JD Explore Academy
Researchers developed and experimentally validated a reinforcement learning-based quantum compiler on a 9-qubit superconducting processor, demonstrating its ability to find shorter, hardware-optimized quantum circuits. This approach achieved superior experimental fidelities on noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) devices compared to conventional compilation methods, notably reducing the 3-qubit Quantum Fourier Transform to just seven CZ gates.
Research from The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou) and collaborators reveals that spiking neurons intrinsically act as low-pass filters, attenuating high-frequency information crucial for network performance. By introducing high-frequency-preserving operators like Max-Pool and Depth-Wise Convolution in Max-Former and Max-ResNet architectures, the work substantially improves SNN accuracy, achieving 82.39% top-1 on ImageNet with 30% less energy than prior spiking models.
ViTPose introduces a straightforward approach to human pose estimation by leveraging plain vision transformers as the exclusive backbone, paired with a minimal decoder. The method demonstrates robust performance, achieving 80.9 AP on the MS COCO test-dev set with a single model and showcasing the strong feature representation capabilities of simple ViT architectures.
A comprehensive survey categorizes self-supervised learning algorithms into context-based, contrastive, generative, and hybrid approaches, exploring their evolution, theoretical underpinnings, and applications in computer vision and natural language processing. It comparatively analyzes their performance characteristics and identifies key future research directions and open questions.
The ONE FOR ALL (OFA) framework introduces a graph foundation model that unifies heterogeneous graph data and diverse graph classification tasks using Large Language Models (LLMs) and a novel graph prompting paradigm, achieving strong performance in supervised, few-shot, and zero-shot learning across various domains. A single OFA model, trained jointly on multiple datasets, consistently performs well across node, link, and graph classification tasks, showcasing cross-domain and cross-task generalization.
AdaMerging presents an adaptive, unsupervised method to merge independently fine-tuned deep learning models for multi-task learning by optimizing task-wise or layer-wise coefficients through entropy minimization on unlabeled test data. This approach significantly enhances multi-task performance, generalization, and robustness, achieving an 11% average accuracy improvement over Task Arithmetic on ViT-B/32 while operating without original training data.
04 Aug 2025
Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models demonstrate significant potential for developing generalized policies in real-world robotic control. This progress inspires researchers to explore fine-tuning these models with Reinforcement Learning (RL). However, fine-tuning VLA models with RL still faces challenges related to sample efficiency, compatibility with action chunking, and training stability. To address these challenges, we explore the fine-tuning of VLA models through offline reinforcement learning incorporating action chunking. In this work, we propose Chunked RL, a novel reinforcement learning framework specifically designed for VLA models. Within this framework, we extend temporal difference (TD) learning to incorporate action chunking, a prominent characteristic of VLA models. Building upon this framework, we propose CO-RFT, an algorithm aimed at fine-tuning VLA models using a limited set of demonstrations (30 to 60 samples). Specifically, we first conduct imitation learning (IL) with full parameter fine-tuning to initialize both the backbone and the policy. Subsequently, we implement offline RL with action chunking to optimize the pretrained policy. Our empirical results in real-world environments demonstrate that CO-RFT outperforms previous supervised methods, achieving a 57% improvement in success rate and a 22.3% reduction in cycle time. Moreover, our method exhibits robust positional generalization capabilities, attaining a success rate of 44.3% in previously unseen positions.
14 Oct 2025
Researchers introduce Reflective Self-Adaptation, a framework that enables Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models to autonomously adapt to novel robotic manipulation tasks by combining failure-driven reinforcement learning with success-driven supervised fine-tuning. This approach achieved an 83.6% average success rate on the LIBERO benchmark and demonstrated faster, more stable convergence on adaptation tasks compared to baselines.
Researchers from The University of Sydney introduced ViTPose++, a framework that uses plain, non-hierarchical Vision Transformers with simple decoders for generic body pose estimation. This approach achieved state-of-the-art performance across human, whole-body, and animal keypoint detection by implementing knowledge factorization, while also showcasing strong scalability and data efficiency.
Weight-Ensembling Mixture of Experts (WEMoE) dynamically integrates shared and task-specific knowledge within Transformer-based vision models, allowing for the unified execution of multiple tasks from separately fine-tuned models. This method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art static merging techniques and traditional multi-task learning baselines, achieving a 0.5% average accuracy improvement over MTL for CLIP-ViT-B/32 models while also demonstrating strong generalization and robustness.
A new method, CommFormer, learns an optimal communication graph for multi-agent systems through a bi-level optimization framework, achieving performance comparable to fully connected communication while utilizing only 40% of possible communication channels in environments like StarCraft II.
Learning-based optical flow estimation has been dominated with the pipeline of cost volume with convolutions for flow regression, which is inherently limited to local correlations and thus is hard to address the long-standing challenge of large displacements. To alleviate this, the state-of-the-art framework RAFT gradually improves its prediction quality by using a large number of iterative refinements, achieving remarkable performance but introducing linearly increasing inference time. To enable both high accuracy and efficiency, we completely revamp the dominant flow regression pipeline by reformulating optical flow as a global matching problem, which identifies the correspondences by directly comparing feature similarities. Specifically, we propose a GMFlow framework, which consists of three main components: a customized Transformer for feature enhancement, a correlation and softmax layer for global feature matching, and a self-attention layer for flow propagation. We further introduce a refinement step that reuses GMFlow at higher feature resolution for residual flow prediction. Our new framework outperforms 31-refinements RAFT on the challenging Sintel benchmark, while using only one refinement and running faster, suggesting a new paradigm for accurate and efficient optical flow estimation. Code is available at this https URL.
Researchers from JD Explore Academy and academic partners introduce HOIGen-1M, a dataset of over 1 million high-quality human-object interaction videos with detailed captions, along with new evaluation metrics and a multi-expert captioning system that enables more accurate generation of interaction-focused videos.
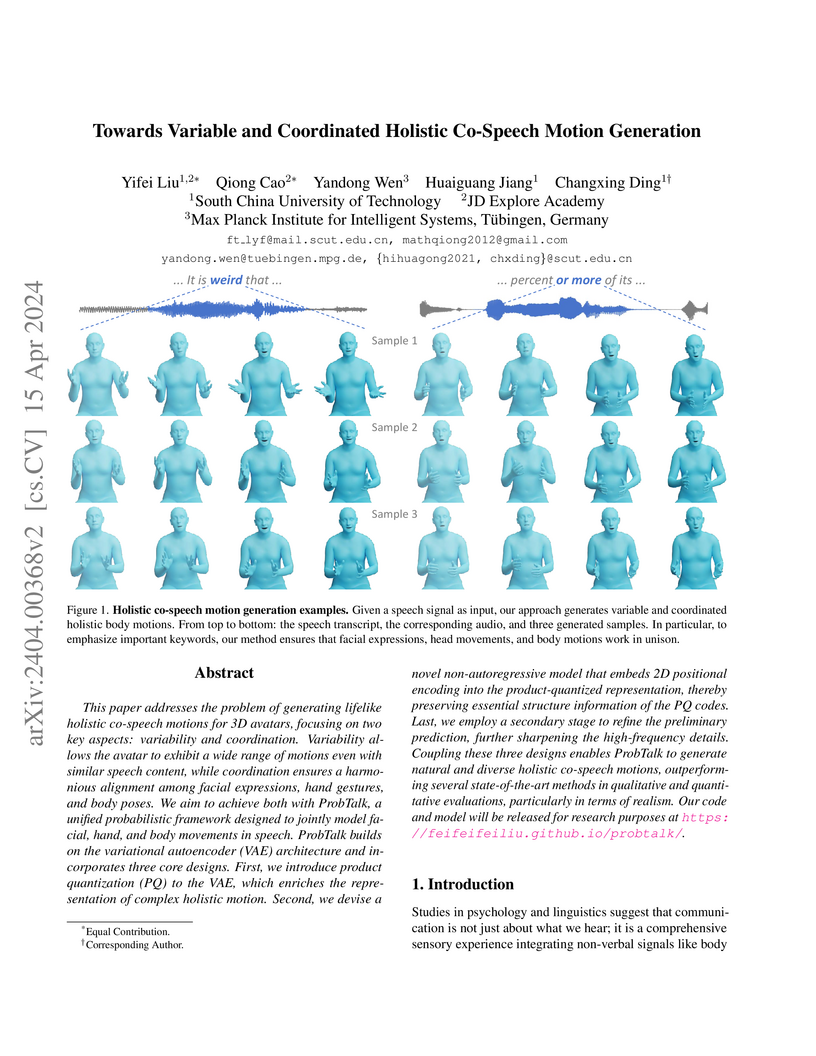
A unified probabilistic framework, ProbTalk, enables the generation of variable and coordinated holistic co-speech motions for faces, hands, and bodies. It produces highly realistic and diverse movements efficiently, outperforming existing state-of-the-art methods on standard benchmarks.
Recent advancements in offline reinforcement learning (RL) have underscored the capabilities of Conditional Sequence Modeling (CSM), a paradigm that learns the action distribution based on history trajectory and target returns for each state. However, these methods often struggle with stitching together optimal trajectories from sub-optimal ones due to the inconsistency between the sampled returns within individual trajectories and the optimal returns across multiple trajectories. Fortunately, Dynamic Programming (DP) methods offer a solution by leveraging a value function to approximate optimal future returns for each state, while these techniques are prone to unstable learning behaviors, particularly in long-horizon and sparse-reward scenarios. Building upon these insights, we propose the Q-value regularized Transformer (QT), which combines the trajectory modeling ability of the Transformer with the predictability of optimal future returns from DP methods. QT learns an action-value function and integrates a term maximizing action-values into the training loss of CSM, which aims to seek optimal actions that align closely with the behavior policy. Empirical evaluations on D4RL benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of QT over traditional DP and CSM methods, highlighting the potential of QT to enhance the state-of-the-art in offline RL.
ST-P3 proposes an end-to-end vision-based autonomous driving framework that integrates perception, prediction, and planning via spatial-temporal feature learning. It achieves state-of-the-art performance on nuScenes and CARLA benchmarks, demonstrating enhanced BEV scene understanding, robust future prediction, and safe closed-loop planning compared to prior vision-only methods.
A new method called L-LoRA enhances multi-task model fusion for parameter-efficiently fine-tuned models by partially linearizing adapter modules, demonstrating improved performance and reduced representational interference while maintaining computational efficiency.
Representation Surgery addresses "representation bias," a key limitation in multi-task models created by merging independently trained models, by introducing lightweight, task-specific modules that align the merged model's feature distributions with those of individual models. This method significantly improves multi-task performance, bringing merged models like AdaMerging within 1.4% of traditional joint training on ViT-B/32 for average accuracy across eight vision tasks.
We present a unified formulation and model for three motion and 3D perception tasks: optical flow, rectified stereo matching and unrectified stereo depth estimation from posed images. Unlike previous specialized architectures for each specific task, we formulate all three tasks as a unified dense correspondence matching problem, which can be solved with a single model by directly comparing feature similarities. Such a formulation calls for discriminative feature representations, which we achieve using a Transformer, in particular the cross-attention mechanism. We demonstrate that cross-attention enables integration of knowledge from another image via cross-view interactions, which greatly improves the quality of the extracted features. Our unified model naturally enables cross-task transfer since the model architecture and parameters are shared across tasks. We outperform RAFT with our unified model on the challenging Sintel dataset, and our final model that uses a few additional task-specific refinement steps outperforms or compares favorably to recent state-of-the-art methods on 10 popular flow, stereo and depth datasets, while being simpler and more efficient in terms of model design and inference speed.
A zero-shot Sparse Mixture of Low-rank Experts (SMILE) framework enables the efficient construction of multi-task models from pre-trained foundation models without requiring additional training data. This approach effectively mitigates parameter interference and achieves performance comparable to individual fine-tuned models with minimal parameter overhead, such as a 2% increase for LoRA-tuned Flan-T5.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.