SINTEF Digital
Norwegian researchers develop MyoTracker, a low-complexity deep learning framework for tracking myocardium points in 2D echocardiography, achieving higher accuracy than existing methods while reducing computational requirements and enabling accurate Right Ventricle Free Wall Strain measurements with narrow limits of agreement (-6.1% to 5.4%) compared to reference values.
Access to trajectory data is a key requirement for developing and validating Air Traffic Management (ATM) solutions, yet many secondary and regional airports face severe data scarcity. This limits the applicability of machine learning methods and the ability to perform large-scale simulations or "what-if" analyses. In this paper, we investigate whether generative models trained on data-rich airports can be efficiently adapted to data-scarce airports using transfer learning. We adapt state-of-the-art diffusion- and flow-matching-based architectures to the aviation domain and evaluate their transferability between Zurich (source) and Dublin (target) landing trajectory datasets. Models are pretrained on Zurich and fine-tuned on Dublin with varying amounts of local data, ranging from 0% to 100%. Results show that diffusion-based models achieve competitive performance with as little as 5% of the Dublin data and reach baseline-level performance around 20%, consistently outperforming models trained from scratch across metrics and visual inspections. Latent flow matching and latent diffusion models also benefit from pretraining, though with more variable gains, while flow matching models show weaker generalization. Despite challenges in capturing rare trajectory patterns, these findings demonstrate the potential of transfer learning to substantially reduce data requirements for trajectory generation in ATM, enabling realistic synthetic data generation even in environments with limited historical records.
Purpose: Registration and segmentation of magnetic resonance (MR) and ultrasound (US) images play an essential role in surgical planning and resection of brain tumors. However, validating these techniques is challenging due to the scarcity of publicly accessible sources with high-quality ground truth information. To this end, we propose a unique annotation dataset of tumor tissues and resection cavities from the previously published RESECT dataset (Xiao et al. 2017) to encourage a more rigorous assessments of image processing techniques. Acquisition and validation methods: The RESECT database consists of MR and intraoperative US (iUS) images of 23 patients who underwent resection surgeries. The proposed dataset contains tumor tissues and resection cavity annotations of the iUS images. The quality of annotations were validated by two highly experienced neurosurgeons through several assessment criteria. Data format and availability: Annotations of tumor tissues and resection cavities are provided in 3D NIFTI formats. Both sets of annotations are accessible online in the \url{this https URL}. Discussion and potential applications: The proposed database includes tumor tissue and resection cavity annotations from real-world clinical ultrasound brain images to evaluate segmentation and registration methods. These labels could also be used to train deep learning approaches. Eventually, this dataset should further improve the quality of image guidance in neurosurgery.
The increased usage of Internet of Things devices at the network edge and the
proliferation of microservice-based applications create new orchestration
challenges in Edge computing. These include detecting overutilized resources
and scaling out overloaded microservices in response to surging requests. This
work presents ADApt, an extension of the ADA-PIPE tool developed in the
DataCloud project, by monitoring Edge devices, detecting the utilization-based
anomalies of processor or memory, investigating the scalability in
microservices, and adapting the application executions. To reduce the
overutilization bottleneck, we first explore monitored devices executing
microservices over various time slots, detecting overutilization-based
processing events, and scoring them. Thereafter, based on the memory
requirements, ADApt predicts the processing requirements of the microservices
and estimates the number of replicas running on the overutilized devices. The
prediction results show that the gradient boosting regression-based replica
prediction reduces the MAE, MAPE, and RMSE compared to others. Moreover, ADApt
can estimate the number of replicas close to the actual data and reduce the CPU
utilization of the device by 14%-28%.
24 Sep 2025
Approximating solutions to partial differential equations (PDEs) is fundamental for the modeling of dynamical systems in science and engineering. Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) are a recent machine learning-based approach, for which many properties and limitations remain unknown. PINNs are widely accepted as inferior to traditional methods for solving PDEs, such as the finite element method, both with regard to computation time and accuracy. However, PINNs are commonly claimed to show promise in solving inverse problems and handling noisy or incomplete data. We compare the performance of PINNs in solving inverse problems with that of a traditional approach using the finite element method combined with a numerical optimizer. The models are tested on a series of increasingly difficult fluid mechanics problems, with and without noise. We find that while PINNs may require less human effort and specialized knowledge, they are outperformed by the traditional approach. However, the difference appears to decrease with higher dimensions and more data. We identify common failures during training to be addressed if the performance of PINNs on noisy inverse problems is to become more competitive.
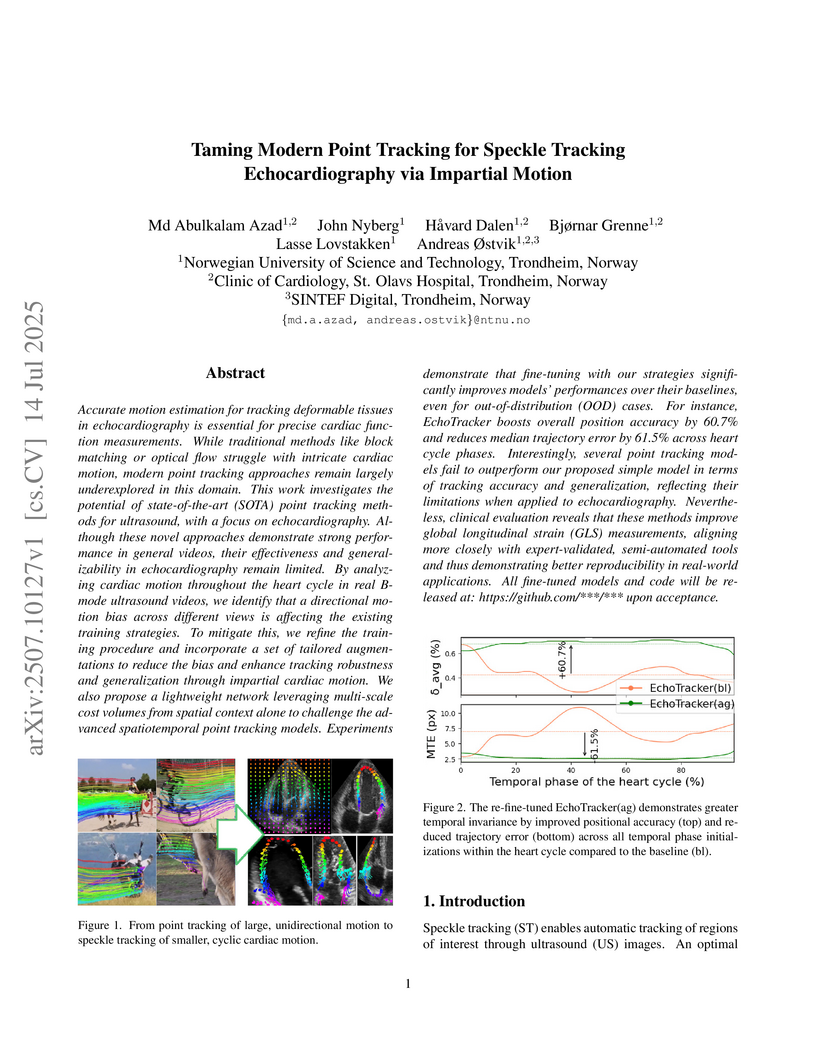
Accurate motion estimation for tracking deformable tissues in echocardiography is essential for precise cardiac function measurements. While traditional methods like block matching or optical flow struggle with intricate cardiac motion, modern point tracking approaches remain largely underexplored in this domain. This work investigates the potential of state-of-the-art (SOTA) point tracking methods for ultrasound, with a focus on echocardiography. Although these novel approaches demonstrate strong performance in general videos, their effectiveness and generalizability in echocardiography remain limited. By analyzing cardiac motion throughout the heart cycle in real B-mode ultrasound videos, we identify that a directional motion bias across different views is affecting the existing training strategies. To mitigate this, we refine the training procedure and incorporate a set of tailored augmentations to reduce the bias and enhance tracking robustness and generalization through impartial cardiac motion. We also propose a lightweight network leveraging multi-scale cost volumes from spatial context alone to challenge the advanced spatiotemporal point tracking models. Experiments demonstrate that fine-tuning with our strategies significantly improves models' performances over their baselines, even for out-of-distribution (OOD) cases. For instance, EchoTracker boosts overall position accuracy by 60.7% and reduces median trajectory error by 61.5% across heart cycle phases. Interestingly, several point tracking models fail to outperform our proposed simple model in terms of tracking accuracy and generalization, reflecting their limitations when applied to echocardiography. Nevertheless, clinical evaluation reveals that these methods improve GLS measurements, aligning more closely with expert-validated, semi-automated tools and thus demonstrating better reproducibility in real-world applications.
We introduce a data-driven method for learning the equations of motion of
mechanical systems directly from position measurements, without requiring
access to velocity data. This is particularly relevant in system identification
tasks where only positional information is available, such as motion capture,
pixel data or low-resolution tracking. Our approach takes advantage of the
discrete Lagrange-d'Alembert principle and the forced discrete Euler-Lagrange
equations to construct a physically grounded model of the system's dynamics. We
decompose the dynamics into conservative and non-conservative components, which
are learned separately using feed-forward neural networks. In the absence of
external forces, our method reduces to a variational discretization of the
action principle naturally preserving the symplectic structure of the
underlying Hamiltonian system. We validate our approach on a variety of
synthetic and real-world datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness compared to
baseline methods. In particular, we apply our model to (1) measured human
motion data and (2) latent embeddings obtained via an autoencoder trained on
image sequences. We demonstrate that we can faithfully reconstruct and separate
both the conservative and forced dynamics, yielding interpretable and
physically consistent predictions.
AI-Dentify: Deep learning for proximal caries detection on bitewing x-ray -- HUNT4 Oral Health Study
AI-Dentify: Deep learning for proximal caries detection on bitewing x-ray -- HUNT4 Oral Health Study
Deep learning models were developed to detect proximal caries on bitewing X-rays using a large dataset from the HUNT4 Oral Health Study, demonstrating superior performance compared to individual human experts. The top-performing YOLOv5 model achieved a mean Average Precision of 0.633 and a mean False Negative Rate of 0.176 on a challenging consensus test set.
We present and analyze a framework for designing symplectic neural networks
(SympNets) based on geometric integrators for Hamiltonian differential
equations. The SympNets are universal approximators in the space of Hamiltonian
diffeomorphisms, interpretable and have a non-vanishing gradient property. We
also give a representation theory for linear systems, meaning the proposed
P-SympNets can exactly parameterize any symplectic map corresponding to
quadratic Hamiltonians. Extensive numerical tests demonstrate increased
expressiveness and accuracy -- often several orders of magnitude better -- for
lower training cost over existing architectures. Lastly, we show how to perform
symbolic Hamiltonian regression with SympNets for polynomial systems using
backward error analysis.
30 Sep 2021
Psychological safety has been postulated as a key factor for the success of agile software development teams, yet there is a lack of empirical studies investigating the role of psychological safety in this context. The present study examines how work design characteristics of software development teams (autonomy, task interdependence, and role clarity) influence psychological safety and, further, how psychological safety impacts team performance, either directly or indirectly through team reflexivity. We test our model using survey data from 236 team members in 43 software development teams in Norway. Our results show that autonomy boosts psychological safety in software teams, and that psychological safety again has a positive effect on team reflexivity and a direct effect on team performance.
29 Aug 2025
Quantum circuits are typically represented by a (ordered) sequence of gates over a set of virtual qubits. During compilation, the virtual qubits of the gates are assigned to the physical qubits of the underlying quantum hardware, a step often referred to as the qubit assignment problem. To ensure that the resulting circuit respects hardware connectivity constraints, additional SWAP gates are inserted as needed, which is known as the qubit routing problem. Together, they are called the Qubit Mapping Problem (QMP), which is known to be NP-hard. A very common way to deal with the complexity of the QMP is to partition the sequence of gates into a sequence of gate groups (or layers). However, this imposes a couple of important restrictions: (1) SWAP gates can only be added between pairs of consecutive groups, and (2) all the gates belonging to a certain group have to be executed (in parallel) in the same time slot. The first one prevents gates to be re-arranged optimally, while the second one imposes a time discretization that practically ignores gate execution time. While this clearly reduces the size of the feasible space, little is still known about how much is actually lost by imposing a fixed layering when looking at the minimization of either the number of SWAPs or the makespan of the compiled circuit. In this paper, we present a flexible branch and bound algorithm for a generalized version of the QMP that either considers or ignores the gate layering and the gate execution time. The algorithm can find find proven optimal solutions for all variations of the QMP, but also offers a great platform for different heuristic algorithms. We present results on several benchmark sets of small quantum circuits, and we show how ignoring the layering can significantly improve some key performance indicators of the compiled circuit.
02 Jan 2024
Pseudo-Hamiltonian neural networks (PHNN) were recently introduced for
learning dynamical systems that can be modelled by ordinary differential
equations. In this paper, we extend the method to partial differential
equations. The resulting model is comprised of up to three neural networks,
modelling terms representing conservation, dissipation and external forces, and
discrete convolution operators that can either be learned or be given as input.
We demonstrate numerically the superior performance of PHNN compared to a
baseline model that models the full dynamics by a single neural network.
Moreover, since the PHNN model consists of three parts with different physical
interpretations, these can be studied separately to gain insight into the
system, and the learned model is applicable also if external forces are removed
or changed.
26 Jan 2018
Software development projects have undergone remarkable changes with the arrival of agile development methods. While intended for small, self-managing teams, these methods are increasingly used also for large development programs. A major challenge in programs is to coordinate the work of many teams, due to high uncertainty in tasks, a high degree of interdependence between tasks and because of the large number of people involved. This revelatory case study focuses on how knowledge work is coordinated in large-scale agile development programs by providing a rich description of the coordination practices used and how these practices change over time in a four year development program with 12 development teams. The main findings highlight the role of coordination modes based on feedback, the use of a number of mechanisms far beyond what is described in practitioner advice, and finally how coordination practices change over time. The findings are important to improve the outcome of large knowledge-based development programs by tailoring coordination practices to needs and ensuring adjustment over time.
Cardiac valve event timing plays a crucial role when conducting clinical
measurements using echocardiography. However, established automated approaches
are limited by the need of external electrocardiogram sensors, and manual
measurements often rely on timing from different cardiac cycles. Recent methods
have applied deep learning to cardiac timing, but they have mainly been
restricted to only detecting two key time points, namely end-diastole (ED) and
end-systole (ES). In this work, we propose a deep learning approach that
leverages triplane recordings to enhance detection of valve events in
echocardiography. Our method demonstrates improved performance detecting six
different events, including valve events conventionally associated with ED and
ES. Of all events, we achieve an average absolute frame difference (aFD) of
maximum 1.4 frames (29 ms) for start of diastasis, down to 0.6 frames (12 ms)
for mitral valve opening when performing a ten-fold cross-validation with test
splits on triplane data from 240 patients. On an external independent test
consisting of apical long-axis data from 180 other patients, the worst
performing event detection had an aFD of 1.8 (30 ms). The proposed approach has
the potential to significantly impact clinical practice by enabling more
accurate, rapid and comprehensive event detection, leading to improved clinical
measurements.
23 Jan 2023
Hybrid machine learning based on Hamiltonian formulations has recently been
successfully demonstrated for simple mechanical systems, both energy conserving
and not energy conserving. We introduce a pseudo-Hamiltonian formulation that
is a generalization of the Hamiltonian formulation via the port-Hamiltonian
formulation, and show that pseudo-Hamiltonian neural network models can be used
to learn external forces acting on a system. We argue that this property is
particularly useful when the external forces are state dependent, in which case
it is the pseudo-Hamiltonian structure that facilitates the separation of
internal and external forces. Numerical results are provided for a forced and
damped mass-spring system and a tank system of higher complexity, and a
symmetric fourth-order integration scheme is introduced for improved training
on sparse and noisy data.
Nowadays, the continuous improvement and automation of industrial processes
has become a key factor in many fields, and in the chemical industry, it is no
exception. This translates into a more efficient use of resources, reduced
production time, output of higher quality and reduced waste. Given the
complexity of today's industrial processes, it becomes infeasible to monitor
and optimize them without the use of information technologies and analytics. In
recent years, machine learning methods have been used to automate processes and
provide decision support. All of this, based on analyzing large amounts of data
generated in a continuous manner. In this paper, we present the results of
applying machine learning methods during a chemical sulphonation process with
the objective of automating the product quality analysis which currently is
performed manually. We used data from process parameters to train different
models including Random Forest, Neural Network and linear regression in order
to predict product quality values. Our experiments showed that it is possible
to predict those product quality values with good accuracy, thus, having the
potential to reduce time. Specifically, the best results were obtained with
Random Forest with a mean absolute error of 0.089 and a correlation of 0.978.
15 Nov 2023
With the growing need for automation and the ongoing merge of OT and IT,
industrial networks have to transport a high amount of heterogeneous data with
mixed criticality such as control traffic, sensor data, and configuration
messages. Current advances in IT technologies furthermore enable a new set of
automation scenarios under the roof of Industry 4.0 and IIoT where industrial
networks now have to meet new requirements in flexibility and reliability. The
necessary real-time guarantees will place significant demands on the networks.
In this paper, we identify IIoT use cases and infer real-time requirements
along several axes before bridging the gap between real-time network
technologies and the identified scenarios. We review real-time networking
technologies and present peer-reviewed works from the past 5 years for
industrial environments. We investigate how these can be applied to
controllers, systems, and embedded devices. Finally, we discuss open challenges
for real-time communication technologies to enable the identified scenarios.
The review shows academic interest in the field of real-time communication
technologies but also highlights a lack of a fixed set of standards important
for trust in safety and reliability, especially where wireless technologies are
concerned.
06 Jun 2023
We introduce the mean inverse integrator (MII), a novel approach to increase
the accuracy when training neural networks to approximate vector fields of
dynamical systems from noisy data. This method can be used to average multiple
trajectories obtained by numerical integrators such as Runge-Kutta methods. We
show that the class of mono-implicit Runge-Kutta methods (MIRK) has particular
advantages when used in connection with MII. When training vector field
approximations, explicit expressions for the loss functions are obtained when
inserting the training data in the MIRK formulae, unlocking symmetric and
high-order integrators that would otherwise be implicit for initial value
problems. The combined approach of applying MIRK within MII yields a
significantly lower error compared to the plain use of the numerical integrator
without averaging the trajectories. This is demonstrated with experiments using
data from several (chaotic) Hamiltonian systems. Additionally, we perform a
sensitivity analysis of the loss functions under normally distributed
perturbations, supporting the favorable performance of MII.
Autonomous surface vessels (ASVs) are becoming increasingly significant in
enhancing the safety and sustainability of maritime operations. To ensure the
reliability of modern control algorithms utilized in these vessels, digital
twins (DTs) provide a robust framework for conducting safe and effective
simulations within a virtual environment. Digital twins are generally
classified on a scale from 0 to 5, with each level representing a progression
in complexity and functionality: Level 0 (Standalone) employs offline modeling
techniques; Level 1 (Descriptive) integrates sensors and online modeling to
enhance situational awareness; Level 2 (Diagnostic) focuses on condition
monitoring and cybersecurity; Level 3 (Predictive) incorporates predictive
analytics; Level 4 (Prescriptive) embeds decision-support systems; and Level 5
(Autonomous) enables advanced functionalities such as collision avoidance and
path following. These digital representations not only provide insights into
the vessel's current state and operational efficiency but also predict future
scenarios and assess life endurance. By continuously updating with real-time
sensor data, the digital twin effectively corrects modeling errors and enhances
decision-making processes. Since DTs are key enablers for complex autonomous
systems, this paper introduces a comprehensive methodology for establishing a
digital twin framework specifically tailored for ASVs. Through a detailed
literature survey, we explore existing state-of-the-art enablers across the
defined levels, offering valuable recommendations for future research and
development in this rapidly evolving field.
24 Jun 2024
We present an investigation of how topological data analysis (TDA) can be
applied to condition-based monitoring (CBM) of wind turbines for energy
generation. TDA is a branch of data analysis focusing on extracting meaningful
information from complex datasets by analyzing their structure in state space
and computing their underlying topological features. By representing data in a
high-dimensional state space, TDA enables the identification of patterns,
anomalies, and trends in the data that may not be apparent through traditional
signal processing methods. For this study, wind turbine data was acquired from
a wind park in Norway via standard vibration sensors at different locations of
the turbine's gearbox. Both the vibration acceleration data and its frequency
spectra were recorded at infrequent intervals for a few seconds at high
frequency and failure events were labelled as either gear-tooth or ball-bearing
failures. The data processing and analysis are based on a pipeline where the
time series data is first split into intervals and then transformed into
multi-dimensional point clouds via a time-delay embedding. The shape of the
point cloud is analyzed with topological methods such as persistent homology to
generate topology-based key health indicators based on Betti numbers,
information entropy and signal persistence. Such indicators are tested for CBM
and diagnosis (fault detection) to identify faults in wind turbines and
classify them accordingly. Topological indicators are shown to be an
interesting alternative for failure identification and diagnosis of operational
failures in wind turbines.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.