JP Morgan AI Research
02 Oct 2025
We present DexUMI - a data collection and policy learning framework that uses the human hand as the natural interface to transfer dexterous manipulation skills to various robot hands. DexUMI includes hardware and software adaptations to minimize the embodiment gap between the human hand and various robot hands. The hardware adaptation bridges the kinematics gap using a wearable hand exoskeleton. It allows direct haptic feedback in manipulation data collection and adapts human motion to feasible robot hand motion. The software adaptation bridges the visual gap by replacing the human hand in video data with high-fidelity robot hand inpainting. We demonstrate DexUMI's capabilities through comprehensive real-world experiments on two different dexterous robot hand hardware platforms, achieving an average task success rate of 86%.
Im2Flow2Act introduces object flow as a cross-domain manipulation interface, enabling robots to learn real-world skills from human demonstration videos and simulated robot play data without requiring real-world robot training. The framework achieved up to 90% success rates on diverse manipulation tasks involving rigid, articulated, and deformable objects in real-world environments.
MaxMin-RLHF introduces a framework for aligning large language models with diverse human preferences, demonstrating that single-reward models inherently fail to represent minority opinions. It learns distinct reward functions for different user sub-populations and optimizes to maximize the minimum utility across these groups, achieving more equitable alignment outcomes on both small-scale (GPT-2) and large-scale (Tulu2-7B) language models.
Graph Belief Propagation Networks (GBPNs) integrate the statistical rigor of Collective Classification with the scalability of Graph Neural Networks for semi-supervised node classification, modeling node labels as a Conditional Random Field with learned self-potentials and interpretable coupling potentials. The model demonstrates superior accuracy on synthetic MRF data and competitive to superior performance on empirical datasets, notably achieving a 3.8% F1 score improvement over baselines on the 'Payments' financial dataset and effectively handling heterophilous graphs.
Machine unlearning techniques aim to mitigate unintended memorization in large language models (LLMs). However, existing approaches predominantly focus on the explicit removal of isolated facts, often overlooking latent inferential dependencies and the non-deterministic nature of knowledge within LLMs. Consequently, facts presumed forgotten may persist implicitly through correlated information. To address these challenges, we propose a knowledge unlearning evaluation framework that more accurately captures the implicit structure of real-world knowledge by representing relevant factual contexts as knowledge graphs with associated confidence scores. We further develop an inference-based evaluation protocol leveraging powerful LLMs as judges; these judges reason over the extracted knowledge subgraph to determine unlearning success. Our LLM judges utilize carefully designed prompts and are calibrated against human evaluations to ensure their trustworthiness and stability. Extensive experiments on our newly constructed benchmark demonstrate that our framework provides a more realistic and rigorous assessment of unlearning performance. Moreover, our findings reveal that current evaluation strategies tend to overestimate unlearning effectiveness. Our code is publicly available at this https URL.
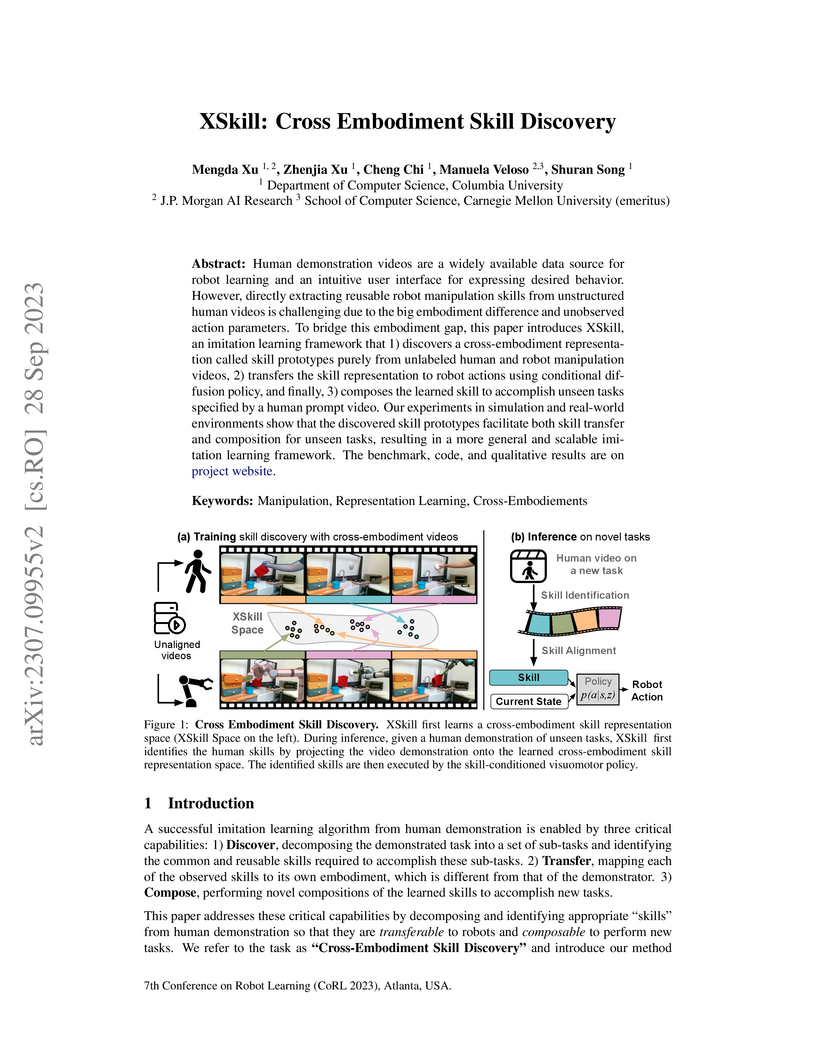
XSkill enables robots to acquire complex manipulation skills from unlabeled, unaligned human demonstration videos by discovering shared skill representations across different embodiments. This framework allows for one-shot learning of novel tasks through skill composition, achieving up to 70.2% success in simulation and 60% in real-world four-subtask compositions with human video prompts.
While financial data presents one of the most challenging and interesting sequence modelling tasks due to high noise, heavy tails, and strategic interactions, progress in this area has been hindered by the lack of consensus on quantitative evaluation paradigms. To address this, we present LOB-Bench, a benchmark, implemented in python, designed to evaluate the quality and realism of generative message-by-order data for limit order books (LOB) in the LOBSTER format. Our framework measures distributional differences in conditional and unconditional statistics between generated and real LOB data, supporting flexible multivariate statistical evaluation. The benchmark also includes features commonly used LOB statistics such as spread, order book volumes, order imbalance, and message inter-arrival times, along with scores from a trained discriminator network. Lastly, LOB-Bench contains "market impact metrics", i.e. the cross-correlations and price response functions for specific events in the data. We benchmark generative autoregressive state-space models, a (C)GAN, as well as a parametric LOB model and find that the autoregressive GenAI approach beats traditional model classes.
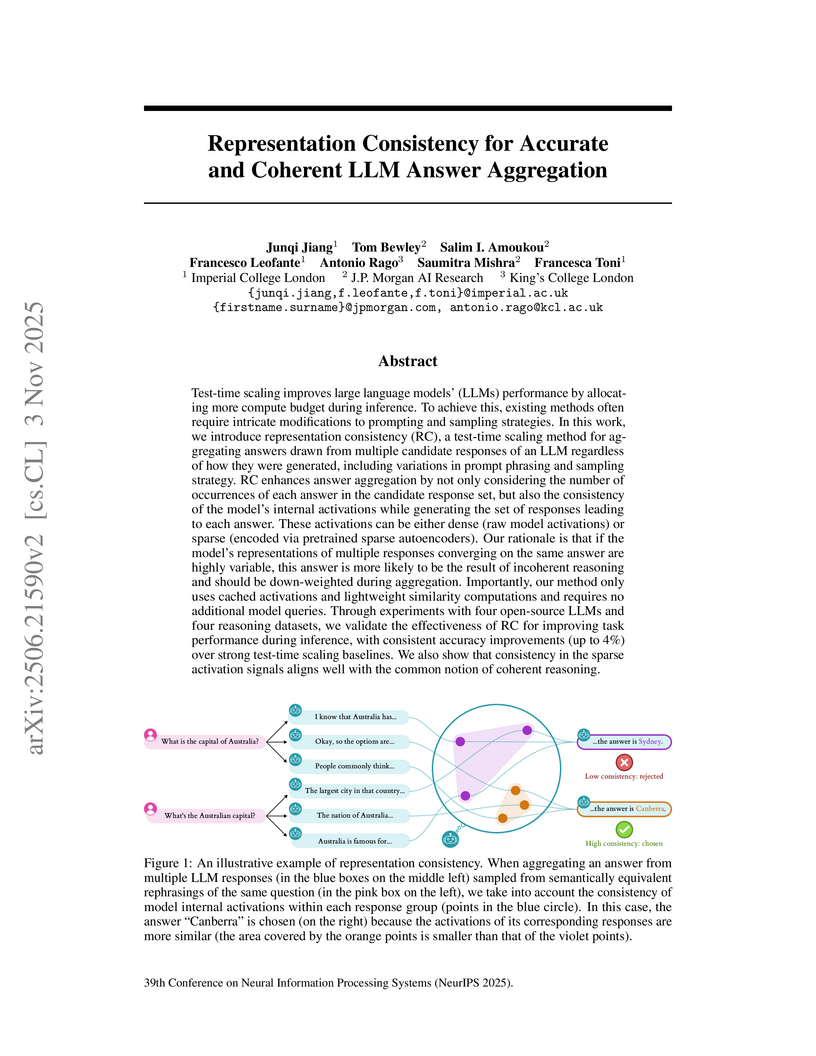
Test-time scaling improves large language models' (LLMs) performance by allocating more compute budget during inference. To achieve this, existing methods often require intricate modifications to prompting and sampling strategies. In this work, we introduce representation consistency (RC), a test-time scaling method for aggregating answers drawn from multiple candidate responses of an LLM regardless of how they were generated, including variations in prompt phrasing and sampling strategy. RC enhances answer aggregation by not only considering the number of occurrences of each answer in the candidate response set, but also the consistency of the model's internal activations while generating the set of responses leading to each answer. These activations can be either dense (raw model activations) or sparse (encoded via pretrained sparse autoencoders). Our rationale is that if the model's representations of multiple responses converging on the same answer are highly variable, this answer is more likely to be the result of incoherent reasoning and should be down-weighted during aggregation. Importantly, our method only uses cached activations and lightweight similarity computations and requires no additional model queries. Through experiments with four open-source LLMs and four reasoning datasets, we validate the effectiveness of RC for improving task performance during inference, with consistent accuracy improvements (up to 4%) over strong test-time scaling baselines. We also show that consistency in the sparse activation signals aligns well with the common notion of coherent reasoning.
A framework named AdaptAgent enables web agents to quickly adapt to new websites and domains by learning from a few human demonstrations. It improves success rates by 3.36% for proprietary models and up to 7.21% for open-weight models, leveraging multimodal inputs and meta-learning or in-context learning.
There exist several methods that aim to address the crucial task of
understanding the behaviour of AI/ML models. Arguably, the most popular among
them are local explanations that focus on investigating model behaviour for
individual instances. Several methods have been proposed for local analysis,
but relatively lesser effort has gone into understanding if the explanations
are robust and accurately reflect the behaviour of underlying models. In this
work, we present a survey of the works that analysed the robustness of two
classes of local explanations (feature importance and counterfactual
explanations) that are popularly used in analysing AI/ML models in finance. The
survey aims to unify existing definitions of robustness, introduces a taxonomy
to classify different robustness approaches, and discusses some interesting
results. Finally, the survey introduces some pointers about extending current
robustness analysis approaches so as to identify reliable explainability
methods.
SOPStruct, developed by JP Morgan AI Research, transforms unstructured natural language Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) into structured, decision-tree-based Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) using Large Language Models. This methodology improves SOP management by enabling more comprehensible representations and facilitating automation, outperforming baseline methods across various datasets.
We present pyRDDLGym, a Python framework for auto-generation of OpenAI Gym
environments from RDDL declerative description. The discrete time step
evolution of variables in RDDL is described by conditional probability
functions, which fits naturally into the Gym step scheme. Furthermore, since
RDDL is a lifted description, the modification and scaling up of environments
to support multiple entities and different configurations becomes trivial
rather than a tedious process prone to errors. We hope that pyRDDLGym will
serve as a new wind in the reinforcement learning community by enabling easy
and rapid development of benchmarks due to the unique expressive power of RDDL.
By providing explicit access to the model in the RDDL description, pyRDDLGym
can also facilitate research on hybrid approaches for learning from interaction
while leveraging model knowledge. We present the design and built-in examples
of pyRDDLGym, and the additions made to the RDDL language that were
incorporated into the framework.
Travel planning is a complex task that involves generating a sequence of
actions related to visiting places subject to constraints and maximizing some
user satisfaction criteria. Traditional approaches rely on problem formulation
in a given formal language, extracting relevant travel information from web
sources, and use an adequate problem solver to generate a valid solution. As an
alternative, recent Large Language Model (LLM) based approaches directly output
plans from user requests using language. Although LLMs possess extensive travel
domain knowledge and provide high-level information like points of interest and
potential routes, current state-of-the-art models often generate plans that
lack coherence, fail to satisfy constraints fully, and do not guarantee the
generation of high-quality solutions. We propose TRIP-PAL, a hybrid method that
combines the strengths of LLMs and automated planners, where (i) LLMs get and
translate travel information and user information into data structures that can
be fed into planners; and (ii) automated planners generate travel plans that
guarantee constraint satisfaction and optimize for users' utility. Our
experiments across various travel scenarios show that TRIP-PAL outperforms an
LLM when generating travel plans.
Interpretability in Table Question Answering (Table QA) is critical, especially in high-stakes domains like finance and healthcare. While recent Table QA approaches based on Large Language Models (LLMs) achieve high accuracy, they often produce ambiguous explanations of how answers are derived.
We propose Plan-of-SQLs (POS), a new Table QA method that makes the model's decision-making process interpretable. POS decomposes a question into a sequence of atomic steps, each directly translated into an executable SQL command on the table, thereby ensuring that every intermediate result is transparent. Through extensive experiments, we show that: First, POS generates the highest-quality explanations among compared methods, which markedly improves the users' ability to simulate and verify the model's decisions. Second, when evaluated on standard Table QA benchmarks (TabFact, WikiTQ, and FeTaQA), POS achieves QA accuracy that is competitive to existing methods, while also offering greater efficiency-requiring significantly fewer LLM calls and table database queries (up to 25x fewer)-and more robust performance on large-sized tables. Finally, we observe high agreement (up to 90.59% in forward simulation) between LLMs and human users when making decisions based on the same explanations, suggesting that LLMs could serve as an effective proxy for humans in evaluating Table QA explanations.
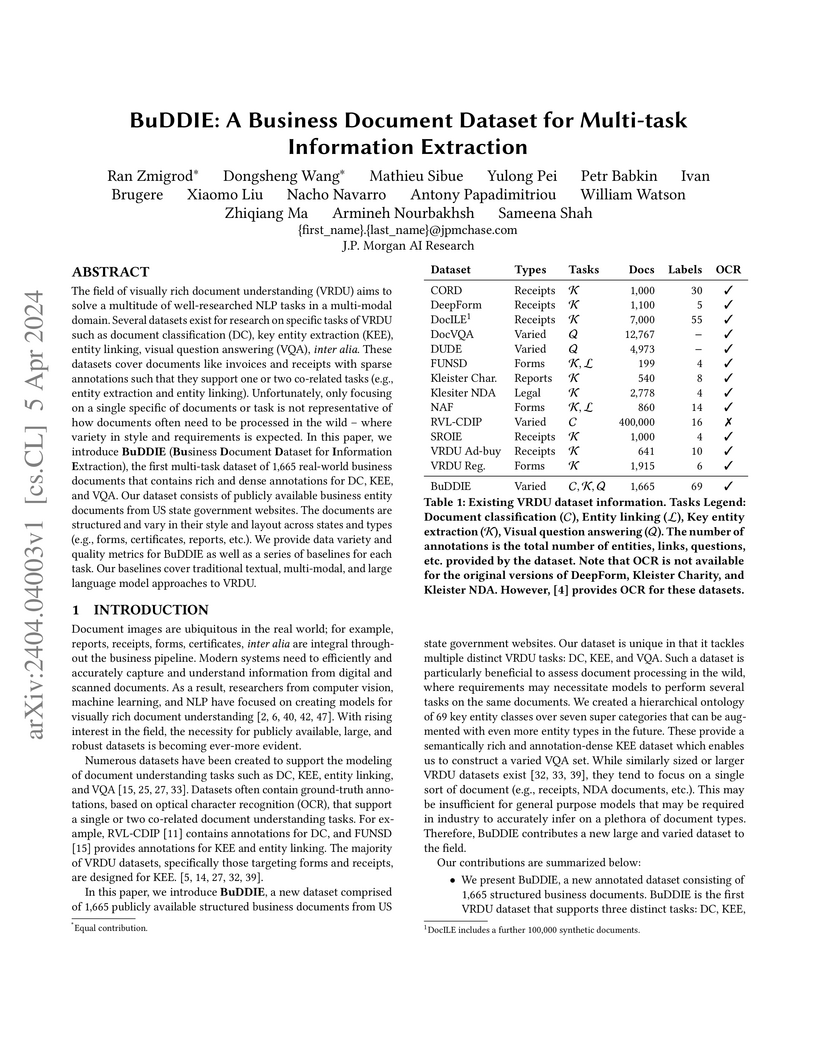
The field of visually rich document understanding (VRDU) aims to solve a multitude of well-researched NLP tasks in a multi-modal domain. Several datasets exist for research on specific tasks of VRDU such as document classification (DC), key entity extraction (KEE), entity linking, visual question answering (VQA), inter alia. These datasets cover documents like invoices and receipts with sparse annotations such that they support one or two co-related tasks (e.g., entity extraction and entity linking). Unfortunately, only focusing on a single specific of documents or task is not representative of how documents often need to be processed in the wild - where variety in style and requirements is expected. In this paper, we introduce BuDDIE (Business Document Dataset for Information Extraction), the first multi-task dataset of 1,665 real-world business documents that contains rich and dense annotations for DC, KEE, and VQA. Our dataset consists of publicly available business entity documents from US state government websites. The documents are structured and vary in their style and layout across states and types (e.g., forms, certificates, reports, etc.). We provide data variety and quality metrics for BuDDIE as well as a series of baselines for each task. Our baselines cover traditional textual, multi-modal, and large language model approaches to VRDU.
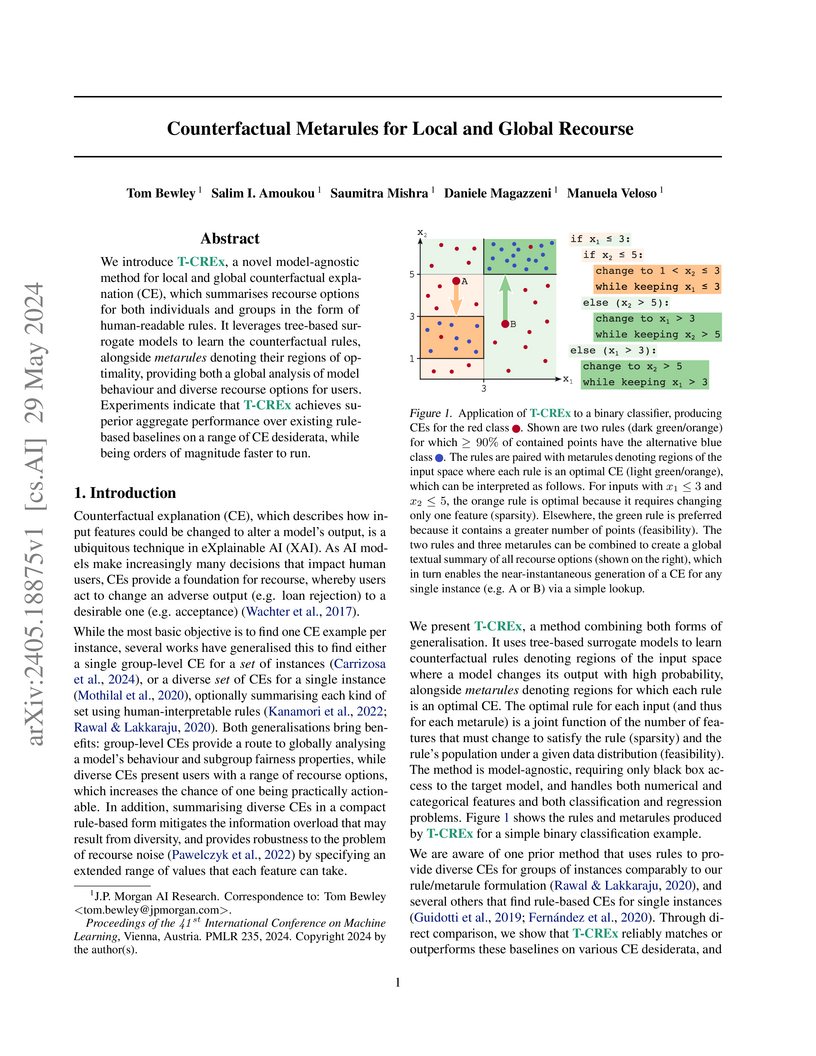
We introduce T-CREx, a novel model-agnostic method for local and global counterfactual explanation (CE), which summarises recourse options for both individuals and groups in the form of human-readable rules. It leverages tree-based surrogate models to learn the counterfactual rules, alongside 'metarules' denoting their regions of optimality, providing both a global analysis of model behaviour and diverse recourse options for users. Experiments indicate that T-CREx achieves superior aggregate performance over existing rule-based baselines on a range of CE desiderata, while being orders of magnitude faster to run.
Shape assembly is a ubiquitous task in daily life, integral for constructing complex 3D structures like IKEA furniture. While significant progress has been made in developing autonomous agents for shape assembly, existing datasets have not yet tackled the 4D grounding of assembly instructions in videos, essential for a holistic understanding of assembly in 3D space over time. We introduce IKEA Video Manuals, a dataset that features 3D models of furniture parts, instructional manuals, assembly videos from the Internet, and most importantly, annotations of dense spatio-temporal alignments between these data modalities. To demonstrate the utility of IKEA Video Manuals, we present five applications essential for shape assembly: assembly plan generation, part-conditioned segmentation, part-conditioned pose estimation, video object segmentation, and furniture assembly based on instructional video manuals. For each application, we provide evaluation metrics and baseline methods. Through experiments on our annotated data, we highlight many challenges in grounding assembly instructions in videos to improve shape assembly, including handling occlusions, varying viewpoints, and extended assembly sequences.
Large Language Models (LLMs) offer the potential for automatic time series
analysis and reporting, which is a critical task across many domains, spanning
healthcare, finance, climate, energy, and many more. In this paper, we propose
a framework for rigorously evaluating the capabilities of LLMs on time series
understanding, encompassing both univariate and multivariate forms. We
introduce a comprehensive taxonomy of time series features, a critical
framework that delineates various characteristics inherent in time series data.
Leveraging this taxonomy, we have systematically designed and synthesized a
diverse dataset of time series, embodying the different outlined features, each
accompanied by textual descriptions. This dataset acts as a solid foundation
for assessing the proficiency of LLMs in comprehending time series. Our
experiments shed light on the strengths and limitations of state-of-the-art
LLMs in time series understanding, revealing which features these models
readily comprehend effectively and where they falter. In addition, we uncover
the sensitivity of LLMs to factors including the formatting of the data, the
position of points queried within a series and the overall time series length.
The PARL framework models Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback as a novel bilevel optimization problem, allowing an agent's policy to achieve near-oracle alignment and up to 63% improved sample efficiency in continuous control robotics tasks compared to prior iterative methods. This approach explicitly addresses the dependency between the data used to train the reward model and the optimal policy that generates it.
We introduce Mechanistic Error Reduction with Abstention (MERA), a principled framework for steering language models (LMs) to mitigate errors through selective, adaptive interventions. Unlike existing methods that rely on fixed, manually tuned steering strengths, often resulting in under or oversteering, MERA addresses these limitations by (i) optimising the intervention direction, and (ii) calibrating when, and how much to steer, thereby provably improving performance or abstaining when no confident correction is possible. Experiments across diverse datasets, and LM families demonstrate safe, effective, non-degrading error correction, and that MERA outperforms existing baselines. Moreover, MERA can be applied on top of existing steering techniques to further enhance their performance, establishing it as a general-purpose, and efficient approach to mechanistic activation steering.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.