Hon Hai Research Institute
A comprehensive tutorial bridges the gap between classical machine learning and quantum computing, offering AI practitioners a systematic pathway into quantum machine learning through accessible frameworks, theoretical foundations, and practical implementations - marking a significant educational milestone in making quantum computing concepts approachable for the broader AI community.
This survey provides a comprehensive overview of backdoor threats in Large Language Models (LLMs), systematically classifying attack methods and corresponding defense mechanisms across the LLM development lifecycle. It synthesizes current research, identifies critical gaps in attack realism and defense generalizability, and pinpoints limitations in existing evaluation methodologies, guiding future research toward more robust and trustworthy LLM systems.
The GREAT (Global Regulation and Excitation via Attention Tuning) framework enhances iterative stereo matching algorithms by systematically incorporating global contextual information into cost volume construction. This approach improves disparity prediction in challenging regions like occlusions and textureless surfaces, achieving state-of-the-art performance on multiple benchmarks and enabling comparable accuracy with significantly fewer iterations.
QCNeXt presents a next-generation Transformer-based framework for joint multi-agent trajectory prediction, achieving state-of-the-art performance on the Argoverse 2 benchmark. It models future social interactions explicitly, demonstrating that joint prediction can outperform marginal prediction models even on individual agent accuracy metrics.
Tackling complex optimization problems often relies on expert-designed
heuristics, typically crafted through extensive trial and error. Recent
advances demonstrate that large language models (LLMs), when integrated into
well-designed evolutionary search frameworks, can autonomously discover
high-performing heuristics at a fraction of the traditional cost. However,
existing approaches predominantly rely on verbal guidance, i.e., manipulating
the prompt generation process, to steer the evolution of heuristics, without
adapting the underlying LLM. We propose a hybrid framework that combines verbal
and numerical guidance, the latter achieved by fine-tuning the LLM via
reinforcement learning based on the quality of generated heuristics. This joint
optimization allows the LLM to co-evolve with the search process. Our method
outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) baselines across various optimization
tasks, running locally on a single 24GB GPU using a 7B model with INT4
quantization. It surpasses methods that rely solely on verbal guidance, even
when those use significantly more powerful API-based models.
09 Oct 2025
Researchers developed a single-shot universal fault-tolerant quantum computation protocol for high-rate quantum LDPC codes using a novel code-switching mechanism, enabling all operations to be performed with constant-depth circuits. This approach eliminates the need for magic state distillation and includes a simplified construction for transversal CCZ gates in 3D hypergraph product codes, with fault-tolerance proven against both adversarial and local-stochastic noise.
02 Oct 2025
Quantum Phase Estimation (QPE) is a cornerstone algorithm for fault-tolerant quantum computation, especially for electronic structure calculations of chemical systems. To accommodate the diverse characteristics of quantum chemical systems, numerous variants of QPE have been developed, each with distinct qubit and gate cost implications. In this paper, we quantify the impact of three key parameters on the overall quantum resource costs for the QPE algorithm: the choice between trotterization and qubitization, the use of molecular orbitals versus plane-wave basis-sets, and the selection of the fermion-to-qubit encoding scheme. From this, we establish clear performance trade-offs and delineate specific parameter regimes that minimize resource costs for relevant molecular systems. When performing phase estimation on large molecules in the fault-tolerant setting, we found the first-quantized qubitization circuit using the plane-wave basis to be the most efficient, with a gate cost scaling of O~([N4/3M2/3+N8/3M1/3]/ε) for a system of N electrons and M orbitals, which is the best known scaling to date. On the other hand, when only noisy intermediate-scale or near-term fault-tolerant systems are available, the phase estimation of small molecules can be performed with gate cost of O(M7/ε2) via trotterization in the MO basis. Furthermore, we provide numerical estimations of qubit and T gate costs required to perform QPE for several real-world molecular systems under these different parameter choices.
ModeSeq introduces a sequential mode modeling paradigm for sparse multimodal motion prediction, moving beyond parallel decoding to inherently encourage diversity and better confidence calibration. The approach, coupled with an Early-Match-Take-All (EMTA) training strategy, achieves improved performance on Waymo Open Motion and Argoverse 2 datasets while offering an end-to-end solution without heuristic post-processing.
BehaviorGPT, developed by a team including researchers from CityU and CMU, achieved first place in the Waymo Open Sim Agents Challenge 2024 by introducing a fully autoregressive Transformer with a Next-Patch Prediction Paradigm for realistic multi-agent traffic simulation, demonstrating superior realism and accuracy with only 3 million parameters.
A self-correcting quantum memory is a type of quantum error correcting code that can correct errors passively through cooling. A major open question in the field is whether self-correcting quantum memories can exist in 3D. In this work, we propose two candidate constructions for 3D self-correcting quantum memories. The first construction is an extension of Haah's code, which retains translation invariance. The second construction is based on fractals with greater flexibility in its design. Additionally, we review existing 3D quantum codes and suggest that they are not self-correcting.
This survey systematically reviews the application of Large Language Models (LLMs) across static, dynamic, and hybrid program analysis techniques. It categorizes current research, highlights the capabilities of LLMs in improving tasks like vulnerability detection and fuzzing, and identifies ongoing challenges and future directions in the field.
04 May 2025
Gradient-based optimization drives the unprecedented performance of modern
deep neural network models across diverse applications. Adaptive algorithms
have accelerated neural network training due to their rapid convergence rates;
however, they struggle to find ``flat minima" reliably, resulting in suboptimal
generalization compared to stochastic gradient descent (SGD). By revisiting
various adaptive algorithms' mechanisms, we propose the Frankenstein optimizer,
which combines their advantages. The proposed Frankenstein dynamically adjusts
first- and second-momentum coefficients according to the optimizer's current
state to directly maintain consistent learning dynamics and immediately reflect
sudden gradient changes. Extensive experiments across several research domains
such as computer vision, natural language processing, few-shot learning, and
scientific simulations show that Frankenstein surpasses existing adaptive
algorithms and SGD empirically regarding convergence speed and generalization
performance. Furthermore, this research deepens our understanding of adaptive
algorithms through centered kernel alignment analysis and loss landscape
visualization during the learning process. Code is available at
this https URL
Over the past decade, the dominance of deep learning has prevailed across various domains of artificial intelligence, including natural language processing, computer vision, and biomedical signal processing. While there have been remarkable improvements in model accuracy, deploying these models on lightweight devices, such as mobile phones and microcontrollers, is constrained by limited resources. In this survey, we provide comprehensive design guidance tailored for these devices, detailing the meticulous design of lightweight models, compression methods, and hardware acceleration strategies. The principal goal of this work is to explore methods and concepts for getting around hardware constraints without compromising the model's accuracy. Additionally, we explore two notable paths for lightweight deep learning in the future: deployment techniques for TinyML and Large Language Models. Although these paths undoubtedly have potential, they also present significant challenges, encouraging research into unexplored areas.
Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate strong task-specific capabilities
through fine-tuning, but merging multiple fine-tuned models often leads to
degraded performance due to overlapping instruction-following components. Task
Arithmetic (TA), which combines task vectors derived from fine-tuning, enables
multi-task learning and task forgetting but struggles to isolate task-specific
knowledge from general instruction-following behavior. To address this, we
propose Layer-Aware Task Arithmetic (LATA), a novel approach that assigns
layer-specific weights to task vectors based on their alignment with
instruction-following or task-specific components. By amplifying task-relevant
layers and attenuating instruction-following layers, LATA improves task
learning and forgetting performance while preserving overall model utility.
Experiments on multiple benchmarks, including WikiText-2, GSM8K, and HumanEval,
demonstrate that LATA outperforms existing methods in both multi-task learning
and selective task forgetting, achieving higher task accuracy and alignment
with minimal degradation in output quality. Our findings highlight the
importance of layer-wise analysis in disentangling task-specific and
general-purpose knowledge, offering a robust framework for efficient model
merging and editing.
04 Aug 2025
Generating realistic and controllable traffic scenes from natural language can greatly enhance the development and evaluation of autonomous driving systems. However, this task poses unique challenges: (1) grounding free-form text into spatially valid and semantically coherent layouts, (2) composing scenarios without predefined locations, and (3) planning multi-agent behaviors and selecting roads that respect agents' configurations. To address these, we propose a modular framework, TTSG, comprising prompt analysis, road retrieval, agent planning, and a novel plan-aware road ranking algorithm to solve these challenges. While large language models (LLMs) are used as general planners, our design integrates them into a tightly controlled pipeline that enforces structure, feasibility, and scene diversity. Notably, our ranking strategy ensures consistency between agent actions and road geometry, enabling scene generation without predefined routes or spawn points. The framework supports both routine and safety-critical scenarios, as well as multi-stage event composition. Experiments on SafeBench demonstrate that our method achieves the lowest average collision rate (3.5\%) across three critical scenarios. Moreover, driving captioning models trained on our generated scenes improve action reasoning by over 30 CIDEr points. These results underscore our proposed framework for flexible, interpretable, and safety-oriented simulation.
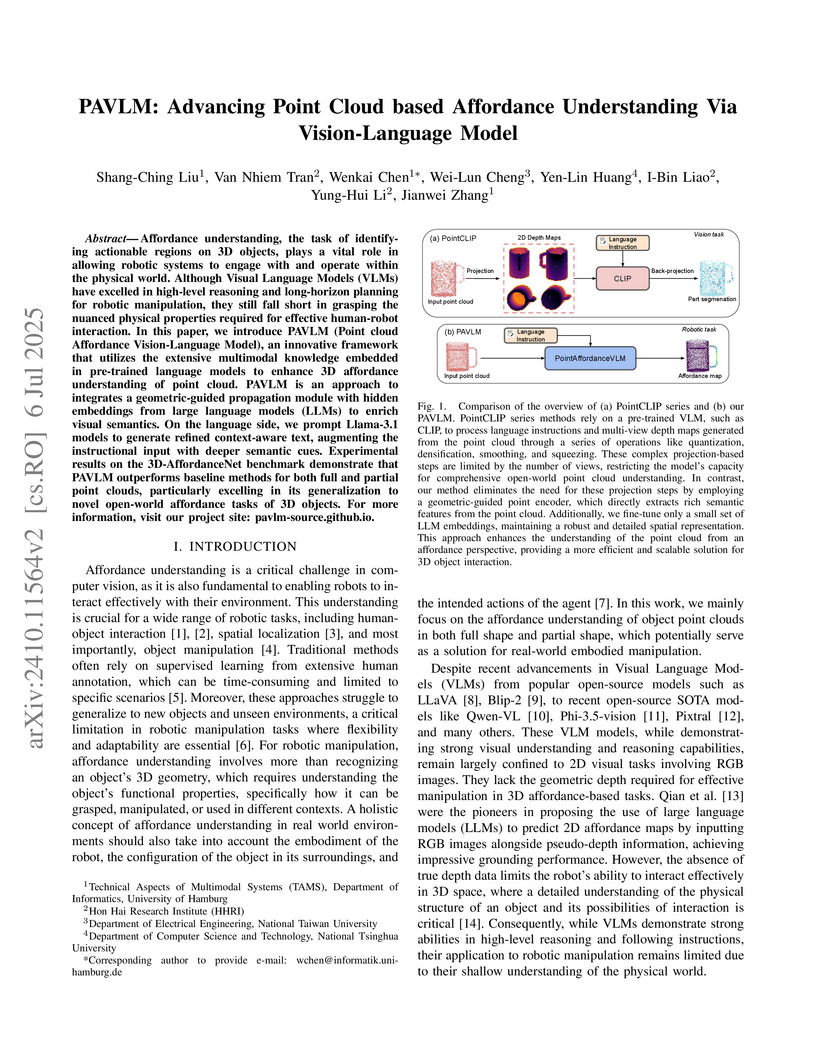
Affordance understanding, the task of identifying actionable regions on 3D objects, plays a vital role in allowing robotic systems to engage with and operate within the physical world. Although Visual Language Models (VLMs) have excelled in high-level reasoning and long-horizon planning for robotic manipulation, they still fall short in grasping the nuanced physical properties required for effective human-robot interaction. In this paper, we introduce PAVLM (Point cloud Affordance Vision-Language Model), an innovative framework that utilizes the extensive multimodal knowledge embedded in pre-trained language models to enhance 3D affordance understanding of point cloud. PAVLM integrates a geometric-guided propagation module with hidden embeddings from large language models (LLMs) to enrich visual semantics. On the language side, we prompt Llama-3.1 models to generate refined context-aware text, augmenting the instructional input with deeper semantic cues. Experimental results on the 3D-AffordanceNet benchmark demonstrate that PAVLM outperforms baseline methods for both full and partial point clouds, particularly excelling in its generalization to novel open-world affordance tasks of 3D objects. For more information, visit our project site: this http URL.
26 Sep 2024
We investigate microwave interference from a spin ensemble and its mirror
image in a one-dimensional waveguide. Away from the mirror, the resonance
frequencies of the Kittel mode (KM) inside a ferrimagnetic spin ensemble have
sinusoidal shifts as the normalized distance between the spin ensemble and the
mirror increases compared to the setup without the mirror. These shifts are a
consequence of the KM's interaction with its own image. Furthermore, the
variation of the magnon radiative decay into the waveguide shows a cosine
squared oscillation and is enhanced twofold when the KM sits at the magnetic
antinode of the corresponding eigenmode. We can finely tune the KM to achieve
the maximum adsorption of the input photons at the critical coupling point.
Moreover, by placing the KM in proximity to the node of the resonance field,
its lifetime is extended to more than eight times compared to its positioning
near the antinode.
As Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed as black-box components in real-world applications, evaluating their safety-especially under adversarial prompting-has become critical. Arguably, effective safety evaluations should be adaptive, evolving with LLM capabilities, and also cover a broad spectrum of harmful topics and real-world scenarios to fully expose potential vulnerabilities. Existing manual safety benchmarks, built on handcrafted adversarial prompts, are limited by their static nature and the intensive labor required to update them, making it difficult to keep pace with rapidly advancing LLMs. In contrast, automated adversarial prompt generation offers a promising path toward adaptive evaluation. However, current methods often suffer from insufficient adversarial topic coverage (topic-level diversity) and weak alignment with real-world contexts. These shortcomings stem from the exploration-exploitation dilemma in black-box optimization and a lack of real-world contextualization, resulting in adversarial prompts that are both topically narrow and scenario-repetitive. To address these issues, we propose Reality-Oriented Safety Evaluation (ROSE), a novel framework that uses multi-objective reinforcement learning to fine-tune an adversarial LLM for generating topically diverse and contextually rich adversarial prompts. Experiments show that ROSE outperforms existing methods in uncovering safety vulnerabilities in state-of-the-art LLMs, with notable improvements in integrated evaluation metrics. We hope ROSE represents a step toward more practical and reality-oriented safety evaluation of LLMs. WARNING: This paper contains examples of potentially harmful text.
Red teaming has proven to be an effective method for identifying and
mitigating vulnerabilities in Large Language Models (LLMs). Reinforcement
Fine-Tuning (RFT) has emerged as a promising strategy among existing red
teaming techniques. However, a lack of a unified benchmark hinders current
RFT-based red teaming methods. Implementation details, especially in Proximal
Policy Optimization (PPO)-based RFT, significantly affect outcome stability and
reproducibility. To address this issue, we introduce RedRFT, a lightweight
benchmark designed to simplify and standardize the implementation and
evaluation of RFT-based red teaming. RedRFT combines the design strengths of
both single-file CleanRL and highly modularized Tianshou, offering high-quality
single-file red teaming implementations and modular PPO core components, such
as the General Advantage Estimator. It supports a variety of token and sentence
diversity metrics, featuring modularized intrinsic reward computation that
facilitates plug-and-play experimentation. To clarify their influence on RFT
performance, we conducted an extensive ablation study on key components,
including Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence, and
Lagrange Multiplier. We hope this work contributes to 1) gaining a
comprehensive understanding of the implementation nuances of RFT-based red
teaming algorithms, and 2) enabling rapid prototyping of innovative features
for RFT-based red teaming. Code for the benchmark can be accessed at
this https URL
28 Feb 2025
The increasing adoption of large language models (LLMs) for code-related
tasks has raised concerns about the security of their training datasets. One
critical threat is dead code poisoning, where syntactically valid but
functionally redundant code is injected into training data to manipulate model
behavior. Such attacks can degrade the performance of neural code search
systems, leading to biased or insecure code suggestions. Existing detection
methods, such as token-level perplexity analysis, fail to effectively identify
dead code due to the structural and contextual characteristics of programming
languages. In this paper, we propose DePA (Dead Code Perplexity Analysis), a
novel line-level detection and cleansing method tailored to the structural
properties of code. DePA computes line-level perplexity by leveraging the
contextual relationships between code lines and identifies anomalous lines by
comparing their perplexity to the overall distribution within the file. Our
experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that DePA significantly
outperforms existing methods, achieving 0.14-0.19 improvement in detection
F1-score and a 44-65% increase in poisoned segment localization precision.
Furthermore, DePA enhances detection speed by 0.62-23x, making it practical for
large-scale dataset cleansing. Overall, by addressing the unique challenges of
dead code poisoning, DePA provides a robust and efficient solution for
safeguarding the integrity of code generation model training datasets.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.