Li Auto
Tsinghua University and Li Auto developed DriveVLM and DriveVLM-Dual, a VLM-integrated autonomous driving system that enhances scene understanding and planning, especially in complex "long-tail" scenarios. The hybrid DriveVLM-Dual system achieved state-of-the-art performance on the nuScenes planning task and demonstrated real-time asynchronous operation on production vehicle hardware with an average inference speed of 410 ms.
Street Gaussians presents an explicit 3D Gaussian Splatting framework tailored for modeling dynamic urban scenes, achieving real-time novel view synthesis and drastically reduced training times compared to prior methods. The approach renders at 135 FPS and trains in just half an hour on the Waymo Open Dataset, while producing sharper and more detailed views, especially for moving objects, leading to a PSNR of 34.61 and 30.23 for dynamic elements.
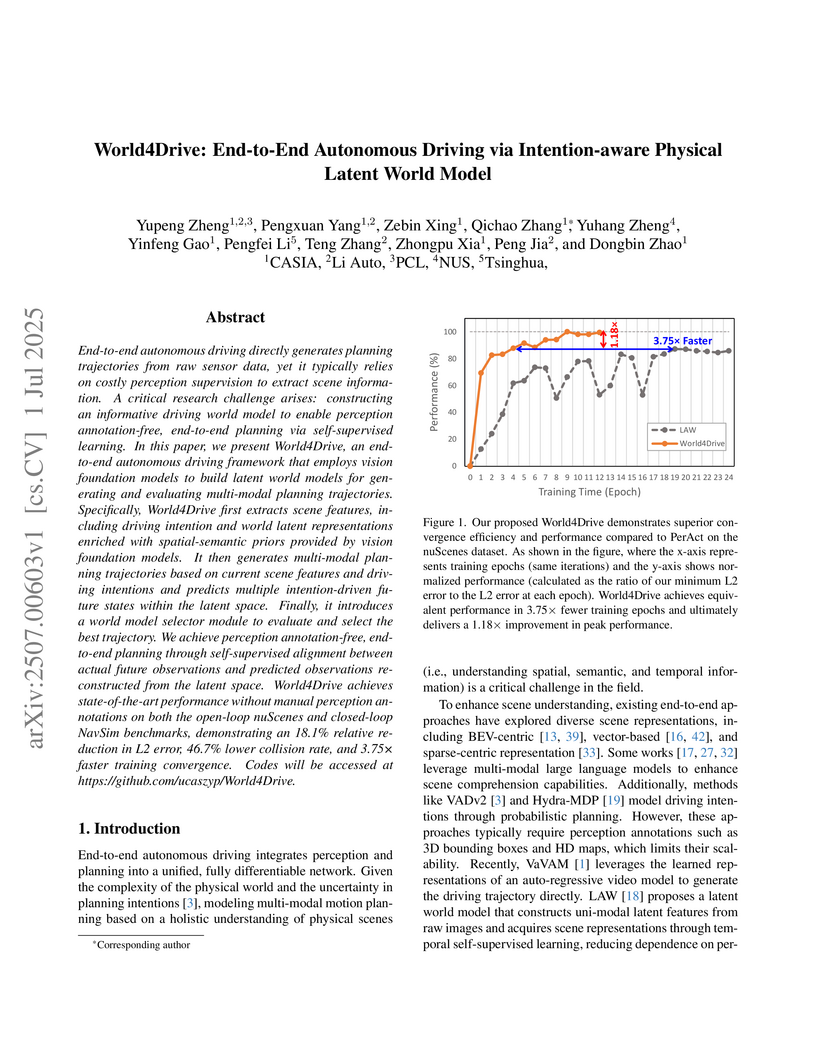
World4Drive presents an end-to-end autonomous driving framework that generates planning trajectories directly from raw sensor data, eliminating the need for manual perception annotations by leveraging intention-aware physical latent world models. This system achieves a 46.7% relative reduction in collision rate and 3.75x faster training convergence compared to previous self-supervised methods on the nuScenes dataset.
A framework synthesizes photorealistic street view videos with precise camera control by conditioning a video diffusion model on LiDAR point clouds. This method enables superior view extrapolation in dynamic urban scenes and facilitates real-time rendering through distillation into a 3D Gaussian Splatting representation.
26 Oct 2025
Training expressive flow-based policies with off-policy reinforcement learning is notoriously unstable due to gradient pathologies in the multi-step action sampling process. We trace this instability to a fundamental connection: the flow rollout is algebraically equivalent to a residual recurrent computation, making it susceptible to the same vanishing and exploding gradients as RNNs. To address this, we reparameterize the velocity network using principles from modern sequential models, introducing two stable architectures: Flow-G, which incorporates a gated velocity, and Flow-T, which utilizes a decoded velocity. We then develop a practical SAC-based algorithm, enabled by a noise-augmented rollout, that facilitates direct end-to-end training of these policies. Our approach supports both from-scratch and offline-to-online learning and achieves state-of-the-art performance on continuous control and robotic manipulation benchmarks, eliminating the need for common workarounds like policy distillation or surrogate objectives.
Researchers from Li Auto provide a comprehensive survey and categorization of memory mechanisms in Large Language Models, mapping them to human cognitive memory types. The work details current approaches for memory acquisition, management, and utilization, while also identifying key limitations when compared to human cognitive abilities like generalization and adaptive forgetting.
This paper introduces a new Gaussian-centric framework for end-to-end autonomous driving that uses 3D Gaussian scene representations to balance comprehensiveness and efficiency
DETR3D, developed by researchers from MIT, Toyota Research Institute, and others, introduces an end-to-end framework for 3D object detection directly from multi-view images. It achieves state-of-the-art performance among camera-only methods on the nuScenes dataset by leveraging 3D-to-2D projection and multi-view feature aggregation with learnable object queries.
PosePilot introduces a lightweight, plug-and-play module that enhances camera pose controllability in generative world models by explicitly integrating self-supervised depth and ego-motion estimation. This approach significantly improves geometric consistency and accuracy in generated videos, particularly for autonomous driving simulations, and demonstrates strong cross-domain adaptability.
ChunkLLM introduces a lightweight, pluggable framework to accelerate large language model inference, achieving up to 4.48x speedup and reducing KV cache usage by nearly 50% on long texts. This is accomplished while maintaining high performance across various long- and short-text benchmarks through dynamic semantic chunking, attention distillation, and an Intra-Chunk Attention Consistency mechanism.
HDMapNet introduces an online framework for constructing local, vectorized high-definition (HD) semantic maps in real-time using only onboard camera and/or LiDAR sensors. The system achieves state-of-the-art performance, with a camera-LiDAR fusion model yielding an IoU of 44.5% and a mAP of 30.6% on the nuScenes dataset, significantly outperforming previous methods and single-modal approaches.
Real-time, high-fidelity reconstruction of dynamic driving scenes is challenged by complex dynamics and sparse views, with prior methods struggling to balance quality and efficiency. We propose DrivingScene, an online, feed-forward framework that reconstructs 4D dynamic scenes from only two consecutive surround-view images. Our key innovation is a lightweight residual flow network that predicts the non-rigid motion of dynamic objects per camera on top of a learned static scene prior, explicitly modeling dynamics via scene flow. We also introduce a coarse-to-fine training paradigm that circumvents the instabilities common to end-to-end approaches. Experiments on nuScenes dataset show our image-only method simultaneously generates high-quality depth, scene flow, and 3D Gaussian point clouds online, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art methods in both dynamic reconstruction and novel view synthesis.
A new fine-tuning framework called QR-LoRA was developed, employing QR decomposition to enable disentangled control of visual attributes in text-to-image generative models. It produced higher quality images with independent content and style manipulation while reducing trainable parameters by 50% compared to traditional LoRA, consistently performing well on SDXL, SD3, and FLUX.1-dev.
17 Oct 2025
Researchers at LI AUTO's Code Intelligence Team developed SIADAFIX, an adaptive framework for automated program repair that integrates "fast" and "slow thinking" modes to intelligently orchestrate repair workflows. By analyzing issue descriptions and dynamically adjusting the repair strategy, SIADAFIX achieves a 60.7% Pass@1 on the SWE-bench Lite benchmark with Claude-4 Sonnet, improving upon existing LLM-based approaches.
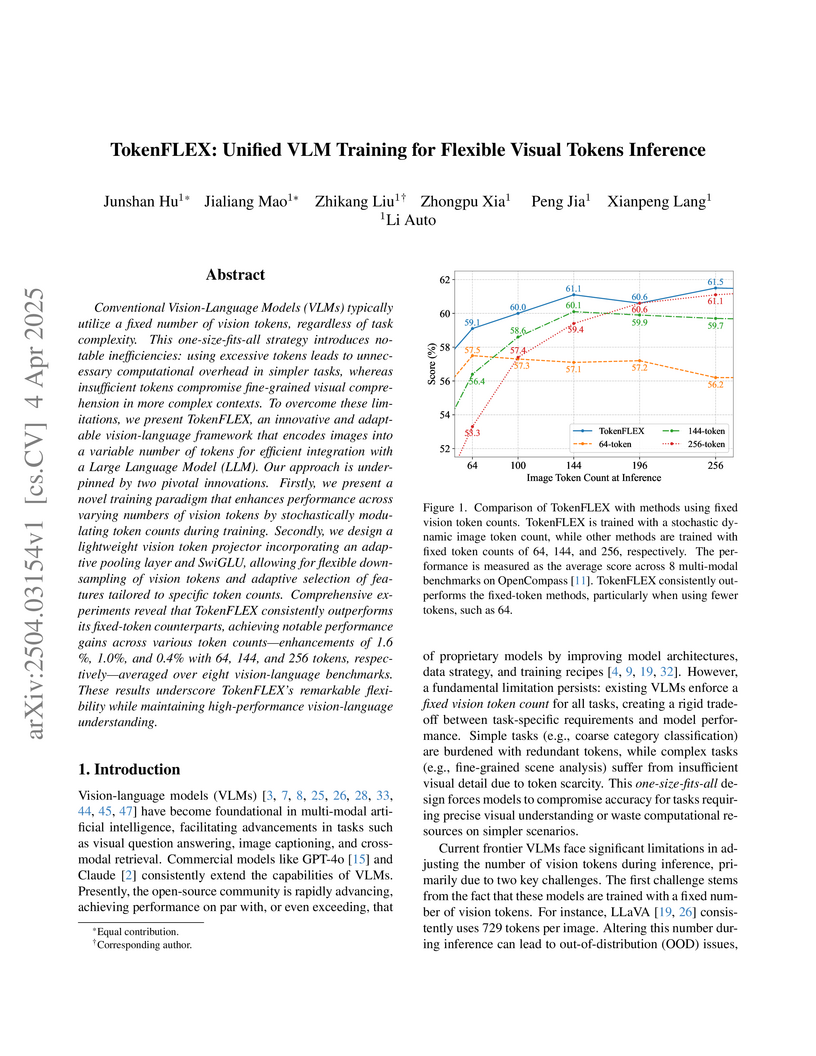
Li Auto researchers introduce TokenFLEX, a framework enabling flexible visual token counts in Vision-Language Models through dynamic token training and an adaptive projector architecture, reducing visual token usage by 28% and training time by 13% while maintaining competitive performance across benchmarks when compared to fixed-token approaches.
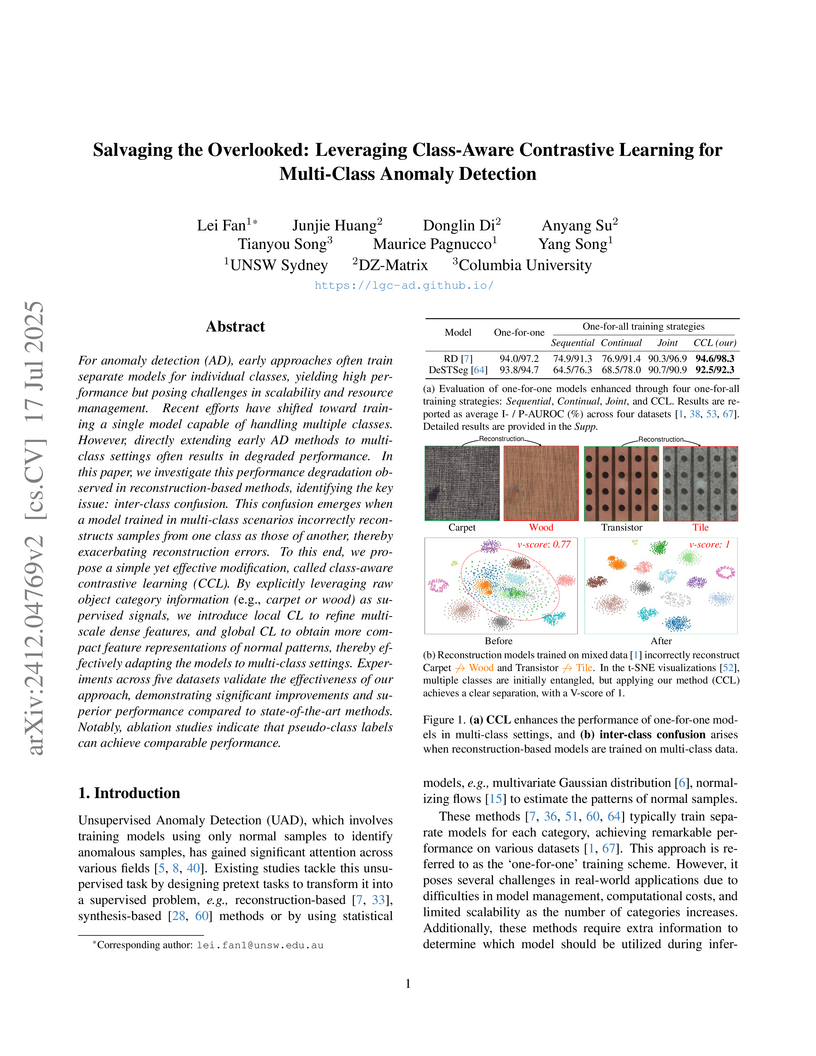
Researchers at UNSW Sydney developed Class-aware Contrastive Learning (CCL), a modular framework that mitigates inter-class confusion in multi-class anomaly detection by integrating local and global contrastive losses with existing reconstruction-based models. This approach achieved an Image-level AUROC of 90.6% across 60 object categories and demonstrated comparable performance using pseudo-class labels, making it suitable for truly unsupervised scenarios.
Researchers at Li Auto developed GeoGramBench, a new benchmark to evaluate Large Language Models' ability to derive spatial geometric understanding from procedural code. The evaluation revealed that current LLMs struggle with constructing global spatial representations from symbolic instructions, particularly on complex tasks where even top models achieved less than 50% accuracy.
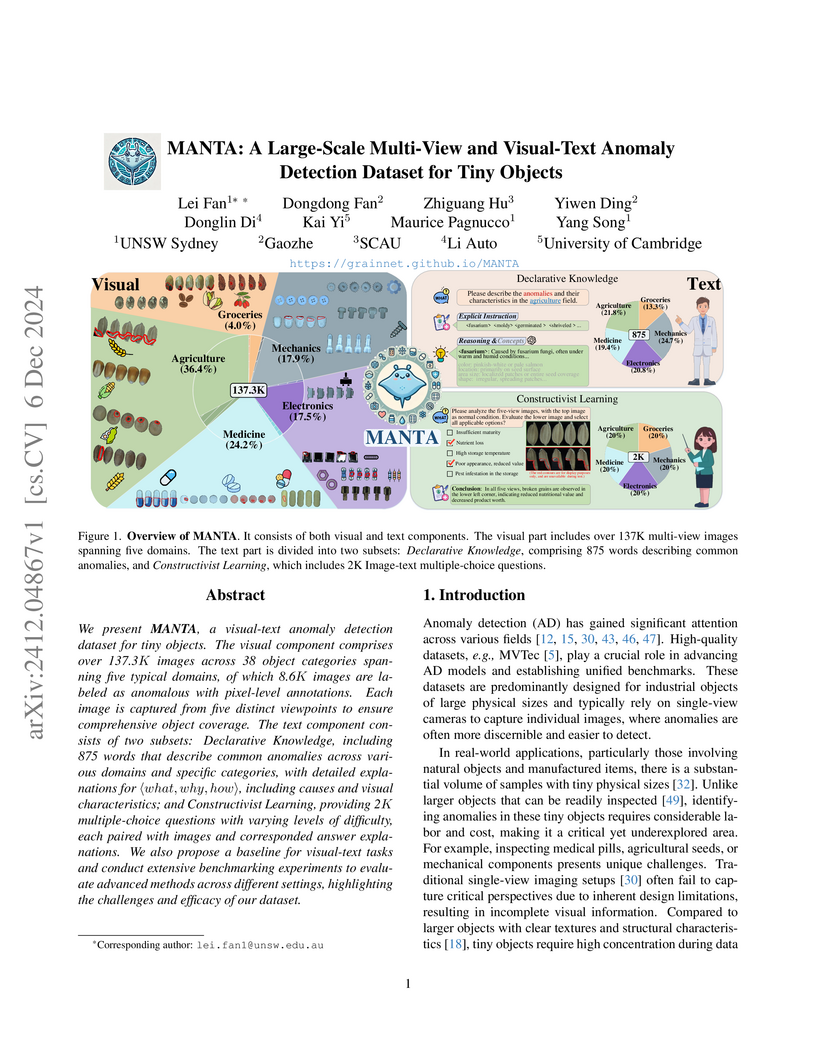
The MANTA dataset, developed by researchers from UNSW Sydney and collaborators, introduces the first large-scale, multi-view, visual-text resource for anomaly detection in tiny objects (4-20 mm³), featuring over 137,000 multi-view images across 38 categories. This dataset addresses challenges like object heterogeneity and unpredictable poses, demonstrating that multi-view approaches significantly improve anomaly detection, with an average I-AUROC of 91% on its visual tasks.
Driving scene generation is a critical domain for autonomous driving, enabling downstream applications, including perception and planning evaluation. Occupancy-centric methods have recently achieved state-of-the-art results by offering consistent conditioning across frames and modalities; however, their performance heavily depends on annotated occupancy data, which still remains scarce. To overcome this limitation, we curate Nuplan-Occ, the largest semantic occupancy dataset to date, constructed from the widely used Nuplan benchmark. Its scale and diversity facilitate not only large-scale generative modeling but also autonomous driving downstream applications. Based on this dataset, we develop a unified framework that jointly synthesizes high-quality semantic occupancy, multi-view videos, and LiDAR point clouds. Our approach incorporates a spatio-temporal disentangled architecture to support high-fidelity spatial expansion and temporal forecasting of 4D dynamic occupancy. To bridge modal gaps, we further propose two novel techniques: a Gaussian splatting-based sparse point map rendering strategy that enhances multi-view video generation, and a sensor-aware embedding strategy that explicitly models LiDAR sensor properties for realistic multi-LiDAR simulation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves superior generation fidelity and scalability compared to existing approaches, and validates its practical value in downstream tasks. Repo: this https URL
MV-VTON, developed by researchers from Harbin Institute of Technology, Peking University, and Li Auto, introduces and solves the Multi-View Virtual Try-On task by generating realistic images of a person wearing a garment from various angles. The work leverages diffusion models with novel view-adaptive feature selection and joint attention blocks, outperforming existing methods on both multi-view and frontal-view tasks and demonstrating superior garment detail preservation. A new Multi-View Garment (MVG) dataset was also collected and released to support this novel research direction.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.