Ask or search anything...
This survey paper systematically synthesizes advancements in Reinforcement Learning (RL) for Large Reasoning Models (LRMs), moving beyond human alignment to focus on enhancing intrinsic reasoning capabilities through verifiable rewards. It identifies key components, challenges, and future directions for scaling RL towards Artificial SuperIntelligence (ASI).
View blogCopyrightShield, developed by researchers from Nanyang Technological University and Beihang University, establishes a defense framework to protect diffusion models from copyright infringement attacks by detecting poisoned training samples and mitigating their influence. The approach achieves an F1-score of 0.665 for poisoned sample detection, which is a 25% improvement over prior attribution methods, and reduces the copyright infringement rate by 56.7% while delaying attack initiation by 115.2%, all without compromising generative quality.
View blogThis research introduces "Thinking with Video," a new paradigm that leverages video generation for multimodal reasoning by enabling dynamic visualization and human-like imagination in problem-solving. It evaluates frontier video models like Sora-2 on a new, comprehensive benchmark, VideoThinkBench, showcasing their unexpected capabilities across vision and text-centric tasks.
View blogA comprehensive synthesis of Large Language Models for automated software development covers the entire model lifecycle, from data curation to autonomous agents, and offers practical guidance derived from empirical experiments on pre-training, fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning, alongside a detailed analysis of challenges and future directions.
View blogResearchers from Tsinghua University and NUS developed RLPR, a verifier-free reinforcement learning framework that enhances Large Language Model reasoning across general domains by using an intrinsic probability-based reward. This method achieved an average 24.9% improvement on general-domain benchmarks and consistently outperformed existing RLVR and concurrent verifier-free approaches by removing the need for external verification.
View blogMemoryBank introduces a novel long-term memory mechanism for Large Language Models, enabling them to retain and recall information across extended interactions by simulating human-like forgetting and reinforcement. The system, demonstrated through the SiliconFriend chatbot, significantly enhances contextual understanding, personalizes user interactions through dynamic user portraits, and provides empathetic responses, showing strong performance across various LLMs in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations.
View blogResearchers from Harbin Institute of Technology and collaborating institutions provide a systematic survey of Long Chain-of-Thought (Long CoT) in Large Language Models, establishing a formal distinction from Short CoT. The survey proposes a novel taxonomy based on deep reasoning, extensive exploration, and feasible reflection, and analyzes key phenomena observed in advanced reasoning models.
View blogResearchers from Harbin Institute of Technology and collaborators present a systematic survey of Artificial Intelligence for Scientific Research (AI4Research), defining its scope, proposing a comprehensive taxonomy across the entire research lifecycle, and identifying critical future directions. The study clarifies the distinction between AI4Research and AI4Science, demonstrating AI's growing capabilities from scientific comprehension to peer review, while highlighting significant challenges in achieving ethical, explainable, and fully autonomous systems.
View blogRLinf-VLA presents a unified and efficient framework for training Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models with reinforcement learning (RL), achieving up to 2.27x speedup and establishing new performance benchmarks, including a 98.11% success rate on LIBERO-130 and improved real-world zero-shot generalization over supervised methods.
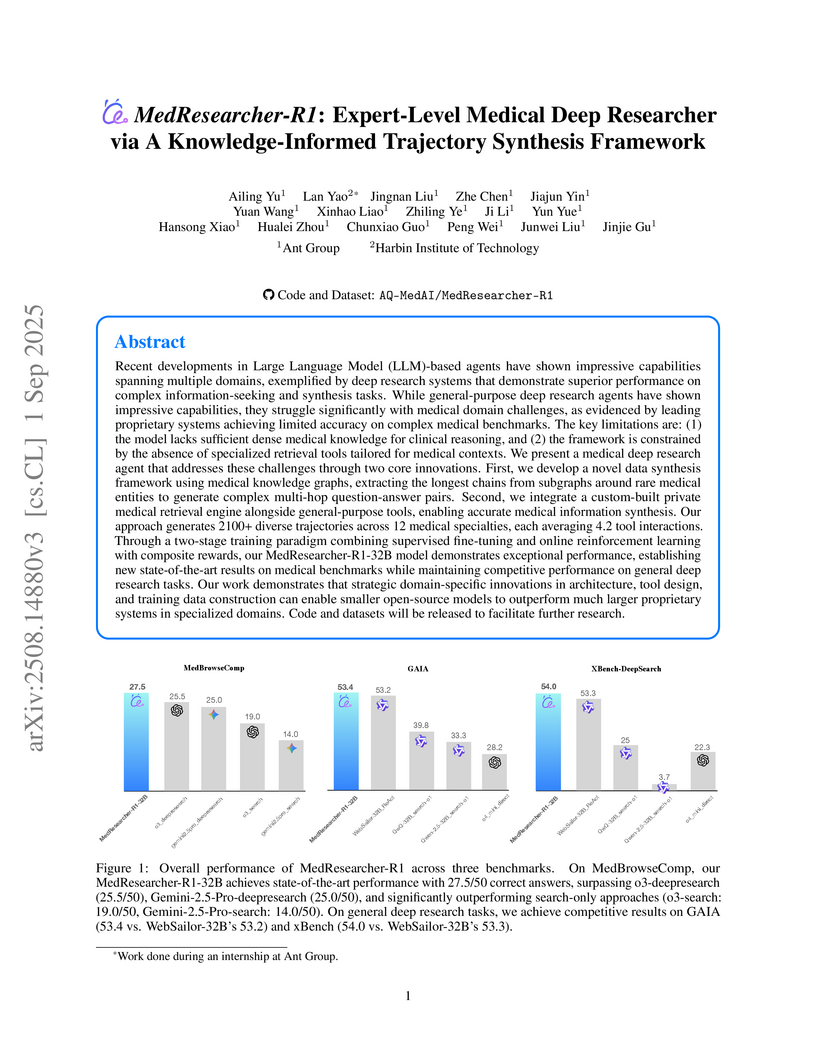
View blogAnt Group researchers developed MedResearcher-R1, an expert-level medical deep research agent capable of complex, multi-hop reasoning over medical information using specialized tools. It achieved a new state-of-the-art pass@1 score of 27.5/50 on the MedBrowseComp benchmark, outperforming leading proprietary systems, while maintaining competitive performance on general deep research tasks.
View blogGenPRM, from researchers at Tsinghua University and Shanghai AI Laboratory, introduces a generative approach to Process Reward Models (PRMs) that produces explicit Chain-of-Thought reasoning and integrates code verification, enabling the PRM itself to benefit from test-time scaling. This allows GenPRM to outperform prior classification-based PRMs and serve as an effective verifier and critic for policy models in mathematical reasoning.
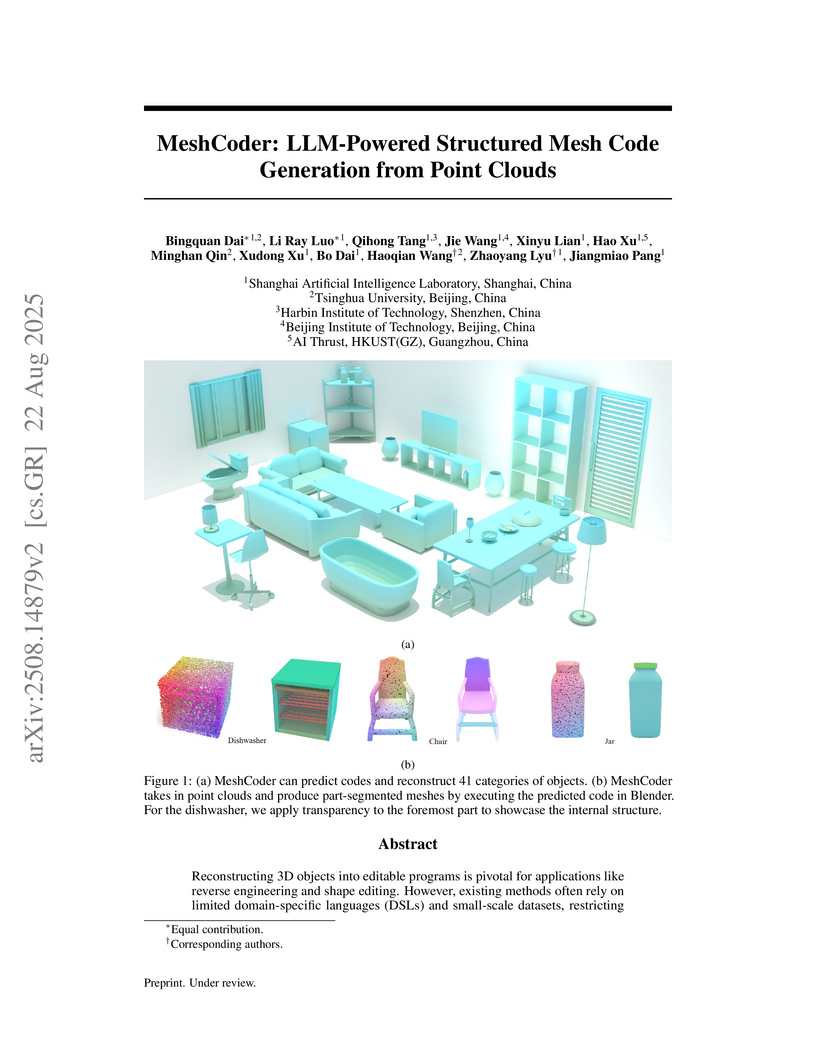
View blogMeshCoder reconstructs complex 3D objects from point clouds into editable Blender Python scripts, achieving an L2 Chamfer Distance of 0.06 (x10^-2) while enabling precise geometric and topological editing. This method allows large language models to better reason about 3D shapes through semantically rich code, substantially outperforming existing shape-to-code baselines.
View blogThis paper comprehensively surveys Video Temporal Grounding with Multimodal Large Language Models (VTG-MLLMs), presenting a novel three-dimensional taxonomy to classify methodologies and analyzing performance across diverse tasks and benchmarks. It provides a structured overview of architectural integrations, training strategies, and video feature processing techniques, consolidating advancements in the field.
View blogEfficientVLA presents a training-free framework that accelerates and compresses diffusion-based Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models by systematically addressing redundancies in the language module, visual processing, and iterative action head. The approach achieved a 1.93x inference speedup and over 70% FLOPs reduction with only a 0.6% drop in success rate, enabling more practical deployment on robotic platforms.
View blogTool-R1, developed by Harbin Institute of Technology and Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab, introduces a reinforcement learning framework that enables Large Language Models to use external tools by generating executable Python code, achieving sample-efficient training through dynamic data management and outcome-driven rewards. This framework elevates agentic capabilities, reaching an Answer Accuracy of 26.67% on the GAIA benchmark, outperforming baselines with significantly less training data.
View blog University of Washington
University of Washington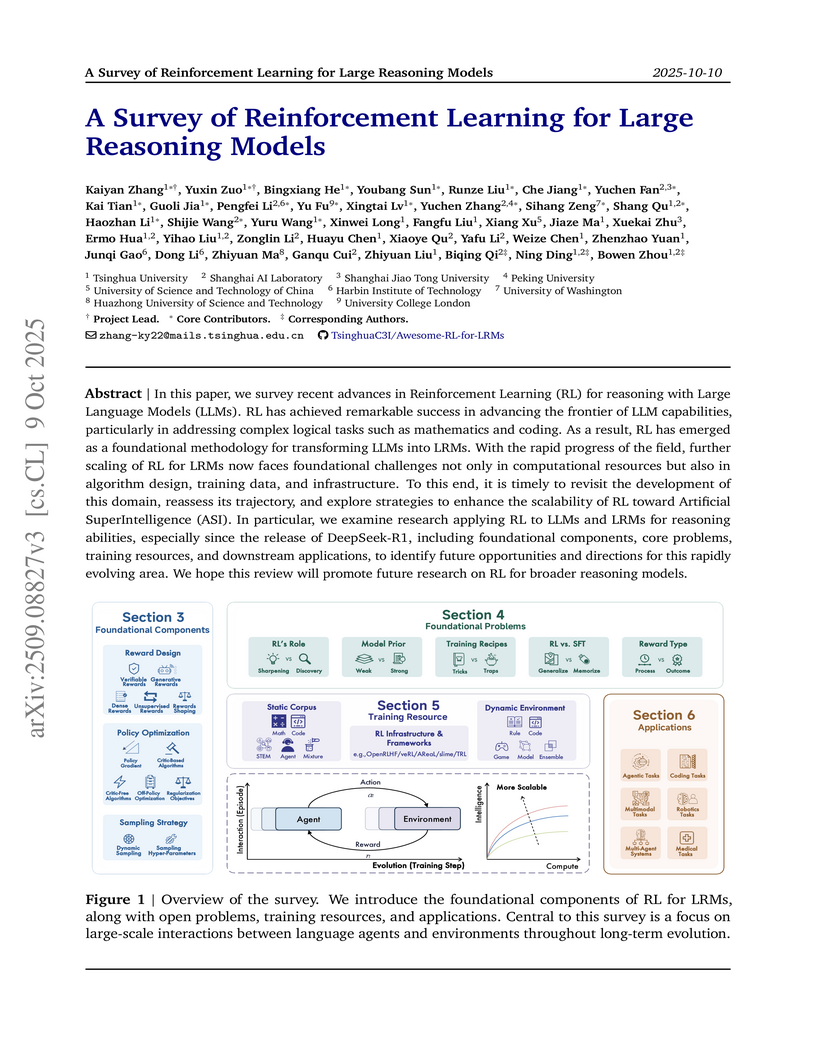
 National University of Singapore
National University of Singapore Beihang University
Beihang University

 Fudan University
Fudan University The Chinese University of Hong Kong
The Chinese University of Hong Kong
 Monash University
Monash University
 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign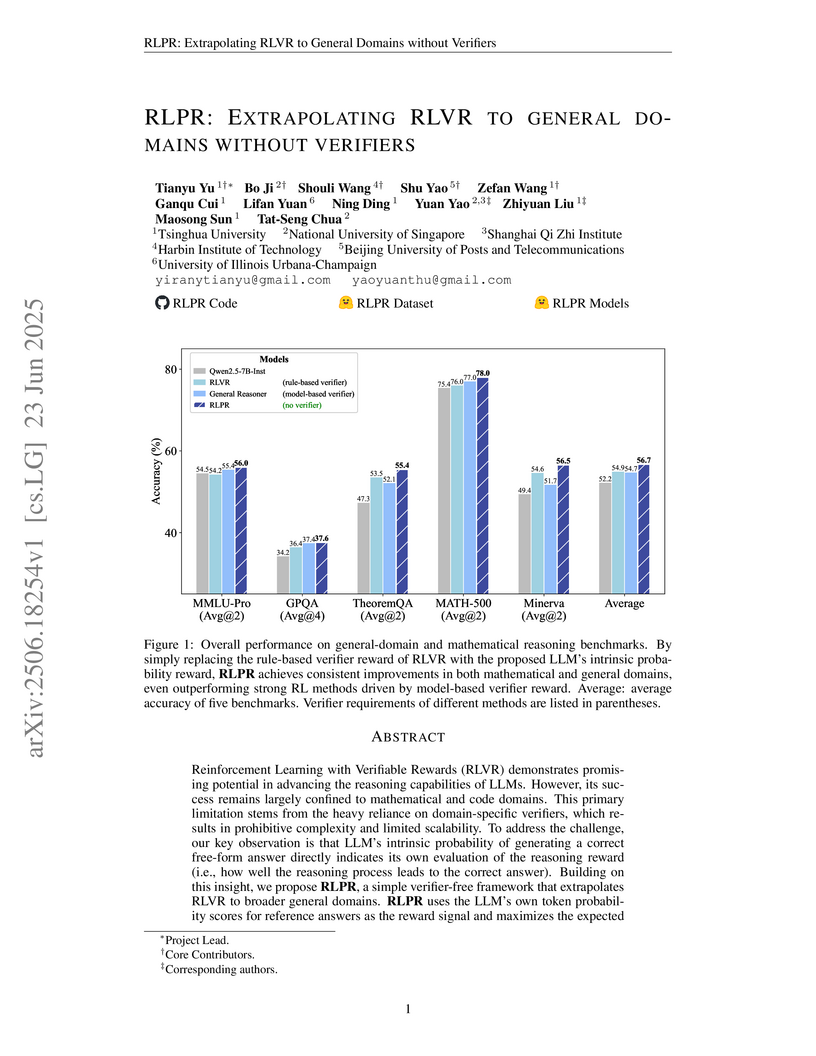
 Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University


 UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley
 Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University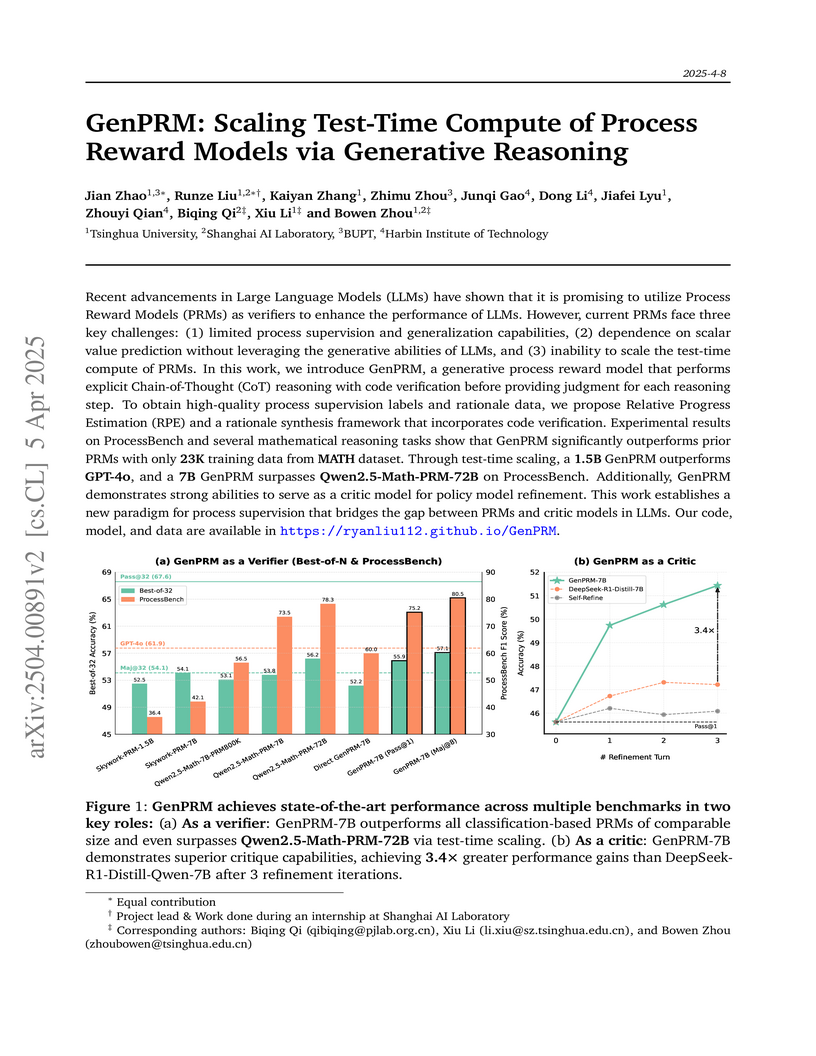
 ByteDance
ByteDance


 The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
 Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University
