Chemnitz University of Technology
 University of Cambridge
University of Cambridge UCLA
UCLA University College LondonUniversity of Innsbruck
University College LondonUniversity of Innsbruck Johns Hopkins UniversityINRIA ParisUniversity of BathChemnitz University of TechnologyJohannes Kepler University LinzUniversite Paris Dauphine-PSLUniversity of Applied Sciences Kufstein["École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne"]
Johns Hopkins UniversityINRIA ParisUniversity of BathChemnitz University of TechnologyJohannes Kepler University LinzUniversite Paris Dauphine-PSLUniversity of Applied Sciences Kufstein["École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne"]In recent years, a variety of learned regularization frameworks for solving inverse problems in imaging have emerged. These offer flexible modeling together with mathematical insights. The proposed methods differ in their architectural design and training strategies, making direct comparison challenging due to non-modular implementations. We address this gap by collecting and unifying the available code into a common framework. This unified view allows us to systematically compare the approaches and highlight their strengths and limitations, providing valuable insights into their future potential. We also provide concise descriptions of each method, complemented by practical guidelines.
07 Nov 2025
Controlling nonlinear dynamical systems remains a central challenge in a wide range of applications, particularly when accurate first-principle models are unavailable. Data-driven approaches offer a promising alternative by designing controllers directly from observed trajectories. A wide range of data-driven methods relies on the Koopman-operator framework that enables linear representations of nonlinear dynamics via lifting into higher-dimensional observable spaces. Finite-dimensional approximations, such as extended dynamic mode decomposition (EDMD) and its controlled variants, make prediction and feedback control tractable but introduce approximation errors that must be accounted for to provide rigorous closed-loop guarantees. This survey provides a systematic overview of Koopman-based control, emphasizing the connection between data-driven surrogate models, approximation errors, controller design, and closed-loop guarantees. We review theoretical foundations, error bounds, and both linear and bilinear EDMD-based control schemes, highlighting robust strategies that ensure stability and performance. Finally, we discuss open challenges and future directions at the interface of operator theory, approximation theory, and nonlinear control.
 CNRSUniversity of Edinburgh
CNRSUniversity of Edinburgh University of Texas at Austin
University of Texas at Austin KU Leuven
KU Leuven EPFL
EPFL Université Paris-Saclay
Université Paris-Saclay Inria
Inria CEAENS de LyonUniv LyonHeriot-Watt UniversityChemnitz University of TechnologyUniversité Paris Dauphine-PSLUniversidad Industrial de SantanderIMTIRFUINSA de LyonUniversité Paris-Saclay OrsayCNRS UAR 851Universit
de Toulouse
CEAENS de LyonUniv LyonHeriot-Watt UniversityChemnitz University of TechnologyUniversité Paris Dauphine-PSLUniversidad Industrial de SantanderIMTIRFUINSA de LyonUniversité Paris-Saclay OrsayCNRS UAR 851Universit
de ToulouseDeepInverse is an open-source PyTorch-based library for solving imaging inverse problems. The library covers all crucial steps in image reconstruction from the efficient implementation of forward operators (e.g., optics, MRI, tomography), to the definition and resolution of variational problems and the design and training of advanced neural network architectures. In this paper, we describe the main functionality of the library and discuss the main design choices.
This tutorial, authored by researchers from Chemnitz University of Technology, University of Koblenz, and the QUT Centre for Robotics, serves as the first comprehensive guide to Visual Place Recognition (VPR). It unifies terminology, systematically categorizes VPR problem types, details a generic algorithmic pipeline, and provides an in-depth evaluation framework, accompanied by practical Python code examples and an online repository.
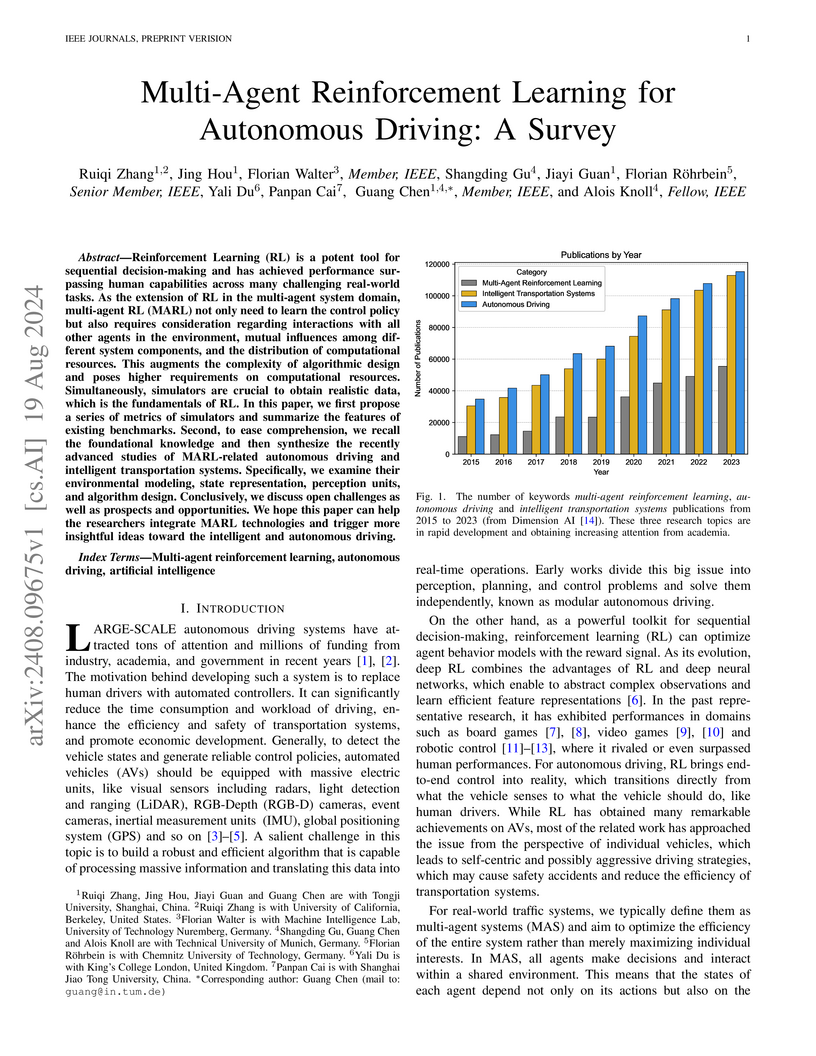
This survey synthesizes the latest advancements in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) for autonomous driving (AD), categorizing existing benchmarks and methodologies, and outlining challenges and future research directions. It details dominant learning schemes like Centralized Training-Decentralized Execution (CTDE) and Decentralized Training-Decentralized Execution (DTDE), while exploring trends such as enhanced safety guarantees and the integration of language models.
14 Oct 2025
We study ergodicity of composition operators on rearrangement-invariant Banach function spaces. More precisely, we give a natural and easy-to-check condition on the symbol of the operator which entails mean ergodicity on a very large class of rearrangement-invariant Banach function spaces. Further, we present some natural additional assumptions that allow us to obtain pointwise ergodicity. The class of spaces covered by our results contains many non-reflexive spaces, such as the Lorentz spaces Lp,1 and Lp,∞, p∈(1,∞), Orlicz spaces LlogαL and expLα, α>0, and the spaces L1 and L∞ over measure spaces of finite measure. The main novelty in our approach is the application of a new locally convex topology which we introduce and which lies strictly between the norm topology and the weak topology induced by the associate space. Throughout, we give several examples which illustrate the applicability of our results as well as highlight the necessity and optimality of our assumptions.
18 May 2025
Deep learning (DL) has greatly advanced audio classification, yet the field
is limited by the scarcity of large-scale benchmark datasets that have
propelled progress in other domains. While AudioSet is a pivotal step to bridge
this gap as a universal-domain dataset, its restricted accessibility and
limited range of evaluation use cases challenge its role as the sole resource.
Therefore, we introduce BirdSet, a large-scale benchmark dataset for audio
classification focusing on avian bioacoustics. BirdSet surpasses AudioSet with
over 6,800 recording hours (↑17%) from nearly 10,000 classes
(↑18×) for training and more than 400 hours
(↑7×) across eight strongly labeled evaluation datasets. It
serves as a versatile resource for use cases such as multi-label
classification, covariate shift or self-supervised learning. We benchmark six
well-known DL models in multi-label classification across three distinct
training scenarios and outline further evaluation use cases in audio
classification. We host our dataset on Hugging Face for easy accessibility and
offer an extensive codebase to reproduce our results.
Deep neural networks (DNNs) often perform poorly in the presence of domain shift and category shift. How to upcycle DNNs and adapt them to the target task remains an important open problem. Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA), especially recently proposed Source-free Domain Adaptation (SFDA), has become a promising technology to address this issue. Nevertheless, existing SFDA methods require that the source domain and target domain share the same label space, consequently being only applicable to the vanilla closed-set setting. In this paper, we take one step further and explore the Source-free Universal Domain Adaptation (SF-UniDA). The goal is to identify "known" data samples under both domain and category shift, and reject those "unknown" data samples (not present in source classes), with only the knowledge from standard pre-trained source model. To this end, we introduce an innovative global and local clustering learning technique (GLC). Specifically, we design a novel, adaptive one-vs-all global clustering algorithm to achieve the distinction across different target classes and introduce a local k-NN clustering strategy to alleviate negative transfer. We examine the superiority of our GLC on multiple benchmarks with different category shift scenarios, including partial-set, open-set, and open-partial-set DA. Remarkably, in the most challenging open-partial-set DA scenario, GLC outperforms UMAD by 14.8\% on the VisDA benchmark. The code is available at this https URL.
A core aspect of compositionality, systematicity is a desirable property in
ML models as it enables strong generalization to novel contexts. This has led
to numerous studies proposing benchmarks to assess systematic generalization,
as well as models and training regimes designed to enhance it. Many of these
efforts are framed as addressing the challenge posed by Fodor and Pylyshyn.
However, while they argue for systematicity of representations, existing
benchmarks and models primarily focus on the systematicity of behaviour. We
emphasize the crucial nature of this distinction. Furthermore, building on
Hadley's (1994) taxonomy of systematic generalization, we analyze the extent to
which behavioural systematicity is tested by key benchmarks in the literature
across language and vision. Finally, we highlight ways of assessing
systematicity of representations in ML models as practiced in the field of
mechanistic interpretability.
Deep neural networks often exhibit sub-optimal performance under covariate and category shifts. Source-Free Domain Adaptation (SFDA) presents a promising solution to this dilemma, yet most SFDA approaches are restricted to closed-set scenarios. In this paper, we explore Source-Free Universal Domain Adaptation (SF-UniDA) aiming to accurately classify "known" data belonging to common categories and segregate them from target-private "unknown" data. We propose a novel Global and Local Clustering (GLC) technique, which comprises an adaptive one-vs-all global clustering algorithm to discern between target classes, complemented by a local k-NN clustering strategy to mitigate negative transfer. Despite the effectiveness, the inherent closed-set source architecture leads to uniform treatment of "unknown" data, impeding the identification of distinct "unknown" categories. To address this, we evolve GLC to GLC++, integrating a contrastive affinity learning strategy. We examine the superiority of GLC and GLC++ across multiple benchmarks and category shift scenarios. Remarkably, in the most challenging open-partial-set scenarios, GLC and GLC++ surpass GATE by 16.8\% and 18.9\% in H-score on VisDA, respectively. GLC++ enhances the novel category clustering accuracy of GLC by 4.1\% in open-set scenarios on Office-Home. Furthermore, the introduced contrastive learning strategy not only enhances GLC but also significantly facilitates existing methodologies. The code is available at this https URL.
Inspired by the human visual perception system, hexagonal image processing in the context of machine learning deals with the development of image processing systems that combine the advantages of evolutionary motivated structures based on biological models. While conventional state-of-the-art image processing systems of recording and output devices almost exclusively utilize square arranged methods, their hexagonal counterparts offer a number of key advantages that can benefit both researchers and users. This contribution serves as a general application-oriented approach the synthesis of the therefore designed hexagonal image processing framework, called Hexnet, the processing steps of hexagonal image transformation, and dependent methods. The results of our created test environment show that the realized framework surpasses current approaches of hexagonal image processing systems, while hexagonal artificial neural networks can benefit from the implemented hexagonal architecture. As hexagonal lattice format based deep neural networks, also called H-DNN, can be compared to their square counterparts by transforming classical square lattice based data sets into their hexagonal representation, they can also result in a reduction of trainable parameters as well as result in increased training and test rates.
13 Oct 2025
Kernels are key in machine learning for modeling interactions. Unfortunately, brute-force computation of the related kernel sums scales quadratically with the number of samples. Recent Fourier-slicing methods lead to an improved linear complexity, provided that the kernel can be sliced and its Fourier coefficients are known. To obtain these coefficients, we view the slicing relation as an inverse problem and present two algorithms for their recovery. Extensive numerical experiments demonstrate the speed and accuracy of our methods.
Data-driven techniques for analysis, modeling, and control of complex dynamical systems are on the uptake. Koopman theory provides the theoretical foundation for the popular kernel extended dynamic mode decomposition (kEDMD). In this work, we propose a novel kEDMD scheme to approximate nonlinear control systems accompanied by an in-depth error analysis. Key features are regularization-based robustness and an adroit decomposition into micro and macro grids enabling flexible sampling. But foremost, we prove proportionality, i.e., explicit dependence on the distance to the (controlled) equilibrium, of the derived bound on the full approximation error. Leveraging this key property, we rigorously show that asymptotic stability of the data-driven surrogate (control) system implies asymptotic stability of the original (control) system and vice versa.
Researchers applied Automated Concept-based Explanation (ACE) to a deep learning model for plant disease classification, achieving 95% classification accuracy and revealing the specific visual concepts influencing model decisions. The method successfully identified both biologically relevant features and undesirable dataset biases like background and shadow correlations impacting model reliability.
Automated bioacoustic analysis aids understanding and protection of both
marine and terrestrial animals and their habitats across extensive
spatiotemporal scales, and typically involves analyzing vast collections of
acoustic data. With the advent of deep learning models, classification of
important signals from these datasets has markedly improved. These models power
critical data analyses for research and decision-making in biodiversity
monitoring, animal behaviour studies, and natural resource management. However,
deep learning models are often data-hungry and require a significant amount of
labeled training data to perform well. While sufficient training data is
available for certain taxonomic groups (e.g., common bird species), many
classes (such as rare and endangered species, many non-bird taxa, and
call-type) lack enough data to train a robust model from scratch. This study
investigates the utility of feature embeddings extracted from audio
classification models to identify bioacoustic classes other than the ones these
models were originally trained on. We evaluate models on diverse datasets,
including different bird calls and dialect types, bat calls, marine mammals
calls, and amphibians calls. The embeddings extracted from the models trained
on bird vocalization data consistently allowed higher quality classification
than the embeddings trained on general audio datasets. The results of this
study indicate that high-quality feature embeddings from large-scale acoustic
bird classifiers can be harnessed for few-shot transfer learning, enabling the
learning of new classes from a limited quantity of training data. Our findings
reveal the potential for efficient analyses of novel bioacoustic tasks, even in
scenarios where available training data is limited to a few samples.
We derive novel deterministic bounds on the approximation error of data-based bilinear surrogate models for unknown nonlinear systems. The surrogate models are constructed using kernel-based extended dynamic mode decomposition to approximate the Koopman operator in a reproducing kernel Hilbert space. Unlike previous methods that require restrictive assumptions on the invariance of the dictionary, our approach leverages kernel-based dictionaries that allow us to control the projection error via pointwise error bounds, overcoming a significant limitation of existing theoretical guarantees. The derived state- and input-dependent error bounds allow for direct integration into Koopman-based robust controller designs with closed-loop guarantees for the unknown nonlinear system. Numerical examples illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework.
09 May 2025
In this paper, we analyze nonlinear model predictive control (MPC) using
data-driven surrogates in the prediction and optimization step. First, we
establish asymptotic stability of the origin, a controlled steady state, w.r.t.
the MPC closed loop without stabilizing terminal conditions. To this end, we
prove that cost controllability of the original system is preserved if
proportional bounds on the approximation error hold. Here, proportional refers
to state and control, while the respective constants depend on the
approximation accuracy. The proportionality of the error bounds is a key
element to derive asymptotic stability in presence of modeling errors and not
only practical asymptotic stability. Second, we exemplarily verify the imposed
assumptions for data-driven surrogates generated with kernel extended dynamic
mode decomposition based on the Koopman operator. Hereby, we do not impose
invariance assumptions on finite dictionaries, but rather derive all conditions
under non-restrictive data requirements. Finally, we verify our findings with
numerical simulations.
11 Jun 2025
We prove convergence rates of linear sampling recovery of functions in abstract Bochner spaces satisfying weighted summability of their generalized polynomial chaos expansion coefficients. The underlying algorithm is a function-valued extension of the least squares method widely used and thoroughly studied in scalar-valued function recovery. We apply our theory to collocation approximation of solutions to parametric elliptic or parabolic PDEs with log-normal random inputs and to relevant approximation of infinite dimensional holomorphic functions on R∞. The application allows us to significantly improve known results in Computational Uncertainty Quantification for these problems. Our results are also applicable for parametric PDEs with affine inputs, where they match the known rates.
28 May 2024
Drivers' role changes with increasing automation from the primary driver to a system supervisor. This study investigates how supervising an SAE L2 and L3 automated vehicle (AV) affects drivers' mental workload and sleepiness compared to manual driving. Using an AV prototype on a test track, the oscillatory brain activity of 23 adult participants was recorded during L2, L3, and manual driving. Results showed decreased mental workload and increased sleepiness in L3 drives compared to L2 and manual drives, indicated by self-report scales and changes in the frontal alpha and theta power spectral density. These findings suggest that fatigue and mental underload are significant issues in L3 driving and should be considered when designing future AV interfaces.
Within (semi-)automated visual industrial inspection, learning-based approaches for assessing visual defects, including deep neural networks, enable the processing of otherwise small defect patterns in pixel size on high-resolution imagery. The emergence of these often rarely occurring defect patterns explains the general need for labeled data corpora. To alleviate this issue and advance the current state of the art in unsupervised visual inspection, this work proposes a DifferNet-based solution enhanced with attention modules: AttentDifferNet. It improves image-level detection and classification capabilities on three visual anomaly detection datasets for industrial inspection: InsPLAD-fault, MVTec AD, and Semiconductor Wafer. In comparison to the state of the art, AttentDifferNet achieves improved results, which are, in turn, highlighted throughout our quali-quantitative study. Our quantitative evaluation shows an average improvement - compared to DifferNet - of 1.77 +/- 0.25 percentage points in overall AUROC considering all three datasets, reaching SOTA results in InsPLAD-fault, an industrial inspection in-the-wild dataset. As our variants to AttentDifferNet show great prospects in the context of currently investigated approaches, a baseline is formulated, emphasizing the importance of attention for industrial anomaly detection both in the wild and in controlled environments.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.