-regularity problems.
Traditional recommender systems are typically passive in that they try to adapt their recommendations to the user's historical interests. However, it is highly desirable for commercial applications, such as e-commerce, advertisement placement, and news portals, to be able to expand the users' interests so that they would accept items that they were not originally aware of or interested in to increase customer interactions. In this paper, we present Influential Recommender System (IRS), a new recommendation paradigm that aims to proactively lead a user to like a given objective item by progressively recommending to the user a sequence of carefully selected items (called an influence path). We propose the Influential Recommender Network (IRN), which is a Transformer-based sequential model to encode the items' sequential dependencies. Since different people react to external influences differently, we introduce the Personalized Impressionability Mask (PIM) to model how receptive a user is to external influence to generate the most effective influence path for the user. To evaluate IRN, we design several performance metrics to measure whether or not the influence path can smoothly expand the user interest to include the objective item while maintaining the user's satisfaction with the recommendation. Experimental results show that IRN significantly outperforms the baseline recommenders and demonstrates its capability of influencing users' interests.
Diversity in demonstration selection is critical for enhancing model
generalization by enabling broader coverage of structures and concepts.
Constructing appropriate demonstration sets remains a key research challenge.
This paper introduces the Relevance-Diversity Enhanced Selection (RDES), an
innovative approach that leverages reinforcement learning (RL) frameworks to
optimize the selection of diverse reference demonstrations for tasks amenable
to in-context learning (ICL), particularly text classification and reasoning,
in few-shot prompting scenarios. RDES employs frameworks like Q-learning and a
PPO-based variant to dynamically identify demonstrations that maximize both
diversity (quantified by label distribution) and relevance to the task
objective. This strategy ensures a balanced representation of reference data,
leading to improved accuracy and generalization. Through extensive experiments
on multiple benchmark datasets, including diverse reasoning tasks, and
involving 14 closed-source and open-source LLMs, we demonstrate that RDES
significantly enhances performance compared to ten established baselines. Our
evaluation includes analysis of performance across varying numbers of
demonstrations on selected datasets. Furthermore, we investigate incorporating
Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning, which further boosts predictive performance.
The results highlight the potential of RL for adaptive demonstration selection
and addressing challenges in ICL.
In this paper, we present WonderHuman to reconstruct dynamic human avatars from a monocular video for high-fidelity novel view synthesis. Previous dynamic human avatar reconstruction methods typically require the input video to have full coverage of the observed human body. However, in daily practice, one typically has access to limited viewpoints, such as monocular front-view videos, making it a cumbersome task for previous methods to reconstruct the unseen parts of the human avatar. To tackle the issue, we present WonderHuman, which leverages 2D generative diffusion model priors to achieve high-quality, photorealistic reconstructions of dynamic human avatars from monocular videos, including accurate rendering of unseen body parts. Our approach introduces a Dual-Space Optimization technique, applying Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) in both canonical and observation spaces to ensure visual consistency and enhance realism in dynamic human reconstruction. Additionally, we present a View Selection strategy and Pose Feature Injection to enforce the consistency between SDS predictions and observed data, ensuring pose-dependent effects and higher fidelity in the reconstructed avatar. In the experiments, our method achieves SOTA performance in producing photorealistic renderings from the given monocular video, particularly for those challenging unseen parts. The project page and source code can be found at this https URL.
Dynamic reconstruction of deformable tissues in endoscopic video is a key technology for robot-assisted surgery. Recent reconstruction methods based on neural radiance fields (NeRFs) have achieved remarkable results in the reconstruction of surgical scenes. However, based on implicit representation, NeRFs struggle to capture the intricate details of objects in the scene and cannot achieve real-time rendering. In addition, restricted single view perception and occluded instruments also propose special challenges in surgical scene reconstruction. To address these issues, we develop SurgicalGaussian, a deformable 3D Gaussian Splatting method to model dynamic surgical scenes. Our approach models the spatio-temporal features of soft tissues at each time stamp via a forward-mapping deformation MLP and regularization to constrain local 3D Gaussians to comply with consistent movement. With the depth initialization strategy and tool mask-guided training, our method can remove surgical instruments and reconstruct high-fidelity surgical scenes. Through experiments on various surgical videos, our network outperforms existing method on many aspects, including rendering quality, rendering speed and GPU usage. The project page can be found at this https URL.
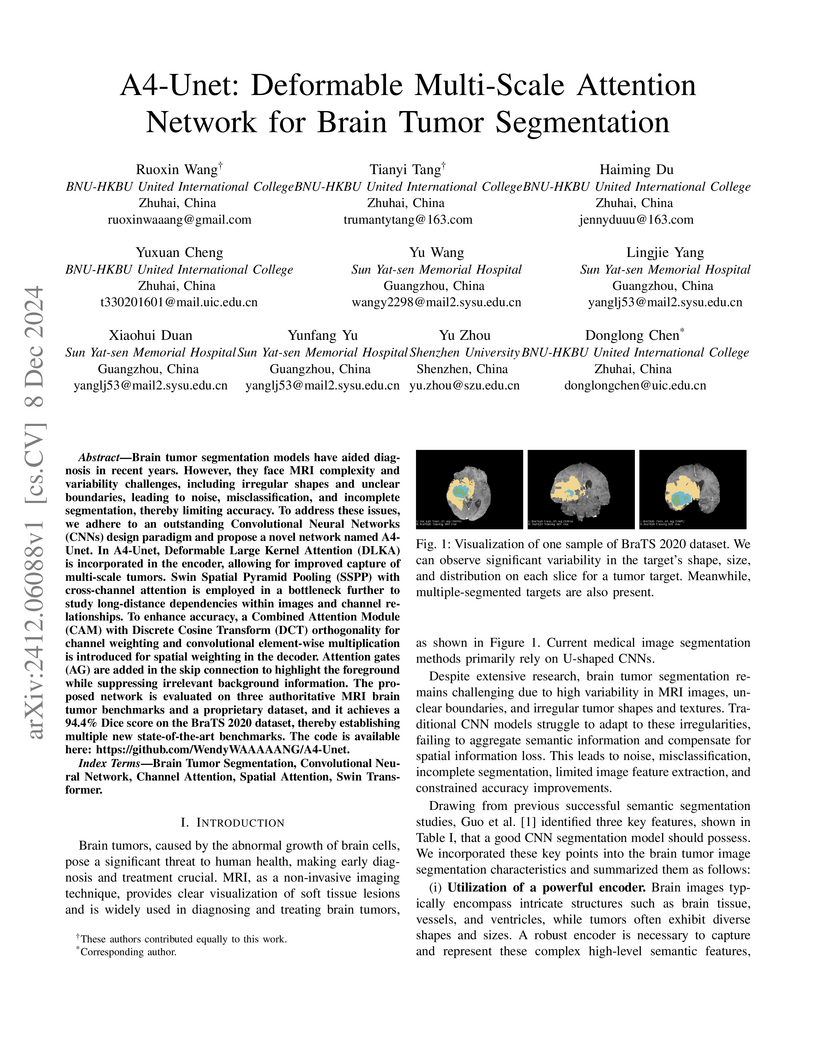
Brain tumor segmentation models have aided diagnosis in recent years. However, they face MRI complexity and variability challenges, including irregular shapes and unclear boundaries, leading to noise, misclassification, and incomplete segmentation, thereby limiting accuracy. To address these issues, we adhere to an outstanding Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) design paradigm and propose a novel network named A4-Unet. In A4-Unet, Deformable Large Kernel Attention (DLKA) is incorporated in the encoder, allowing for improved capture of multi-scale tumors. Swin Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SSPP) with cross-channel attention is employed in a bottleneck further to study long-distance dependencies within images and channel relationships. To enhance accuracy, a Combined Attention Module (CAM) with Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) orthogonality for channel weighting and convolutional element-wise multiplication is introduced for spatial weighting in the decoder. Attention gates (AG) are added in the skip connection to highlight the foreground while suppressing irrelevant background information. The proposed network is evaluated on three authoritative MRI brain tumor benchmarks and a proprietary dataset, and it achieves a 94.4% Dice score on the BraTS 2020 dataset, thereby establishing multiple new state-of-the-art benchmarks. The code is available here: this https URL.
Researchers at BNU-HKBU United International College leveraged a fine-tuned Chinese BERT-wwm model to extract sentiment from 73,836 professional Chinese analyst reports, demonstrating its predictive power for next-day stock volatility, excess returns, and trading volume in the Chinese market with observed asymmetric impacts.
Prompt optimization automatically refines prompting expressions, unlocking the full potential of LLMs in downstream tasks. However, current prompt optimization methods are costly to train and lack sufficient interpretability. This paper proposes enhancing LLMs' reasoning performance by eliciting their causal inference ability from prompting instructions to correct answers. Specifically, we introduce the Self-Causal Instruction Enhancement (SCIE) method, which enables LLMs to generate high-quality, low-quantity observational data, then estimates the causal effect based on these data, and ultimately generates instructions with the optimized causal effect. In SCIE, the instructions are treated as the treatment, and textual features are used to process natural language, establishing causal relationships through treatments between instructions and downstream tasks. Additionally, we propose applying Object-Relational (OR) principles, where the uncovered causal relationships are treated as the inheritable class across task objects, ensuring low-cost reusability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method effectively generates instructions that enhance reasoning performance with reduced training cost of prompts, leveraging interpretable textual features to provide actionable insights.
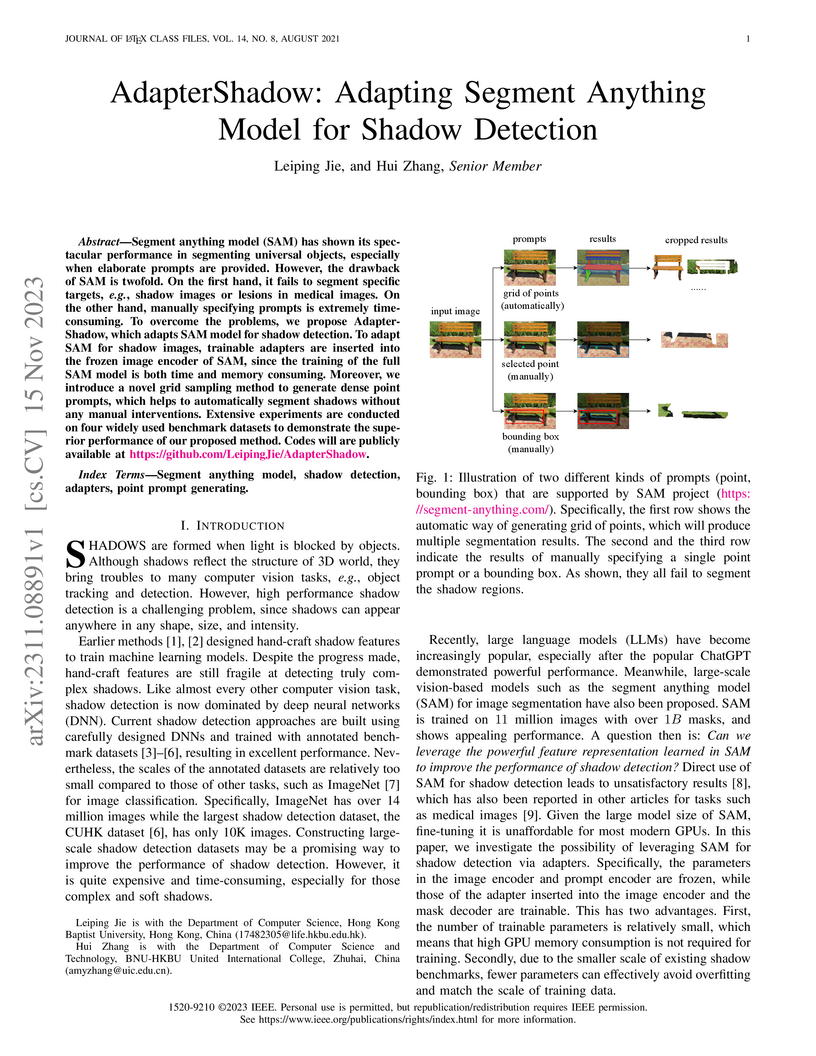
AdapterShadow adapts the Segment Anything Model (SAM) for accurate shadow detection by employing parameter-efficient fine-tuning with lightweight adapters and an automated grid-sampling prompt generation module. The method achieves state-of-the-art performance on various benchmark datasets, such as a Balanced Error Rate (BER) of 0.86% on the ISTD dataset, while maintaining computational efficiency with a low number of trainable parameters.
Fixed length summarization aims at generating summaries with a preset number
of words or characters. Most recent researches incorporate length information
with word embeddings as the input to the recurrent decoding unit, causing a
compromise between length controllability and summary quality. In this work, we
present an effective length controlling unit Length Attention (LenAtten) to
break this trade-off. Experimental results show that LenAtten not only brings
improvements in length controllability and ROGUE scores but also has great
generalization ability. In the task of generating a summary with the target
length, our model is 732 times better than the best-performing length
controllable summarizer in length controllability on the CNN/Daily Mail
dataset.
We introduce RMAvatar, a novel human avatar representation with Gaussian splatting embedded on mesh to learn clothed avatar from a monocular video. We utilize the explicit mesh geometry to represent motion and shape of a virtual human and implicit appearance rendering with Gaussian Splatting. Our method consists of two main modules: Gaussian initialization module and Gaussian rectification module. We embed Gaussians into triangular faces and control their motion through the mesh, which ensures low-frequency motion and surface deformation of the avatar. Due to the limitations of LBS formula, the human skeleton is hard to control complex non-rigid transformations. We then design a pose-related Gaussian rectification module to learn fine-detailed non-rigid deformations, further improving the realism and expressiveness of the avatar. We conduct extensive experiments on public datasets, RMAvatar shows state-of-the-art performance on both rendering quality and quantitative evaluations. Please see our project page at this https URL.
Predicting user preferences and sequential dependencies based on historical behavior is the core goal of sequential recommendation. Although attention-based models have shown effectiveness in this field, they often struggle with inference inefficiency due to the quadratic computational complexity inherent in attention mechanisms, especially with long-range behavior sequences. Drawing inspiration from the recent advancements of state space models (SSMs) in control theory, which provide a robust framework for modeling and controlling dynamic systems, we introduce EchoMamba4Rec. Control theory emphasizes the use of SSMs for managing long-range dependencies and maintaining inferential efficiency through structured state matrices. EchoMamba4Rec leverages these control relationships in sequential recommendation and integrates bi-directional processing with frequency-domain filtering to capture complex patterns and dependencies in user interaction data more effectively. Our model benefits from the ability of state space models (SSMs) to learn and perform parallel computations, significantly enhancing computational efficiency and scalability. It features a bi-directional Mamba module that incorporates both forward and reverse Mamba components, leveraging information from both past and future interactions. Additionally, a filter layer operates in the frequency domain using learnable Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) and learnable filters, followed by an inverse FFT to refine item embeddings and reduce noise. We also integrate Gate Linear Units (GLU) to dynamically control information flow, enhancing the model's expressiveness and training stability. Experimental results demonstrate that EchoMamba significantly outperforms existing models, providing more accurate and personalized recommendations.
Although large models have shown a strong capacity to solve large-scale problems in many areas including natural language and computer vision, their voluminous parameters are hard to deploy in a real-time system due to computational and energy constraints. Addressing this, knowledge distillation through Teacher-Student architecture offers a sustainable pathway to compress the knowledge of large models into more manageable sizes without significantly compromising performance. To enhance the robustness and interpretability of this framework, it is critical to understand how individual training data impact model performance, which is an area that remains underexplored. We propose the \textbf{Knowledge Distillation with Adaptive Influence Weight (KD-AIF)} framework which leverages influence functions from robust statistics to assign weights to training data, grounded in the four key SAFE principles: Sustainability, Accuracy, Fairness, and Explainability. This novel approach not only optimizes distillation but also increases transparency by revealing the significance of different data. The exploration of various update mechanisms within the KD-AIF framework further elucidates its potential to significantly improve learning efficiency and generalization in student models, marking a step toward more explainable and deployable Large Models. KD-AIF is effective in knowledge distillation while also showing exceptional performance in semi-supervised learning with outperforms existing baselines and methods in multiple benchmarks (CIFAR-100, CIFAR-10-4k, SVHN-1k, and GLUE).
Missing values are a common problem that poses significant challenges to data analysis and machine learning. This problem necessitates the development of an effective imputation method to fill in the missing values accurately, thereby enhancing the overall quality and utility of the datasets. Existing imputation methods, however, fall short of explicitly considering the `missingness' information in the data during the embedding initialization stage and modeling the entangled feature and sample correlations during the learning process, thus leading to inferior performance. We propose M3-Impute, which aims to explicitly leverage the missingness information and such correlations with novel masking schemes. M3-Impute first models the data as a bipartite graph and uses a graph neural network to learn node embeddings, where the refined embedding initialization process directly incorporates the missingness information. They are then optimized through M3-Impute's novel feature correlation unit (FRU) and sample correlation unit (SRU) that effectively captures feature and sample correlations for imputation. Experiment results on 25 benchmark datasets under three different missingness settings show the effectiveness of M3-Impute by achieving 20 best and 4 second-best MAE scores on average.
Streaming data clustering is a popular research topic in data mining and machine learning. Since streaming data is usually analyzed in data chunks, it is more susceptible to encounter the dynamic cluster imbalance issue. That is, the imbalance ratio of clusters changes over time, which can easily lead to fluctuations in either the accuracy or the efficiency of streaming data clustering. Therefore, we propose an accurate and efficient streaming data clustering approach to adapt the drifting and imbalanced cluster distributions. We first design a Self-Growth Map (SGM) that can automatically arrange neurons on demand according to local distribution, and thus achieve fast and incremental adaptation to the streaming distributions. Since SGM allocates an excess number of density-sensitive neurons to describe the global distribution, it can avoid missing small clusters among imbalanced distributions. We also propose a fast hierarchical merging strategy to combine the neurons that break up the relatively large clusters. It exploits the maintained SGM to quickly retrieve the intra-cluster distribution pairs for merging, which circumvents the most laborious global searching. It turns out that the proposed SGM can incrementally adapt to the distributions of new chunks, and the Self-grOwth map-guided Hierarchical merging for Imbalanced data clustering (SOHI) approach can quickly explore a true number of imbalanced clusters. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SOHI can efficiently and accurately explore cluster distributions for streaming data.
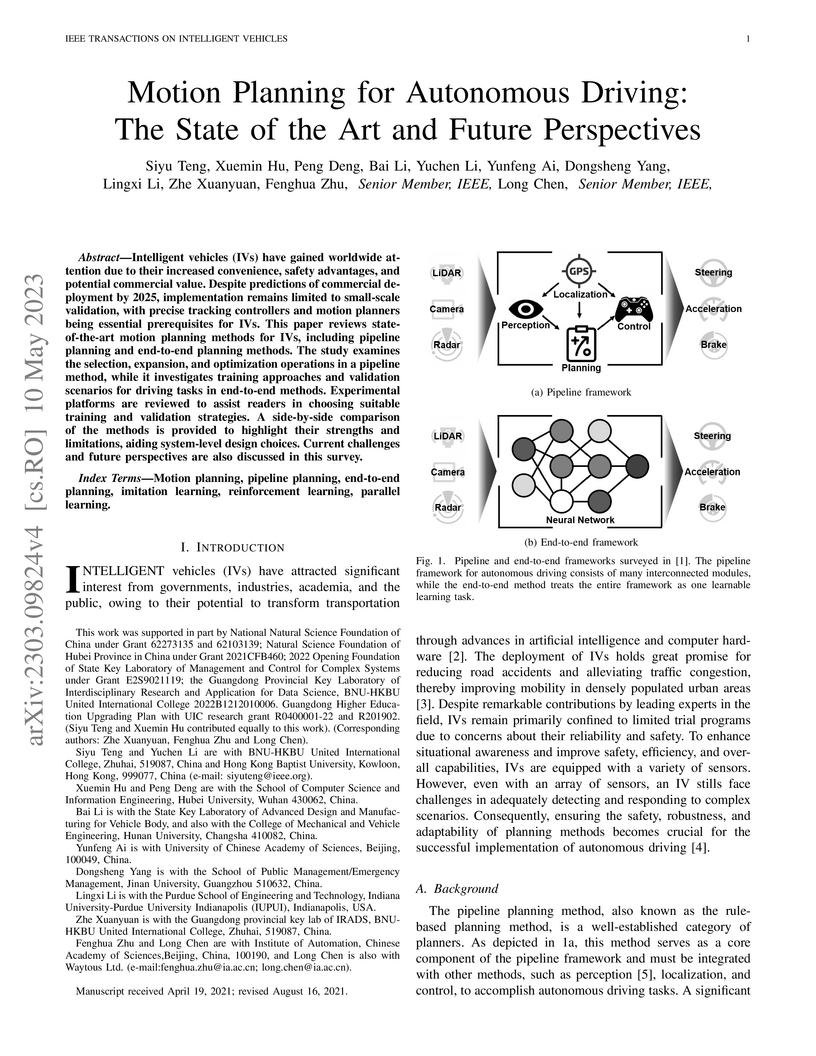
Intelligent vehicles (IVs) have gained worldwide attention due to their increased convenience, safety advantages, and potential commercial value. Despite predictions of commercial deployment by 2025, implementation remains limited to small-scale validation, with precise tracking controllers and motion planners being essential prerequisites for IVs. This paper reviews state-of-the-art motion planning methods for IVs, including pipeline planning and end-to-end planning methods. The study examines the selection, expansion, and optimization operations in a pipeline method, while it investigates training approaches and validation scenarios for driving tasks in end-to-end methods. Experimental platforms are reviewed to assist readers in choosing suitable training and validation strategies. A side-by-side comparison of the methods is provided to highlight their strengths and limitations, aiding system-level design choices. Current challenges and future perspectives are also discussed in this survey.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.