The Ohio State University
The Ohio State UniversityThe "early experience" paradigm enables autonomous language agents to learn and continuously improve from their own interactions with the environment, leveraging implicit feedback from observed future states rather than explicit reward signals. This approach consistently improves task effectiveness, enhances out-of-domain generalization, and provides a robust foundation for subsequent reinforcement learning.
Researchers at Ohio State University developed PIAD-SRNN, a physics-informed recurrent neural network with adaptive decomposition for time series forecasting and imputation of indoor air quality (IAQ) data. The model consistently achieved superior accuracy (lowest MSE and MAE) for both multi-horizon forecasting and missing data imputation, while maintaining high computational efficiency compared to leading deep learning and linear models.
02 Aug 2025
 Google DeepMind
Google DeepMind University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Université de Montréal
Université de Montréal University of Southern California
University of Southern California Stanford University
Stanford University Mila - Quebec AI Institute
Mila - Quebec AI Institute The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Yale University
Yale University University of Georgia
University of Georgia Nanyang Technological University
Nanyang Technological University Microsoft
Microsoft Argonne National Laboratory
Argonne National Laboratory Duke University
Duke University HKUSTKing Abdullah University of Science and Technology
HKUSTKing Abdullah University of Science and Technology University of Sydney
University of Sydney The Ohio State UniversityPenn State UniversityMetaGPT
The Ohio State UniversityPenn State UniversityMetaGPTA comprehensive, brain-inspired framework integrates diverse research areas of LLM-based intelligent agents, encompassing individual architecture, collaborative systems, and safety. The framework formally conceptualizes agent components, maps AI capabilities to human cognition to identify research gaps, and outlines a roadmap for developing autonomous, adaptive, and safe AI.
HippoRAG 2 presents a non-parametric continual learning framework for large language models that integrates factual, sense-making, and associative memory capabilities within a single system. It achieves the highest average F1 score (59.8) and improved recall across diverse QA benchmarks, outperforming existing RAG methods without sacrificing performance on basic factual recall tasks.
HippoRAG, developed by researchers at The Ohio State University and Stanford University, introduces a neurobiologically inspired long-term memory system for LLMs. It achieves single-step multi-hop knowledge integration by constructing a dynamic knowledge graph, outperforming state-of-the-art RAG methods with up to 20% higher Recall@5 on 2WikiMultiHopQA and being 10-30 times faster than iterative approaches.
AGENTBENCH introduces a multi-dimensional benchmark with 8 interactive environments to systematically evaluate Large Language Models (LLMs) as agents. The benchmark reveals a significant performance gap between commercial and open-source LLMs, identifying predominant failure modes in long-term reasoning and instruction following.
09 Oct 2025
Academia SinicaNational Astronomical Observatory of Japan UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley University College LondonNational Taiwan University
University College LondonNational Taiwan University University of Michigan
University of Michigan Boston UniversityKavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the UniverseThe University of Texas at Dallas
Boston UniversityKavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the UniverseThe University of Texas at Dallas Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Sorbonne UniversitéFermi National Accelerator LaboratoryUniversitat Politècnica de CatalunyaUniversity of Portsmouth
Sorbonne UniversitéFermi National Accelerator LaboratoryUniversitat Politècnica de CatalunyaUniversity of Portsmouth The Ohio State UniversitySejong UniversityUniversidad Nacional Autónoma de MéxicoUniversitat Autònoma de Barcelona
The Ohio State UniversitySejong UniversityUniversidad Nacional Autónoma de MéxicoUniversitat Autònoma de Barcelona University of California, Santa CruzNSF NOIRLabUniversidad de Los AndesUniversity of WyomingCIEMATInstitut de Física d’Altes Energies (IFAE)Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis AvançatsSiena CollegeInstituto Astrofisica de CanariasInstitute of Space Sciences (ICE–CSIC)Universit
degli Studi di MilanoINAF
Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera
University of California, Santa CruzNSF NOIRLabUniversidad de Los AndesUniversity of WyomingCIEMATInstitut de Física d’Altes Energies (IFAE)Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis AvançatsSiena CollegeInstituto Astrofisica de CanariasInstitute of Space Sciences (ICE–CSIC)Universit
degli Studi di MilanoINAF
Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera
 UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley University College LondonNational Taiwan University
University College LondonNational Taiwan University University of Michigan
University of Michigan Boston UniversityKavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the UniverseThe University of Texas at Dallas
Boston UniversityKavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the UniverseThe University of Texas at Dallas Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Sorbonne UniversitéFermi National Accelerator LaboratoryUniversitat Politècnica de CatalunyaUniversity of Portsmouth
Sorbonne UniversitéFermi National Accelerator LaboratoryUniversitat Politècnica de CatalunyaUniversity of Portsmouth The Ohio State UniversitySejong UniversityUniversidad Nacional Autónoma de MéxicoUniversitat Autònoma de Barcelona
The Ohio State UniversitySejong UniversityUniversidad Nacional Autónoma de MéxicoUniversitat Autònoma de Barcelona University of California, Santa CruzNSF NOIRLabUniversidad de Los AndesUniversity of WyomingCIEMATInstitut de Física d’Altes Energies (IFAE)Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis AvançatsSiena CollegeInstituto Astrofisica de CanariasInstitute of Space Sciences (ICE–CSIC)Universit
degli Studi di MilanoINAF
Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera
University of California, Santa CruzNSF NOIRLabUniversidad de Los AndesUniversity of WyomingCIEMATInstitut de Física d’Altes Energies (IFAE)Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis AvançatsSiena CollegeInstituto Astrofisica de CanariasInstitute of Space Sciences (ICE–CSIC)Universit
degli Studi di MilanoINAF
Osservatorio Astronomico di BreraThis study comprehensively characterized the cool circumgalactic medium (CGM) around galaxies at redshifts below 0.4 using data from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) Year 1 survey. It reveals persistent correlations between cool gas absorption and galaxy properties like stellar mass and star formation rate, along with an unexpected absence of azimuthal anisotropy, indicating a possible evolution in CGM dynamics at lower redshifts.
LLaVA-Critic-R1 demonstrates a novel paradigm where a single multimodal model, trained as a critic via reinforcement learning, surprisingly excels as a strong policy model. This approach achieves state-of-the-art performance for 7B-scale models on MMMU (71.9), MathVista (82.1), MathVerse (74.1), and Charxiv Reasoning (62.5), while simultaneously enhancing its self-evaluation capabilities.
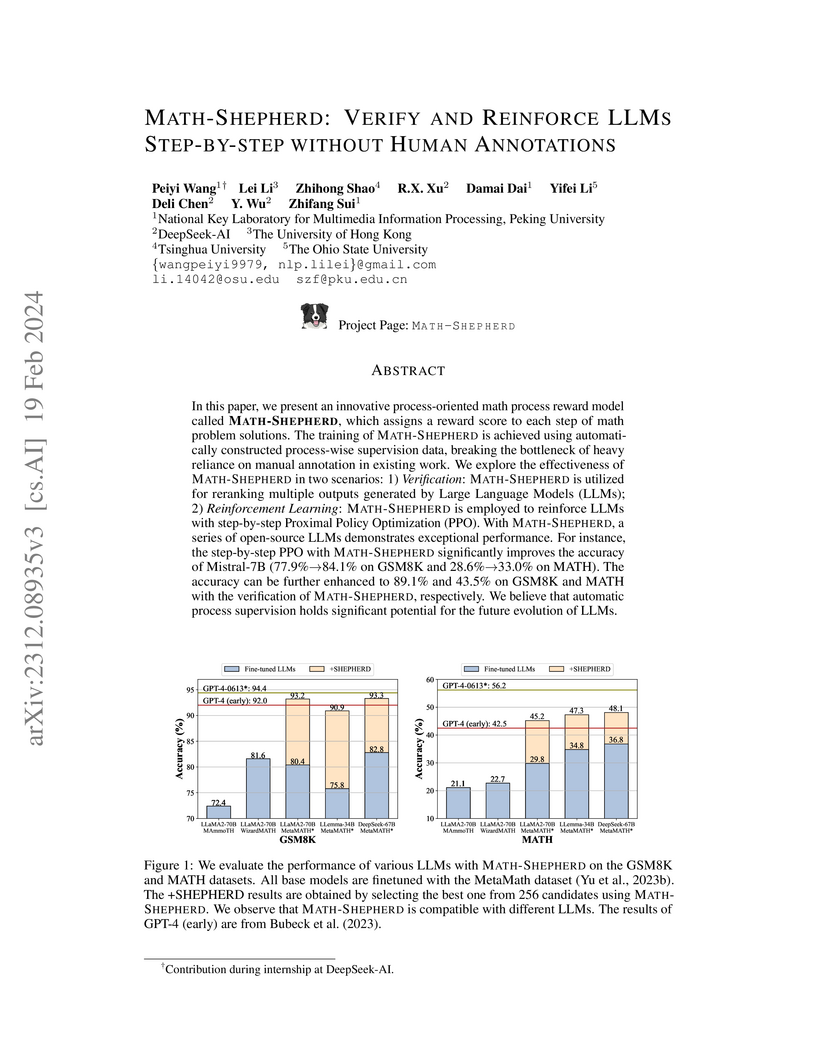
MATH-SHEPHERD, a collaborative effort by Peking University and DeepSeek-AI, presents an automatic process annotation framework for training a process reward model without human intervention. This approach enables open-source LLMs like DeepSeek-67B to achieve 93.3% accuracy on GSM8K and 48.1% on MATH through verification and step-by-step reinforcement learning, improving mathematical reasoning capabilities and outperforming existing methods.
08 Dec 2025
Modern science advances fastest when thought meets action. LabOS represents the first AI co-scientist that unites computational reasoning with physical experimentation through multimodal perception, self-evolving agents, and Extended-Reality(XR)-enabled human-AI collaboration. By connecting multi-model AI agents, smart glasses, and robots, LabOS allows AI to see what scientists see, understand experimental context, and assist in real-time execution. Across applications -- from cancer immunotherapy target discovery to stem-cell engineering and material science -- LabOS shows that AI can move beyond computational design to participation, turning the laboratory into an intelligent, collaborative environment where human and machine discovery evolve together.
Researchers from the University of Waterloo, The Ohio State University, and collaborators present MMMU, a new benchmark designed to evaluate Large Multimodal Models on expert-level, multi-discipline understanding and reasoning. The benchmark, featuring over 11,000 college-level questions with diverse image types, reveals that even leading models like GPT-4o and Gemini 1.5 Pro significantly trail human experts, struggling with domain-specific visual perception, deep knowledge, and complex reasoning.
MIND2WEB introduces a large-scale dataset of over 2,000 human-demonstrated web interaction tasks collected from 137 real-world websites, designed to benchmark generalist agents. The paper also presents MINDACT, a two-stage LLM-based framework that achieves up to 55.1% element accuracy and 52.0% step success rate in cross-task generalization, though overall task success rates are in single digits.
01 Apr 2025
Researchers introduce WEBDREAMER, a model-based planning framework that uses large language models as world models to simulate web environment dynamics and evaluate future states before executing actions. This approach improves web agent performance and efficiency, demonstrating that a specialized 7B-parameter model, Dreamer-7B, can achieve performance comparable to GPT-4o on real-world web tasks.
The Adaptive Reasoning Model (ARM) enables large reasoning models to adaptively select appropriate reasoning formats based on task difficulty, reducing token generation by an average of 30% and up to 70% on easy tasks while maintaining strong performance. This approach, using an adapted reinforcement learning algorithm, mitigates the "overthinking" problem and achieves a ~2x training speedup.
SRPO enhances multimodal large language models by integrating explicit self-reflection and self-correction capabilities through a two-stage training framework. The approach achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source models, scoring 78.5% on MathVista with SRPO-32B, and showing competitive results against leading closed-source models across diverse reasoning benchmarks.
Researchers from Fudan University, The Ohio State University, The Pennsylvania State University, and Meta AI introduced TravelPlanner, a challenging benchmark for real-world planning with language agents, centered on multi-day travel itinerary generation. Evaluations revealed current state-of-the-art LLMs, including GPT-4-Turbo, achieve an extremely low 0.6% success rate in end-to-end planning tasks on this benchmark.
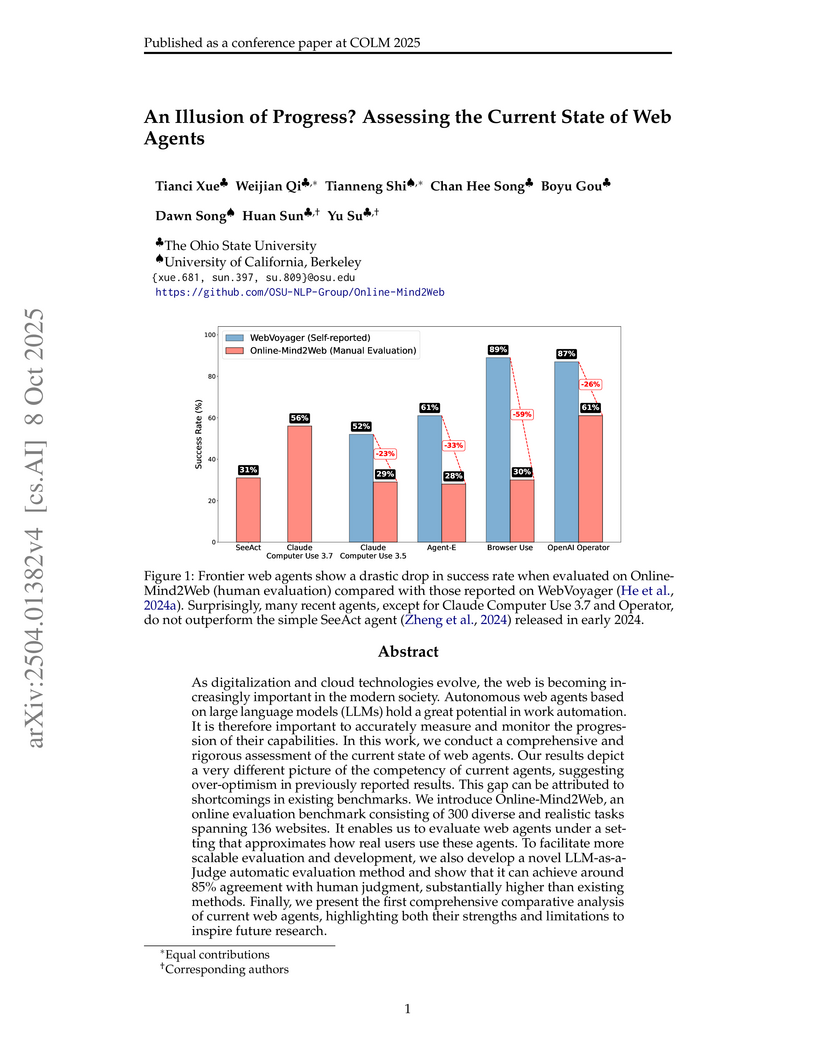
Researchers from The Ohio State University and UC Berkeley rigorously assessed the current state of web agents, revealing that frontier models exhibit substantially lower success rates on a new, more challenging online benchmark compared to previous reports. They introduced Online-Mind2Web, a diverse benchmark of 300 tasks on 136 live websites, and WebJudge, an automatic evaluation method that achieves 85.7% agreement with human judgments.
An investigation into TabPFN v2 illuminates its ability to handle data heterogeneity and its potential as a feature encoder, while proposing test-time divide-and-conquer strategies that extend its applicability to high-dimensional, multi-class, and large-scale tabular datasets.
Computer-using agents (CUAs) must plan task workflows across diverse and evolving applications, yet progress is limited by the lack of large-scale, high-quality training data. Existing datasets are narrow, static, and costly to annotate, while synthetic data often yields oversimplified or misaligned behaviors. We present Watch & Learn (W&L), a framework that converts readily available Internet videos of human computer use into executable UI trajectories at scale. Instead of directly generating actions or relying on handcrafted heuristics, we cast trajectory annotation as an inverse dynamics problem that predicts user actions from consecutive screen states, which simplifies learning and generalizes across domains. Through a task-aware retrieval and labeling pipeline, W&L yields over 53K high-quality trajectories that enhance CUAs both as in-context exemplars and as supervised training data. On OSWorld, it consistently improves general-purpose and specialized CUAs, while on WindowsAgentArena it achieves state-of-the-art performance among 7B-scale models under the 15-step limit. These results show that web-scale human demonstration videos can serve as a practical and scalable foundation for advancing real-world CUAs.
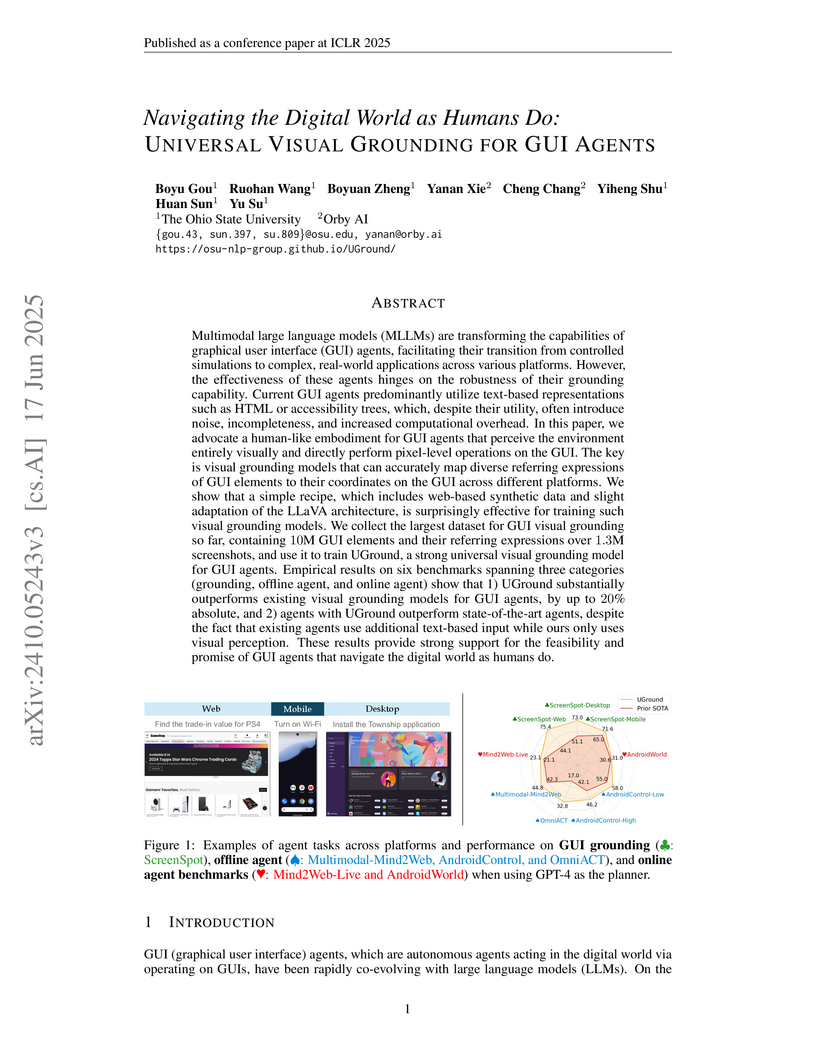
This research introduces UGround, a universal visual grounding model, and integrates it into the SeeAct-V framework, enabling GUI agents to interact with digital environments purely through visual observation and pixel-level operations. The method demonstrates superior performance over state-of-the-art text-based approaches across web, desktop, and mobile GUI tasks, primarily due to its robust grounding capabilities developed from a large synthetic dataset.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.