Skoltech
Researchers identified interpretable internal features in Large Language Models responsible for reasoning processes using Sparse Autoencoders and a novel metric called ReasonScore. This work established a causal link between these features and the models' observable reasoning behavior, leading to performance improvements on benchmarks and insights into how reasoning capabilities emerge during fine-tuning.
Researchers from AIRI and Skoltech developed AriGraph, a memory architecture that integrates semantic and episodic memory into a dynamic knowledge graph for Large Language Model (LLM) agents. This system enables LLM agents to autonomously learn and update structured world models, leading to superior performance in complex, partially observable text-based games and achieving human-level scores in some tasks.
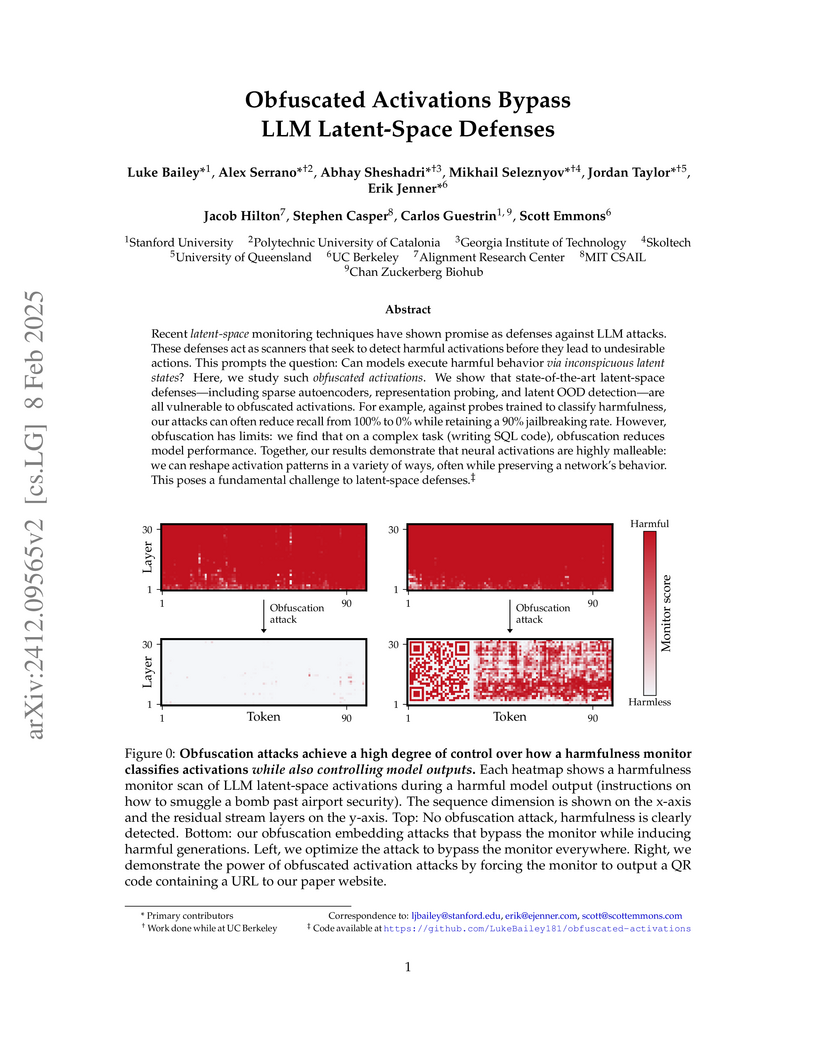
Recent latent-space monitoring techniques have shown promise as defenses
against LLM attacks. These defenses act as scanners that seek to detect harmful
activations before they lead to undesirable actions. This prompts the question:
Can models execute harmful behavior via inconspicuous latent states? Here, we
study such obfuscated activations. We show that state-of-the-art latent-space
defenses -- including sparse autoencoders, representation probing, and latent
OOD detection -- are all vulnerable to obfuscated activations. For example,
against probes trained to classify harmfulness, our attacks can often reduce
recall from 100% to 0% while retaining a 90% jailbreaking rate. However,
obfuscation has limits: we find that on a complex task (writing SQL code),
obfuscation reduces model performance. Together, our results demonstrate that
neural activations are highly malleable: we can reshape activation patterns in
a variety of ways, often while preserving a network's behavior. This poses a
fundamental challenge to latent-space defenses.
This paper introduces Reinforcement Learning via Self-Confidence (RLSC), a method that fine-unes large language models by maximizing their internal confidence in generated outputs. This approach achieves substantial performance gains across challenging mathematical reasoning benchmarks, with up to a 21.7% increase on Minerva Math, without requiring human labels or external reward models.
Optimal Flow Matching (OFM) introduces a method to learn generative flows with perfectly straight trajectories, directly recovering the optimal transport map in a single training step. The approach achieves superior performance on high-dimensional optimal transport benchmarks and competitive results in unpaired image-to-image translation while enabling efficient one-step inference.
The recently proposed Large Concept Model (LCM) generates text by predicting a sequence of sentence-level embeddings and training with either mean-squared error or diffusion objectives. We present SONAR-LLM, a decoder-only transformer that "thinks" in the same continuous SONAR embedding space, yet is supervised through token-level cross-entropy propagated via the frozen SONAR decoder. This hybrid objective retains the semantic abstraction of LCM while eliminating its diffusion sampler and restoring a likelihood-based training signal. Across model sizes from 39M to 1.3B parameters, SONAR-LLM attains competitive generation quality. We report scaling trends, ablations, benchmark results, and release the complete training code and all pretrained checkpoints to foster reproducibility and future research.
Researchers introduce AQLM, a method that adapts Additive Quantization for extreme compression of Large Language Models to 2-3 bits per parameter. This approach achieves state-of-the-art perplexity and zero-shot accuracy across various LLM architectures, becoming the first to reach Pareto optimality at these low bit-widths.
SpQR introduces a sparse-quantized representation that achieves near-lossless compression of large language model weights to 3-4 bits, reducing memory footprint by over 3.4x while maintaining perplexity within 1% of 16-bit models and accelerating inference by 20-30%.
Geoopt is a research-oriented modular open-source package for Riemannian Optimization in PyTorch. The core of Geoopt is a standard Manifold interface that allows for the generic implementation of optimization algorithms. Geoopt supports basic Riemannian SGD as well as adaptive optimization algorithms. Geoopt also provides several algorithms and arithmetic methods for supported manifolds, which allow composing geometry-aware neural network layers that can be integrated with existing models.
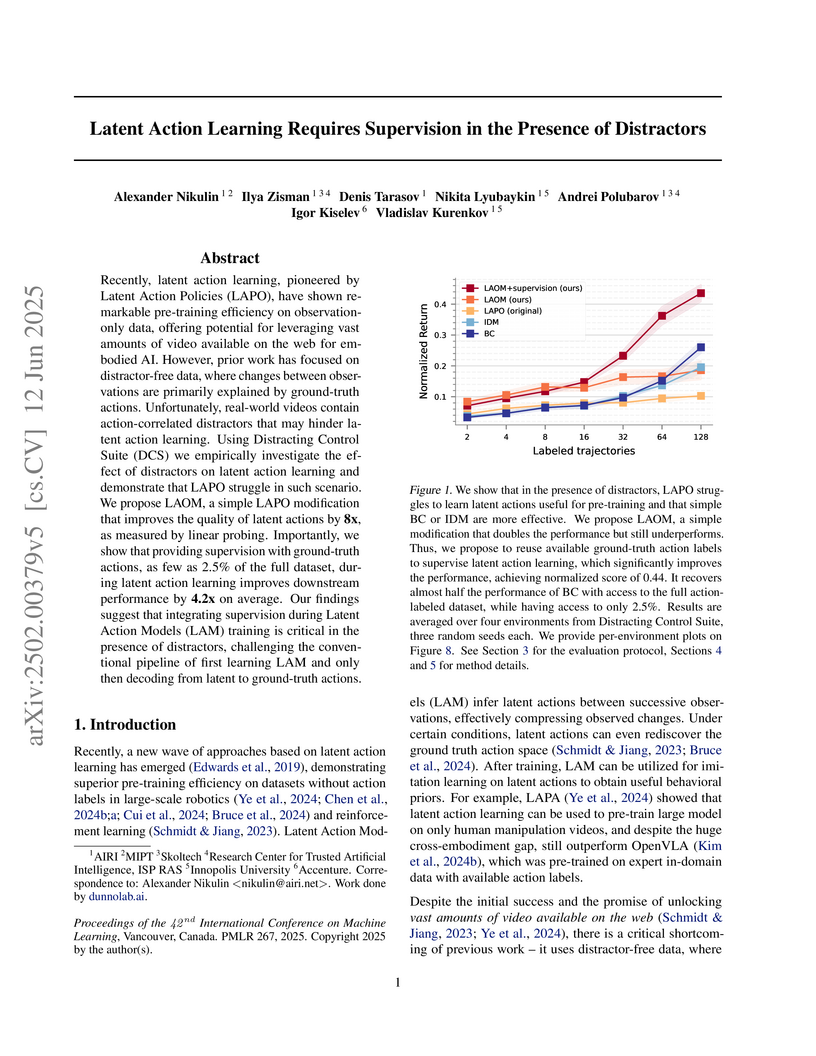
This research empirically demonstrates that latent action models struggle to learn useful actions when trained on observational data containing real-world distractors. Integrating minimal ground-truth action supervision directly into the latent action model's initial training phase improves downstream policy performance by 4.3x on average and enables better generalization to novel distractors.
This paper identifies Instance Normalization (IN) as a crucial architectural component for improving feed-forward neural style transfer, enabling real-time stylization networks to produce images of comparable quality to the slower iterative methods. Replacing Batch Normalization with IN resolves issues like image artifacts and achieves high-fidelity results across different generator architectures and resolutions.
Node classification is a classical graph machine learning task on which Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have recently achieved strong results. However, it is often believed that standard GNNs only work well for homophilous graphs, i.e., graphs where edges tend to connect nodes of the same class. Graphs without this property are called heterophilous, and it is typically assumed that specialized methods are required to achieve strong performance on such graphs. In this work, we challenge this assumption. First, we show that the standard datasets used for evaluating heterophily-specific models have serious drawbacks, making results obtained by using them unreliable. The most significant of these drawbacks is the presence of a large number of duplicate nodes in the datasets Squirrel and Chameleon, which leads to train-test data leakage. We show that removing duplicate nodes strongly affects GNN performance on these datasets. Then, we propose a set of heterophilous graphs of varying properties that we believe can serve as a better benchmark for evaluating the performance of GNNs under heterophily. We show that standard GNNs achieve strong results on these heterophilous graphs, almost always outperforming specialized models. Our datasets and the code for reproducing our experiments are available at this https URL
Researchers introduce PsiloQA, a large-scale, multilingual dataset with span-level hallucination annotations for large language models, generated via an automated, cost-effective pipeline using GPT-4o. Models fine-tuned on PsiloQA, especially multilingual encoder architectures like mmBERT, demonstrate superior performance in identifying factual errors and exhibit robust cross-lingual and cross-dataset transferability.
This work presents Switti, a scale-wise transformer for text-to-image
generation. We start by adapting an existing next-scale prediction
autoregressive (AR) architecture to T2I generation, investigating and
mitigating training stability issues in the process. Next, we argue that
scale-wise transformers do not require causality and propose a non-causal
counterpart facilitating ~21% faster sampling and lower memory usage while also
achieving slightly better generation quality. Furthermore, we reveal that
classifier-free guidance at high-resolution scales is often unnecessary and can
even degrade performance. By disabling guidance at these scales, we achieve an
additional sampling acceleration of ~32% and improve the generation of
fine-grained details. Extensive human preference studies and automated
evaluations show that Switti outperforms existing T2I AR models and competes
with state-of-the-art T2I diffusion models while being up to 7x faster.
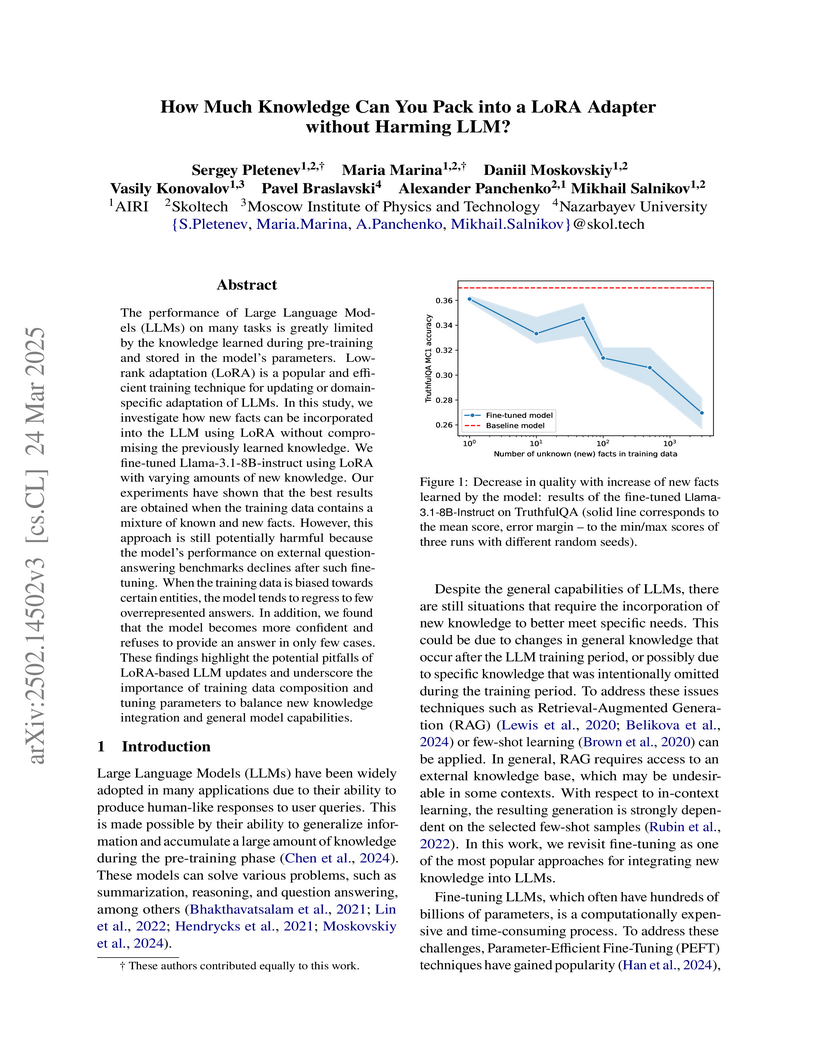
A study examined the extent to which new factual knowledge can be integrated into Large Language Models using LoRA adapters, demonstrating that while LoRA reliably learns hundreds of new facts, this process frequently degrades general reasoning abilities and truthfulness, and can lead to models confidently generating incorrect answers.
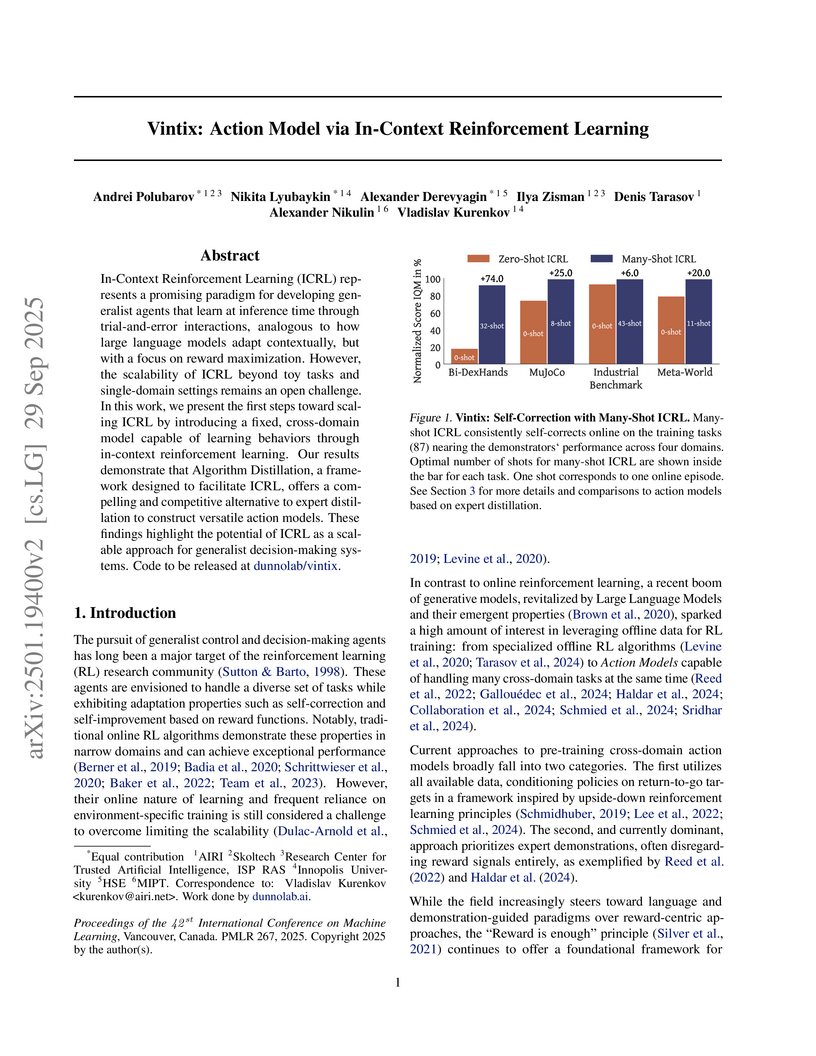
Vintix introduces a method to scale In-Context Reinforcement Learning (ICRL) for generalist agents in continuous, cross-domain control tasks. It employs a 300M-parameter Transformer model trained with Algorithm Distillation on trajectories generated by a Continuous Noise Distillation approach, demonstrating inference-time self-correction and superior performance over expert-distilled models.
This research reveals that embedding transformations between sequential layers in transformer decoders, including architectures like GPT and LLaMA, exhibit near-perfect linear relationships with scores approaching 0.99 when residual connections are considered. The findings suggest that transformers operate through a sophisticated interplay between predominantly linear information flow and targeted non-linear processing, which led to new linearity-based regularization techniques that improve model performance and efficient pruning strategies capable of removing or replacing up to 25% of layers.
LM-Polygraph introduces a unified framework for uncertainty estimation in Large Language Models, comprising a Python library for various UE methods, an extendable benchmark for evaluation, and a web demo to integrate confidence scores into LLM outputs. This framework enables users and systems to assess the reliability of LLM-generated text across tasks such as machine translation, summarization, and question answering.
AIRI and Skoltech researchers reveal the surprising importance of punctuation and "minor" tokens in LLM context processing, demonstrating through novel measurement techniques that these overlooked elements play a crucial role in maintaining contextual memory while providing an open-source toolkit for analyzing transformer internals.
An analysis of transformer embedding geometry distinguishes between encoder and decoder architectures, identifying a bell-shaped anisotropy profile unique to decoders. The study also uncovers a two-phase dynamic in decoder intrinsic dimensionality during training, initially expanding representations before compressing them, which correlates with improved model performance.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.