Baichuan Inc.
23 Sep 2025
The ReSearch framework enables Large Language Models to integrate multi-step reasoning with external search, learning interactively via reinforcement learning without supervised intermediate steps. It yields substantial performance gains on complex multi-hop question answering benchmarks and reveals emergent self-correction capabilities.
ShortGPT introduces a simple layer pruning method for Large Language Models, leveraging a novel Block Influence (BI) metric to identify and remove redundant layers. This approach consistently outperforms existing structured pruning methods, achieving significant parameter reduction (e.g., 25%) with minimal performance degradation on various benchmarks and demonstrating compatibility with quantization techniques.
Baichuan Inc. and Peking University developed BUTTON, a pipeline for generating synthetic instruction tuning data to enhance Large Language Models' ability to perform multi-turn function calls. Models fine-tuned with BUTTONInstruct demonstrated substantial performance gains on multi-turn benchmarks, often rivaling or exceeding proprietary state-of-the-art LLMs like GPT-4o.
Baichuan-M1 introduces a series of Large Language Models specifically optimized for medical applications, trained from scratch on a vast, curated dataset. The 14B-parameter version demonstrated superior performance over larger open-source models on medical benchmarks and significantly reduced the performance gap with leading proprietary models.
DualToken introduces a unified vision tokenizer that employs dual visual vocabularies, disentangling high-level semantic and low-level perceptual features to achieve state-of-the-art performance in both visual understanding and high-fidelity image generation within a single autoregressive multimodal large language model.
The STAIR framework equips Large Language Models (LLMs) with introspective reasoning to enhance safety alignment, enabling more robust refusal of harmful queries, especially against jailbreak attacks, while mitigating performance trade-offs. It achieves a 0.9391 goodness score on StrongReject, outperforming GPT-4o and improving LLaMA-3.1's helpfulness metrics.
According to the Test-Time Scaling, the integration of External Slow-Thinking
with the Verify mechanism has been demonstrated to enhance multi-round
reasoning in large language models (LLMs). However, in the multimodal (MM)
domain, there is still a lack of a strong MM-Verifier. In this paper, we
introduce MM-Verifier and MM-Reasoner to enhance multimodal reasoning through
longer inference and more robust verification. First, we propose a two-step MM
verification data synthesis method, which combines a simulation-based tree
search with verification and uses rejection sampling to generate high-quality
Chain-of-Thought (COT) data. This data is then used to fine-tune the
verification model, MM-Verifier. Additionally, we present a more efficient
method for synthesizing MMCOT data, bridging the gap between text-based and
multimodal reasoning. The synthesized data is used to fine-tune MM-Reasoner.
Our MM-Verifier outperforms all larger models on the MathCheck, MathVista, and
MathVerse benchmarks. Moreover, MM-Reasoner demonstrates strong effectiveness
and scalability, with performance improving as data size increases. Finally,
our approach achieves strong performance when combining MM-Reasoner and
MM-Verifier, reaching an accuracy of 65.3 on MathVista, surpassing GPT-4o
(63.8) with 12 rollouts.
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance on a
variety of natural language tasks based on just a few examples of natural
language instructions, reducing the need for extensive feature engineering.
However, most powerful LLMs are closed-source or limited in their capability
for languages other than English. In this technical report, we present Baichuan
2, a series of large-scale multilingual language models containing 7 billion
and 13 billion parameters, trained from scratch, on 2.6 trillion tokens.
Baichuan 2 matches or outperforms other open-source models of similar size on
public benchmarks like MMLU, CMMLU, GSM8K, and HumanEval. Furthermore, Baichuan
2 excels in vertical domains such as medicine and law. We will release all
pre-training model checkpoints to benefit the research community in better
understanding the training dynamics of Baichuan 2.
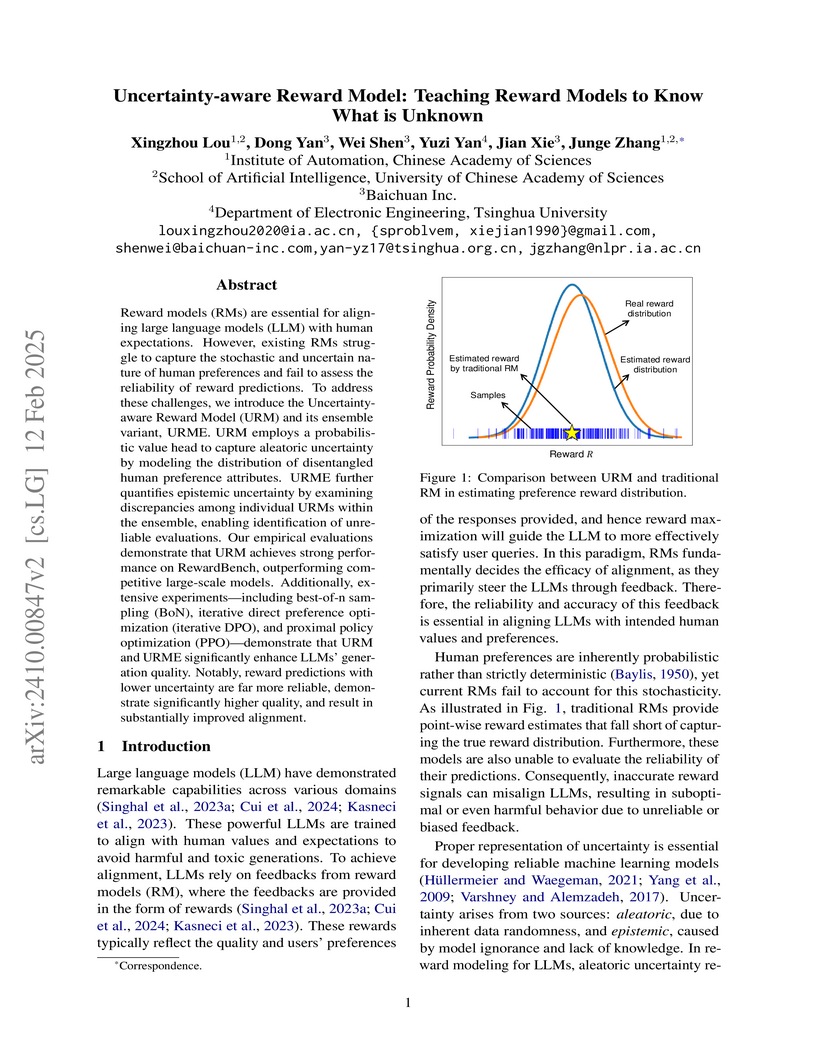
Researchers developed the Uncertainty-aware Reward Model (URM) and its ensemble variant (URME) to quantify both inherent data variability (aleatoric) and model knowledge gaps (epistemic) in large language model reward systems. This approach significantly improves LLM alignment by filtering unreliable feedback, leading to higher generation quality and achieving a 92.9 score on the RewardBench benchmark with URM(S).
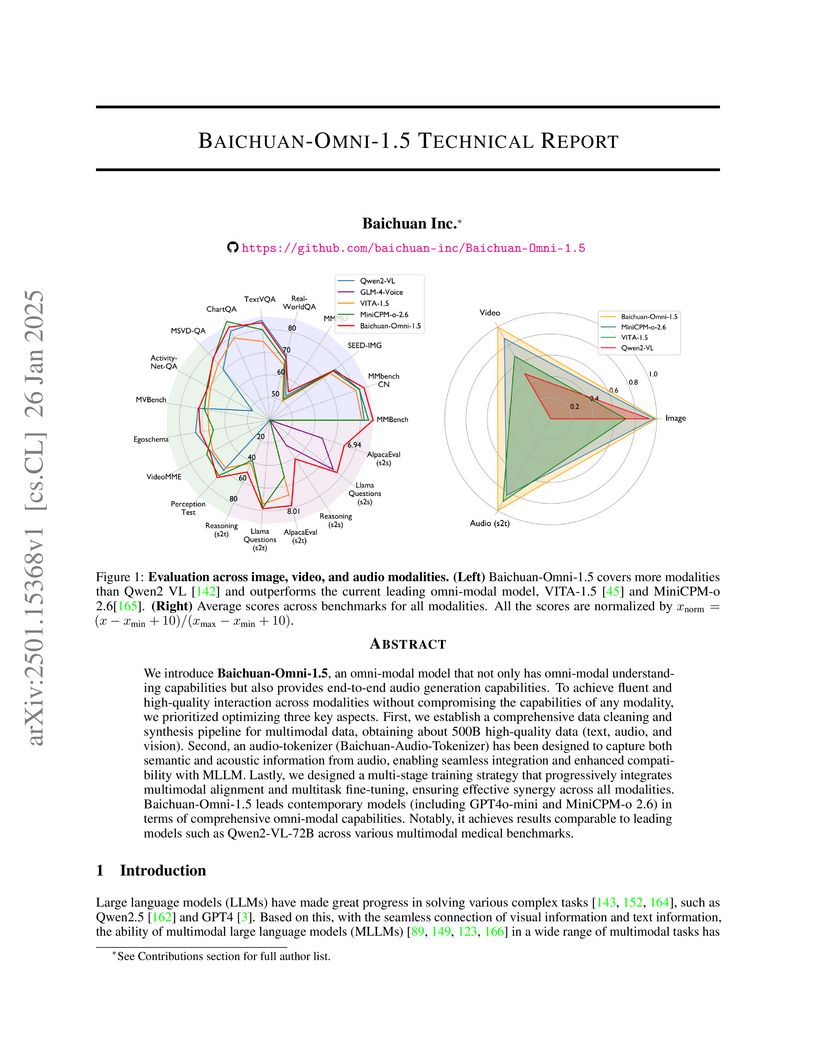
Baichuan Inc. introduces Baichuan-Omni-1.5, a groundbreaking unified multimodal model that seamlessly processes text, images, video, and audio while achieving state-of-the-art performance across modalities, featuring a novel audio tokenizer and demonstrating particularly strong results in medical applications through comprehensive training on 500B high-quality samples.
09 Oct 2025
In medical scenarios, effectively retrieving external knowledge and leveraging it for rigorous logical reasoning is of significant importance. Despite their potential, existing work has predominantly focused on enhancing either retrieval or reasoning capabilities of the models in isolation, with little attention given to their joint optimization, which leads to limited coordination between the two processes. Additionally, current methods rely heavily on supervised fine-tuning (SFT), which can cause models to memorize existing problem-solving pathways, thereby restricting their generalization ability when confronted with novel problem contexts. Furthermore, while some studies have explored to improve retrieval-augmented reasoning in general domains via reinforcement learning, their reward function designs do not adequately capture the specific demands of the medical domain. To address these challenges, we introduce **Med-R3**, a **Med**ical **R**etrieval-augmented **R**easoning framework driven by progressive **R**einforcement learning. In this framework, we first develop the model's ability to perform logical reasoning over medical problems. Subsequently, on the basis of this foundation, we adaptively optimize the retrieval capability to better align with the characteristics of knowledge corpus and external information utilization throughout the reasoning process. Finally, we conduct joint optimization of the model's retrieval and reasoning coordination. Extensive experiments indicate that **Med-R3** could achieve state-of-the-art performances, with LLaMA3.1-8B-Instruct + Med-R3 surpassing closed-sourced GPT-4o-mini by 3.93\% at a comparable parameter scale, while Qwen2.5-14B augmented with Med-R3 shows a more substantial gain of 13.53\%.
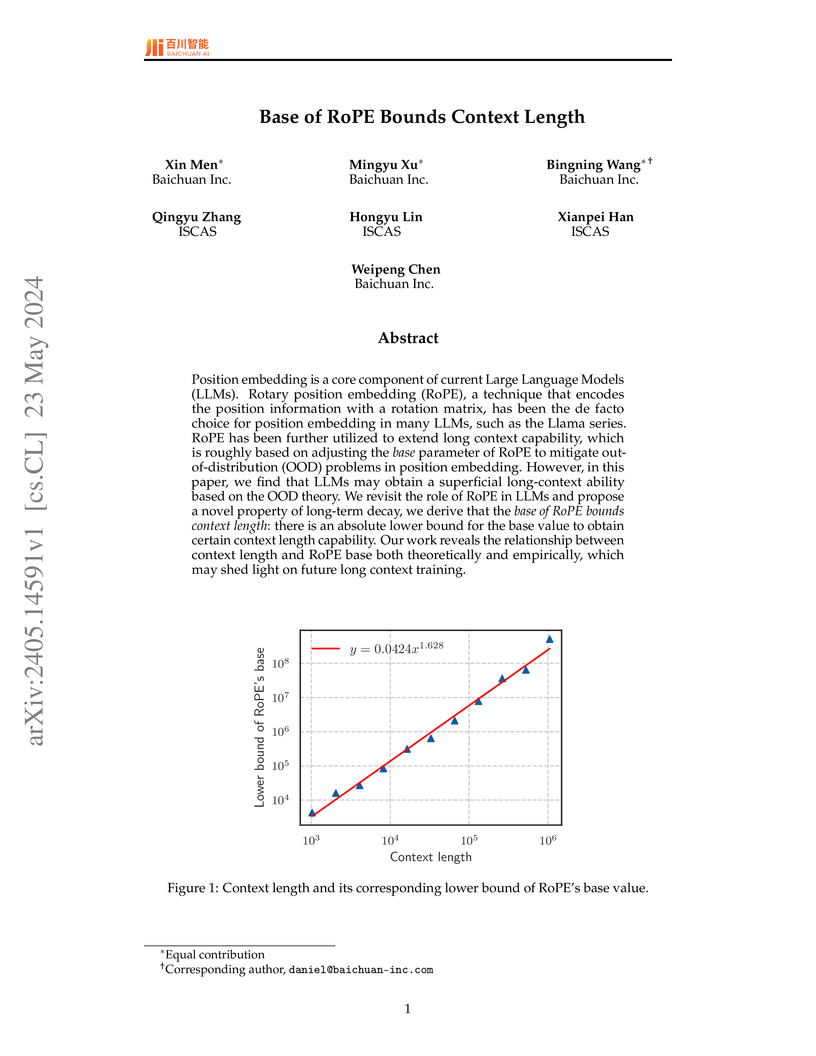
Researchers from Baichuan Inc. and the Institute of Software, Chinese Academy of Sciences, introduce "long-term decay" as a critical property governing the effective context length of LLMs with Rotary Position Embedding (RoPE), showing that simply avoiding out-of-distribution angles is insufficient and deriving a power-law lower bound for the RoPE base parameter to achieve genuine long-context understanding.
PQCache introduces a Product Quantization-based KVCache management system for Large Language Models, reframing KVCache storage and retrieval as an embedding retrieval problem. This approach enables efficient inference with context lengths up to 128K tokens and beyond, achieving higher model quality compared to existing baselines while maintaining low, stable serving latency.
Peking University researchers introduce align-anything-200k, a comprehensive human preference dataset spanning text, image, audio, and video, and Learning from Language Feedback (LLF), an algorithm that leverages language-based critiques to enhance all-modality model alignment. Their approach demonstrates an average 5.83 times improvement over baseline RLHF, and they include a new evaluation framework, eval-anything, to assess these models comprehensively.
This research introduces EMA, an Efficient Motion-Aware Video MLLM that directly utilizes compressed video structures and motion vectors for video understanding. The approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on motion-centric tasks and competitive results on general video question-answering benchmarks while significantly improving computational efficiency.
CFBench, a comprehensive Chinese benchmark, was developed to evaluate how well Large Language Models follow instructions with complex constraints. It features 1,000 real-world samples, a hierarchical constraint framework, and a user-centric evaluation metric (PSR) to assess LLM performance beyond general proficiency, revealing that even leading LLMs struggle significantly with complex constrained instructions, especially those involving contradictory requirements.
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have shown impressive capabilities across various domains, excelling in processing and understanding information from multiple modalities. Despite the rapid progress made previously, insufficient OCR ability hinders MLLMs from excelling in text-related tasks. In this paper, we present \textbf{Ocean-OCR}, a 3B MLLM with state-of-the-art performance on various OCR scenarios and comparable understanding ability on general tasks. We employ Native Resolution ViT to enable variable resolution input and utilize a substantial collection of high-quality OCR datasets to enhance the model performance. We demonstrate the superiority of Ocean-OCR through comprehensive experiments on open-source OCR benchmarks and across various OCR scenarios. These scenarios encompass document understanding, scene text recognition, and handwritten recognition, highlighting the robust OCR capabilities of Ocean-OCR. Note that Ocean-OCR is the first MLLM to outperform professional OCR models such as TextIn and PaddleOCR.
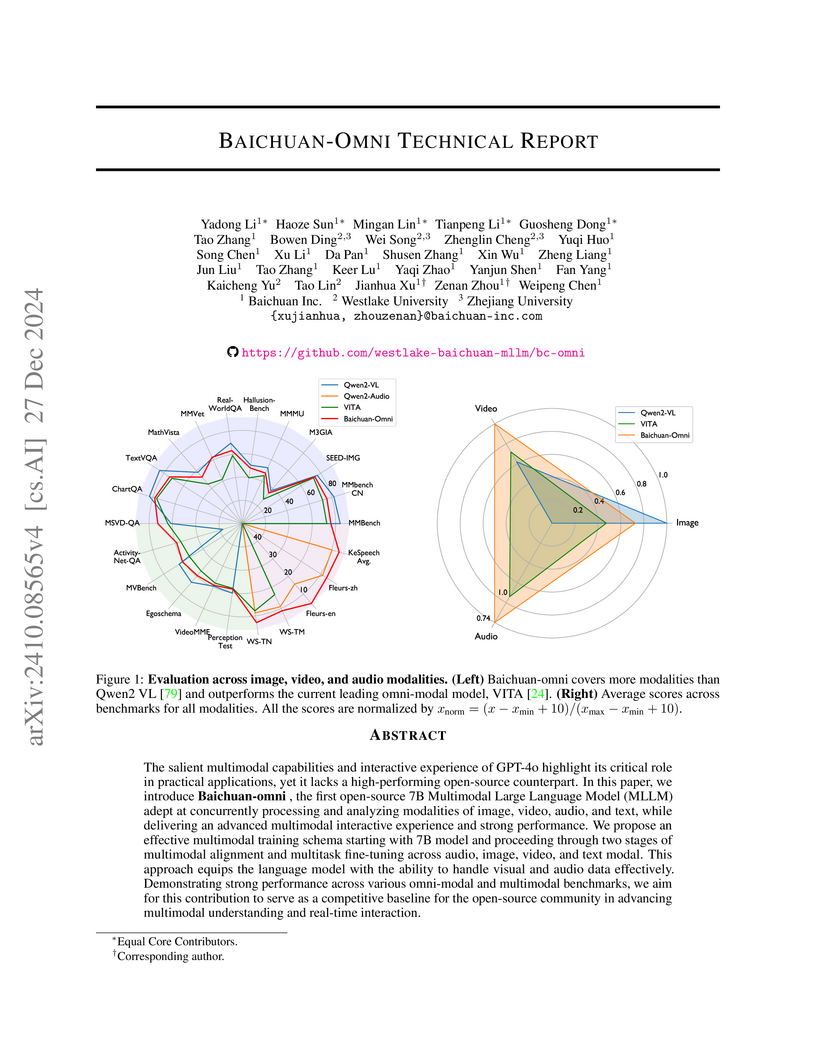
The salient multimodal capabilities and interactive experience of GPT-4o highlight its critical role in practical applications, yet it lacks a high-performing open-source counterpart. In this paper, we introduce Baichuan-omni, the first open-source 7B Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) adept at concurrently processing and analyzing modalities of image, video, audio, and text, while delivering an advanced multimodal interactive experience and strong performance. We propose an effective multimodal training schema starting with 7B model and proceeding through two stages of multimodal alignment and multitask fine-tuning across audio, image, video, and text modal. This approach equips the language model with the ability to handle visual and audio data effectively. Demonstrating strong performance across various omni-modal and multimodal benchmarks, we aim for this contribution to serve as a competitive baseline for the open-source community in advancing multimodal understanding and real-time interaction.
Peking University and Baichuan Inc. researchers developed Med-R², a framework that integrates Evidence-Based Medicine principles into Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance their capabilities in clinical settings. This approach improves the precision of medical knowledge retrieval and the effectiveness of evidence-based reasoning, enabling LLMs to serve as more reliable and proficient "LLM physicians," often outperforming frontier models like GPT-4o.
Researchers from Baichuan Inc. and Renmin University of China developed a patient simulator trained on real dialogue strategies, achieving a 0.31% hallucination rate and an 0.87 anthropomorphism score. Their work established that the quality of inquiry in online medical consultations adheres to Liebig's Law of the Minimum, directly impacting diagnostic accuracy.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.