Shanghai Qi-Zhi Institute
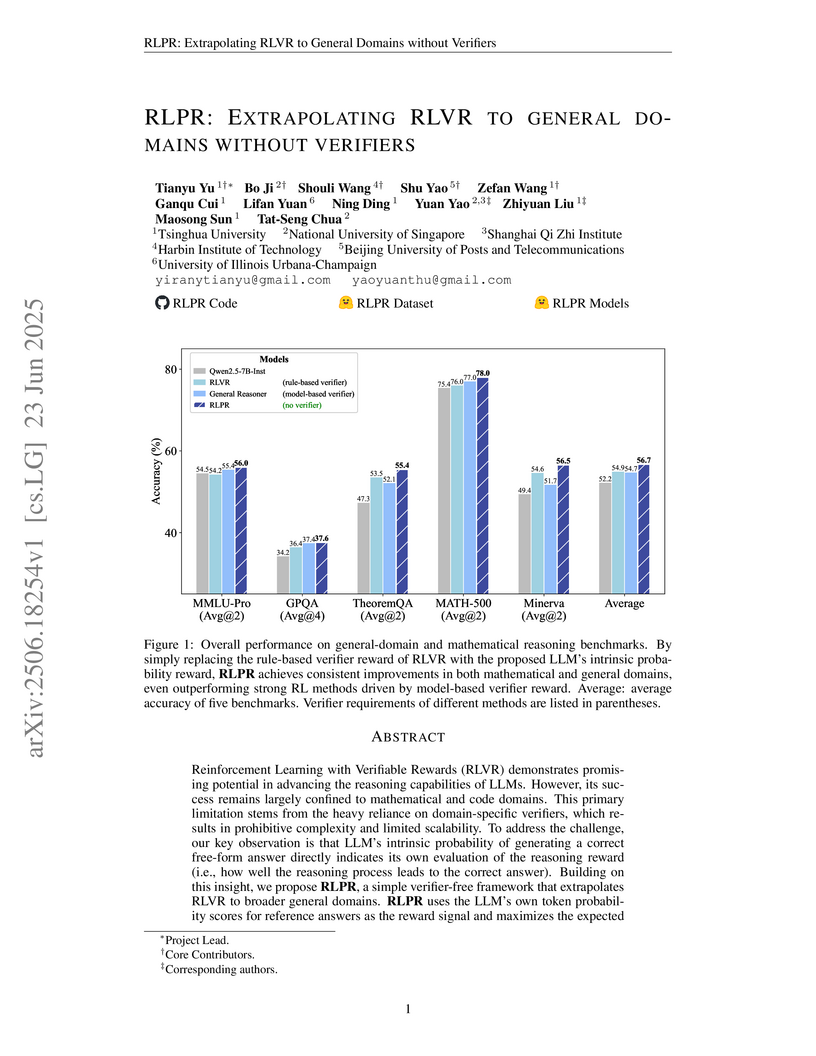
Researchers from Tsinghua University and NUS developed RLPR, a verifier-free reinforcement learning framework that enhances Large Language Model reasoning across general domains by using an intrinsic probability-based reward. This method achieved an average 24.9% improvement on general-domain benchmarks and consistently outperformed existing RLVR and concurrent verifier-free approaches by removing the need for external verification.
30 Sep 2025
A two-stage Reinforcement Learning framework for humanoids, called Any2Track, enables robust motion tracking across diverse, highly dynamic, and contact-rich movements, coupled with online adaptation to real-world disturbances. The system demonstrates superior tracking quality and stable operation on both simulation and a physical Unitree G1 robot, with successful zero-shot transfer.
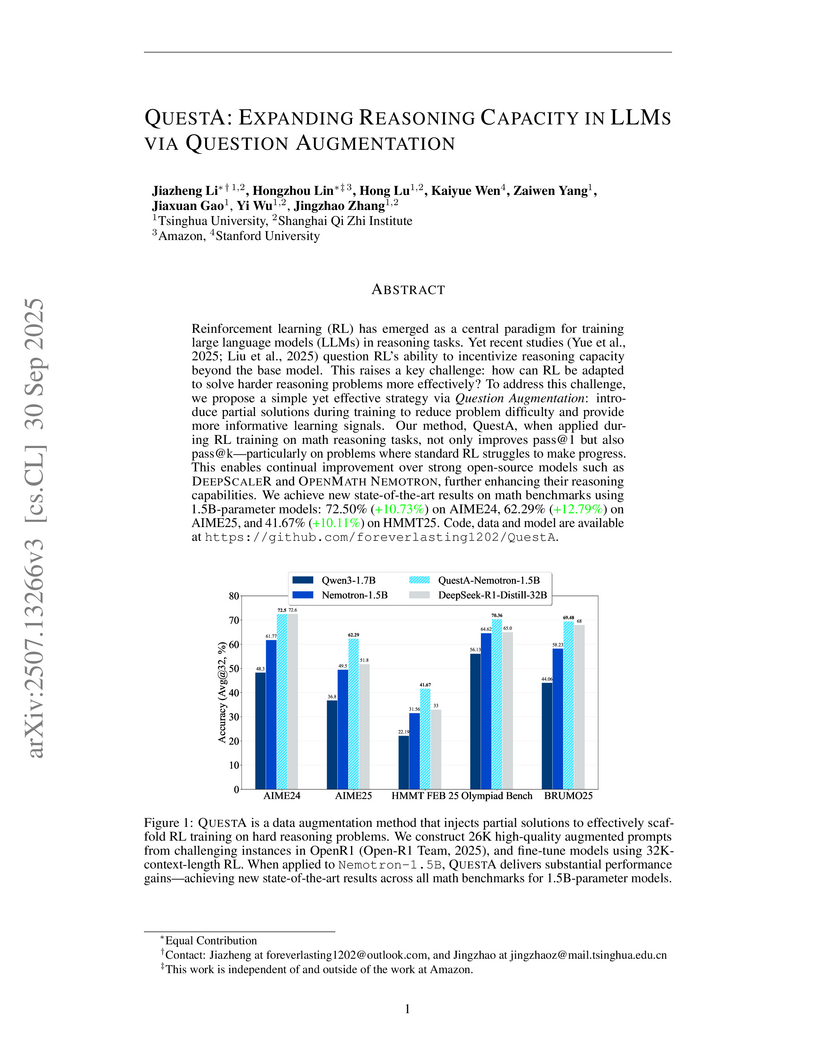
QUESTA enhances the reasoning capacity of Large Language Models by introducing a question augmentation strategy that uses partial solutions to improve Reinforcement Learning (RL) efficiency on challenging problems. This method enables 1.5B-parameter models to achieve state-of-the-art performance on mathematical reasoning benchmarks, often matching or surpassing much larger models, while preserving solution diversity.
The Regularized Policy Gradient (RPG) framework provides a unified theoretical foundation for designing KL-regularized policy gradient algorithms for large language models, correcting prior inconsistencies in methods like GRPO. RPG-REINFORCE, particularly with its novel RPG-Style Clip, achieved up to +6 absolute percentage points higher accuracy on mathematical reasoning benchmarks, along with improved training stability and scalability.
Researchers from Tsinghua University, Shanghai Qi Zhi Institute, UCLA, and Princeton University developed Tensor Product Attention (TPA), an attention mechanism utilizing contextual tensor decompositions for queries, keys, and values. This method reduces KV cache memory usage by an order of magnitude, improves model quality on various benchmarks, and maintains native compatibility with RoPE, thereby enabling more efficient long-context processing in Large Language Models.
Researchers from Tsinghua University and the University of California, Berkeley empirically show that Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) achieves competitive or superior performance and sample efficiency compared to state-of-the-art off-policy methods in cooperative multi-agent games, challenging the common perception of its limitations in resource-constrained academic settings. The study identifies specific implementation factors and hyperparameters crucial for PPO's strong empirical performance, offering practical guidance for its effective deployment.
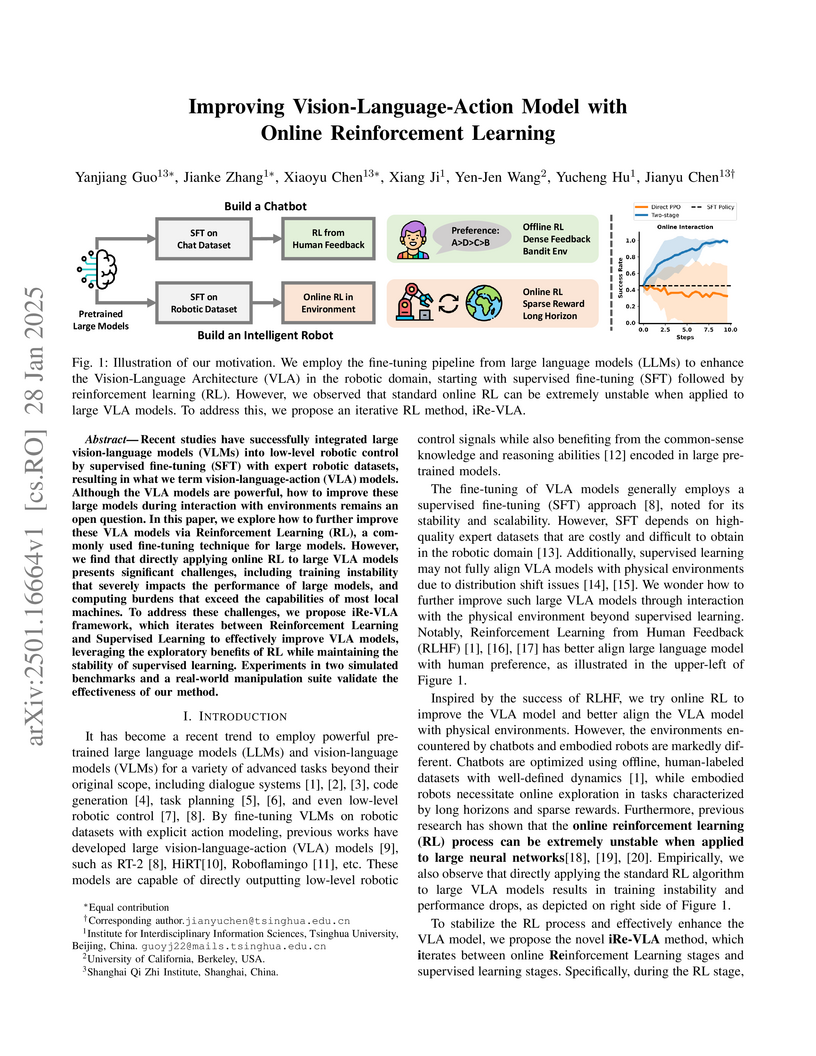
Tsinghua University and UC Berkeley researchers present iRe-VLA, a groundbreaking framework that enables continuous improvement of Vision-Language-Action models through online reinforcement learning, demonstrating significant performance gains across both seen and unseen robotic manipulation tasks while maintaining training stability through a novel two-stage approach.
A new benchmark, OmniSpatial, offers a comprehensive evaluation of Vision-Language Models' spatial reasoning by integrating principles from cognitive psychology into 50 fine-grained subtasks. The benchmark reveals that state-of-the-art VLMs perform over 30 percentage points below human accuracy, particularly struggling with complex spatial logic and perspective-taking.
22 Sep 2025
Wuhan University Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University Peking UniversityTHOUGHTHere's the plan:The user wants me to extract organization names from the first section of the paper, specifically from the author affiliations.I must only include organizations that authors are explicitly affiliated with and check if the organization names correspond to author email domains (though I don't have email domains here, I'll assume the listed affiliations are valid).I should avoid department names if the institution is not mentioned, project names, or any other organizations not directly tied to author affiliations.1. Scan the author list and their superscripts.2. Match superscripts to the numbered affiliation list.3. Extract the full organization name from the affiliation list.4. Filter out any non-organization names (e.g., general descriptions, project names).5. Ensure each organization corresponds to at least one author's affiliation.Shanghai Qi-Zhi Institute":
Peking UniversityTHOUGHTHere's the plan:The user wants me to extract organization names from the first section of the paper, specifically from the author affiliations.I must only include organizations that authors are explicitly affiliated with and check if the organization names correspond to author email domains (though I don't have email domains here, I'll assume the listed affiliations are valid).I should avoid department names if the institution is not mentioned, project names, or any other organizations not directly tied to author affiliations.1. Scan the author list and their superscripts.2. Match superscripts to the numbered affiliation list.3. Extract the full organization name from the affiliation list.4. Filter out any non-organization names (e.g., general descriptions, project names).5. Ensure each organization corresponds to at least one author's affiliation.Shanghai Qi-Zhi Institute":
 Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University Peking UniversityTHOUGHTHere's the plan:The user wants me to extract organization names from the first section of the paper, specifically from the author affiliations.I must only include organizations that authors are explicitly affiliated with and check if the organization names correspond to author email domains (though I don't have email domains here, I'll assume the listed affiliations are valid).I should avoid department names if the institution is not mentioned, project names, or any other organizations not directly tied to author affiliations.1. Scan the author list and their superscripts.2. Match superscripts to the numbered affiliation list.3. Extract the full organization name from the affiliation list.4. Filter out any non-organization names (e.g., general descriptions, project names).5. Ensure each organization corresponds to at least one author's affiliation.Shanghai Qi-Zhi Institute":
Peking UniversityTHOUGHTHere's the plan:The user wants me to extract organization names from the first section of the paper, specifically from the author affiliations.I must only include organizations that authors are explicitly affiliated with and check if the organization names correspond to author email domains (though I don't have email domains here, I'll assume the listed affiliations are valid).I should avoid department names if the institution is not mentioned, project names, or any other organizations not directly tied to author affiliations.1. Scan the author list and their superscripts.2. Match superscripts to the numbered affiliation list.3. Extract the full organization name from the affiliation list.4. Filter out any non-organization names (e.g., general descriptions, project names).5. Ensure each organization corresponds to at least one author's affiliation.Shanghai Qi-Zhi Institute":A framework called MotionTrans allows robotic manipulation policies to learn new motions directly from human VR demonstrations for zero-shot task execution on a real robot. This approach yielded an average 20% success rate for novel tasks without robot-specific data and improved few-shot learning by 40% on average through pretraining with a combined human-robot dataset.
Researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Peking University, Tsinghua University, and LiAuto developed TrajHF, a framework that leverages diffusion models and reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) to generate personalized driving styles. The system successfully adapts to aggressive and defensive preferences, showing superior alignment with human judgments and robust generalization across scenarios.
DexNDM introduces a sim-to-real framework that leverages a joint-wise neural dynamics model and autonomous data collection to achieve generalized in-hand object rotation. This approach enables robust manipulation of diverse objects, including those with challenging geometries, under various wrist orientations and rotation axes in real-world scenarios.
17 May 2025
Researchers from Tsinghua University and collaborating institutions introduce OneTwoVLA, a unified vision-language-action model that dynamically switches between reasoning and acting modes for robotic control, alongside a scalable pipeline for generating embodied reasoning data that enables enhanced performance on long-horizon tasks while maintaining real-time responsiveness.
18 Oct 2025
Reinforcement learning (RL) has emerged as an effective paradigm for enhancing model reasoning. However, existing RL methods like GRPO often rely on unstructured self-sampling to fit scalar rewards, often producing inefficient rollouts that fail to capture transferable problem-solving strategies. To address these limitations, we propose **TemplateRL**, a structured template-guided RL framework that augments policy optimization with explicit template guidance. Our approach first constructs a problem-solving template library via MCTS on a small seed set, then seamlessly integrates this high-level structured guidance into RL training. By guiding rollout generation to align with proven template structures, TemplateRL significantly improves high-quality trajectory hit rates while reducing ineffective exploration. This structure-guided design steers the policy toward validated strategic patterns, stabilizing training dynamics, and enhancing RL sampling efficiency. Notably, the explicit template library is interpretable, editable, and supports online updates-enabling continuous updates during both training and inference. Extensive experiments demonstrate that TemplateRL outperforms GRPO by 99% on AIME and 41% on AMC, with superior stability on weak models and remarkable cross-domain generalization, highlighting its potential for broader tasks.
Entropy Regularizing Activation (ERA) introduces a new paradigm for entropy-constrained training by integrating entropy constraints directly into network architectures via specialized activation functions. The method enhances performance in continuous control by over 30% on HumanoidBench, boosts LLM mathematical reasoning by 37.4% on AIME'25, and improves ImageNet top-1 accuracy by 0.69%, all with minimal computational overhead.
This research introduces the Reactive Diffusion Policy (RDP), a novel slow-fast visual-tactile learning approach, paired with TactAR, a low-cost augmented reality teleoperation system, to enable precise and reactive robot manipulation in contact-rich environments. RDP achieves over 35% improvement in performance across tasks like peeling and wiping compared to existing baselines, demonstrating human-like reactive behaviors and immediate adaptation to disturbances.
25 Feb 2025
We propose the concept of Intra-Query Runtime Elasticity (IQRE) for
cloud-native data analysis. IQRE enables a cloud-native OLAP engine to
dynamically adjust a query's Degree of Parallelism (DOP) during execution. This
capability allows users to utilize cloud computing resources more
cost-effectively. We present Accordion, the first IQRE query engine. Accordion
can adjust the parallelism of a query at any point during query execution
without pausing data processing. It features a user-friendly interface and an
auto-tuner backed by a "what-if" service to allow users to adjust the DOP
according to their query latency constraints. The design of Accordion follows
the execution model in Presto, an open-source distributed SQL query engine
developed at Meta. We present the implementation of Accordion and demonstrate
its ease of use, showcasing how it enables users to minimize compute resource
consumption while meeting their query time constraints.
While spatial reasoning has made progress in object localization relationships, it often overlooks object orientation-a key factor in 6-DoF fine-grained manipulation. Traditional pose representations rely on pre-defined frames or templates, limiting generalization and semantic grounding. In this paper, we introduce the concept of semantic orientation, which defines object orientations using natural language in a reference-frame-free manner (e.g., the "plug-in" direction of a USB or the "handle" direction of a cup). To support this, we construct OrienText300K, a large-scale dataset of 3D objects annotated with semantic orientations, and develop PointSO, a general model for zero-shot semantic orientation prediction. By integrating semantic orientation into VLM agents, our SoFar framework enables 6-DoF spatial reasoning and generates robotic actions. Extensive experiments demonstrated the effectiveness and generalization of our SoFar, e.g., zero-shot 48.7% successful rate on Open6DOR and zero-shot 74.9% successful rate on SIMPLER-Env.
A comprehensive study investigates the comparative performance of Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) and Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) for large language model (LLM) alignment, revealing that a properly optimized PPO consistently achieves superior and more robust alignment across diverse tasks compared to DPO, which is shown to be susceptible to exploiting out-of-distribution responses.
26 Sep 2025
DriveAgent-R1 integrates active perception and a hybrid-thinking framework into Vision-Language Model-based autonomous driving, enabling agents to proactively seek visual information and adaptively switch reasoning modes. This approach achieves planning accuracy competitive with human drivers and larger closed models while significantly reducing computational overhead through efficient, on-demand visual information retrieval.
24 Feb 2025
DemoGen generates hundreds of synthetic robotic manipulation demonstrations from a single human-collected example by adapting both actions and 3D point cloud observations to new object configurations. This approach significantly reduces the data required for training robust visuomotor policies and improves spatial generalization across diverse tasks and robotic platforms.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.