University of Magdeburg
 ETH Zurich
ETH Zurich University of Washington
University of Washington CNRS
CNRS University of Pittsburgh
University of Pittsburgh University of CambridgeUniversity of FreiburgHeidelberg UniversityLeibniz University Hannover
University of CambridgeUniversity of FreiburgHeidelberg UniversityLeibniz University Hannover Northeastern University
Northeastern University UCLA
UCLA Imperial College London
Imperial College London University of ManchesterUniversity of Zurich
University of ManchesterUniversity of Zurich New York UniversityUniversity of BernUniversity of Stuttgart
New York UniversityUniversity of BernUniversity of Stuttgart UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley University College London
University College London Fudan University
Fudan University Georgia Institute of TechnologyNational Taiwan University
Georgia Institute of TechnologyNational Taiwan University the University of Tokyo
the University of Tokyo University of California, IrvineUniversity of BonnTechnical University of Berlin
University of California, IrvineUniversity of BonnTechnical University of Berlin University of Bristol
University of Bristol University of MichiganUniversity of EdinburghUniversity of Hong KongUniversity of Alabama at Birmingham
University of MichiganUniversity of EdinburghUniversity of Hong KongUniversity of Alabama at Birmingham Northwestern UniversityUniversity of Bamberg
Northwestern UniversityUniversity of Bamberg University of Florida
University of Florida Emory UniversityUniversity of CologneHarvard Medical School
Emory UniversityUniversity of CologneHarvard Medical School University of Pennsylvania
University of Pennsylvania University of SouthamptonFlorida State University
University of SouthamptonFlorida State University EPFL
EPFL University of Wisconsin-MadisonMassachusetts General HospitalChongqing UniversityKeio University
University of Wisconsin-MadisonMassachusetts General HospitalChongqing UniversityKeio University University of Alberta
University of Alberta King’s College LondonFriedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-NürnbergUniversity of Luxembourg
King’s College LondonFriedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-NürnbergUniversity of Luxembourg Technical University of MunichUniversity of Duisburg-EssenSapienza University of RomeUniversity of HeidelbergUniversity of Sheffield
Technical University of MunichUniversity of Duisburg-EssenSapienza University of RomeUniversity of HeidelbergUniversity of Sheffield HKUSTUniversity of GenevaWashington University in St. LouisTU BerlinUniversity of GlasgowUniversity of SiegenUniversity of PotsdamUniversidade Estadual de CampinasUniversity of Oldenburg
HKUSTUniversity of GenevaWashington University in St. LouisTU BerlinUniversity of GlasgowUniversity of SiegenUniversity of PotsdamUniversidade Estadual de CampinasUniversity of Oldenburg The Ohio State UniversityUniversity of LeicesterGerman Cancer Research Center (DKFZ)University of BremenUniversity of ToulouseUniversity of Miami
The Ohio State UniversityUniversity of LeicesterGerman Cancer Research Center (DKFZ)University of BremenUniversity of ToulouseUniversity of Miami Karlsruhe Institute of TechnologyPeking Union Medical CollegeUniversity of OuluUniversity of HamburgUniversity of RegensburgUniversity of BirminghamUniversity of LeedsChinese Academy of Medical SciencesINSERM
Karlsruhe Institute of TechnologyPeking Union Medical CollegeUniversity of OuluUniversity of HamburgUniversity of RegensburgUniversity of BirminghamUniversity of LeedsChinese Academy of Medical SciencesINSERM University of BaselPeking Union Medical College HospitalUniversity of LausanneUniversity of LilleUniversity of PoitiersUniversity of PassauUniversity of LübeckKing Fahd University of Petroleum and MineralsUniversity of LondonUniversity of NottinghamUniversity of Erlangen-NurembergUniversity of BielefeldSorbonne UniversityUniversity of South FloridaWake Forest UniversityUniversity of CalgaryUniversity of Picardie Jules VerneIBM
University of BaselPeking Union Medical College HospitalUniversity of LausanneUniversity of LilleUniversity of PoitiersUniversity of PassauUniversity of LübeckKing Fahd University of Petroleum and MineralsUniversity of LondonUniversity of NottinghamUniversity of Erlangen-NurembergUniversity of BielefeldSorbonne UniversityUniversity of South FloridaWake Forest UniversityUniversity of CalgaryUniversity of Picardie Jules VerneIBM University of GöttingenUniversity of BordeauxUniversity of MannheimUniversity of California San FranciscoNIHUniversity of KonstanzUniversity of Electro-CommunicationsUniversity of WuppertalUniversity of ReunionUNICAMPUniversity of TrierHasso Plattner InstituteUniversity of BayreuthHeidelberg University HospitalUniversity of StrasbourgDKFZUniversity of LorraineInselspital, Bern University Hospital, University of BernUniversity of WürzburgUniversity of La RochelleUniversity of LyonUniversity of HohenheimUniversity Medical Center Hamburg-EppendorfUniversity of UlmUniversity Hospital ZurichUniversity of TuebingenUniversity of KaiserslauternUniversity of NantesUniversity of MainzUniversity of PaderbornUniversity of KielMedical University of South CarolinaUniversity of RostockThe University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer CenterNational Research Council (CNR)Hannover Medical SchoolItalian National Research CouncilUniversity of MuensterUniversity of MontpellierUniversity of LeipzigUniversity of GreifswaldUniversity Hospital BernSiemens HealthineersThe University of Alabama at BirminghamNational Institutes of HealthUniversity of MarburgUniversity of Paris-SaclayUniversity of LimogesUniversity of Clermont AuvergneUniversity of DortmundUniversity of GiessenKITUniversity of ToulonChildren’s Hospital of PhiladelphiaUniversity of JenaNational Taiwan University HospitalUniversity of SaarlandUniversity of ErlangenNational Cancer InstituteUniversity Hospital HeidelbergSwiss Federal Institute of Technology LausanneUniversity of Texas Health Science Center at HoustonNational Institute of Biomedical Imaging and BioengineeringUniversity of New CaledoniaUniversity of Koblenz-LandauParis Diderot UniversityUniversity of ParisInselspital, Bern University HospitalUniversity of Grenoble AlpesUniversity Hospital BaselMD Anderson Cancer CenterUniversity of AngersUniversity of French PolynesiaUniversity of MagdeburgUniversity of Geneva, SwitzerlandOulu University HospitalUniversity of ToursFriedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-NurnbergUniversity of Rennes 1Wake Forest School of MedicineNIH Clinical CenterParis Descartes UniversityUniversity of Rouen NormandieUniversity of Aix-MarseilleUniversity of Perpignan Via DomitiaUniversity of Caen NormandieUniversity of FrankfurtUniversity of BochumUniversity of Bourgogne-Franche-ComtéUniversity of Corsica Pasquale PaoliNational Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeUniversity of HannoverRoche DiagnosticsUniversity of South BrittanyUniversity of DüsseldorfUniversity of Reims Champagne-ArdenneUniversity of HalleIRCCS Fondazione Santa LuciaUniversity of Applied Sciences TrierUniversity of Southampton, UKUniversity of Nice–Sophia AntipolisUniversit
de LorraineUniversité Paris-Saclay["École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne"]RWTH Aachen UniversityUniversity of Bern, Institute for Advanced Study in Biomedical InnovationCRIBIS University of AlbertaThe Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA)Fraunhofer Institute for Medical Image Computing MEVISMedical School of HannoverIstituto di Ricovero e Cura a Carattere Scientifico NeuromedFondazione Santa Lucia IRCCSCEA, LIST, Laboratory of Image and Biomedical SystemsUniversity of Alberta, CanadaHeidelberg University Hospital, Department of NeuroradiologyUniversity of Bern, SwitzerlandUniversity of DresdenUniversity of SpeyerUniversity of Trier, GermanyUniversity of Lorraine, FranceUniversity of Le Havre NormandieUniversity of Bretagne OccidentaleUniversity of French GuianaUniversity of the AntillesUniversity of Bern, Institute of Surgical Technology and BiomechanicsUniversity of Bern, ARTORG Center for Biomedical Engineering ResearchUniversity of Geneva, Department of RadiologyUniversity of Zürich, Department of NeuroradiologyRuhr-University-Bochum
University of GöttingenUniversity of BordeauxUniversity of MannheimUniversity of California San FranciscoNIHUniversity of KonstanzUniversity of Electro-CommunicationsUniversity of WuppertalUniversity of ReunionUNICAMPUniversity of TrierHasso Plattner InstituteUniversity of BayreuthHeidelberg University HospitalUniversity of StrasbourgDKFZUniversity of LorraineInselspital, Bern University Hospital, University of BernUniversity of WürzburgUniversity of La RochelleUniversity of LyonUniversity of HohenheimUniversity Medical Center Hamburg-EppendorfUniversity of UlmUniversity Hospital ZurichUniversity of TuebingenUniversity of KaiserslauternUniversity of NantesUniversity of MainzUniversity of PaderbornUniversity of KielMedical University of South CarolinaUniversity of RostockThe University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer CenterNational Research Council (CNR)Hannover Medical SchoolItalian National Research CouncilUniversity of MuensterUniversity of MontpellierUniversity of LeipzigUniversity of GreifswaldUniversity Hospital BernSiemens HealthineersThe University of Alabama at BirminghamNational Institutes of HealthUniversity of MarburgUniversity of Paris-SaclayUniversity of LimogesUniversity of Clermont AuvergneUniversity of DortmundUniversity of GiessenKITUniversity of ToulonChildren’s Hospital of PhiladelphiaUniversity of JenaNational Taiwan University HospitalUniversity of SaarlandUniversity of ErlangenNational Cancer InstituteUniversity Hospital HeidelbergSwiss Federal Institute of Technology LausanneUniversity of Texas Health Science Center at HoustonNational Institute of Biomedical Imaging and BioengineeringUniversity of New CaledoniaUniversity of Koblenz-LandauParis Diderot UniversityUniversity of ParisInselspital, Bern University HospitalUniversity of Grenoble AlpesUniversity Hospital BaselMD Anderson Cancer CenterUniversity of AngersUniversity of French PolynesiaUniversity of MagdeburgUniversity of Geneva, SwitzerlandOulu University HospitalUniversity of ToursFriedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-NurnbergUniversity of Rennes 1Wake Forest School of MedicineNIH Clinical CenterParis Descartes UniversityUniversity of Rouen NormandieUniversity of Aix-MarseilleUniversity of Perpignan Via DomitiaUniversity of Caen NormandieUniversity of FrankfurtUniversity of BochumUniversity of Bourgogne-Franche-ComtéUniversity of Corsica Pasquale PaoliNational Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeUniversity of HannoverRoche DiagnosticsUniversity of South BrittanyUniversity of DüsseldorfUniversity of Reims Champagne-ArdenneUniversity of HalleIRCCS Fondazione Santa LuciaUniversity of Applied Sciences TrierUniversity of Southampton, UKUniversity of Nice–Sophia AntipolisUniversit
de LorraineUniversité Paris-Saclay["École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne"]RWTH Aachen UniversityUniversity of Bern, Institute for Advanced Study in Biomedical InnovationCRIBIS University of AlbertaThe Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA)Fraunhofer Institute for Medical Image Computing MEVISMedical School of HannoverIstituto di Ricovero e Cura a Carattere Scientifico NeuromedFondazione Santa Lucia IRCCSCEA, LIST, Laboratory of Image and Biomedical SystemsUniversity of Alberta, CanadaHeidelberg University Hospital, Department of NeuroradiologyUniversity of Bern, SwitzerlandUniversity of DresdenUniversity of SpeyerUniversity of Trier, GermanyUniversity of Lorraine, FranceUniversity of Le Havre NormandieUniversity of Bretagne OccidentaleUniversity of French GuianaUniversity of the AntillesUniversity of Bern, Institute of Surgical Technology and BiomechanicsUniversity of Bern, ARTORG Center for Biomedical Engineering ResearchUniversity of Geneva, Department of RadiologyUniversity of Zürich, Department of NeuroradiologyRuhr-University-BochumGliomas are the most common primary brain malignancies, with different
degrees of aggressiveness, variable prognosis and various heterogeneous
histologic sub-regions, i.e., peritumoral edematous/invaded tissue, necrotic
core, active and non-enhancing core. This intrinsic heterogeneity is also
portrayed in their radio-phenotype, as their sub-regions are depicted by
varying intensity profiles disseminated across multi-parametric magnetic
resonance imaging (mpMRI) scans, reflecting varying biological properties.
Their heterogeneous shape, extent, and location are some of the factors that
make these tumors difficult to resect, and in some cases inoperable. The amount
of resected tumor is a factor also considered in longitudinal scans, when
evaluating the apparent tumor for potential diagnosis of progression.
Furthermore, there is mounting evidence that accurate segmentation of the
various tumor sub-regions can offer the basis for quantitative image analysis
towards prediction of patient overall survival. This study assesses the
state-of-the-art machine learning (ML) methods used for brain tumor image
analysis in mpMRI scans, during the last seven instances of the International
Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) challenge, i.e., 2012-2018. Specifically, we
focus on i) evaluating segmentations of the various glioma sub-regions in
pre-operative mpMRI scans, ii) assessing potential tumor progression by virtue
of longitudinal growth of tumor sub-regions, beyond use of the RECIST/RANO
criteria, and iii) predicting the overall survival from pre-operative mpMRI
scans of patients that underwent gross total resection. Finally, we investigate
the challenge of identifying the best ML algorithms for each of these tasks,
considering that apart from being diverse on each instance of the challenge,
the multi-institutional mpMRI BraTS dataset has also been a continuously
evolving/growing dataset.
Do LLMs understand the meaning of the texts they generate? Do they possess a
semantic grounding? And how could we understand whether and what they
understand? I start the paper with the observation that we have recently
witnessed a generative turn in AI, since generative models, including LLMs, are
key for self-supervised learning. To assess the question of semantic grounding,
I distinguish and discuss five methodological ways. The most promising way is
to apply core assumptions of theories of meaning in philosophy of mind and
language to LLMs. Grounding proves to be a gradual affair with a
three-dimensional distinction between functional, social and causal grounding.
LLMs show basic evidence in all three dimensions. A strong argument is that
LLMs develop world models. Hence, LLMs are neither stochastic parrots nor
semantic zombies, but already understand the language they generate, at least
in an elementary sense.
Existing language and vision models achieve impressive performance in
image-text understanding. Yet, it is an open question to what extent they can
be used for language understanding in 3D environments and whether they
implicitly acquire 3D object knowledge, e.g. about different views of an
object. In this paper, we investigate whether a state-of-the-art language and
vision model, CLIP, is able to ground perspective descriptions of a 3D object
and identify canonical views of common objects based on text queries. We
present an evaluation framework that uses a circling camera around a 3D object
to generate images from different viewpoints and evaluate them in terms of
their similarity to natural language descriptions. We find that a pre-trained
CLIP model performs poorly on most canonical views and that fine-tuning using
hard negative sampling and random contrasting yields good results even under
conditions with little available training data.
Krylov subspace methods are considered a standard tool to solve large systems of linear algebraic equations in many scientific disciplines such as image restoration or solving partial differential equations in mechanics of continuum. In the context of computer tomography however, the mostly used algebraic reconstruction techniques are based on classical iterative schemes. In this work we present software package that implements fully 3D cone beam projection operator and uses Krylov subspace methods, namely CGLS and LSQR to solve related tomographic reconstruction problems. It also implements basic preconditioning strategies. On the example of the cone beam CT reconstruction of 3D Shepp-Logan phantom we show that the speed of convergence of the CGLS clearly outperforms PSIRT algorithm. Therefore Krylov subspace methods present an interesting option for the reconstruction of large 3D cone beam CT problems.
14 Jun 2021
We investigate scaling and efficiency of the deep neural network multigrid
method (DNN-MG).
DNN-MG is a novel neural network-based technique for the simulation of the
Navier-Stokes equations that combines an adaptive geometric multigrid solver,
i.e. a highly efficient
classical solution scheme, with a recurrent neural network with memory.
The neural network replaces in DNN-MG one or multiple finest multigrid layers
and provides a correction for the classical solve in the next time step.
This leads to little degradation in the solution quality while substantially
reducing the overall computational costs.
At the same time, the use of the multigrid solver at the coarse scales allows
for a compact network that is easy to train, generalizes well, and allows for
the incorporation of physical constraints.
Previous work on DNN-MG focused on the overall scheme and how to enforce
divergence freedom in the solution.
In this work, we investigate how the network size affects training and
solution quality and the overall runtime of the computations.
Our results demonstrate that larger networks are able to capture the
flow behavior better while requiring only little additional training time.
At runtime, the use of the neural network correction can even reduce the
computation time compared to a classical multigrid simulation through a faster
convergence of the nonlinear solve that is required at every time step.
04 Aug 2021
We discuss how to handle matching-adjusted indirect comparison (MAIC) from a data analyst's perspective. We introduce several multivariate data analysis methods to assess the appropriateness of MAIC for a given data set. These methods focus on comparing the baseline variables used in the matching from a study that provides the summary statistics, or aggregated data (AD) and a study that provides individual patient level data (IPD). The methods identify situations when no numerical solutions are possible with the MAIC method. This helps to avoid misleading results being produced. Moreover, it has been observed that sometimes contradicting results are reported by two sets of MAIC analyses produced by two teams, each having their own IPD and applying MAIC using the AD published by the other team. We show that an intrinsic property of the MAIC estimated weights can be a contributing factor for this phenomenon.
01 Nov 2023
We extend and analyze the deep neural network multigrid solver (DNN-MG) for the Navier-Stokes equations in three dimensions. The idea of the method is to augment a finite element simulation on coarse grids with fine scale information obtained using deep neural networks.
The neural network operates locally on small patches of grid elements. The local approach proves to be highly efficient, since the network can be kept (relatively) small and since it can be applied in parallel on all grid patches. However, the main advantage of the local approach is the inherent generalizability of the method. Since the network only processes data of small sub-areas, it never ``sees'' the global problem and thus does not learn false biases.
We describe the method with a focus on the interplay between the finite element method and deep neural networks. Further, we demonstrate with numerical examples the excellent efficiency of the hybrid approach, which allows us to achieve very high accuracy with a coarse grid and thus reduce the computation time by orders of magnitude.
11 Aug 2021
Narrative visualization aims to communicate scientific results to a general
audience and garners significant attention in various applications. Merging
exploratory and explanatory visualization could effectively support a
non-expert understanding of scientific processes. Medical research results,
e.g., mechanisms of the healthy human body, explanations of pathological
processes, or avoidable risk factors for diseases, are also interesting to a
general audience that includes patients and their relatives. This paper
discusses how narrative techniques can be applied to medical visualization to
tell data-driven stories about diseases. We address the general public
comprising people interested in medicine without specific medical background
knowledge. We derived a general template for the narrative medical
visualization of diseases. Applying this template to three diseases selected to
span bone, vascular, and organ systems, we discuss how narrative techniques can
support visual communication and facilitate understanding of medical data.
Other scientists can adapt our proposed template to inform an audience on other
diseases. With our work, we show the potential of narrative medical
visualization and conclude with a comprehensive research agenda.
This study's objective was to segment spinal metastases in diagnostic MR
images using a deep learning-based approach. Segmentation of such lesions can
present a pivotal step towards enhanced therapy planning and validation, as
well as intervention support during minimally invasive and image-guided
surgeries like radiofrequency ablations. For this purpose, we used a U-Net like
architecture trained with 40 clinical cases including both, lytic and sclerotic
lesion types and various MR sequences. Our proposed method was evaluated with
regards to various factors influencing the segmentation quality, e.g. the used
MR sequences and the input dimension. We quantitatively assessed our
experiments using Dice coefficients, sensitivity and specificity rates.
Compared to expertly annotated lesion segmentations, the experiments yielded
promising results with average Dice scores up to 77.6% and mean sensitivity
rates up to 78.9%. To our best knowledge, our proposed study is one of the
first to tackle this particular issue, which limits direct comparability with
related works. In respect to similar deep learning-based lesion segmentations,
e.g. in liver MR images or spinal CT images, our experiments showed similar or
in some respects superior segmentation quality. Overall, our automatic approach
can provide almost expert-like segmentation accuracy in this challenging and
ambitious task.
04 Aug 2021
We discuss how to handle matching-adjusted indirect comparison (MAIC) from a data analyst's perspective. We introduce several multivariate data analysis methods to assess the appropriateness of MAIC for a given data set. These methods focus on comparing the baseline variables used in the matching from a study that provides the summary statistics, or aggregated data (AD) and a study that provides individual patient level data (IPD). The methods identify situations when no numerical solutions are possible with the MAIC method. This helps to avoid misleading results being produced. Moreover, it has been observed that sometimes contradicting results are reported by two sets of MAIC analyses produced by two teams, each having their own IPD and applying MAIC using the AD published by the other team. We show that an intrinsic property of the MAIC estimated weights can be a contributing factor for this phenomenon.
Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is essential for ensuring the reliability of deep learning models operating in open-world scenarios. Current OOD detectors mainly rely on statistical models to identify unusual patterns in the latent representations of a deep neural network. This work proposes to augment existing OOD detectors with probabilistic reasoning, utilizing Markov logic networks (MLNs). MLNs connect first-order logic with probabilistic reasoning to assign probabilities to inputs based on weighted logical constraints defined over human-understandable concepts, which offers improved explainability. Through extensive experiments on multiple datasets, we demonstrate that MLNs can significantly enhance the performance of a wide range of existing OOD detectors while maintaining computational efficiency. Furthermore, we introduce a simple algorithm for learning logical constraints for OOD detection from a dataset and showcase its effectiveness.
29 Nov 2021
We present the deep neural network multigrid solver (DNN-MG) that we develop
for the instationary Navier-Stokes equations. DNN-MG improves computational
efficiency using a judicious combination of a geometric multigrid solver and a
recurrent neural network with memory. DNN-MG uses the multi-grid method to
classically solve on coarse levels while the neural network corrects
interpolated solutions on fine ones, thus avoiding the increasingly expensive
computations that would have to be performed there. This results in a reduction
in computation time through DNN-MG's highly compact neural network. The
compactness results from its design for local patches and the available coarse
multigrid solutions that provides a "guide" for the corrections. A compact
neural network with a small number of parameters also reduces training time and
data. Furthermore, the network's locality facilitates generalizability and
allows one to use DNN-MG trained on one mesh domain also on different ones. We
demonstrate the efficacy of DNN-MG for variations of the 2D laminar flow around
an obstacle. For these, our method significantly improves the solutions as well
as lift and drag functionals while requiring only about half the computation
time of a full multigrid solution. We also show that DNN-MG trained for the
configuration with one obstacle can be generalized to other time dependent
problems that can be solved efficiently using a geometric multigrid method.
01 Jun 2016
Qualitative Spatial and Temporal Reasoning (QSTR) is concerned with symbolic
knowledge representation, typically over infinite domains. The motivations for
employing QSTR techniques range from exploiting computational properties that
allow efficient reasoning to capture human cognitive concepts in a
computational framework. The notion of a qualitative calculus is one of the
most prominent QSTR formalisms. This article presents the first overview of all
qualitative calculi developed to date and their computational properties,
together with generalized definitions of the fundamental concepts and methods,
which now encompass all existing calculi. Moreover, we provide a classification
of calculi according to their algebraic properties.
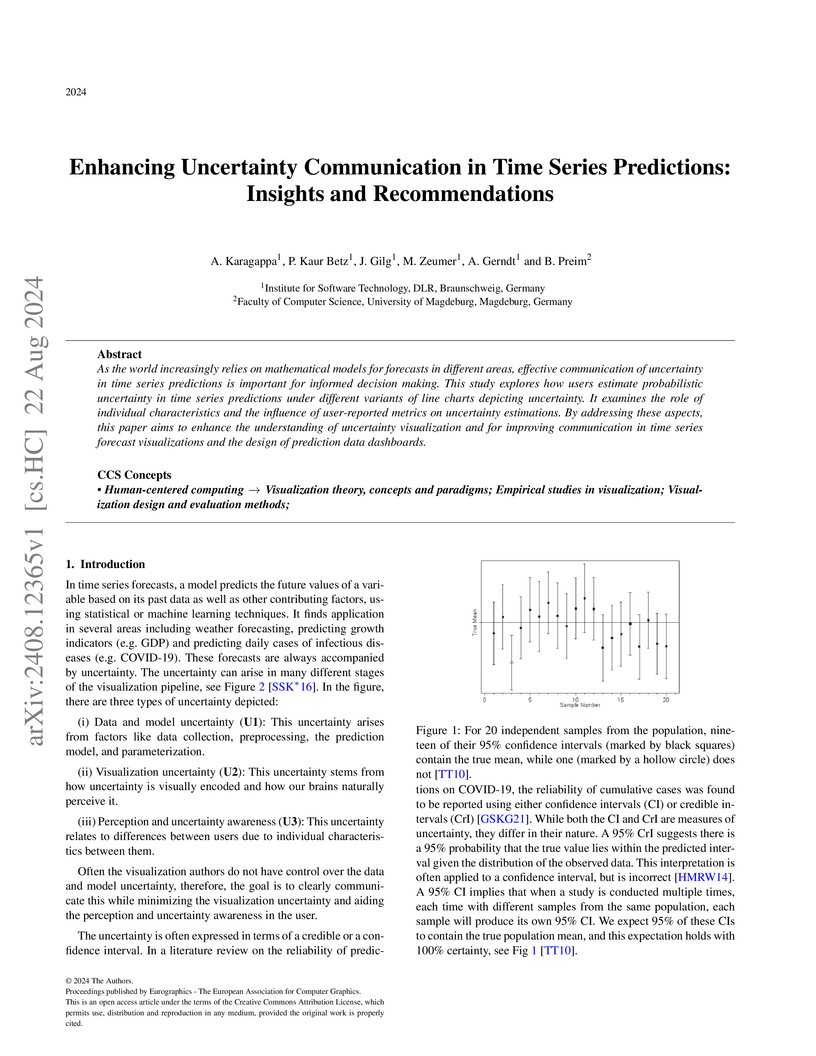
As the world increasingly relies on mathematical models for forecasts in different areas, effective communication of uncertainty in time series predictions is important for informed decision making. This study explores how users estimate probabilistic uncertainty in time series predictions under different variants of line charts depicting uncertainty. It examines the role of individual characteristics and the influence of user-reported metrics on uncertainty estimations. By addressing these aspects, this paper aims to enhance the understanding of uncertainty visualization and for improving communication in time series forecast visualizations and the design of prediction data this http URL the world increasingly relies on mathematical models for forecasts in different areas, effective communication of uncertainty in time series predictions is important for informed decision making. This study explores how users estimate probabilistic uncertainty in time series predictions under different variants of line charts depicting uncertainty. It examines the role of individual characteristics and the influence of user-reported metrics on uncertainty estimations. By addressing these aspects, this paper aims to enhance the understanding of uncertainty visualization and for improving communication in time series forecast visualizations and the design of prediction data dashboards.
In various fields, including medicine, age distributions are crucial. Despite
widespread media coverage of health topics, there remains a need to enhance
health communication. Narrative medical visualization is promising for
improving information comprehension and retention. This study explores the most
effective ways to present age distributions of diseases through narrative
visualizations. We conducted a thorough analysis of existing visualizations,
held workshops with a broad audience, and reviewed relevant literature. From
this, we identified design choices focusing on comprehension, aesthetics,
engagement, and memorability. We specifically tested three pictogram variants:
pictograms as bars, stacked pictograms, and annotations. After evaluating 18
visualizations with 72 participants and three expert reviews, we determined
that annotations were most effective for comprehension and aesthetics. However,
traditional bar charts were preferred for engagement, and other variants were
more memorable. The study provides a set of design recommendations based on
these insights.
In this paper, we introduce a novel class of projectors for 3D cone beam tomographic reconstruction. Analytical formulas are derived to compute the relationship between the volume of a voxel projected onto a detector pixel and its contribution to the line integral of attenuation recorded by that pixel. Based on these formulas, we construct a near-exact projector and backprojector, particularly suited for algebraic reconstruction techniques and hierarchical reconstruction approaches with nonuniform voxel grids. Unlike traditional projectors, which assume a uniform grid with fixed voxel sizes, our method enables local refinement of voxels, allowing for adaptive grid resolution and improved reconstruction quality in regions of interest. We have implemented this cutting voxel projector along with a relaxed, speed-optimized version and compared them to two established projectors: a ray-tracing projector based on Siddon's algorithm and a TT footprint projector. Our results demonstrate that the cutting voxel projector achieves higher accuracy than the TT projector, especially for large cone beam angles. Furthermore, the relaxed version of the cutting voxel projector offers a significant speed advantage over current footprint projector implementations, while maintaining comparable accuracy. In contrast, Siddon's algorithm, when achieving similar accuracy, is considerably slower than the cutting voxel projector. All algorithms are implemented in an open-source framework for algebraic reconstruction using OpenCL and C++, optimized for efficient GPU computation. GitHub repository of the project this https URL.
04 Mar 2025
The comparison of different medical treatments from observational studies or
across different clinical studies is often biased by confounding factors such
as systematic differences in patient demographics or in the inclusion criteria
for the trials. Propensity score matching is a popular method to adjust for
such confounding. It compares weighted averages of patient responses. The
weights are calculated from logistic regression models with the intention to
reduce differences between the confounders in the treatment groups. However,
the groups are only "roughly matched" with no generally accepted principle to
determine when a match is "good enough".
In this manuscript, we propose an alternative approach to the matching
problem by considering it as a constrained optimization problem. We investigate
the conditions for exact matching in the sense that the average values of
confounders are identical in the treatment groups after matching. Our approach
is similar to the matching-adjusted indirect comparison approach by
Signorovitch et al. (2010) but with two major differences: First, we do not
impose any specific functional form on the matching weights; second, the
proposed approach can be applied to individual patient data from several
treatment groups as well as to a mix of individual patient and aggregated data.
11 May 2025
We provide an error analysis for the solution of the nonstationary Stokes
problem by a variational method in space and time. We use finite elements of
higher order for the approximation in space and a Galerkin-Petrov method with
first order polynomials for the approximation in time. We require global
continuity of the discrete velocity trajectory in time, while allowing the
discrete pressure trajectory to be discontinuous at the endpoints of the time
intervals. We show existence and uniqueness of the discrete velocity solution,
characterize the set of all discrete pressure solutions and prove an optimal
second order estimate in time for the pressure error in the midpoints of the
time intervals. The key result and innovation is the construction of
approximations to the pressure trajectory by means of post-processing together
with the proof of optimal order error estimates. We propose two variants for a
post-processed pressure within the set of pressure solutions based on
collocation techniques or interpolation. Both variants guarantee that the
pressure error measured in the L2-norm converges with optimal second order in
time and optimal order in space. For the discrete velocity solution, we prove
error estimates of optimal order in time and space. We present some numerical
tests to support our theoretical results.
09 Sep 2019
The paper continues the authors' work on the adaptive Wynn algorithm in a nonlinear regression model. In the present paper it is shown that if the mean response function satisfies a condition of `saturated identifiability', which was introduced by Pronzato \cite{Pronzato}, then the adaptive least squares estimators are strongly consistent. The condition states that the regression parameter is identifiable under any saturated design, i.e., the values of the mean response function at any p distinct design points determine the parameter point uniquely where, typically, p is the dimension of the regression parameter vector. Further essential assumptions are compactness of the experimental region and of the parameter space together with some natural continuity assumptions. If the true parameter point is an interior point of the parameter space then under some smoothness assumptions and asymptotic homoscedasticity of random errors the asymptotic normality of adaptive least squares estimators is obtained.
05 Jul 2019
For a nonlinear regression model the information matrices of designs depend on the parameter of the model. The adaptive Wynn-algorithm for D-optimal design estimates the parameter at each step on the basis of the employed design points and observed responses so far, and selects the next design point as in the classical Wynn-algorithm for D-optimal design. The name `Wynn-algorithm' is in honor of Henry P. Wynn who established the latter `classical' algorithm in his 1970 paper. The asymptotics of the sequences of designs and maximum likelihood estimates generated by the adaptive algorithm is studied for an important class of nonlinear regression models: generalized linear models whose (univariate) response variables follow a distribution from a one-parameter exponential family. Under the assumptions of compactness of the experimental region and of the parameter space together with some natural continuity assumptions it is shown that the adaptive ML-estimators are strongly consistent and the design sequence is asymptotically locally D-optimal at the true parameter point. If the true parameter point is an interior point of the parameter space then under some smoothness assumptions the asymptotic normality of the adaptive ML-estimators is obtained.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.