Dongguan University of Technology
StableGuard: Towards Unified Copyright Protection and Tamper Localization in Latent Diffusion Models
StableGuard: Towards Unified Copyright Protection and Tamper Localization in Latent Diffusion Models
Researchers from South China University of Technology, Singapore Management University, and Dongguan University of Technology developed StableGuard, a unified framework for copyright protection and tamper localization in latent diffusion models. It achieves superior image fidelity, watermark extraction accuracy (99.97%), and tampering localization performance (0.98 F1-score) by seamlessly integrating these functions into the image generation process.
Researchers from Dongguan University of Technology, City University of Hong Kong, Tsinghua University, and Guangzhou University reveal that Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) unexpectedly underperform general-purpose LLMs in personalization tasks when rich user context is available through retrieval-augmented generation, despite their superior logical capabilities, prompting development of the Reinforced Reasoning for Personalization (R2P) framework that uses hierarchical reasoning templates, process intervention, and self-referencing to achieve state-of-the-art performance across the LaMP benchmark while generating shorter, more focused outputs that challenge conventional assumptions about token length and output quality.
26 Mar 2025
Researchers from multiple Chinese universities introduce RALLREC+, a framework that enhances LLM-based recommendation systems by combining representation learning with reasoning capabilities, achieving improved accuracy across three real-world datasets through joint textual-collaborative embeddings and knowledge-injected prompting without requiring additional training.
LLaVA-SpaceSGG introduces a new framework for open-vocabulary Scene Graph Generation by enhancing Multimodal Large Language Models with detailed spatial reasoning. The work presents SpaceSGG, a novel instruction-tuning dataset that integrates 2D and 3D scene information, and a two-stage training paradigm, resulting in improved performance on standard SGG benchmarks and superior spatial understanding demonstrated on a dedicated spatial validation set.
Large Language Models (LLMs) have been integrated into recommendation systems
to enhance user behavior comprehension. The Retrieval Augmented Generation
(RAG) technique is further incorporated into these systems to retrieve more
relevant items and improve system performance. However, existing RAG methods
rely primarily on textual semantics and often fail to incorporate the most
relevant items, limiting the effectiveness of the systems.
In this paper, we propose Representation learning for retrieval-Augmented
Large Language model Recommendation (RALLRec). Specifically, we enhance textual
semantics by prompting LLMs to generate more detailed item descriptions,
followed by joint representation learning of textual and collaborative
semantics, which are extracted by the LLM and recommendation models,
respectively. Considering the potential time-varying characteristics of user
interest, a simple yet effective reranking method is further introduced to
capture the dynamics of user preference. We conducted extensive experiments on
three real-world datasets, and the evaluation results validated the
effectiveness of our method. Code is made public at
this https URL
DETR-based methods, which use multi-layer transformer decoders to refine
object queries iteratively, have shown promising performance in 3D indoor
object detection. However, the scene point features in the transformer decoder
remain fixed, leading to minimal contributions from later decoder layers,
thereby limiting performance improvement. Recently, State Space Models (SSM)
have shown efficient context modeling ability with linear complexity through
iterative interactions between system states and inputs. Inspired by SSMs, we
propose a new 3D object DEtection paradigm with an interactive STate space
model (DEST). In the interactive SSM, we design a novel state-dependent SSM
parameterization method that enables system states to effectively serve as
queries in 3D indoor detection tasks. In addition, we introduce four key
designs tailored to the characteristics of point cloud and SSM: The
serialization and bidirectional scanning strategies enable bidirectional
feature interaction among scene points within the SSM. The inter-state
attention mechanism models the relationships between state points, while the
gated feed-forward network enhances inter-channel correlations. To the best of
our knowledge, this is the first method to model queries as system states and
scene points as system inputs, which can simultaneously update scene point
features and query features with linear complexity. Extensive experiments on
two challenging datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our DEST-based
method. Our method improves the GroupFree baseline in terms of AP50 on ScanNet
V2 (+5.3) and SUN RGB-D (+3.2) datasets. Based on the VDETR baseline, Our
method sets a new SOTA on the ScanNetV2 and SUN RGB-D datasets.
Topolectrical circuits provide a versatile platform for exploring and simulating modern physical models. However, existing approaches suffer from incomplete programmability and ineffective feature prediction and control mechanisms, hindering the investigation of physical phenomena on an integrated platform and limiting their translation into practical applications. Here, we present a deep learning empowered programmable topolectrical circuits (DLPTCs) platform for physical modeling and analysis. By integrating fully independent, continuous tuning of both on site and off site terms of the lattice Hamiltonian, physics graph informed inverse state design, and immediate hardware verification, our system bridges the gap between theoretical modeling and practical realization. Through flexible control and adiabatic path engineering, we experimentally observe the boundary states without global symmetry in higher order topological systems, their adiabatic phase transitions, and the flat band like characteristic corresponding to Landau levels in the circuit. Incorporating a physics graph informed mechanism with a generative AI model for physics exploration, we realize arbitrary, position controllable on board Anderson localization, surpassing conventional random localization. Utilizing this unique capability with high fidelity hardware implementation, we further demonstrate a compelling cryptographic application: hash based probabilistic information encryption by leveraging Anderson localization with extensive disorder configurations, enabling secure delivery of full ASCII messages.
Anomaly detection is a critical task in data mining and management with applications spanning fraud detection, network security, and log monitoring. Despite extensive research, existing unsupervised anomaly detection methods still face fundamental challenges including conflicting distributional assumptions, computational inefficiency, and difficulty handling different anomaly types. To address these problems, we propose ISER (Isolation-based Spherical Ensemble Representations) that extends existing isolation-based methods by using hypersphere radii as proxies for local density characteristics while maintaining linear time and constant space complexity. ISER constructs ensemble representations where hypersphere radii encode density information: smaller radii indicate dense regions while larger radii correspond to sparse areas. We introduce a novel similarity-based scoring method that measures pattern consistency by comparing ensemble representations against a theoretical anomaly reference pattern. Additionally, we enhance the performance of Isolation Forest by using ISER and adapting the scoring function to address axis-parallel bias and local anomaly detection limitations. Comprehensive experiments on 22 real-world datasets demonstrate ISER's superior performance over 11 baseline methods.
Occluded person re-identification (Re-ID) is a challenging task as persons
are frequently occluded by various obstacles or other persons, especially in
the crowd scenario. To address these issues, we propose a novel end-to-end
Part-Aware Transformer (PAT) for occluded person Re-ID through diverse part
discovery via a transformer encoderdecoder architecture, including a pixel
context based transformer encoder and a part prototype based transformer
decoder. The proposed PAT model enjoys several merits. First, to the best of
our knowledge, this is the first work to exploit the transformer
encoder-decoder architecture for occluded person Re-ID in a unified deep model.
Second, to learn part prototypes well with only identity labels, we design two
effective mechanisms including part diversity and part discriminability.
Consequently, we can achieve diverse part discovery for occluded person Re-ID
in a weakly supervised manner. Extensive experimental results on six
challenging benchmarks for three tasks (occluded, partial and holistic Re-ID)
demonstrate that our proposed PAT performs favorably against stat-of-the-art
methods.
02 Jul 2025
Massive multi-input multi-output (MIMO) combined with orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) modulation has emerged as a promising technique for high-mobility scenarios. However, its performance could be severely degraded due to channel aging caused by user mobility and high processing latency. In this paper, an integrated scheme of uplink (UL) channel estimation and downlink (DL) channel prediction is proposed to alleviate channel aging in time division duplex (TDD) massive MIMO-OTFS systems. Specifically, first, an iterative basis expansion model (BEM) based UL channel estimation scheme is proposed to accurately estimate UL channels with the aid of carefully designed OTFS frame pattern. Then a set of Slepian sequences are used to model the estimated UL channels, and the dynamic Slepian coefficients are fitted by a set of orthogonal polynomials. A channel predictor is derived to predict DL channels by iteratively extrapolating the Slepian coefficients. Simulation results verify that the proposed UL channel estimation and DL channel prediction schemes outperform the existing schemes in terms of normalized mean square error of channel estimation/prediction and DL spectral efficiency, with less pilot overhead.
Evaluating performance across optimization algorithms on many problems presents a complex challenge due to the diversity of numerical scales involved. Traditional data processing methods, such as hypothesis testing and Bayesian inference, often employ ranking-based methods to normalize performance values across these varying scales. However, a significant issue emerges with this ranking-based approach: the introduction of new algorithms can potentially disrupt the original rankings. This paper extensively explores the problem, making a compelling case to underscore the issue and conducting a thorough analysis of its root causes. These efforts pave the way for a comprehensive examination of potential solutions. Building on this research, this paper introduces a new mathematical model called "absolute ranking" and a sampling-based computational method. These contributions come with practical implementation recommendations, aimed at providing a more robust framework for addressing the challenge of numerical scale variation in the assessment of performance across multiple algorithms and problems.
Measuring similarity between incomplete data is a fundamental challenge in web mining, recommendation systems, and user behavior analysis. Traditional approaches either discard incomplete data or perform imputation as a preprocessing step, leading to information loss and biased similarity estimates. This paper presents the proximity kernel, a new similarity measure that directly computes similarity between incomplete data in kernel feature space without explicit imputation in the original space. The proposed method introduces data-dependent binning combined with proximity assignment to project data into a high-dimensional sparse representation that adapts to local density variations. For missing value handling, we propose a cascading fallback strategy to estimate missing feature distributions. We conduct clustering tasks on the proposed kernel representation across 12 real world incomplete datasets, demonstrating superior performance compared to existing methods while maintaining linear time complexity. All the code are available at this https URL.
Abstraction is an important and useful concept in the field of artificial intelligence. To the best of our knowledge, there is no syntactic method to compute a sound and complete abstraction from a given low-level basic action theory and a refinement mapping. This paper aims to address this this http URL this end, we first present a variant of situation calculus,namely linear integer situation calculus, which serves as the formalization of high-level basic action theory. We then migrate Banihashemi, De Giacomo, and Lespérance's abstraction framework to one from linear integer situation calculus to extended situation calculus. Furthermore, we identify a class of Golog programs, namely guarded actions,that is used to restrict low-level Golog programs, and impose some restrictions on refinement mappings. Finally, we design a syntactic approach to computing a sound and complete abstraction from a low-level basic action theory and a restricted refinement mapping.
Adversarial training (AT) with projected gradient descent is the most popular method to improve model robustness under adversarial attacks. However, computational overheads become prohibitively large when AT is applied to large backbone models. AT is also known to have the issue of robust overfitting. This paper contributes to solving both problems simultaneously towards building more trustworthy foundation models. In particular, we propose a new adapter-based approach for efficient AT directly in the feature space. We show that the proposed adapter-based approach can improve the inner-loop convergence quality by eliminating robust overfitting. As a result, it significantly increases computational efficiency and improves model accuracy by generalizing adversarial robustness to unseen attacks. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the new adapter-based approach in different backbone architectures and in AT at scale.
10 Oct 2024
University of CincinnatiNational United University University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Beijing Normal University
Beijing Normal University University of Science and Technology of ChinaNational Taiwan University
University of Science and Technology of ChinaNational Taiwan University University of California, Irvine
University of California, Irvine Tsinghua UniversityIllinois Institute of TechnologyJoint Institute for Nuclear Research
Tsinghua UniversityIllinois Institute of TechnologyJoint Institute for Nuclear Research Yale UniversityUniversity of Wisconsin
Yale UniversityUniversity of Wisconsin The University of Hong Kong
The University of Hong Kong Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryShenzhen University
Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryShenzhen University Virginia Tech
Virginia Tech Shandong UniversityTemple UniversityChinese University of Hong KongGuangxi UniversityDongguan University of TechnologyXian Jiaotong UniversityNorth China Electric Power UniversityInstitute of high-energy PhysicsChina Institute of Atomic EnergySiena CollegeNational Chiao Tung UniversitySun Yat-sen (Zhongshan) UniversityCharles University, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics
Shandong UniversityTemple UniversityChinese University of Hong KongGuangxi UniversityDongguan University of TechnologyXian Jiaotong UniversityNorth China Electric Power UniversityInstitute of high-energy PhysicsChina Institute of Atomic EnergySiena CollegeNational Chiao Tung UniversitySun Yat-sen (Zhongshan) UniversityCharles University, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Beijing Normal University
Beijing Normal University University of Science and Technology of ChinaNational Taiwan University
University of Science and Technology of ChinaNational Taiwan University University of California, Irvine
University of California, Irvine Tsinghua UniversityIllinois Institute of TechnologyJoint Institute for Nuclear Research
Tsinghua UniversityIllinois Institute of TechnologyJoint Institute for Nuclear Research Yale UniversityUniversity of Wisconsin
Yale UniversityUniversity of Wisconsin The University of Hong Kong
The University of Hong Kong Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryShenzhen University
Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryShenzhen University Virginia Tech
Virginia Tech Shandong UniversityTemple UniversityChinese University of Hong KongGuangxi UniversityDongguan University of TechnologyXian Jiaotong UniversityNorth China Electric Power UniversityInstitute of high-energy PhysicsChina Institute of Atomic EnergySiena CollegeNational Chiao Tung UniversitySun Yat-sen (Zhongshan) UniversityCharles University, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics
Shandong UniversityTemple UniversityChinese University of Hong KongGuangxi UniversityDongguan University of TechnologyXian Jiaotong UniversityNorth China Electric Power UniversityInstitute of high-energy PhysicsChina Institute of Atomic EnergySiena CollegeNational Chiao Tung UniversitySun Yat-sen (Zhongshan) UniversityCharles University, Faculty of Mathematics and PhysicsThis Letter reports the first measurement of the oscillation amplitude and frequency of reactor antineutrinos at Daya Bay via neutron capture on hydrogen using 1958 days of data. With over 3.6 million signal candidates, an optimized candidate selection, improved treatment of backgrounds and efficiencies, refined energy calibration, and an energy response model for the capture-on-hydrogen sensitive region, the relative νe rates and energy spectra variation among the near and far detectors gives sin22θ13=0.0759−0.0049+0.0050 and Δm322=(2.72−0.15+0.14)×10−3 eV2 assuming the normal neutrino mass ordering, and Δm322=(−2.83−0.14+0.15)×10−3 eV2 for the inverted neutrino mass ordering. This estimate of sin22θ13 is consistent with and essentially independent from the one obtained using the capture-on-gadolinium sample at Daya Bay. The combination of these two results yields sin22θ13=0.0833±0.0022, which represents an 8% relative improvement in precision regarding the Daya Bay full 3158-day capture-on-gadolinium result.
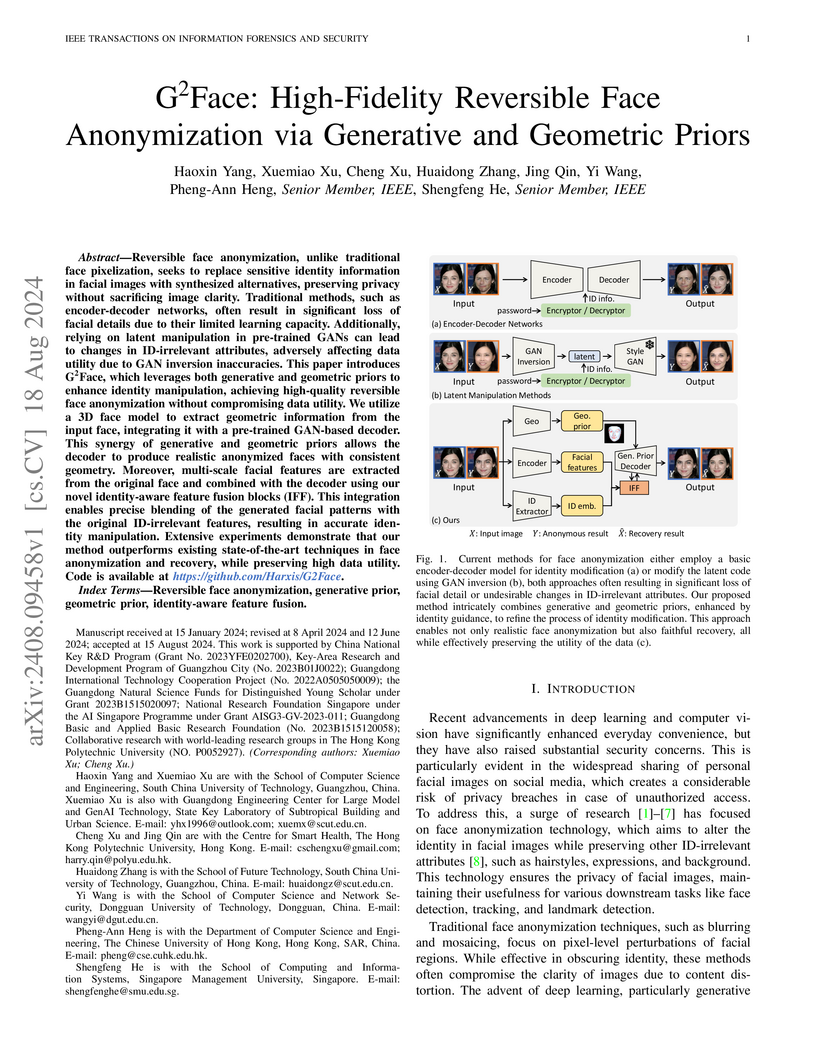
Reversible face anonymization, unlike traditional face pixelization, seeks to
replace sensitive identity information in facial images with synthesized
alternatives, preserving privacy without sacrificing image clarity. Traditional
methods, such as encoder-decoder networks, often result in significant loss of
facial details due to their limited learning capacity. Additionally, relying on
latent manipulation in pre-trained GANs can lead to changes in ID-irrelevant
attributes, adversely affecting data utility due to GAN inversion inaccuracies.
This paper introduces G\textsuperscript{2}Face, which leverages both generative
and geometric priors to enhance identity manipulation, achieving high-quality
reversible face anonymization without compromising data utility. We utilize a
3D face model to extract geometric information from the input face, integrating
it with a pre-trained GAN-based decoder. This synergy of generative and
geometric priors allows the decoder to produce realistic anonymized faces with
consistent geometry. Moreover, multi-scale facial features are extracted from
the original face and combined with the decoder using our novel identity-aware
feature fusion blocks (IFF). This integration enables precise blending of the
generated facial patterns with the original ID-irrelevant features, resulting
in accurate identity manipulation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our
method outperforms existing state-of-the-art techniques in face anonymization
and recovery, while preserving high data utility. Code is available at
this https URL
University of CincinnatiNational United UniversityCharles University Beijing Normal University
Beijing Normal University UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley University of Science and Technology of ChinaNational Taiwan University
University of Science and Technology of ChinaNational Taiwan University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Tsinghua UniversityNankai UniversityJoint Institute for Nuclear Research
Tsinghua UniversityNankai UniversityJoint Institute for Nuclear Research Yale UniversityEast China University of Science and Technology
Yale UniversityEast China University of Science and Technology The University of Hong Kong
The University of Hong Kong Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory University of Wisconsin-Madison
University of Wisconsin-Madison Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryShenzhen University
Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryShenzhen University Virginia TechUniversity of Houston
Virginia TechUniversity of Houston Shandong UniversityTemple UniversityChinese University of Hong KongDongguan University of TechnologyXian Jiaotong UniversityNorth China Electric Power UniversityInstitute of high-energy PhysicsChina Institute of Atomic EnergySiena CollegeNational Chiao Tung UniversitySun Yat-sen (Zhongshan) University
Shandong UniversityTemple UniversityChinese University of Hong KongDongguan University of TechnologyXian Jiaotong UniversityNorth China Electric Power UniversityInstitute of high-energy PhysicsChina Institute of Atomic EnergySiena CollegeNational Chiao Tung UniversitySun Yat-sen (Zhongshan) University
 Beijing Normal University
Beijing Normal University UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley University of Science and Technology of ChinaNational Taiwan University
University of Science and Technology of ChinaNational Taiwan University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Tsinghua UniversityNankai UniversityJoint Institute for Nuclear Research
Tsinghua UniversityNankai UniversityJoint Institute for Nuclear Research Yale UniversityEast China University of Science and Technology
Yale UniversityEast China University of Science and Technology The University of Hong Kong
The University of Hong Kong Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory University of Wisconsin-Madison
University of Wisconsin-Madison Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryShenzhen University
Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryShenzhen University Virginia TechUniversity of Houston
Virginia TechUniversity of Houston Shandong UniversityTemple UniversityChinese University of Hong KongDongguan University of TechnologyXian Jiaotong UniversityNorth China Electric Power UniversityInstitute of high-energy PhysicsChina Institute of Atomic EnergySiena CollegeNational Chiao Tung UniversitySun Yat-sen (Zhongshan) University
Shandong UniversityTemple UniversityChinese University of Hong KongDongguan University of TechnologyXian Jiaotong UniversityNorth China Electric Power UniversityInstitute of high-energy PhysicsChina Institute of Atomic EnergySiena CollegeNational Chiao Tung UniversitySun Yat-sen (Zhongshan) UniversityWe report a measurement of electron antineutrino oscillation from the Daya
Bay Reactor Neutrino Experiment with nearly 4 million reactor
νe inverse beta decay candidates observed over 1958 days of
data collection. The installation of a Flash-ADC readout system and a special
calibration campaign using different source enclosures reduce uncertainties in
the absolute energy calibration to less than 0.5% for visible energies larger
than 2 MeV. The uncertainty in the cosmogenic 9Li and 8He background is
reduced from 45% to 30% in the near detectors. A detailed investigation of the
spent nuclear fuel history improves its uncertainty from 100% to 30%. Analysis
of the relative νe rates and energy spectra among detectors
yields
sin22θ13=0.0856±0.0029 and $\Delta
m^2_{32}=(2.471^{+0.068}_{-0.070})\times 10^{-3}~\mathrm{eV}^2$ assuming the
normal hierarchy, and $\Delta m^2_{32}=-(2.575^{+0.068}_{-0.070})\times
10^{-3}~\mathrm{eV}^2$ assuming the inverted hierarchy.
While classic video anomaly detection (VAD) requires labeled normal videos for training, emerging unsupervised VAD (UVAD) aims to discover anomalies directly from fully unlabeled videos. However, existing UVAD methods still rely on shallow models to perform detection or initialization, and they are evidently inferior to classic VAD methods. This paper proposes a full deep neural network (DNN) based solution that can realize highly effective UVAD. First, we, for the first time, point out that deep reconstruction can be surprisingly effective for UVAD, which inspires us to unveil a property named "normality advantage", i.e., normal events will enjoy lower reconstruction loss when DNN learns to reconstruct unlabeled videos. With this property, we propose Localization based Reconstruction (LBR) as a strong UVAD baseline and a solid foundation of our solution. Second, we propose a novel self-paced refinement (SPR) scheme, which is synthesized into LBR to conduct UVAD. Unlike ordinary self-paced learning that injects more samples in an easy-to-hard manner, the proposed SPR scheme gradually drops samples so that suspicious anomalies can be removed from the learning process. In this way, SPR consolidates normality advantage and enables better UVAD in a more proactive way. Finally, we further design a variant solution that explicitly takes the motion cues into account. The solution evidently enhances the UVAD performance, and it sometimes even surpasses the best classic VAD methods. Experiments show that our solution not only significantly outperforms existing UVAD methods by a wide margin (5% to 9% AUROC), but also enables UVAD to catch up with the mainstream performance of classic VAD.
13 Oct 2021
National United UniversityCharles UniversityNational Central University Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University
Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China Beihang UniversityNational Taiwan University
Beihang UniversityNational Taiwan University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Tsinghua UniversityNankai UniversityJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchJilin University
Tsinghua UniversityNankai UniversityJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchJilin University Shandong UniversityXiangtan UniversitySoochow UniversityTechnische Universität MünchenUniversity of HamburgAix Marseille UniversityUniversità degli Studi di PaviaUniversity of JyväskyläUniversity of AlabamaINFN, Sezione di PaviaDongguan University of TechnologyUniversità degli Studi di BolognaXian Jiaotong UniversityINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiEberhard-Karls-Universität TübingenNorth China Electric Power UniversityComenius UniversityINFN, Sezione di MilanoInstitute of high-energy PhysicsChina Institute of Atomic EnergyINFN - Sezione di PadovaUniversità degli Studi di CataniaInstitute for Nuclear Research, Russian Academy of SciencesKing Mongkut’s Institute of Technology LadkrabangPalacký UniversityParis-Saclay UniversityINFN, Sezione di CataniaINFN-Sezione di BolognaUniversitá dell’InsubriaUniversità degli Studi di Roma TreSkobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics, Moscow State UniversityZhongshan UniversityDaya Bay Nuclear Power Joint LaboratoryLAPP, Université Savoie Mont Blanc, CNRS/IN2P3INFN-Sezione di Roma TreINFN-Sezione di FerraraUniversit
degli Studi di GenovaUniversit
degli Studi di PerugiaUniversit
Libre de BruxellesUniversit
degli Studi di PadovaNational Research Nuclear University ","MEPhIRWTH Aachen University
Shandong UniversityXiangtan UniversitySoochow UniversityTechnische Universität MünchenUniversity of HamburgAix Marseille UniversityUniversità degli Studi di PaviaUniversity of JyväskyläUniversity of AlabamaINFN, Sezione di PaviaDongguan University of TechnologyUniversità degli Studi di BolognaXian Jiaotong UniversityINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiEberhard-Karls-Universität TübingenNorth China Electric Power UniversityComenius UniversityINFN, Sezione di MilanoInstitute of high-energy PhysicsChina Institute of Atomic EnergyINFN - Sezione di PadovaUniversità degli Studi di CataniaInstitute for Nuclear Research, Russian Academy of SciencesKing Mongkut’s Institute of Technology LadkrabangPalacký UniversityParis-Saclay UniversityINFN, Sezione di CataniaINFN-Sezione di BolognaUniversitá dell’InsubriaUniversità degli Studi di Roma TreSkobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics, Moscow State UniversityZhongshan UniversityDaya Bay Nuclear Power Joint LaboratoryLAPP, Université Savoie Mont Blanc, CNRS/IN2P3INFN-Sezione di Roma TreINFN-Sezione di FerraraUniversit
degli Studi di GenovaUniversit
degli Studi di PerugiaUniversit
Libre de BruxellesUniversit
degli Studi di PadovaNational Research Nuclear University ","MEPhIRWTH Aachen University
 Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University
Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China Beihang UniversityNational Taiwan University
Beihang UniversityNational Taiwan University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Tsinghua UniversityNankai UniversityJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchJilin University
Tsinghua UniversityNankai UniversityJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchJilin University Shandong UniversityXiangtan UniversitySoochow UniversityTechnische Universität MünchenUniversity of HamburgAix Marseille UniversityUniversità degli Studi di PaviaUniversity of JyväskyläUniversity of AlabamaINFN, Sezione di PaviaDongguan University of TechnologyUniversità degli Studi di BolognaXian Jiaotong UniversityINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiEberhard-Karls-Universität TübingenNorth China Electric Power UniversityComenius UniversityINFN, Sezione di MilanoInstitute of high-energy PhysicsChina Institute of Atomic EnergyINFN - Sezione di PadovaUniversità degli Studi di CataniaInstitute for Nuclear Research, Russian Academy of SciencesKing Mongkut’s Institute of Technology LadkrabangPalacký UniversityParis-Saclay UniversityINFN, Sezione di CataniaINFN-Sezione di BolognaUniversitá dell’InsubriaUniversità degli Studi di Roma TreSkobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics, Moscow State UniversityZhongshan UniversityDaya Bay Nuclear Power Joint LaboratoryLAPP, Université Savoie Mont Blanc, CNRS/IN2P3INFN-Sezione di Roma TreINFN-Sezione di FerraraUniversit
degli Studi di GenovaUniversit
degli Studi di PerugiaUniversit
Libre de BruxellesUniversit
degli Studi di PadovaNational Research Nuclear University ","MEPhIRWTH Aachen University
Shandong UniversityXiangtan UniversitySoochow UniversityTechnische Universität MünchenUniversity of HamburgAix Marseille UniversityUniversità degli Studi di PaviaUniversity of JyväskyläUniversity of AlabamaINFN, Sezione di PaviaDongguan University of TechnologyUniversità degli Studi di BolognaXian Jiaotong UniversityINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiEberhard-Karls-Universität TübingenNorth China Electric Power UniversityComenius UniversityINFN, Sezione di MilanoInstitute of high-energy PhysicsChina Institute of Atomic EnergyINFN - Sezione di PadovaUniversità degli Studi di CataniaInstitute for Nuclear Research, Russian Academy of SciencesKing Mongkut’s Institute of Technology LadkrabangPalacký UniversityParis-Saclay UniversityINFN, Sezione di CataniaINFN-Sezione di BolognaUniversitá dell’InsubriaUniversità degli Studi di Roma TreSkobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics, Moscow State UniversityZhongshan UniversityDaya Bay Nuclear Power Joint LaboratoryLAPP, Université Savoie Mont Blanc, CNRS/IN2P3INFN-Sezione di Roma TreINFN-Sezione di FerraraUniversit
degli Studi di GenovaUniversit
degli Studi di PerugiaUniversit
Libre de BruxellesUniversit
degli Studi di PadovaNational Research Nuclear University ","MEPhIRWTH Aachen UniversityJUNO is a massive liquid scintillator detector with a primary scientific goal
of determining the neutrino mass ordering by studying the oscillated
anti-neutrino flux coming from two nuclear power plants at 53 km distance. The
expected signal anti-neutrino interaction rate is only 60 counts per day,
therefore a careful control of the background sources due to radioactivity is
critical. In particular, natural radioactivity present in all materials and in
the environment represents a serious issue that could impair the sensitivity of
the experiment if appropriate countermeasures were not foreseen. In this paper
we discuss the background reduction strategies undertaken by the JUNO
collaboration to reduce at minimum the impact of natural radioactivity. We
describe our efforts for an optimized experimental design, a careful material
screening and accurate detector production handling, and a constant control of
the expected results through a meticulous Monte Carlo simulation program. We
show that all these actions should allow us to keep the background count rate
safely below the target value of 10 Hz in the default fiducial volume, above an
energy threshold of 0.7 MeV.
18 May 2025
Topological disclinations, crystallographic defects that break rotation
lattice symmetry, have attracted great interest and exhibited wide applications
in cavities, waveguides, and lasers. However, topological disclinations have
thus far been predominantly restricted to two-dimensional (2D) systems owing to
the substantial challenges in constructing such defects in three-dimensional
(3D) systems and characterizing their topological features. Here we report the
theoretical proposal and experimental demonstration of a 3D topological
disclination that exhibits fractional (1/2) charge and zero-dimensional (0D)
topological bound states, realized by cutting-and-gluing a 3D acoustic
topological crystalline insulator. Using acoustic pump-probe measurements, we
directly observe 0D topological disclination states at the disclination core,
consistent with the tight-binding model and full-wave simulation results. Our
results extend the research frontier of topological disclinations and open a
new paradigm for exploring the interplay between momentum-space band topology
and the real-space defect topology in 3D and higher dimensions.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.