Hankuk University of Foreign Studies
Researchers systematically evaluated the performance of LLM-as-a-Judge and reward models using a new bilingual (Korean-English) dataset, KUDGE, to assess their efficacy in diverse contexts. The study found that English evaluation capabilities transfer effectively to Korean tasks, yet these automated evaluators exhibit critical weaknesses in detecting subtle factual or cultural errors and assessing complex reasoning challenges.
We propose DeepAries , a novel deep reinforcement learning framework for dynamic portfolio management that jointly optimizes the timing and allocation of rebalancing decisions. Unlike prior reinforcement learning methods that employ fixed rebalancing intervals regardless of market conditions, DeepAries adaptively selects optimal rebalancing intervals along with portfolio weights to reduce unnecessary transaction costs and maximize risk-adjusted returns. Our framework integrates a Transformer-based state encoder, which effectively captures complex long-term market dependencies, with Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) to generate simultaneous discrete (rebalancing intervals) and continuous (asset allocations) actions. Extensive experiments on multiple real-world financial markets demonstrate that DeepAries significantly outperforms traditional fixed-frequency and full-rebalancing strategies in terms of risk-adjusted returns, transaction costs, and drawdowns. Additionally, we provide a live demo of DeepAries at this https URL, along with the source code and dataset at this https URL, illustrating DeepAries' capability to produce interpretable rebalancing and allocation decisions aligned with shifting market regimes. Overall, DeepAries introduces an innovative paradigm for adaptive and practical portfolio management by integrating both timing and allocation into a unified decision-making process.
Large language models (LLMs) typically improve performance by either retrieving semantically similar information, or enhancing reasoning abilities through structured prompts like chain-of-thought. While both strategies are considered crucial, it remains unclear which has a greater impact on model performance or whether a combination of both is necessary. This paper answers this question by proposing a knowledge graph (KG)-based random-walk reasoning approach that leverages causal relationships. We conduct experiments on the commonsense question answering task that is based on a KG. The KG inherently provides both relevant information, such as related entity keywords, and a reasoning structure through the connections between nodes. Experimental results show that the proposed KG-based random-walk reasoning method improves the reasoning ability and performance of LLMs. Interestingly, incorporating three seemingly irrelevant sentences into the query using KG-based random-walk reasoning enhances LLM performance, contrary to conventional wisdom. These findings suggest that integrating causal structures into prompts can significantly improve reasoning capabilities, providing new insights into the role of causality in optimizing LLM performance.
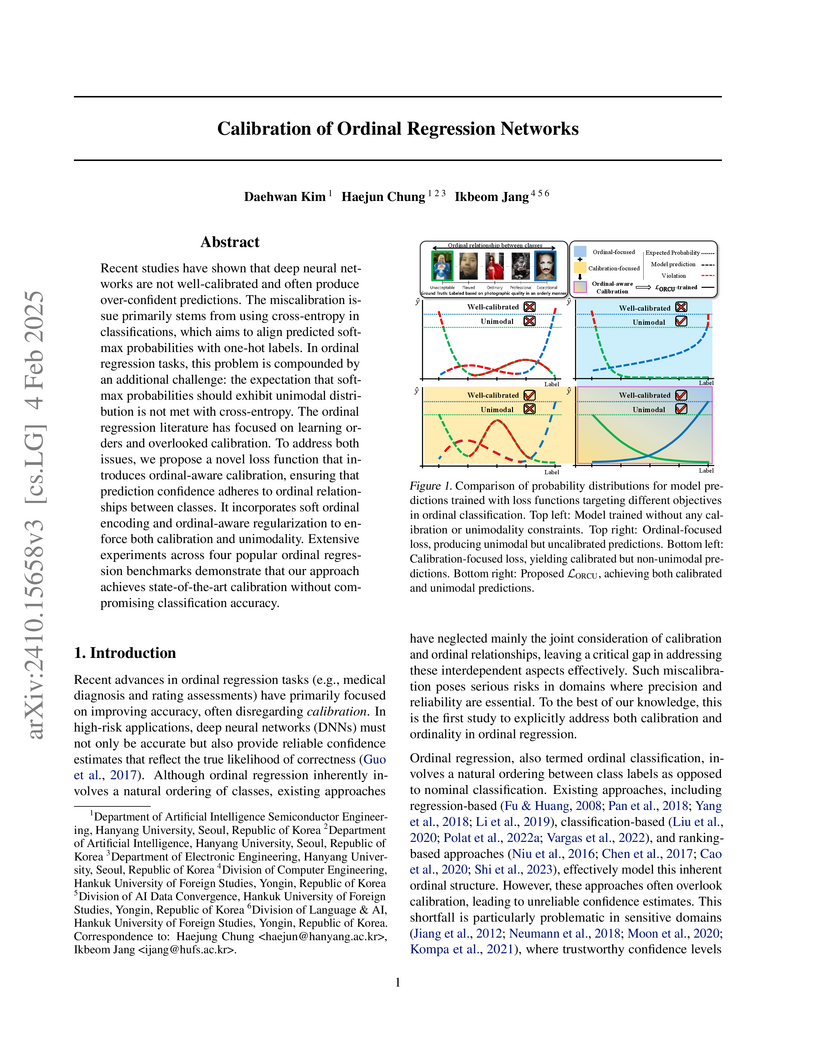
Researchers from Hanyang University and Hankuk University of Foreign Studies developed ORCU, a novel loss function for ordinal regression networks that simultaneously improves prediction calibration and enforces unimodality in output probability distributions. The method consistently achieves superior calibration and unimodality across diverse datasets while maintaining or enhancing classification accuracy metrics.
Conventional autonomous trading systems struggle to balance computational efficiency and market responsiveness due to their fixed operating frequency. We propose Hi-DARTS, a hierarchical multi-agent reinforcement learning framework that addresses this trade-off. Hi-DARTS utilizes a meta-agent to analyze market volatility and dynamically activate specialized Time Frame Agents for high-frequency or low-frequency trading as needed. During back-testing on AAPL stock from January 2024 to May 2025, Hi-DARTS yielded a cumulative return of 25.17% with a Sharpe Ratio of 0.75. This performance surpasses standard benchmarks, including a passive buy-and-hold strategy on AAPL (12.19% return) and the S&P 500 ETF (SPY) (20.01% return). Our work demonstrates that dynamic, hierarchical agents can achieve superior risk-adjusted returns while maintaining high computational efficiency.
Facial wrinkle detection plays a crucial role in cosmetic dermatology. Precise manual segmentation of facial wrinkles is challenging and time-consuming, with inherent subjectivity leading to inconsistent results among graders. To address this issue, we propose two solutions. First, we build and release the first public facial wrinkle dataset, 'FFHQ-Wrinkle', an extension of the NVIDIA FFHQ dataset. It includes 1,000 images with human labels and 50,000 images with automatically generated weak labels. This dataset could serve as a foundation for the research community to develop advanced wrinkle detection algorithms. Second, we introduce a simple training strategy utilizing texture maps, applicable to various segmentation models, to detect wrinkles across the face. Our two-stage training strategy first pretrain models on a large dataset with weak labels (N=50k), or masked texture maps generated through computer vision techniques, without human intervention. We then finetune the models using human-labeled data (N=1k), which consists of manually labeled wrinkle masks. The network takes as input a combination of RGB and masked texture map of the image, comprising four channels, in finetuning. We effectively combine labels from multiple annotators to minimize subjectivity in manual labeling. Our strategies demonstrate improved segmentation performance in facial wrinkle segmentation both quantitatively and visually compared to existing pretraining methods. The dataset is available at this https URL.
LLM-as-a-Judge frameworks exhibit a moderation bias, systematically overvaluing ethical refusals in model responses by rating them approximately four times higher than human evaluators do. This divergence challenges assumptions about automated AI evaluation and highlights a potential conflict between alignment-driven refusal behaviors and human user satisfaction.
GPO-VAE, developed by researchers at Korea University and Hankuk University of Foreign Studies, integrates gene regulatory network information directly into variational autoencoders to provide both accurate predictions of gene perturbation responses and biologically interpretable causal relationships. The model achieves state-of-the-art performance in predicting transcriptional responses while also inferring meaningful gene regulatory networks that align with known biological pathways.
We introduce a novel continued pre-training method, MELT (MatEriaLs-aware continued pre-Training), specifically designed to efficiently adapt the pre-trained language models (PLMs) for materials science. Unlike previous adaptation strategies that solely focus on constructing domain-specific corpus, MELT comprehensively considers both the corpus and the training strategy, given that materials science corpus has distinct characteristics from other domains. To this end, we first construct a comprehensive materials knowledge base from the scientific corpus by building semantic graphs. Leveraging this extracted knowledge, we integrate a curriculum into the adaptation process that begins with familiar and generalized concepts and progressively moves toward more specialized terms. We conduct extensive experiments across diverse benchmarks to verify the effectiveness and generality of MELT. A comprehensive evaluation convincingly supports the strength of MELT, demonstrating superior performance compared to existing continued pre-training methods. The in-depth analysis also shows that MELT enables PLMs to effectively represent materials entities compared to the existing adaptation methods, thereby highlighting its broad applicability across a wide spectrum of materials science.
There is a demand for medical image synthesis or translation to generate
synthetic images of missing modalities from available data. This need stems
from challenges such as restricted access to high-cost imaging devices,
government regulations, or failure to follow up with patients or study
participants. In medical imaging, preserving high-level semantic features is
often more critical than achieving pixel-level accuracy. Perceptual loss
functions are widely employed to train medical image synthesis or translation
models, as they quantify differences in high-level image features using a
pre-trained feature extraction network. While 3D and 2.5D perceptual losses are
used in 3D medical image synthesis, they face challenges, such as the lack of
pre-trained 3D models or difficulties in balancing loss reduction across
different planes. In this work, we focus on synthesizing 3D tau PET images from
3D T1-weighted MR images. We propose a cyclic 2.5D perceptual loss that
sequentially computes the 2D average perceptual loss for each of the axial,
coronal, and sagittal planes over epochs, with the cycle duration gradually
decreasing. Additionally, we process tau PET images using by-manufacturer
standardization to enhance the preservation of high-SUVR regions indicative of
tau pathology and mitigate SUVR variability caused by inter-manufacturer
differences. We combine the proposed loss with SSIM and MSE losses and
demonstrate its effectiveness in improving both quantitative and qualitative
performance across various generative models, including U-Net, UNETR,
SwinUNETR, CycleGAN, and Pix2Pix.
DeepClair, developed in collaboration with Shinhan Bank, effectively integrates pre-trained Transformer-based market forecasting into a deep reinforcement learning framework for automated portfolio selection, leveraging Low-Rank Adaptation for efficient optimization. This hybrid approach yielded superior annualized returns and risk-adjusted metrics across Nasdaq and Dow Jones datasets, demonstrating adaptive behavior during market shifts.
To cope with the negative oil futures price caused by the COVID-19 recession, global commodity futures exchanges temporarily switched the option model from Black--Scholes to Bachelier in 2020. This study reviews the literature on Bachelier's pioneering option pricing model and summarizes the practical results on volatility conversion, risk management, stochastic volatility, and barrier options pricing to facilitate the model transition. In particular, using the displaced Black-Scholes model as a model family with the Black-Scholes and Bachelier models as special cases, we not only connect the two models but also present a continuous spectrum of model choices.
Organizational efforts to utilize and operationalize artificial intelligence (AI) are often accompanied by substantial challenges, including scalability, maintenance, and coordination across teams. In response, the concept of Machine Learning Operations (MLOps) has emerged as a set of best practices that integrate software engineering principles with the unique demands of managing the ML lifecycle. Yet, empirical evidence on whether and how these practices support users in developing and operationalizing AI applications remains limited. To address this gap, this study analyzes over 8,000 user reviews of AI development platforms from this http URL. Using zero-shot classification, we measure review sentiment toward nine established MLOps practices, including continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD), workflow orchestration, reproducibility, versioning, collaboration, and monitoring. Seven of the nine practices show a significant positive relationship with user satisfaction, suggesting that effective MLOps implementation contributes tangible value to AI development. However, organizational context also matters: reviewers from small firms discuss certain MLOps practices less frequently, suggesting that organizational context influences the prevalence and salience of MLOps, though firm size does not moderate the MLOps-satisfaction link. This indicates that once applied, MLOps practices are perceived as universally beneficial across organizational settings.
Hierarchical Mutual Distillation for Multi-View Fusion: Learning from All Possible View Combinations
Hierarchical Mutual Distillation for Multi-View Fusion: Learning from All Possible View Combinations
Multi-view learning often faces challenges in effectively leveraging images captured from different angles and locations. This challenge is particularly pronounced when addressing inconsistencies and uncertainties between views. In this paper, we propose a novel Multi-View Uncertainty-Weighted Mutual Distillation (MV-UWMD) method. Our method enhances prediction consistency by performing hierarchical mutual distillation across all possible view combinations, including single-view, partial multi-view, and full multi-view predictions. This introduces an uncertainty-based weighting mechanism through mutual distillation, allowing effective exploitation of unique information from each view while mitigating the impact of uncertain predictions. We extend a CNN-Transformer hybrid architecture to facilitate robust feature learning and integration across multiple view combinations. We conducted extensive experiments using a large, unstructured dataset captured from diverse, non-fixed viewpoints. The results demonstrate that MV-UWMD improves prediction accuracy and consistency compared to existing multi-view learning approaches.
29 Oct 2025
Accurate prediction of the radar cross section (RCS) of chaff clouds requires careful consideration of aerodynamic effects, as the orientation and spatial distribution of individual chaff elements evolve significantly after deployment. Building upon conventional six-degree-of-freedom (6-DoF) formulations for chaff aerodynamic analysis-which assumed straight or two-dimensionally bent geometries-we extend the framework to incorporate arbitrarily curved three-dimensional chaff geometries. This extension enables accurate modeling of both flattened and helical dynamics induced by aerodynamic moments acting along the roll, pitch, and yaw directions, thereby providing a more comprehensive and realistic description of chaff motion. We then finally develop a coupled aerodynamic-electromagnetic framework that integrates the extended aerodynamic model with our recently developed fast method-of-moments solver, which is optimized for efficiently estimating the RCS of million-scale chaff clouds. The proposed multiphysics coupled framework allows real-time, first-principles prediction of the monostatic and bistatic RCS of large-scale chaff clouds with arbitrary geometries, orientations, and lengths, accurately incorporating their time-varying aerodynamic evolution. Simulation results confirm that the monostatic RCS is strongly influenced by aerodynamic effects, with the coexistence of flattened and helical motions playing a critical role in determining the overall scattering response. The proposed framework thus provides a physically grounded and computationally efficient approach for predicting the RCS of large-scale chaff clouds. Furthermore, it can be directly extended to radar signal processing applications by utilizing multi-frequency complex-valued far-field responses, thereby enabling the reconstruction of Range-Doppler, Range-Angle, and Doppler-Angle maps.
11 May 2024
Relevance evaluation of a query and a passage is essential in Information Retrieval (IR). Recently, numerous studies have been conducted on tasks related to relevance judgment using Large Language Models (LLMs) such as GPT-4, demonstrating significant improvements. However, the efficacy of LLMs is considerably influenced by the design of the prompt. The purpose of this paper is to identify which specific terms in prompts positively or negatively impact relevance evaluation with LLMs. We employed two types of prompts: those used in previous research and generated automatically by LLMs. By comparing the performance of these prompts in both few-shot and zero-shot settings, we analyze the influence of specific terms in the prompts. We have observed two main findings from our study. First, we discovered that prompts using the term answerlead to more effective relevance evaluations than those using relevant. This indicates that a more direct approach, focusing on answering the query, tends to enhance performance. Second, we noted the importance of appropriately balancing the scope of relevance. While the term relevant can extend the scope too broadly, resulting in less precise evaluations, an optimal balance in defining relevance is crucial for accurate assessments. The inclusion of few-shot examples helps in more precisely defining this balance. By providing clearer contexts for the term relevance, few-shot examples contribute to refine relevance criteria. In conclusion, our study highlights the significance of carefully selecting terms in prompts for relevance evaluation with LLMs.
This paper proposes a simple yet effective convolutional module for long-term time series forecasting. The proposed block, inspired by the Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) model, consists of two convolutional components: one for capturing the trend (autoregression) and the other for refining local variations (moving average). Unlike conventional ARIMA, which requires iterative multi-step forecasting, the block directly performs multi-step forecasting, making it easily extendable to multivariate settings. Experiments on nine widely used benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method ARMA achieves competitive accuracy, particularly on datasets exhibiting strong trend variations, while maintaining architectural simplicity. Furthermore, analysis shows that the block inherently encodes absolute positional information, suggesting its potential as a lightweight replacement for positional embeddings in sequential models.
02 Sep 2024
A graph G is k-critical (list k-critical, DP k-critical) if χ(G)=k (χℓ(G)=k, χDP(G)=k) and for every proper subgraph G′ of G, χ(G′)(k−1+⌈2k−7k2−7⌉−1)2n.Thisisthefirstboundonf_\mathrm{DP}(n,k)thatisasymptoticallybetterthanthewell−knownboundonf(n,k)byGallaifrom1963.Theresultalsoyieldsaslightlybetterboundonf_{\ell}(n,k)$ than the ones known before.
Human-AI Interaction (HAI) guidelines and design principles have become
increasingly important in both industry and academia to guide the development
of AI systems that align with user needs and expectations. However, large-scale
empirical evidence on how HAI principles shape user satisfaction in practice
remains limited. This study addresses that gap by analyzing over 100,000 user
reviews of AI-related products from G2.com, a leading review platform for
business software and services. Based on widely adopted industry guidelines, we
identify seven core HAI dimensions and examine their coverage and sentiment
within the reviews. We find that the sentiment on four HAI
dimensions-adaptability, customization, error recovery, and security-is
positively associated with overall user satisfaction. Moreover, we show that
engagement with HAI dimensions varies by professional background: Users with
technical job roles are more likely to discuss system-focused aspects, such as
reliability, while non-technical users emphasize interaction-focused features
like customization and feedback. Interestingly, the relationship between HAI
sentiment and overall satisfaction is not moderated by job role, suggesting
that once an HAI dimension has been identified by users, its effect on
satisfaction is consistent across job roles.
Congenital heart disease is among the most common fetal abnormalities and birth defects. Despite identifying numerous risk factors influencing its onset, a comprehensive understanding of its genesis and management across diverse populations remains limited. Recent advancements in machine learning have demonstrated the potential for leveraging patient data to enable early congenital heart disease detection. Over the past seven years, researchers have proposed various data-driven and algorithmic solutions to address this challenge. This paper presents a systematic review of congential heart disease recognition using machine learning, conducting a meta-analysis of 432 references from leading journals published between 2018 and 2024. A detailed investigation of 74 scholarly works highlights key factors, including databases, algorithms, applications, and solutions. Additionally, the survey outlines reported datasets used by machine learning experts for congenital heart disease recognition. Using a systematic literature review methodology, this study identifies critical challenges and opportunities in applying machine learning to congenital heart disease.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.