Ask or search anything...
 University of Oxford
University of OxfordA comprehensive survey formally defines Agentic Reinforcement Learning (RL) for Large Language Models (LLMs) as a Partially Observable Markov Decision Process (POMDP), distinct from conventional LLM-RL, and provides a two-tiered taxonomy of capabilities and task domains. The work consolidates open-source resources and outlines critical open challenges for the field.
View blogVGGT, developed by VGG at the University of Oxford and Meta AI, introduces a 1.2 billion-parameter feed-forward transformer that directly infers camera parameters, depth maps, and 3D point clouds from multiple input images in a single pass. This model achieves state-of-the-art accuracy in 3D reconstruction and camera pose estimation (e.g., 85.3 AUC@30 on RealEstate10K) while significantly reducing inference time to approximately 0.2 seconds per scene.
View blogA new method, Compute as Teacher (CaT), generates supervision signals for large language models in post-training scenarios lacking traditional ground truth or programmatic verifiers. It leverages inference compute to synthesize reference-free supervision, leading to relative performance increases of up to 33% on MATH-500 and 30% on HealthBench.
View blogA tutorial developed by the University of Oxford and Hugging Face guides readers through modern robot learning, detailing the transition from classical methods to data-driven, learning-based paradigms. It provides conceptual understanding and practical tools using the `lerobot` open-source library, covering Reinforcement Learning, Imitation Learning, and generalist Vision-Language-Action policies with end-to-end examples.
View blogResearchers from University College London and collaborators developed GARNN, an interpretable graph attentive recurrent neural network for predicting blood glucose levels from multivariate time series data. The model consistently achieved state-of-the-art prediction accuracy across four clinical datasets while providing clinically justifiable temporal and global interpretations of variable importance, particularly excelling at attributing sparse event contributions.
View blogResearchers from Imperial College London, Shanghai AI Lab, FLock.io, and HKUST developed zkFL, a system that integrates Zero-Knowledge Proofs to guarantee the integrity of gradient aggregation in Federated Learning against a malicious central aggregator. An extended blockchain-based variant optimizes client-side verification and achieves significantly reduced on-chain costs compared to prior blockchain FL approaches, while maintaining training performance.
View blogResearch from institutions including the UK AI Security Institute and Anthropic demonstrates that poisoning attacks on Large Language Models are determined by a near-constant absolute number of malicious samples, rather than a percentage of the total training data. As few as 250 poisoned documents were sufficient to backdoor models ranging from 600 million to 13 billion parameters, though subsequent alignment training significantly reduced attack success.
View blogResearchers at Meta Superintelligence Labs and University of Oxford empirically demonstrate that Large Language Models acquire separable visual perceptual and reasoning abilities from text-only pre-training, identifying optimal data mixtures for cultivating these "visual priors" and showing improved multimodal performance. The work introduces the Multi-Level Existence Bench (MLE-Bench) for fine-grained perceptual evaluation.
View blogOpenAI researchers and collaborators evaluate GPT-5's utility in accelerating scientific research across diverse fields, demonstrating its capacity for contributing to known result rediscovery, literature search, collaborative problem-solving, and the generation of novel scientific findings. The model proved to compress research timelines from months to hours and provided verifiable new insights in mathematics, physics, and biology.
View blogSakana AI and collaborating institutions developed a comprehensive framework for fully automated scientific discovery, enabling AI agents to conduct an entire research endeavor from hypothesis to peer-reviewed paper. This system generated hundreds of medium-quality papers in machine learning at a cost of under $15 per paper, with its automated reviewer achieving near-human-level performance.
View blogThe paper investigates whether "thinking models" acquire entirely new reasoning capabilities or simply learn to better utilize pre-existing ones from their base counterparts. It demonstrates that base models possess latent reasoning abilities, and thinking models primarily learn *when* and *how* to deploy these mechanisms; a hybrid model steered a base LLM with specific reasoning vectors, recovering up to 91% of the performance gap on mathematical benchmarks.
View blogVGG networks systematically demonstrated that increasing convolutional network depth using homogeneous 3x3 filters consistently improves large-scale image recognition accuracy, achieving top results on ImageNet and establishing powerful, transferable feature extractors.
View blog University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign University of California, Santa Barbara
University of California, Santa Barbara
 Meta
Meta
 Anthropic
Anthropic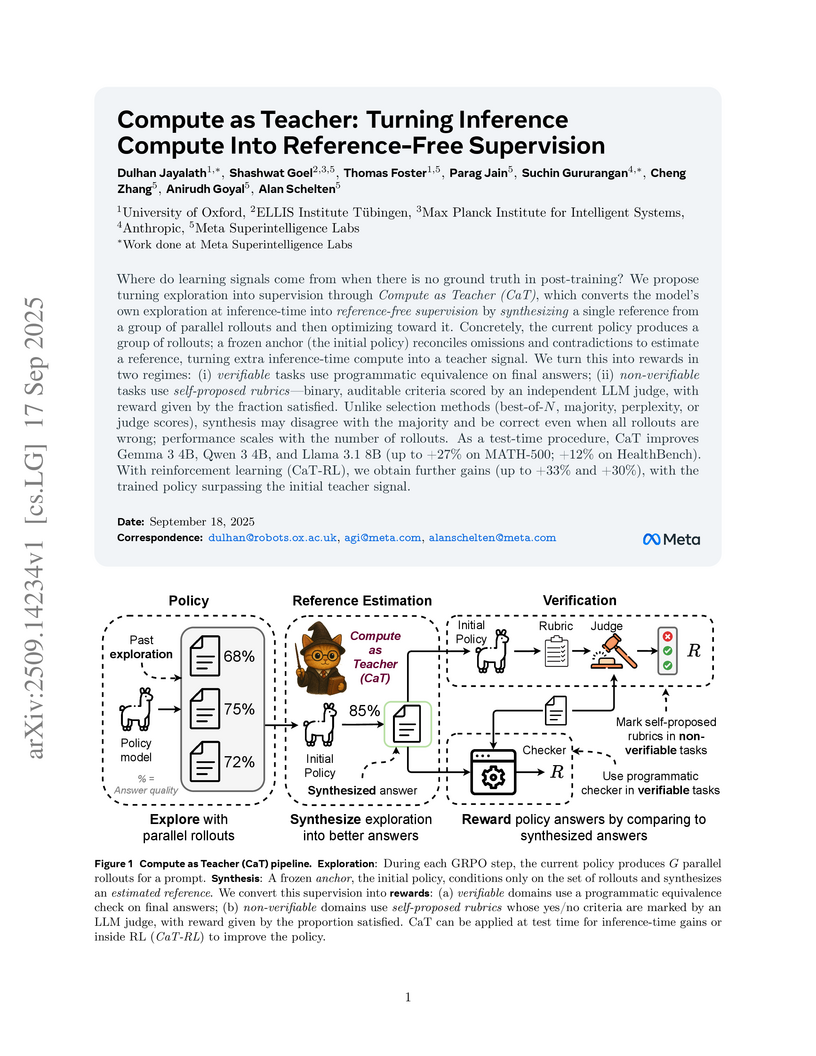
 Hugging Face
Hugging Face
 Imperial College London
Imperial College London University College London
University College London

 CNRS
CNRS

 Tohoku University
Tohoku University California Institute of Technology
California Institute of Technology

 ETH Zurich
ETH Zurich
 KAIST
KAIST University of Washington
University of Washington

 University of Cambridge
University of Cambridge Harvard University
Harvard University


 University of British Columbia
University of British Columbia


