Fraunhofer IISFraunhofer Institute for Integrated Circuits IIS
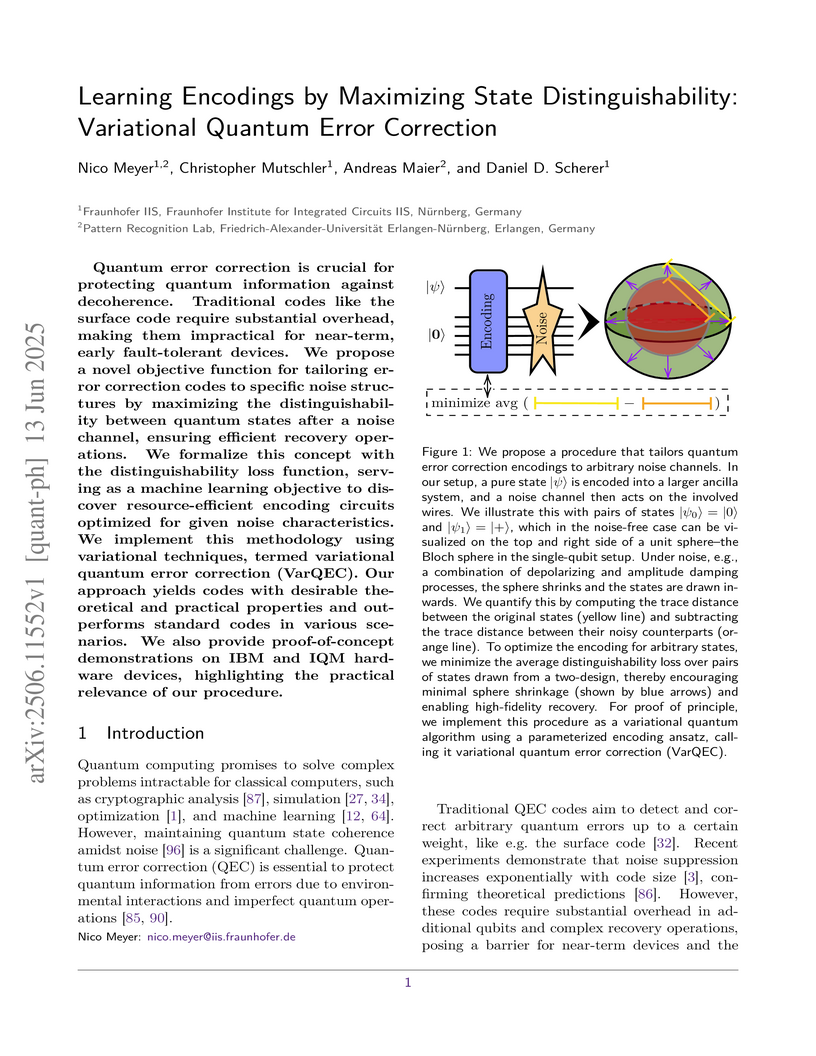
Quantum error correction is crucial for protecting quantum information
against decoherence. Traditional codes like the surface code require
substantial overhead, making them impractical for near-term, early
fault-tolerant devices. We propose a novel objective function for tailoring
error correction codes to specific noise structures by maximizing the
distinguishability between quantum states after a noise channel, ensuring
efficient recovery operations. We formalize this concept with the
distinguishability loss function, serving as a machine learning objective to
discover resource-efficient encoding circuits optimized for given noise
characteristics. We implement this methodology using variational techniques,
termed variational quantum error correction (VarQEC). Our approach yields codes
with desirable theoretical and practical properties and outperforms standard
codes in various scenarios. We also provide proof-of-concept demonstrations on
IBM and IQM hardware devices, highlighting the practical relevance of our
procedure.
This research introduces MEMORYCODE, a synthetic benchmark designed to evaluate how well large language models (LLMs) track and apply evolving coding instructions across multiple dialogue sessions. Experiments demonstrate a severe performance decline in state-of-the-art LLMs when faced with long conversational histories, indicating limitations in their sustained memory and compositional reasoning abilities.
We present two multilingual LLMs, Teuken 7B-base and Teuken 7B-instruct, designed to embrace Europe's linguistic diversity by supporting all 24 official languages of the European Union. Trained on a dataset comprising around 60% non-English data and utilizing a custom multilingual tokenizer, our models address the limitations of existing LLMs that predominantly focus on English or a few high-resource languages. We detail the models' development principles, i.e., data composition, tokenizer optimization, and training methodologies. The models demonstrate strong performance across multilingual benchmarks, as evidenced by their performance on European versions of ARC, HellaSwag, and TruthfulQA.
08 Mar 2024
The survey comprehensively classifies Quantum Reinforcement Learning (QRL) approaches by their 'degree of quantization', detailing quantum-inspired methods, hybrid variational quantum circuit (VQC)-based techniques for noisy intermediate-scale quantum devices, and full-quantum formulations for future fault-tolerant hardware, while outlining their current status and limitations.
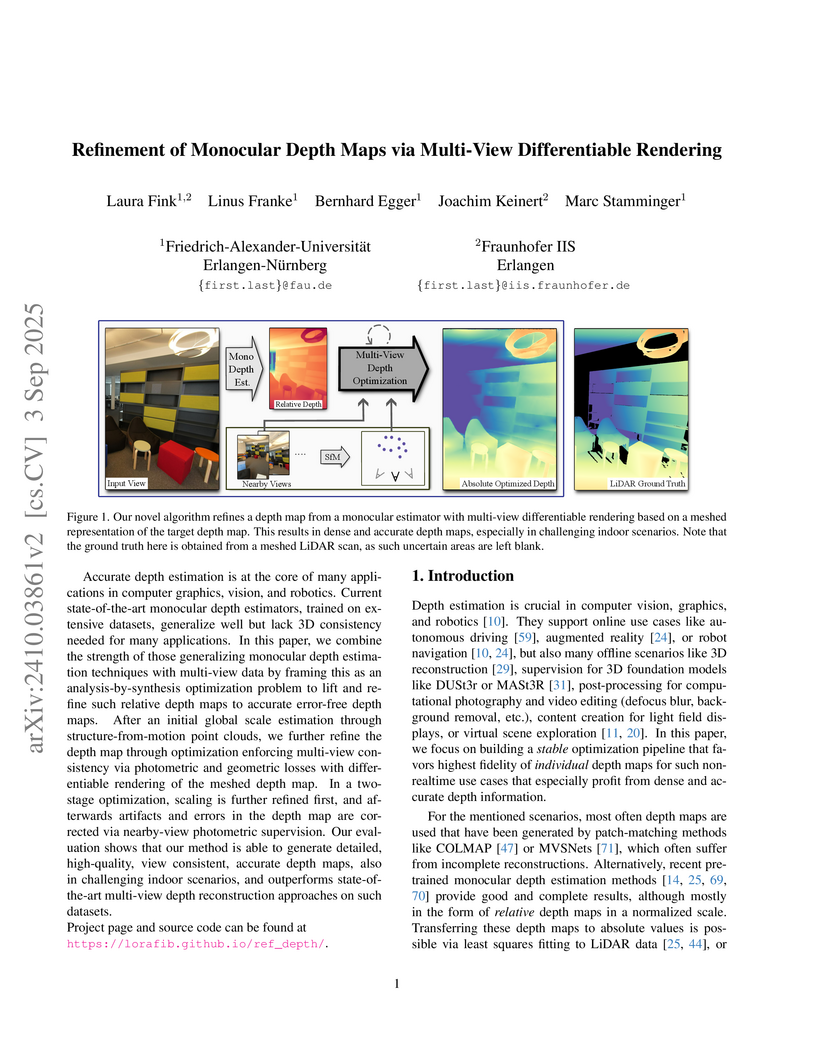
Accurate depth estimation is at the core of many applications in computer graphics, vision, and robotics. Current state-of-the-art monocular depth estimators, trained on extensive datasets, generalize well but lack 3D consistency needed for many applications. In this paper, we combine the strength of those generalizing monocular depth estimation techniques with multi-view data by framing this as an analysis-by-synthesis optimization problem to lift and refine such relative depth maps to accurate error-free depth maps. After an initial global scale estimation through structure-from-motion point clouds, we further refine the depth map through optimization enforcing multi-view consistency via photometric and geometric losses with differentiable rendering of the meshed depth map. In a two-stage optimization, scaling is further refined first, and afterwards artifacts and errors in the depth map are corrected via nearby-view photometric supervision. Our evaluation shows that our method is able to generate detailed, high-quality, view consistent, accurate depth maps, also in challenging indoor scenarios, and outperforms state-of-the-art multi-view depth reconstruction approaches on such datasets.
Project page and source code can be found at this https URL.
06 Apr 2025
This paper introduces FlowMAC, a novel neural audio codec for high-quality
general audio compression at low bit rates based on conditional flow matching
(CFM). FlowMAC jointly learns a mel spectrogram encoder, quantizer and decoder.
At inference time the decoder integrates a continuous normalizing flow via an
ODE solver to generate a high-quality mel spectrogram. This is the first time
that a CFM-based approach is applied to general audio coding, enabling a
scalable, simple and memory efficient training. Our subjective evaluations show
that FlowMAC at 3 kbps achieves similar quality as state-of-the-art GAN-based
and DDPM-based neural audio codecs at double the bit rate. Moreover, FlowMAC
offers a tunable inference pipeline, which permits to trade off complexity and
quality. This enables real-time coding on CPU, while maintaining high
perceptual quality.
Researchers developed a text-to-speech system capable of generating speech in over 7000 languages, including zero-shot synthesis for languages without any training data. The system achieves a median naturalness score of 4 out of 5 for unseen languages and matches or surpasses state-of-the-art baselines for mid-resource languages.
07 Nov 2024
VQC can be understood through the lens of Fourier analysis. It is already well-known that the function space represented by any circuit architecture can be described through a truncated Fourier sum. We show that the spectrum available to that truncated Fourier sum is not entirely determined by the encoding gates of the circuit, since the variational part of the circuit can constrain certain coefficients to zero, effectively removing that frequency from the spectrum. To the best of our knowledge, we give the first description of the functional dependence of the Fourier coefficients on the variational parameters as trigonometric polynomials. This allows us to provide an algorithm which computes the exact spectrum of any given circuit and the corresponding Fourier coefficients. Finally, we demonstrate that by comparing the Fourier transform of the dataset to the available spectra, it is possible to predict which VQC out of a given list of choices will be able to best fit the data.
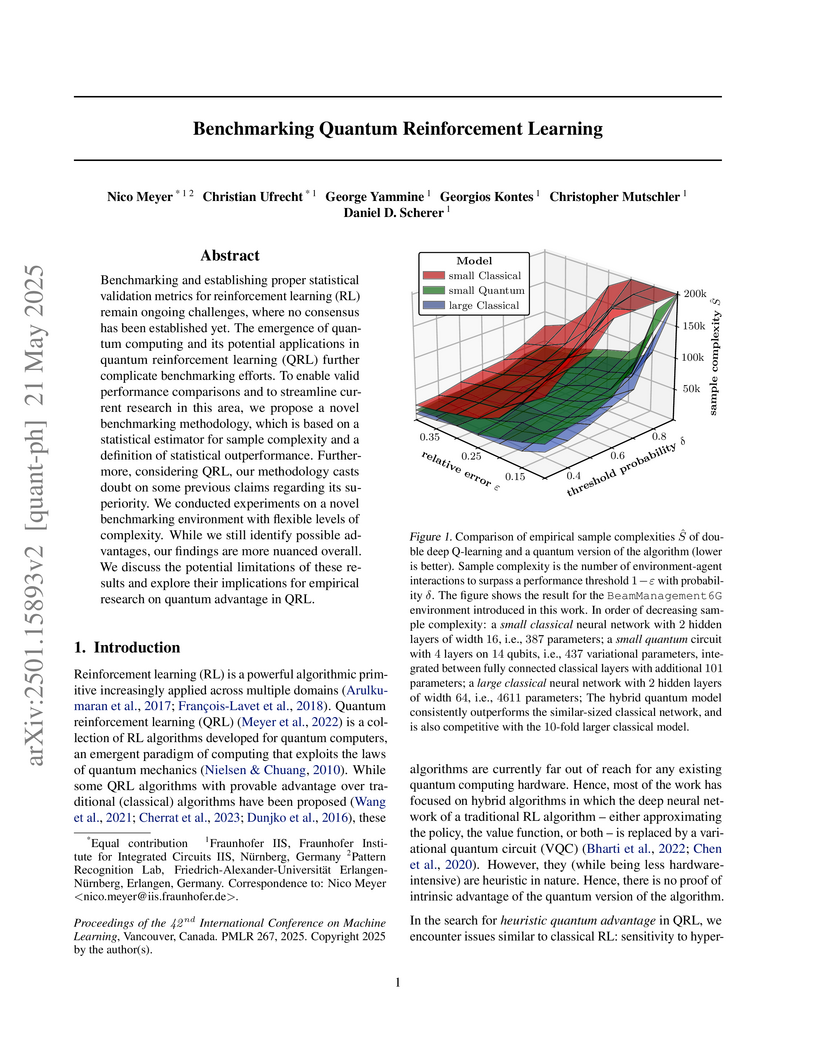
Benchmarking and establishing proper statistical validation metrics for
reinforcement learning (RL) remain ongoing challenges, where no consensus has
been established yet. The emergence of quantum computing and its potential
applications in quantum reinforcement learning (QRL) further complicate
benchmarking efforts. To enable valid performance comparisons and to streamline
current research in this area, we propose a novel benchmarking methodology,
which is based on a statistical estimator for sample complexity and a
definition of statistical outperformance. Furthermore, considering QRL, our
methodology casts doubt on some previous claims regarding its superiority. We
conducted experiments on a novel benchmarking environment with flexible levels
of complexity. While we still identify possible advantages, our findings are
more nuanced overall. We discuss the potential limitations of these results and
explore their implications for empirical research on quantum advantage in QRL.
13 Jun 2025
JPEG XL is a new image coding system offering state-of-the-art compression performance, lossless JPEG recompression, and advanced features. It aims to replace JPEG, PNG, GIF, and other formats with a single universal codec. This article provides an overview of JPEG XL, including its history, design rationale, coding tools, and future potential. It can be used as a companion document to the standard (ISO/IEC 18181), or as a standalone article to better understand JPEG XL, either at a high level or in considerable technical detail.
03 Sep 2024
This paper presents a deep reinforcement learning approach for synthesizing
unitaries into quantum circuits. Unitary synthesis aims to identify a quantum
circuit that represents a given unitary while minimizing circuit depth, total
gate count, a specific gate count, or a combination of these factors. While
past research has focused predominantly on continuous gate sets, synthesizing
unitaries from the parameter-free Clifford+T gate set remains a challenge.
Although the time complexity of this task will inevitably remain exponential in
the number of qubits for general unitaries, reducing the runtime for simple
problem instances still poses a significant challenge. In this study, we apply
the tree-search method Gumbel AlphaZero to solve the problem for a subset of
exactly synthesizable Clifford+T unitaries. Our method effectively synthesizes
circuits for up to five qubits generated from randomized circuits with up to 60
gates, outperforming existing tools like QuantumCircuitOpt and MIN-T-SYNTH in
terms of synthesis time for larger qubit counts. Furthermore, it surpasses
Synthetiq in successfully synthesizing random, exactly synthesizable unitaries.
These results establish a strong baseline for future unitary synthesis
algorithms.
This research introduces a framework for interpreting language models by constructing 'linguistic task spaces,' which reveal how models internally organize their understanding of language. It demonstrates that LMs generalize across higher-level linguistic structures and that their conceptual organization of language remains remarkably stable throughout pre-training.
Recent progress in speech separation has been largely driven by advances in deep neural networks, yet their high computational and memory requirements hinder deployment on resource-constrained devices. A significant inefficiency in conventional systems arises from using static network architectures that maintain constant computational complexity across all input segments, regardless of their characteristics. This approach is sub-optimal for simpler segments that do not require intensive processing, such as silence or non-overlapping speech. To address this limitation, we propose a dynamic slimmable network (DSN) for speech separation that adaptively adjusts its computational complexity based on the input signal. The DSN combines a slimmable network, which can operate at different network widths, with a lightweight gating module that dynamically determines the required width by analyzing the local input characteristics. To balance performance and efficiency, we introduce a signal-dependent complexity loss that penalizes unnecessary computation based on segmental reconstruction error. Experiments on clean and noisy two-speaker mixtures from the WSJ0-2mix and WHAM! datasets show that the DSN achieves a better performance-efficiency trade-off than individually trained static networks of different sizes.
Spatial target speaker extraction isolates a desired speaker's voice in multi-speaker environments using spatial information, such as the direction of arrival (DoA). Although recent deep neural network (DNN)-based discriminative methods have shown significant performance improvements, the potential of generative approaches, such as generative adversarial networks (GANs), remains largely unexplored for this problem. In this work, we demonstrate that a GAN can effectively leverage both noisy mixtures and spatial information to extract and generate the target speaker's speech. By conditioning the GAN on intermediate features of a discriminative spatial filtering model in addition to DoA, we enable steerable target extraction with high spatial resolution of 5 degrees, outperforming state-of-the-art discriminative methods in perceptual quality-based objective metrics.
Optimizers play a decisive role in reducing pre-training times for LLMs and achieving better-performing models. In this study, we compare three major variants: the de-facto standard AdamW, the simpler Lion, developed through an evolutionary search, and the second-order optimizer Sophia. For better generalization, we train with two different base architectures and use a single- and a multiple-epoch approach while keeping the number of tokens constant. Using the Maximal Update Parametrization and smaller proxy models, we tune relevant hyperparameters separately for each combination of base architecture and optimizer. We found that while the results from all three optimizers were in approximately the same range, Sophia exhibited the lowest training and validation loss, Lion was fastest in terms of training GPU hours but AdamW led to the best downstream evaluation results.
15 Apr 2025
We present BenchQC, a research project funded by the state of Bavaria, which
promotes an application-centric perspective for benchmarking real-world quantum
applications. Diverse use cases from industry consortium members are the
starting point of a benchmarking workflow, that builds on the open-source
platform QUARK, encompassing the full quantum software stack from the hardware
provider interface to the application layer. By identifying and evaluating key
metrics across the entire pipeline, we aim to uncover meaningful trends,
provide systematic guidance on quantum utility, and distinguish promising
research directions from less viable approaches. Ultimately, this initiative
contributes to the broader effort of establishing reliable benchmarking
standards that drive the transition from experimental demonstrations to
practical quantum advantage.
This paper presents the Deep learning-based Perceptual Audio Quality metric (DeePAQ) for evaluating general audio quality. Our approach leverages metric learning together with the music foundation model MERT, guided by surrogate labels, to construct an embedding space that captures distortion intensity in general audio. To the best of our knowledge, DeePAQ is the first in the general audio quality domain to leverage weakly supervised labels and metric learning for fine-tuning a music foundation model with Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), a direction not yet explored by other state-of-the-art methods. We benchmark the proposed model against state-of-the-art objective audio quality metrics across listening tests spanning audio coding and source separation. Results show that our method surpasses existing metrics in detecting coding artifacts and generalizes well to unseen distortions such as source separation, highlighting its robustness and versatility.
This paper introduces a novel reference-free (RF) audio quality metric called
the RF-Generative Machine Listener (RF-GML), designed to evaluate coded mono,
stereo, and binaural audio at a 48 kHz sample rate. RF-GML leverages transfer
learning from a state-of-the-art full-reference (FR) Generative Machine
Listener (GML) with minimal architectural modifications. The term "generative"
refers to the model's ability to generate an arbitrary number of simulated
listening scores. Unlike existing RF models, RF-GML accurately predicts
subjective quality scores across diverse content types and codecs. Extensive
evaluations demonstrate its superiority in rating unencoded audio and
distinguishing different levels of coding artifacts. RF-GML's performance and
versatility make it a valuable tool for coded audio quality assessment and
monitoring in various applications, all without the need for a reference
signal.
Generative speech enhancement methods based on generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models have shown promising results in various speech enhancement tasks. However, their performance in very low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) scenarios remains under-explored and limited, as these conditions pose significant challenges to both discriminative and generative state-of-the-art methods. To address this, we propose a method that leverages latent features extracted from discriminative speech enhancement models as generic conditioning features to improve GAN-based speech enhancement. The proposed method, referred to as DisCoGAN, demonstrates performance improvements over baseline models, particularly in low-SNR scenarios, while also maintaining competitive or superior performance in high-SNR conditions and on real-world recordings. We also conduct a comprehensive evaluation of conventional GAN-based architectures, including GANs trained end-to-end, GANs as a first processing stage, and post-filtering GANs, as well as discriminative models under low-SNR conditions. We show that DisCoGAN consistently outperforms existing methods. Finally, we present an ablation study that investigates the contributions of individual components within DisCoGAN and analyzes the impact of the discriminative conditioning method on overall performance.
State-of-the-art intent classification (IC) and slot filling (SF) methods
often rely on data-intensive deep learning models, limiting their practicality
for industry applications. Large language models on the other hand,
particularly instruction-tuned models (Instruct-LLMs), exhibit remarkable
zero-shot performance across various natural language tasks. This study
evaluates Instruct-LLMs on popular benchmark datasets for IC and SF,
emphasizing their capacity to learn from fewer examples. We introduce
ILLUMINER, an approach framing IC and SF as language generation tasks for
Instruct-LLMs, with a more efficient SF-prompting method compared to prior
work. A comprehensive comparison with multiple baselines shows that our
approach, using the FLAN-T5 11B model, outperforms the state-of-the-art joint
IC+SF method and in-context learning with GPT3.5 (175B), particularly in slot
filling by 11.1--32.2 percentage points. Additionally, our in-depth ablation
study demonstrates that parameter-efficient fine-tuning requires less than 6%
of training data to yield comparable performance with traditional full-weight
fine-tuning.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.