uncertainty-estimation
We present Masked Generative Policy (MGP), a novel framework for visuomotor imitation learning. We represent actions as discrete tokens, and train a conditional masked transformer that generates tokens in parallel and then rapidly refines only low-confidence tokens. We further propose two new sampling paradigms: MGP-Short, which performs parallel masked generation with score-based refinement for Markovian tasks, and MGP-Long, which predicts full trajectories in a single pass and dynamically refines low-confidence action tokens based on new observations. With globally coherent prediction and robust adaptive execution capabilities, MGP-Long enables reliable control on complex and non-Markovian tasks that prior methods struggle with. Extensive evaluations on 150 robotic manipulation tasks spanning the Meta-World and LIBERO benchmarks show that MGP achieves both rapid inference and superior success rates compared to state-of-the-art diffusion and autoregressive policies. Specifically, MGP increases the average success rate by 9% across 150 tasks while cutting per-sequence inference time by up to 35x. It further improves the average success rate by 60% in dynamic and missing-observation environments, and solves two non-Markovian scenarios where other state-of-the-art methods fail.
Researchers at RheinMain University of Applied Sciences introduce multicalibration to LLM-based code generation, demonstrating that incorporating code-related contextual information significantly enhances the reliability of confidence scores. The approach achieves up to a 58.4% improvement in binary classification accuracy for code correctness over uncalibrated methods and consistently outperforms traditional calibration baselines.
Edward Y. Chang from Stanford University proposes a "Substrate plus Coordination" framework for Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), arguing that Large Language Models (LLMs) provide a necessary System-1 pattern-matching substrate that requires a System-2 coordination layer to achieve reliable, goal-directed reasoning. This work formalizes semantic anchoring through the Unified Contextual Control Theory (UCCT) and introduces the Multi-Agent Collaborative Intelligence (MACI) architecture to implement this missing layer.
Reward-model-based fine-tuning is a central paradigm in aligning Large Language Models with human preferences. However, such approaches critically rely on the assumption that proxy reward models accurately reflect intended supervision, a condition often violated due to annotation noise, bias, or limited coverage. This misalignment can lead to undesirable behaviors, where models optimize for flawed signals rather than true human values. In this paper, we investigate a novel framework to identify and mitigate such misalignment by treating the fine-tuning process as a form of knowledge integration. We focus on detecting instances of proxy-policy conflicts, cases where the base model strongly disagrees with the proxy. We argue that such conflicts often signify areas of shared ignorance, where neither the policy nor the reward model possesses sufficient knowledge, making them especially susceptible to misalignment. To this end, we propose two complementary metrics for identifying these conflicts: a localized Proxy-Policy Alignment Conflict Score (PACS) and a global Kendall-Tau Distance measure. Building on this insight, we design an algorithm named Selective Human-in-the-loop Feedback via Conflict-Aware Sampling (SHF-CAS) that targets high-conflict QA pairs for additional feedback, refining both the reward model and policy efficiently. Experiments on two alignment tasks demonstrate that our approach enhances general alignment performance, even when trained with a biased proxy reward. Our work provides a new lens for interpreting alignment failures and offers a principled pathway for targeted refinement in LLM training.
08 Dec 2025
A study by NYU Abu Dhabi and UC Davis demonstrated that Large Language Models internalize a signal of code correctness, which can be extracted to rank code candidates more effectively than traditional confidence measures. Their Representation Engineering method improved code selection accuracy by up to 29 percentage points and often surpassed execution-feedback based rankers.
The optimal transport (OT) map is a geometry-driven transformation between high-dimensional probability distributions which underpins a wide range of tasks in statistics, applied probability, and machine learning. However, existing statistical theory for OT map estimation is quite restricted, hinging on Brenier's theorem (quadratic cost, absolutely continuous source) to guarantee existence and uniqueness of a deterministic OT map, on which various additional regularity assumptions are imposed to obtain quantitative error bounds. In many real-world problems these conditions fail or cannot be certified, in which case optimal transportation is possible only via stochastic maps that can split mass. To broaden the scope of map estimation theory to such settings, this work introduces a novel metric for evaluating the transportation quality of stochastic maps. Under this metric, we develop computationally efficient map estimators with near-optimal finite-sample risk bounds, subject to easy-to-verify minimal assumptions. Our analysis further accommodates common forms of adversarial sample contamination, yielding estimators with robust estimation guarantees. Empirical experiments are provided which validate our theory and demonstrate the utility of the proposed framework in settings where existing theory fails. These contributions constitute the first general-purpose theory for map estimation, compatible with a wide spectrum of real-world applications where optimal transport may be intrinsically stochastic.
Verifying closed-loop vision-based control systems remains a fundamental challenge due to the high dimensionality of images and the difficulty of modeling visual environments. While generative models are increasingly used as camera surrogates in verification, their reliance on stochastic latent variables introduces unnecessary overapproximation error. To address this bottleneck, we propose a Deterministic World Model (DWM) that maps system states directly to generative images, effectively eliminating uninterpretable latent variables to ensure precise input bounds. The DWM is trained with a dual-objective loss function that combines pixel-level reconstruction accuracy with a control difference loss to maintain behavioral consistency with the real system. We integrate DWM into a verification pipeline utilizing Star-based reachability analysis (StarV) and employ conformal prediction to derive rigorous statistical bounds on the trajectory deviation between the world model and the actual vision-based system. Experiments on standard benchmarks show that our approach yields significantly tighter reachable sets and better verification performance than a latent-variable baseline.
This paper introduces Provable Diffusion Posterior Sampling (PDPS), a method for Bayesian inverse problems that integrates pre-trained diffusion models as data-driven priors. The approach offers the first non-asymptotic error bounds for diffusion-based posterior score estimation and demonstrates superior performance with reliable uncertainty quantification across various imaging tasks.
We examine the non-asymptotic properties of robust density ratio estimation (DRE) in contaminated settings. Weighted DRE is the most promising among existing methods, exhibiting doubly strong robustness from an asymptotic perspective. This study demonstrates that Weighted DRE achieves sparse consistency even under heavy contamination within a non-asymptotic framework. This method addresses two significant challenges in density ratio estimation and robust estimation. For density ratio estimation, we provide the non-asymptotic properties of estimating unbounded density ratios under the assumption that the weighted density ratio function is bounded. For robust estimation, we introduce a non-asymptotic framework for doubly strong robustness under heavy contamination, assuming that at least one of the following conditions holds: (i) contamination ratios are small, and (ii) outliers have small weighted values. This work provides the first non-asymptotic analysis of strong robustness under heavy contamination.
We revisit the signal denoising problem through the lens of optimal transport: the goal is to recover an unknown scalar signal distribution X∼P from noisy observations Y=X+σZ, with Z being standard Gaussian independent of X and σ>0 a known noise level. Let Q denote the distribution of Y. We introduce a hierarchy of denoisers T0,T1,…,T∞:R→R that are agnostic to the signal distribution P, depending only on higher-order score functions of Q. Each denoiser TK is progressively refined using the (2K−1)-th order score function of Q at noise resolution σ2K, achieving better denoising quality measured by the Wasserstein metric W(TK♯Q,P). The limiting denoiser T∞ identifies the optimal transport map with T∞♯Q=P.
We provide a complete characterization of the combinatorial structure underlying this hierarchy through Bell polynomial recursions, revealing how higher-order score functions encode the optimal transport map for signal denoising. We study two estimation strategies with convergence rates for higher-order scores from i.i.d. samples drawn from Q: (i) plug-in estimation via Gaussian kernel smoothing, and (ii) direct estimation via higher-order score matching. This hierarchy of agnostic denoisers opens new perspectives in signal denoising and empirical Bayes.
08 Dec 2025
Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in settings where reasoning, such as multi-step problem solving and chain-of-thought, is essential. Yet, current evaluation practices overwhelmingly report single-run accuracy while ignoring the intrinsic uncertainty that naturally arises from stochastic decoding. This omission creates a blind spot because practitioners cannot reliably assess whether a method's reported performance is stable, reproducible, or cost-consistent. We introduce ReasonBENCH, the first benchmark designed to quantify the underlying instability in LLM reasoning. ReasonBENCH provides (i) a modular evaluation library that standardizes reasoning frameworks, models, and tasks, (ii) a multi-run protocol that reports statistically reliable metrics for both quality and cost, and (iii) a public leaderboard to encourage variance-aware reporting. Across tasks from different domains, we find that the vast majority of reasoning strategies and models exhibit high instability. Notably, even strategies with similar average performance can display confidence intervals up to four times wider, and the top-performing methods often incur higher and less stable costs. Such instability compromises reproducibility across runs and, consequently, the reliability of reported performance. To better understand these dynamics, we further analyze the impact of prompts, model families, and scale on the trade-off between solve rate and stability. Our results highlight reproducibility as a critical dimension for reliable LLM reasoning and provide a foundation for future reasoning methods and uncertainty quantification techniques. ReasonBENCH is publicly available at this https URL .
Automated skin lesion classification using deep learning has shown remarkable accuracy, yet clinical adoption remains limited due to the "black box" nature of these models. We present MelanomaNet, an explainable deep learning system for multi-class skin lesion classification that addresses this gap through four complementary interpretability mechanisms. Our approach combines an EfficientNet V2 backbone with GradCAM++ attention visualization, automated ABCDE clinical criterion extraction, Fast Concept Activation Vectors (FastCAV) for concept-based explanations, and Monte Carlo Dropout uncertainty quantification. We evaluate our system on the ISIC 2019 dataset containing 25,331 dermoscopic images across 9 diagnostic categories. Our model achieves 85.61% accuracy with a weighted F1 score of 0.8564, while providing clinically meaningful explanations that align model attention with established dermatological assessment criteria. The uncertainty quantification module decomposes prediction confidence into epistemic and aleatoric components, enabling automatic flagging of unreliable predictions for clinical review. Our results demonstrate that high classification performance can be achieved alongside comprehensive interpretability, potentially facilitating greater trust and adoption in clinical dermatology workflows. The source code is available at this https URL
Environmental variables are increasingly affecting agricultural decision-making, yet accessible and scalable tools for soil assessment remain limited. This study presents a robust and scalable modeling system for estimating soil properties in croplands, including soil organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (N), available phosphorus (P), exchangeable potassium (K), and pH, using remote sensing data and environmental covariates. The system employs a hybrid modeling approach, combining the indirect methods of modeling soil through proxies and drivers with direct spectral modeling. We extend current approaches by using interpretable physics-informed covariates derived from radiative transfer models (RTMs) and complex, nonlinear embeddings from a foundation model. We validate the system on a harmonized dataset that covers Europes cropland soils across diverse pedoclimatic zones. Evaluation is conducted under a robust validation framework that enforces strict spatial blocking, stratified splits, and statistically distinct train-test sets, which deliberately make the evaluation harder and produce more realistic error estimates for unseen regions. The models achieved their highest accuracy for SOC and N. This performance held across unseen locations, under both spatial cross-validation and an independent test set. SOC obtained a MAE of 5.12 g/kg and a CCC of 0.77, and N obtained a MAE of 0.44 g/kg and a CCC of 0.77. We also assess uncertainty through conformal calibration, achieving 90 percent coverage at the target confidence level. This study contributes to the digital advancement of agriculture through the application of scalable, data-driven soil analysis frameworks that can be extended to related domains requiring quantitative soil evaluation, such as carbon markets.
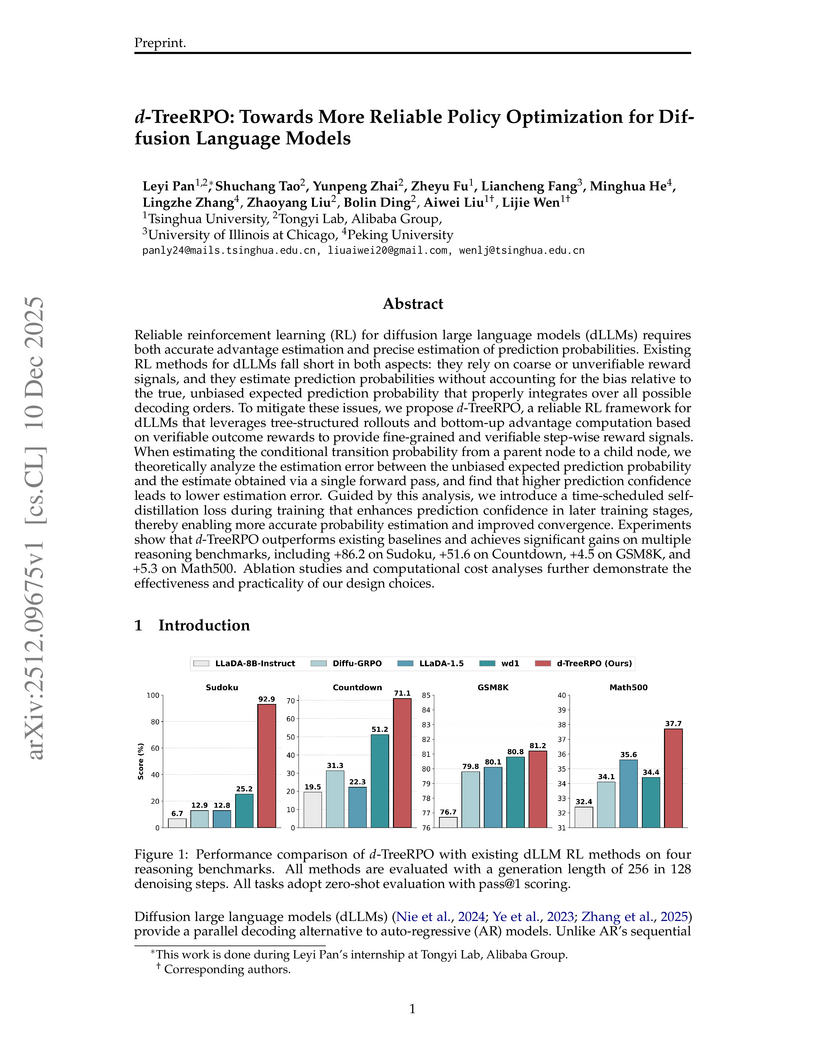
Reliable reinforcement learning (RL) for diffusion large language models (dLLMs) requires both accurate advantage estimation and precise estimation of prediction probabilities. Existing RL methods for dLLMs fall short in both aspects: they rely on coarse or unverifiable reward signals, and they estimate prediction probabilities without accounting for the bias relative to the true, unbiased expected prediction probability that properly integrates over all possible decoding orders. To mitigate these issues, we propose \emph{d}-TreeRPO, a reliable RL framework for dLLMs that leverages tree-structured rollouts and bottom-up advantage computation based on verifiable outcome rewards to provide fine-grained and verifiable step-wise reward signals. When estimating the conditional transition probability from a parent node to a child node, we theoretically analyze the estimation error between the unbiased expected prediction probability and the estimate obtained via a single forward pass, and find that higher prediction confidence leads to lower estimation error. Guided by this analysis, we introduce a time-scheduled self-distillation loss during training that enhances prediction confidence in later training stages, thereby enabling more accurate probability estimation and improved convergence. Experiments show that \emph{d}-TreeRPO outperforms existing baselines and achieves significant gains on multiple reasoning benchmarks, including +86.2 on Sudoku, +51.6 on Countdown, +4.5 on GSM8K, and +5.3 on Math500. Ablation studies and computational cost analyses further demonstrate the effectiveness and practicality of our design choices.
Turbulent flows posses broadband, power-law spectra in which multiscale interactions couple high-wavenumber fluctuations to large-scale dynamics. Although diffusion-based generative models offer a principled probabilistic forecasting framework, we show that standard DDPMs induce a fundamental \emph{spectral collapse}: a Fourier-space analysis of the forward SDE reveals a closed-form, mode-wise signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) that decays monotonically in wavenumber, ∣k∣ for spectra S(k)∝∣k∣−λ, rendering high-wavenumber modes indistinguishable from noise and producing an intrinsic spectral bias. We reinterpret the noise schedule as a spectral regularizer and introduce power-law schedules β(τ)∝τγ that preserve fine-scale structure deeper into diffusion time, along with \emph{Lazy Diffusion}, a one-step distillation method that leverages the learned score geometry to bypass long reverse-time trajectories and prevent high-k degradation. Applied to high-Reynolds-number 2D Kolmogorov turbulence and 1/12∘ Gulf of Mexico ocean reanalysis, these methods resolve spectral collapse, stabilize long-horizon autoregression, and restore physically realistic inertial-range scaling. Together, they show that naïve Gaussian scheduling is structurally incompatible with power-law physics and that physics-aware diffusion processes can yield accurate, efficient, and fully probabilistic surrogates for multiscale dynamical systems.
Researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and Peking University introduce Fast Flow Joint Distillation (F2D2), a framework that simultaneously achieves accurate, few-step log-likelihood evaluation and efficient sampling in flow-based generative models. F2D2 produces calibrated negative log-likelihoods with as few as 1-8 neural function evaluations (NFEs) while maintaining high sample quality and can even improve FID over high-NFE teacher models through maximum likelihood self-guidance.
Consistency-based methods have emerged as an effective approach to uncertainty quantification (UQ) in large language models. These methods typically rely on several generations obtained via multinomial sampling, measuring their agreement level. However, in short-form QA, multinomial sampling is prone to producing duplicates due to peaked distributions, and its stochasticity introduces considerable variance in uncertainty estimates across runs. We introduce a new family of methods that employ beam search to generate candidates for consistency-based UQ, yielding improved performance and reduced variance compared to multinomial sampling. We also provide a theoretical lower bound on the beam set probability mass under which beam search achieves a smaller error than multinomial sampling. We empirically evaluate our approach on six QA datasets and find that its consistent improvements over multinomial sampling lead to state-of-the-art UQ performance.
In this paper, we examine the robustness of Nash equilibria in continuous games, under both strategic and dynamic uncertainty. Starting with the former, we introduce the notion of a robust equilibrium as those equilibria that remain invariant to small -- but otherwise arbitrary -- perturbations to the game's payoff structure, and we provide a crisp geometric characterization thereof. Subsequently, we turn to the question of dynamic robustness, and we examine which equilibria may arise as stable limit points of the dynamics of "follow the regularized leader" (FTRL) in the presence of randomness and uncertainty. Despite their very distinct origins, we establish a structural correspondence between these two notions of robustness: strategic robustness implies dynamic robustness, and, conversely, the requirement of strategic robustness cannot be relaxed if dynamic robustness is to be maintained. Finally, we examine the rate of convergence to robust equilibria as a function of the underlying regularizer, and we show that entropically regularized learning converges at a geometric rate in games with affinely constrained action spaces.
Quantum circuit design is a key bottleneck for practical quantum machine learning on complex, real-world data. We present an automated framework that discovers and refines variational quantum circuits (VQCs) using graph-based Bayesian optimization with a graph neural network (GNN) surrogate. Circuits are represented as graphs and mutated and selected via an expected improvement acquisition function informed by surrogate uncertainty with Monte Carlo dropout. Candidate circuits are evaluated with a hybrid quantum-classical variational classifier on the next generation firewall telemetry and network internet of things (NF-ToN-IoT-V2) cybersecurity dataset, after feature selection and scaling for quantum embedding. We benchmark our pipeline against an MLP-based surrogate, random search, and greedy GNN selection. The GNN-guided optimizer consistently finds circuits with lower complexity and competitive or superior classification accuracy compared to all baselines. Robustness is assessed via a noise study across standard quantum noise channels, including amplitude damping, phase damping, thermal relaxation, depolarizing, and readout bit flip noise. The implementation is fully reproducible, with time benchmarking and export of best found circuits, providing a scalable and interpretable route to automated quantum circuit discovery.
Large Language Models and multi-agent systems have shown promise in decomposing complex tasks, yet they struggle with long-horizon reasoning tasks and escalating computation cost. This work introduces a hierarchical multi-agent architecture that distributes reasoning across a 64*64 grid of lightweight agents, supported by a selective oracle. A spatial curriculum progressively expands the operational region of the grid, ensuring that agents master easier central tasks before tackling harder peripheral ones. To improve reliability, the system integrates Negative Log-Likelihood as a measure of confidence, allowing the curriculum to prioritize regions where agents are both accurate and well calibrated. A Thompson Sampling curriculum manager adaptively chooses training zones based on competence and NLL-driven reward signals. We evaluate the approach on a spatially grounded Tower of Hanoi benchmark, which mirrors the long-horizon structure of many robotic manipulation and planning tasks. Results demonstrate improved stability, reduced oracle usage, and stronger long-range reasoning from distributed agent cooperation.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.