Hong Kong Baptist University
 KAIST
KAIST University of Washington
University of Washington University of Toronto
University of Toronto Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University Université de Montréal
Université de Montréal New York University
New York University University of Chicago
University of Chicago UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley University of Oxford
University of Oxford Stanford University
Stanford University University of Michigan
University of Michigan Cornell University
Cornell University Nanyang Technological UniversityVector InstituteLG AI Research
Nanyang Technological UniversityVector InstituteLG AI Research MIT
MIT HKUSTUniversity of TübingenHong Kong Baptist University
HKUSTUniversity of TübingenHong Kong Baptist University University of California, Santa CruzCenter for AI SafetyGray Swan AIBeneficial AI ResearchConjectureLawZeroUniversity of Wisconsin
–MadisonMorph LabsInstitute for Applied PsychometricsCSER
University of California, Santa CruzCenter for AI SafetyGray Swan AIBeneficial AI ResearchConjectureLawZeroUniversity of Wisconsin
–MadisonMorph LabsInstitute for Applied PsychometricsCSERThe lack of a concrete definition for Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) obscures the gap between today's specialized AI and human-level cognition. This paper introduces a quantifiable framework to address this, defining AGI as matching the cognitive versatility and proficiency of a well-educated adult. To operationalize this, we ground our methodology in Cattell-Horn-Carroll theory, the most empirically validated model of human cognition. The framework dissects general intelligence into ten core cognitive domains-including reasoning, memory, and perception-and adapts established human psychometric batteries to evaluate AI systems. Application of this framework reveals a highly "jagged" cognitive profile in contemporary models. While proficient in knowledge-intensive domains, current AI systems have critical deficits in foundational cognitive machinery, particularly long-term memory storage. The resulting AGI scores (e.g., GPT-4 at 27%, GPT-5 at 57%) concretely quantify both rapid progress and the substantial gap remaining before AGI.
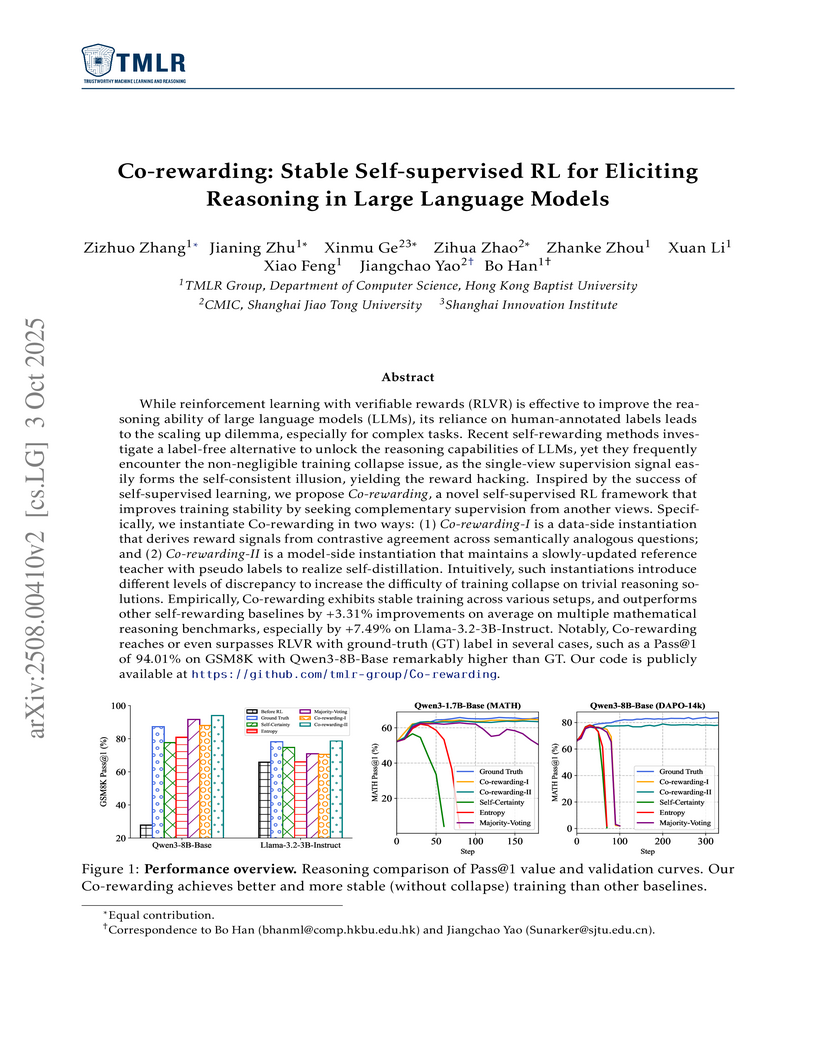
Co-rewarding establishes a stable self-supervised reinforcement learning framework for large language models, leveraging complementary supervision via data-side analogy-invariance and model-side temporal invariance. This effectively prevents training collapse and reward hacking, leading to enhanced reasoning capabilities that often surpass prior self-rewarding methods and sometimes rival ground-truth supervised approaches.
ScreenSpot-Pro introduces a benchmark for GUI grounding in professional, high-resolution computing environments, where existing MLLMs struggle to precisely locate UI elements. The paper also presents ScreenSeekeR, an agentic framework that guides a grounding model through hierarchical visual search, improving accuracy from 18.9% to 48.1% on the new benchmark without retraining.
Llasa introduces a unified, Llama-based architecture for speech synthesis that simplifies the text-to-speech pipeline to a single Transformer and a novel speech tokenizer. The work systematically investigates train-time and inference-time scaling, showing consistent quality improvements and strong performance on both speech generation and understanding tasks.
Revealing hidden causal variables alongside the underlying causal mechanisms is essential to the development of science. Despite the progress in the past decades, existing practice in causal discovery (CD) heavily relies on high-quality measured variables, which are usually given by human experts. In fact, the lack of well-defined high-level variables behind unstructured data has been a longstanding roadblock to a broader real-world application of CD. This procedure can naturally benefit from an automated process that can suggest potential hidden variables in the system. Interestingly, Large language models (LLMs) are trained on massive observations of the world and have demonstrated great capability in processing unstructured data. To leverage the power of LLMs, we develop a new framework termed Causal representatiOn AssistanT (COAT) that incorporates the rich world knowledge of LLMs to propose useful measured variables for CD with respect to high-value target variables on their paired unstructured data. Instead of directly inferring causality with LLMs, COAT constructs feedback from intermediate CD results to LLMs to refine the proposed variables. Given the target variable and the paired unstructured data, we first develop COAT-MB that leverages the predictivity of the proposed variables to iteratively uncover the Markov Blanket of the target variable. Built upon COAT-MB, COAT-PAG further extends to uncover a more complete causal graph, i.e., Partial Ancestral Graph, by iterating over the target variables and actively seeking new high-level variables. Moreover, the reliable CD capabilities of COAT also extend the debiased causal inference to unstructured data by discovering an adjustment set. We establish theoretical guarantees for the CD results and verify their efficiency and reliability across realistic benchmarks and real-world case studies.
Researchers at South China University of Technology and collaborators introduced NSG-VD, a physics-driven method utilizing a Normalized Spatiotemporal Gradient (NSG) and Maximum Mean Discrepancy, to detect AI-generated videos by identifying violations of physical continuity. The approach achieves superior detection performance on advanced generative models like Sora and demonstrates strong robustness in data-imbalanced settings.
The VISIONARY-R1 framework trains visual language models for complex reasoning using reinforcement learning and CoT-free question-answer pairs, outperforming leading proprietary models like GPT-4o on benchmarks such as MathVista. It effectively mitigates shortcut learning in VLMs by enforcing a structured caption-reason-answer output and employing an AI-feedback-based caption reward.
20 Nov 2025
Researchers introduce DualMindVLM, a Visual Language Model capable of automatically switching between fast and slow thinking modes based on task complexity. This approach achieves competitive accuracy with leading reasoning VLMs while reducing token usage by approximately 40% and exhibiting improved hallucination mitigation.
WizardCoder, a Code Large Language Model, leverages a tailored instruction-tuning method called Code Evol-Instruct to generate complex programming tasks. This approach enables open-source models to achieve state-of-the-art performance, surpassing GPT-3.5 on HumanEval+ and leading all open-source baselines across multiple code generation benchmarks.
Researchers from HKUST and collaborators developed X-Codec, an audio codec that embeds semantic information directly into its unified tokens. This design improves the performance of audio Large Language Models across various tasks, including reducing Word Error Rate in Text-to-Speech by up to 58% and enhancing music and general sound generation fidelity.
Model inversion attacks (MIAs) aim to reconstruct class-representative samples from trained models. Recent generative MIAs utilize generative adversarial networks to learn image priors that guide the inversion process, yielding reconstructions with high visual quality and strong fidelity to the private training data. To explore the reason behind their effectiveness, we begin by examining the gradients of inversion loss with respect to synthetic inputs, and find that these gradients are surprisingly noisy. Further analysis reveals that generative inversion implicitly denoises these gradients by projecting them onto the tangent space of the generator manifold, filtering out off-manifold components while preserving informative directions aligned with the manifold. Our empirical measurements show that, in models trained with standard supervision, loss gradients often exhibit large angular deviations from the data manifold, indicating poor alignment with class-relevant directions. This observation motivates our central hypothesis: models become more vulnerable to MIAs when their loss gradients align more closely with the generator manifold. We validate this hypothesis by designing a novel training objective that explicitly promotes such alignment. Building on this insight, we further introduce a training-free approach to enhance gradient-manifold alignment during inversion, leading to consistent improvements over state-of-the-art generative MIAs.
05 Nov 2025
The creation of high-quality datasets to improve Large Language Model (LLM) reasoning remains a significant challenge, as current methods often suffer from generating low-quality/incorrect answers and limited information richness from available data sources. To address this, we propose AgenticMath, a novel agentic pipeline for generating high-quality mathematical question-answer pairs to enhance the supervised fine-tuning of LLMs. Our method operates through four stages: (1) Seed Question Filter that selects questions with high information richness, complexity, and clarity; (2) an Agentic Question Rephrase step that employs a multi-agent system to generate diverse, logically consistent paraphrases; (3) an Answer Augment step where rewrite answers using chain-of-thought reasoning to enhance numerical and logical correctness, without reliance on human-provided labels; and (4) a final Question and Answer Evaluation that retains only the most superior pairs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that, fine-tuning 3B-8B parameter LLMs on AgenticMath generated datasets (comprising only 30-60K math samples) achieves competitive or superior performance on diverse in domain and out-of-domain mathematical reasoning benchmarks compared to baselines trained on much more data (e.g., 400K or 2.3M samples). Our work demonstrates that targeted, high-quality data generation is a more efficient path to improving mathematical reasoning in LLMs than large-scale, low-quality alternatives.
EEPO introduces a "sample-then-forget" mechanism for Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) to combat entropy collapse by temporarily suppressing previously sampled responses during rollouts. It achieves average relative gains of 24.3% on Qwen2.5-3B and 33.0% on Llama3.2-3B-Instruct across mathematical reasoning benchmarks, maintaining higher policy entropy and improved generalization.
This research introduces AR-Bench, a new benchmark to assess Large Language Models' (LLMs) active reasoning abilities under incomplete information, revealing that current LLMs, including GPT-4o, struggle with interactive questioning and iterative information acquisition.
MMCode introduces the first multimodal benchmark to evaluate large multimodal models' (LMMs) ability to generate code from programming problems featuring visually rich information, demonstrating that even state-of-the-art LMMs like GPT-4V achieve only a 19.4% Pass@1 rate, highlighting current models' significant limitations in this domain.
A new Transformer-based architecture introduces the first feed-forward unified framework for 4D language grounding, enabling open-vocabulary querying in dynamic environments without per-scene optimization. This approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on HyperNeRF and Neu3D datasets, demonstrating up to a 3% mIoU improvement and strong generalization capabilities for both time-agnostic and time-sensitive queries.
Researchers identified a 'thinking-language modeling gap' in LLMs, where models learn from language expressions rather than underlying thought processes, often leading to reasoning biases when implicit information is present. They developed Language-of-Thoughts (LoT) prompting, a three-component approach (Observe, Expand, Echo) that explicitly addresses this implicitness, consistently outperforming Chain-of-Thought prompting on various reasoning benchmarks like GPQA, LSAT, and FOLIO across multiple LLM models.
18 Sep 2025
A comprehensive, ethics-informed framework outlines the integration of AI, especially Large Language Models, into academic peer review, systematically addressing challenges and opportunities. It demonstrates how AI can mitigate persistent issues like lengthy publication delays and reviewer burden, offering specific safeguards against concerns such as hallucination and bias, and suggesting advanced AI architectures for improved performance.
Researchers at The Hong Kong Polytechnic University and Hong Kong Baptist University developed DiPro, a framework that models disease progression by disentangling dynamic pathological changes from static anatomical features in sequential chest X-rays and aligning these with electronic health records across multiple timescales. DiPro achieved improved performance in disease progression identification and general ICU prediction tasks while offering clinically aligned interpretations.
The ReG framework improves graph-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation by aligning weak retrievers with Large Language Models, using LLM-refined supervision signals and structure-aware knowledge reorganization. This approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on WebQSP and CWQ datasets, notably outperforming baselines even with 5% of the training data and reducing LLM reasoning token usage by up to 30%.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.