Data61/CSIRO
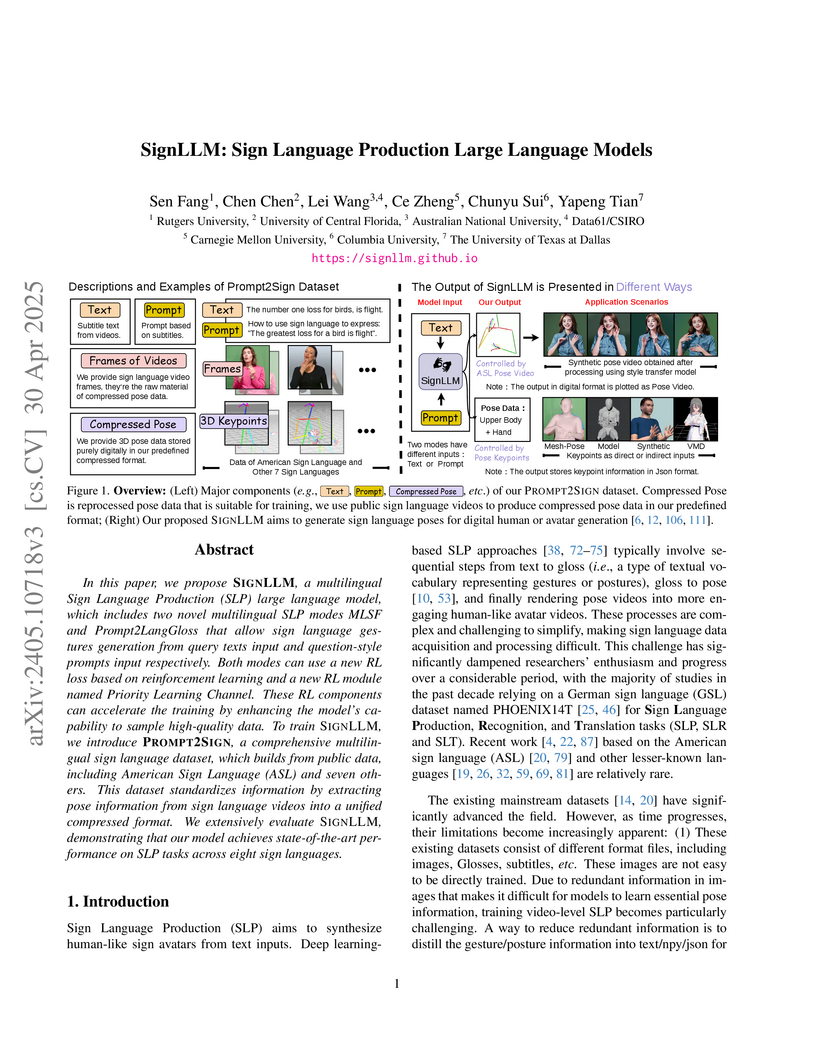
In this paper, we propose SignLLM, a multilingual Sign Language Production
(SLP) large language model, which includes two novel multilingual SLP modes
MLSF and Prompt2LangGloss that allow sign language gestures generation from
query texts input and question-style prompts input respectively. Both modes can
use a new RL loss based on reinforcement learning and a new RL module named
Priority Learning Channel. These RL components can accelerate the training by
enhancing the model's capability to sample high-quality data. To train SignLLM,
we introduce Prompt2Sign, a comprehensive multilingual sign language dataset,
which builds from public data, including American Sign Language (ASL) and seven
others. This dataset standardizes information by extracting pose information
from sign language videos into a unified compressed format. We extensively
evaluate SignLLM, demonstrating that our model achieves state-of-the-art
performance on SLP tasks across eight sign languages.
We propose Graph Consistency Regularization (GCR), a novel framework that injects relational graph structures, derived from model predictions, into the learning process to promote class-aware, semantically meaningful feature representations. Functioning as a form of self-prompting, GCR enables the model to refine its internal structure using its own outputs. While deep networks learn rich representations, these often capture noisy inter-class similarities that contradict the model's predicted semantics. GCR addresses this issue by introducing parameter-free Graph Consistency Layers (GCLs) at arbitrary depths. Each GCL builds a batch-level feature similarity graph and aligns it with a global, class-aware masked prediction graph, derived by modulating softmax prediction similarities with intra-class indicators. This alignment enforces that feature-level relationships reflect class-consistent prediction behavior, acting as a semantic regularizer throughout the network. Unlike prior work, GCR introduces a multi-layer, cross-space graph alignment mechanism with adaptive weighting, where layer importance is learned from graph discrepancy magnitudes. This allows the model to prioritize semantically reliable layers and suppress noisy ones, enhancing feature quality without modifying the architecture or training procedure. GCR is model-agnostic, lightweight, and improves semantic structure across various networks and datasets. Experiments show that GCR promotes cleaner feature structure, stronger intra-class cohesion, and improved generalization, offering a new perspective on learning from prediction structure. [Project website](this https URL) [Code](this https URL)
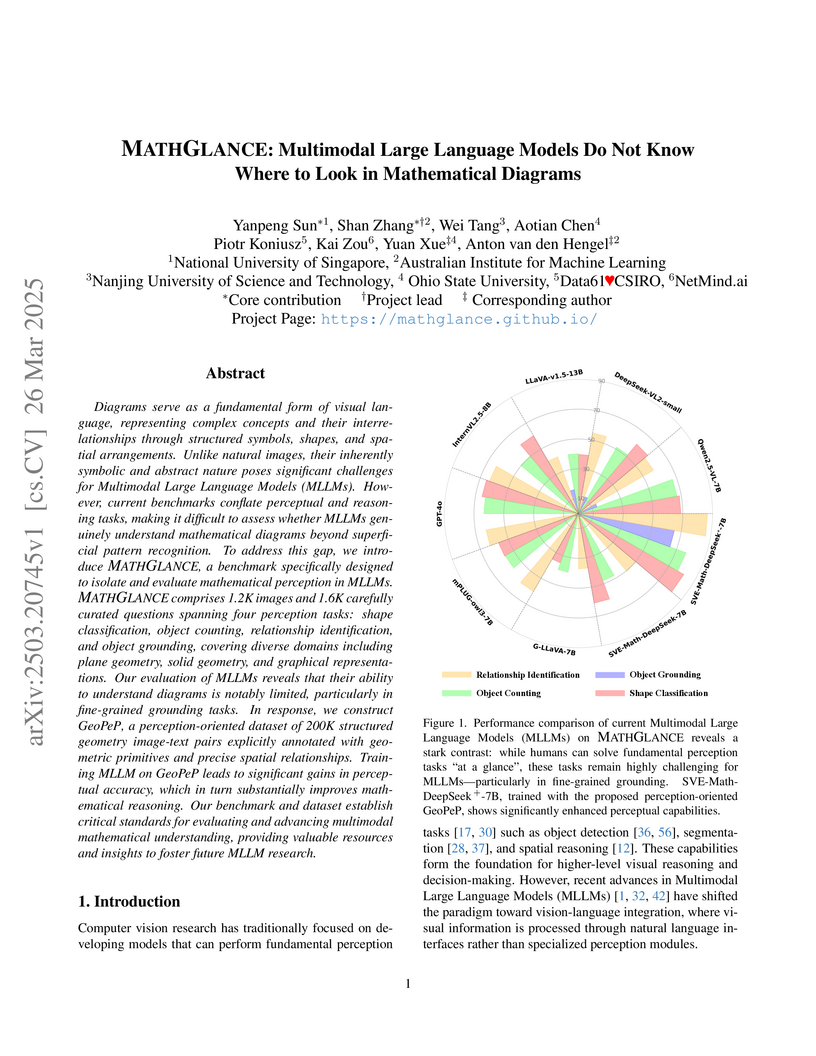
Researchers introduce MATHGLANCE, a benchmark designed to evaluate multimodal large language models' mathematical perception in diagrams, and GeoPeP, a dataset of 200K structured geometry image-text pairs. Training models with GeoPeP significantly improves their mathematical perception and subsequently enhances their mathematical reasoning abilities on complex visual problems.
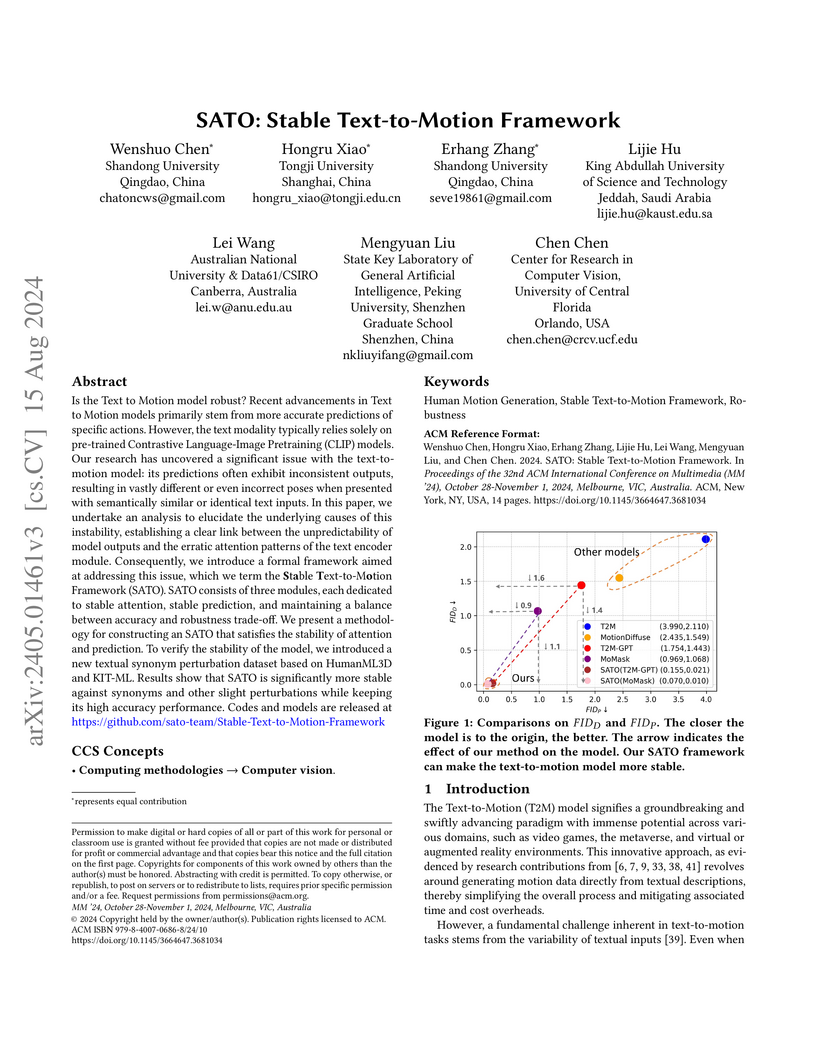
Is the Text to Motion model robust? Recent advancements in Text to Motion models primarily stem from more accurate predictions of specific actions. However, the text modality typically relies solely on pre-trained Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) models. Our research has uncovered a significant issue with the text-to-motion model: its predictions often exhibit inconsistent outputs, resulting in vastly different or even incorrect poses when presented with semantically similar or identical text inputs. In this paper, we undertake an analysis to elucidate the underlying causes of this instability, establishing a clear link between the unpredictability of model outputs and the erratic attention patterns of the text encoder module. Consequently, we introduce a formal framework aimed at addressing this issue, which we term the Stable Text-to-Motion Framework (SATO). SATO consists of three modules, each dedicated to stable attention, stable prediction, and maintaining a balance between accuracy and robustness trade-off. We present a methodology for constructing an SATO that satisfies the stability of attention and prediction. To verify the stability of the model, we introduced a new textual synonym perturbation dataset based on HumanML3D and KIT-ML. Results show that SATO is significantly more stable against synonyms and other slight perturbations while keeping its high accuracy performance.
Graph contrastive learning attracts/disperses node representations for similar/dissimilar node pairs under some notion of similarity. It may be combined with a low-dimensional embedding of nodes to preserve intrinsic and structural properties of a graph. In this paper, we extend the celebrated Laplacian Eigenmaps with contrastive learning, and call them COntrastive Laplacian EigenmapS (COLES). Starting from a GAN-inspired contrastive formulation, we show that the Jensen-Shannon divergence underlying many contrastive graph embedding models fails under disjoint positive and negative distributions, which may naturally emerge during sampling in the contrastive setting. In contrast, we demonstrate analytically that COLES essentially minimizes a surrogate of Wasserstein distance, which is known to cope well under disjoint distributions. Moreover, we show that the loss of COLES belongs to the family of so-called block-contrastive losses, previously shown to be superior compared to pair-wise losses typically used by contrastive methods. We show on popular benchmarks/backbones that COLES offers favourable accuracy/scalability compared to DeepWalk, GCN, Graph2Gauss, DGI and GRACE baselines.
While current diffusion-based models, typically built on U-Net architectures, have shown promising results on the text-to-motion generation task, they still suffer from semantic misalignment and kinematic artifacts. Through analysis, we identify severe gradient attenuation in the deep layers of the network as a key bottleneck, leading to insufficient learning of high-level features. To address this issue, we propose \textbf{LUMA} (\textit{\textbf{L}ow-dimension \textbf{U}nified \textbf{M}otion \textbf{A}lignment}), a text-to-motion diffusion model that incorporates dual-path anchoring to enhance semantic alignment. The first path incorporates a lightweight MoCLIP model trained via contrastive learning without relying on external data, offering semantic supervision in the temporal domain. The second path introduces complementary alignment signals in the frequency domain, extracted from low-frequency DCT components known for their rich semantic content. These two anchors are adaptively fused through a temporal modulation mechanism, allowing the model to progressively transition from coarse alignment to fine-grained semantic refinement throughout the denoising process. Experimental results on HumanML3D and KIT-ML demonstrate that LUMA achieves state-of-the-art performance, with FID scores of 0.035 and 0.123, respectively. Furthermore, LUMA accelerates convergence by 1.4× compared to the baseline, making it an efficient and scalable solution for high-fidelity text-to-motion generation.
Exploiting the foundation models (e.g., CLIP) to build a versatile keypoint
detector has gained increasing attention. Most existing models accept either
the text prompt (e.g., ``the nose of a cat''), or the visual prompt (e.g.,
support image with keypoint annotations), to detect the corresponding keypoints
in query image, thereby, exhibiting either zero-shot or few-shot detection
ability. However, the research on taking multimodal prompt is still
underexplored, and the prompt diversity in semantics and language is far from
opened. For example, how to handle unseen text prompts for novel keypoint
detection and the diverse text prompts like ``Can you detect the nose and ears
of a cat?'' In this work, we open the prompt diversity from three aspects:
modality, semantics (seen v.s. unseen), and language, to enable a more
generalized zero- and few-shot keypoint detection (Z-FSKD). We propose a novel
OpenKD model which leverages multimodal prototype set to support both visual
and textual prompting. Further, to infer the keypoint location of unseen texts,
we add the auxiliary keypoints and texts interpolated from visual and textual
domains into training, which improves the spatial reasoning of our model and
significantly enhances zero-shot novel keypoint detection. We also found large
language model (LLM) is a good parser, which achieves over 96% accuracy to
parse keypoints from texts. With LLM, OpenKD can handle diverse text prompts.
Experimental results show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance
on Z-FSKD and initiates new ways to deal with unseen text and diverse texts.
The source code and data are available at this https URL
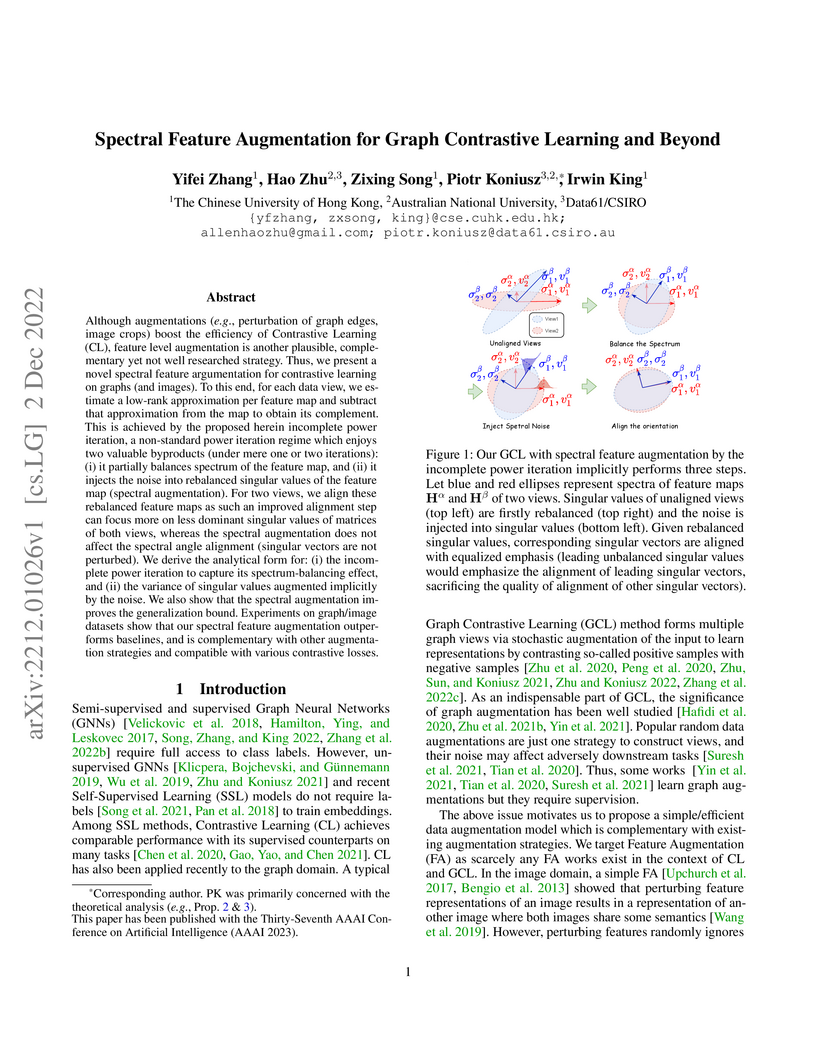
Although augmentations (e.g., perturbation of graph edges, image crops) boost the efficiency of Contrastive Learning (CL), feature level augmentation is another plausible, complementary yet not well researched strategy. Thus, we present a novel spectral feature argumentation for contrastive learning on graphs (and images). To this end, for each data view, we estimate a low-rank approximation per feature map and subtract that approximation from the map to obtain its complement. This is achieved by the proposed herein incomplete power iteration, a non-standard power iteration regime which enjoys two valuable byproducts (under mere one or two iterations): (i) it partially balances spectrum of the feature map, and (ii) it injects the noise into rebalanced singular values of the feature map (spectral augmentation). For two views, we align these rebalanced feature maps as such an improved alignment step can focus more on less dominant singular values of matrices of both views, whereas the spectral augmentation does not affect the spectral angle alignment (singular vectors are not perturbed). We derive the analytical form for: (i) the incomplete power iteration to capture its spectrum-balancing effect, and (ii) the variance of singular values augmented implicitly by the noise. We also show that the spectral augmentation improves the generalization bound. Experiments on graph/image datasets show that our spectral feature augmentation outperforms baselines, and is complementary with other augmentation strategies and compatible with various contrastive losses.
We present a longitudinal study which evaluates the reasoning capability of frontier Large Language Models over an eighteen month period. We measured the accuracy of three leading models from December 2023, September 2024 and June 2025 on true or false questions from the PrOntoQA dataset and their faithfulness to reasoning strategies provided through in-context learning. The improvement in performance from 2023 to 2024 can be attributed to hidden Chain of Thought prompting. The introduction of thinking models allowed for significant improvement in model performance between 2024 and 2025.
We then present a neuro-symbolic architecture which uses LLMs of less than 15 billion parameters to translate the problems into a standardised form. We then parse the standardised forms of the problems into a program to be solved by Z3, an SMT solver, to determine the satisfiability of the query. We report the number of prompt and completion tokens as well as the computational cost in FLOPs for open source models. The neuro-symbolic approach significantly reduces the computational cost while maintaining near perfect performance. The common approximation that the number of inference FLOPs is double the product of the active parameters and total tokens was accurate within 10\% for all experiments.
A new Saliency-guided Vision Transformer (SalViT) is developed for few-shot keypoint detection, enhancing localization accuracy by focusing attention on foreground regions and showing robustness to occlusions. The method achieves state-of-the-art performance on various datasets, leveraging DINO as a unified backbone and saliency detector.
In computer vision tasks, features often come from diverse representations,
domains (e.g., indoor and outdoor), and modalities (e.g., text, images, and
videos). Effectively fusing these features is essential for robust performance,
especially with the availability of powerful pre-trained models like
vision-language models. However, common fusion methods, such as concatenation,
element-wise operations, and non-linear techniques, often fail to capture
structural relationships, deep feature interactions, and suffer from
inefficiency or misalignment of features across domains or modalities. In this
paper, we shift from high-dimensional feature space to a lower-dimensional,
interpretable graph space by constructing relationship graphs that encode
feature relationships at different levels, e.g., clip, frame, patch, token,
etc. To capture deeper interactions, we use graph power expansions and
introduce a learnable graph fusion operator to combine these graph powers for
more effective fusion. Our approach is relationship-centric, operates in a
homogeneous space, and is mathematically principled, resembling element-wise
relationship score aggregation via multilinear polynomials. We demonstrate the
effectiveness of our graph-based fusion method on video anomaly detection,
showing strong performance across multi-representational, multi-modal, and
multi-domain feature fusion tasks.
We address the problem of joint optical flow and camera motion estimation in rigid scenes by incorporating geometric constraints into an unsupervised deep learning framework. Unlike existing approaches which rely on brightness constancy and local smoothness for optical flow estimation, we exploit the global relationship between optical flow and camera motion using epipolar geometry. In particular, we formulate the prediction of optical flow and camera motion as a bi-level optimization problem, consisting of an upper-level problem to estimate the flow that conforms to the predicted camera motion, and a lower-level problem to estimate the camera motion given the predicted optical flow. We use implicit differentiation to enable back-propagation through the lower-level geometric optimization layer independent of its implementation, allowing end-to-end training of the network. With globally-enforced geometric constraints, we are able to improve the quality of the estimated optical flow in challenging scenarios and obtain better camera motion estimates compared to other unsupervised learning methods.
We address the problem of ground-to-satellite image geo-localization, that is, estimating the camera latitude, longitude and orientation (azimuth angle) by matching a query image captured at the ground level against a large-scale database with geotagged satellite images. Our prior arts treat the above task as pure image retrieval by selecting the most similar satellite reference image matching the ground-level query image. However, such an approach often produces coarse location estimates because the geotag of the retrieved satellite image only corresponds to the image center while the ground camera can be located at any point within the image. To further consolidate our prior research findings, we present a novel geometry-aware geo-localization method. Our new method is able to achieve the fine-grained location of a query image, up to pixel size precision of the satellite image, once its coarse location and orientation have been determined. Moreover, we propose a new geometry-aware image retrieval pipeline to improve the coarse localization accuracy. Apart from a polar transform in our conference work, this new pipeline also maps satellite image pixels to the ground-level plane in the ground-view via a geometry-constrained projective transform to emphasize informative regions, such as road structures, for cross-view geo-localization. Extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our newly proposed framework. We also significantly improve the performance of coarse localization results compared to the state-of-the-art in terms of location recalls.
Current non-rigid object keypoint detectors perform well on a chosen kind of
species and body parts, and require a large amount of labelled keypoints for
training. Moreover, their heatmaps, tailored to specific body parts, cannot
recognize novel keypoints (keypoints not labelled for training) on unseen
species. We raise an interesting yet challenging question: how to detect both
base (annotated for training) and novel keypoints for unseen species given a
few annotated samples? Thus, we propose a versatile Few-shot Keypoint Detection
(FSKD) pipeline, which can detect a varying number of keypoints of different
kinds. Our FSKD provides the uncertainty estimation of predicted keypoints.
Specifically, FSKD involves main and auxiliary keypoint representation
learning, similarity learning, and keypoint localization with uncertainty
modeling to tackle the localization noise. Moreover, we model the uncertainty
across groups of keypoints by multivariate Gaussian distribution to exploit
implicit correlations between neighboring keypoints. We show the effectiveness
of our FSKD on (i) novel keypoint detection for unseen species, and (ii)
few-shot Fine-Grained Visual Recognition (FGVR) and (iii) Semantic Alignment
(SA) downstream tasks. For FGVR, detected keypoints improve the classification
accuracy. For SA, we showcase a novel thin-plate-spline warping that uses
estimated keypoint uncertainty under imperfect keypoint corespondences.
Learning new concepts from a few of samples is a standard challenge in
computer vision. The main directions to improve the learning ability of
few-shot training models include (i) a robust similarity learning and (ii)
generating or hallucinating additional data from the limited existing samples.
In this paper, we follow the latter direction and present a novel data
hallucination model. Currently, most datapoint generators contain a specialized
network (i.e., GAN) tasked with hallucinating new datapoints, thus requiring
large numbers of annotated data for their training in the first place. In this
paper, we propose a novel less-costly hallucination method for few-shot
learning which utilizes saliency maps. To this end, we employ a saliency
network to obtain the foregrounds and backgrounds of available image samples
and feed the resulting maps into a two-stream network to hallucinate datapoints
directly in the feature space from viable foreground-background combinations.
To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to leverage saliency maps for
such a task and we demonstrate their usefulness in hallucinating additional
datapoints for few-shot learning. Our proposed network achieves the state of
the art on publicly available datasets.
In this paper, we tackle the challenging problem of Few-shot Object
Detection. Existing FSOD pipelines (i) use average-pooled representations that
result in information loss; and/or (ii) discard position information that can
help detect object instances. Consequently, such pipelines are sensitive to
large intra-class appearance and geometric variations between support and query
images. To address these drawbacks, we propose a Time-rEversed diffusioN tEnsor
Transformer (TENET), which i) forms high-order tensor representations that
capture multi-way feature occurrences that are highly discriminative, and ii)
uses a transformer that dynamically extracts correlations between the query
image and the entire support set, instead of a single average-pooled support
embedding. We also propose a Transformer Relation Head (TRH), equipped with
higher-order representations, which encodes correlations between query regions
and the entire support set, while being sensitive to the positional variability
of object instances. Our model achieves state-of-the-art results on PASCAL VOC,
FSOD, and COCO.
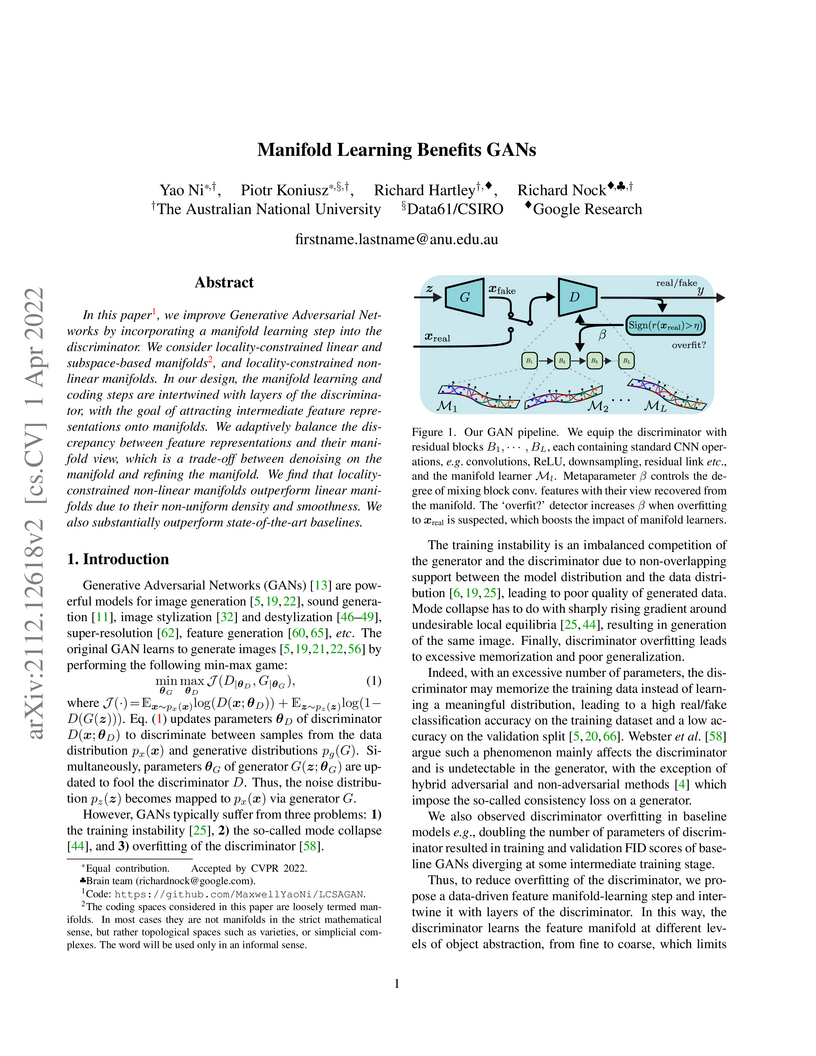
In this paper, we improve Generative Adversarial Networks by incorporating a
manifold learning step into the discriminator. We consider locality-constrained
linear and subspace-based manifolds, and locality-constrained non-linear
manifolds. In our design, the manifold learning and coding steps are
intertwined with layers of the discriminator, with the goal of attracting
intermediate feature representations onto manifolds. We adaptively balance the
discrepancy between feature representations and their manifold view, which is a
trade-off between denoising on the manifold and refining the manifold. We find
that locality-constrained non-linear manifolds outperform linear manifolds due
to their non-uniform density and smoothness. We also substantially outperform
state-of-the-art baselines.
The Inversion-Denoising Paradigm, which is based on diffusion models, excels in diverse image editing and restoration tasks. We revisit its mechanism and reveal a critical, overlooked factor in reconstruction degradation: the approximate noise error. This error stems from approximating the noise at step t with the prediction at step t-1, resulting in severe error accumulation throughout the inversion process. We introduce Projection-Orthogonal Least Squares for Robust and Adaptive Inversion (POLARIS), which reformulates inversion from an error-compensation problem into an error-origin problem. Rather than optimizing embeddings or latent codes to offset accumulated drift, POLARIS treats the guidance scale {\omega} as a step-wise variable and derives a mathematically grounded formula to minimize inversion error at each step. Remarkably, POLARIS improves inversion latent quality with just one line of code. With negligible performance overhead, it substantially mitigates noise approximation errors and consistently improves the accuracy of downstream tasks.
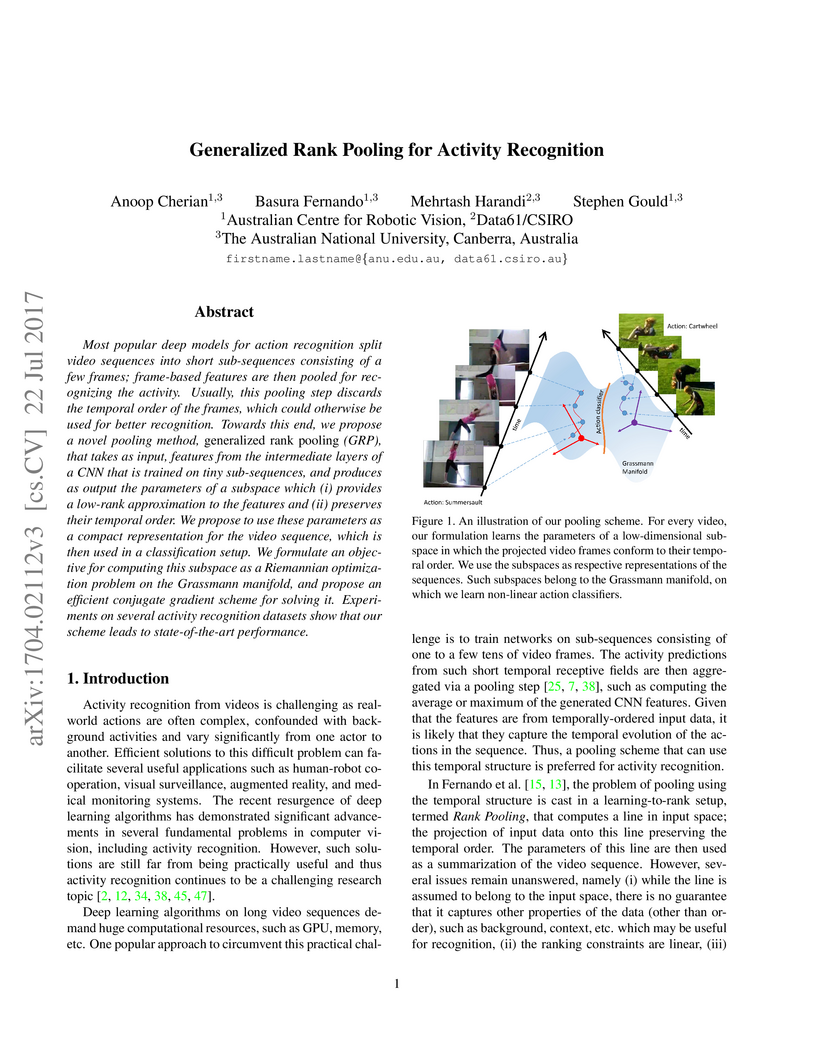
Most popular deep models for action recognition split video sequences into short sub-sequences consisting of a few frames; frame-based features are then pooled for recognizing the activity. Usually, this pooling step discards the temporal order of the frames, which could otherwise be used for better recognition. Towards this end, we propose a novel pooling method, generalized rank pooling (GRP), that takes as input, features from the intermediate layers of a CNN that is trained on tiny sub-sequences, and produces as output the parameters of a subspace which (i) provides a low-rank approximation to the features and (ii) preserves their temporal order. We propose to use these parameters as a compact representation for the video sequence, which is then used in a classification setup. We formulate an objective for computing this subspace as a Riemannian optimization problem on the Grassmann manifold, and propose an efficient conjugate gradient scheme for solving it. Experiments on several activity recognition datasets show that our scheme leads to state-of-the-art performance.
Reconstructing natural images from functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data remains a core challenge in natural decoding due to the mismatch between the richness of visual stimuli and the noisy, low resolution nature of fMRI signals. While recent two-stage models, combining deep variational autoencoders (VAEs) with diffusion models, have advanced this task, they treat all spatial-frequency components of the input equally. This uniform treatment forces the model to extract meaning features and suppress irrelevant noise simultaneously, limiting its effectiveness. We introduce FreqSelect, a lightweight, adaptive module that selectively filters spatial-frequency bands before encoding. By dynamically emphasizing frequencies that are most predictive of brain activity and suppressing those that are uninformative, FreqSelect acts as a content-aware gate between image features and natural data. It integrates seamlessly into standard very deep VAE-diffusion pipelines and requires no additional supervision. Evaluated on the Natural Scenes dataset, FreqSelect consistently improves reconstruction quality across both low- and high-level metrics. Beyond performance gains, the learned frequency-selection patterns offer interpretable insights into how different visual frequencies are represented in the brain. Our method generalizes across subjects and scenes, and holds promise for extension to other neuroimaging modalities, offering a principled approach to enhancing both decoding accuracy and neuroscientific interpretability.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.