Hunan University
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Zhejiang UniversityHunan UniversityAgency for Science, Technology and ResearchAlibaba Inc.Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of MedicineZhejiang University School of MedicineAngelalign Technology Inc.Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Medical Imaging Artificial IntelligenceChina Mobile Group Zhejiang Company Limited
Zhejiang UniversityHunan UniversityAgency for Science, Technology and ResearchAlibaba Inc.Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of MedicineZhejiang University School of MedicineAngelalign Technology Inc.Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Medical Imaging Artificial IntelligenceChina Mobile Group Zhejiang Company LimitedHulu-Med introduces a transparent generalist model for comprehensive medical vision-language understanding across diverse modalities including text, 2D images, 3D volumes, and videos. The model surpassed existing open-source models on 27 of 30 benchmarks and outperformed proprietary systems like GPT-4o on 16 benchmarks, demonstrating competitive performance with accessible training costs.
Researchers from Hunan University and Nanyang Technological University developed Group Training, a strategy that accelerates 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) by up to 30% while enhancing rendering quality. This method dynamically manages Gaussian primitives during training through cyclic caching and opacity-based prioritized sampling, making novel view synthesis more efficient and practical.
Researchers at South China University of Technology and collaborators introduced NSG-VD, a physics-driven method utilizing a Normalized Spatiotemporal Gradient (NSG) and Maximum Mean Discrepancy, to detect AI-generated videos by identifying violations of physical continuity. The approach achieves superior detection performance on advanced generative models like Sora and demonstrates strong robustness in data-imbalanced settings.
INP-Former++ introduces a unified framework for universal anomaly detection by extracting "Intrinsic Normal Prototypes" directly from test images, rather than relying on external references. This approach achieves state-of-the-art performance across diverse anomaly detection tasks, including multi-class (I-AUROC 99.8, P-AUROC 98.7 on MVTec-AD) and few-shot settings, while demonstrating high efficiency with a 99.2% reduction in attention computational cost.
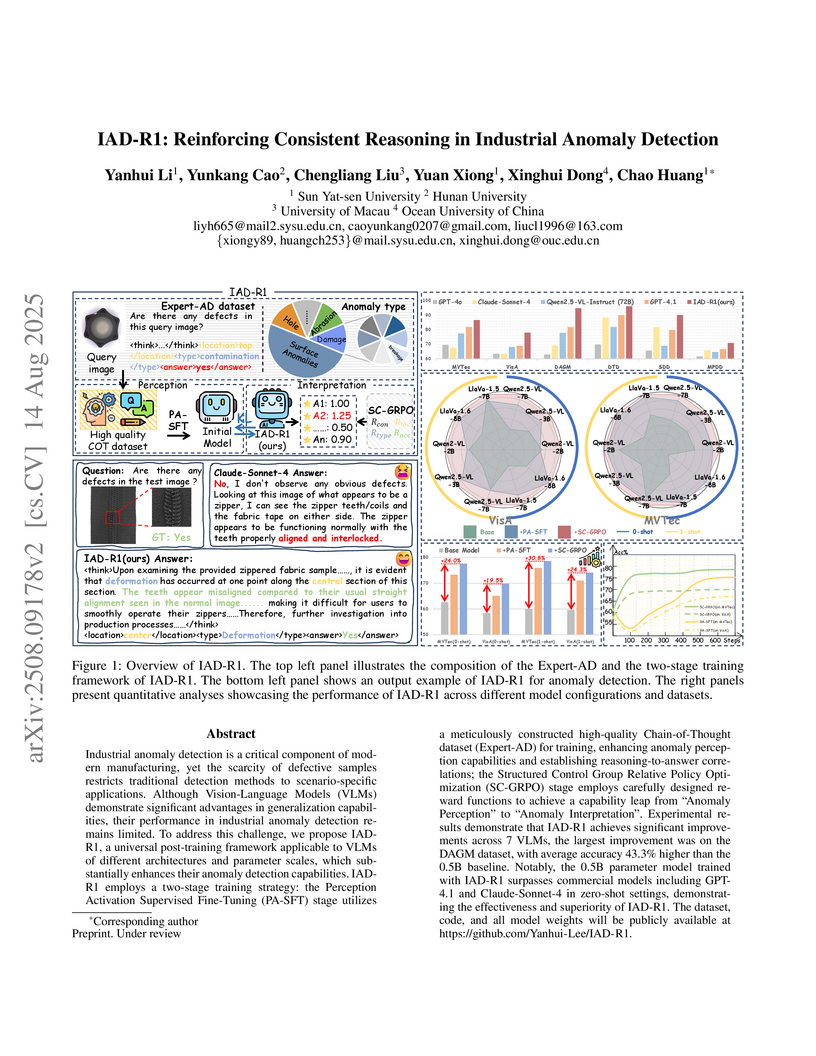
Industrial anomaly detection is a critical component of modern manufacturing, yet the scarcity of defective samples restricts traditional detection methods to scenario-specific applications. Although Vision-Language Models (VLMs) demonstrate significant advantages in generalization capabilities, their performance in industrial anomaly detection remains limited. To address this challenge, we propose IAD-R1, a universal post-training framework applicable to VLMs of different architectures and parameter scales, which substantially enhances their anomaly detection capabilities. IAD-R1 employs a two-stage training strategy: the Perception Activation Supervised Fine-Tuning (PA-SFT) stage utilizes a meticulously constructed high-quality Chain-of-Thought dataset (Expert-AD) for training, enhancing anomaly perception capabilities and establishing reasoning-to-answer correlations; the Structured Control Group Relative Policy Optimization (SC-GRPO) stage employs carefully designed reward functions to achieve a capability leap from "Anomaly Perception" to "Anomaly Interpretation". Experimental results demonstrate that IAD-R1 achieves significant improvements across 7 VLMs, the largest improvement was on the DAGM dataset, with average accuracy 43.3% higher than the 0.5B baseline. Notably, the 0.5B parameter model trained with IAD-R1 surpasses commercial models including GPT-4.1 and Claude-Sonnet-4 in zero-shot settings, demonstrating the effectiveness and superiority of IAD-R1. The dataset, code, and all model weights will be publicly available at this https URL.
Whole-Slide Image (WSI) is an important tool for estimating cancer prognosis. Current studies generally follow a conventional cancer-specific paradigm in which each cancer corresponds to a single model. However, this paradigm naturally struggles to scale to rare tumors and cannot leverage knowledge from other cancers. While multi-task learning frameworks have been explored recently, they often place high demands on computational resources and require extensive training on ultra-large, multi-cancer WSI datasets. To this end, this paper shifts the paradigm to knowledge transfer and presents the first preliminary yet systematic study on cross-cancer prognosis knowledge transfer in WSIs, called CROPKT. It comprises three major parts. (1) We curate a large dataset (UNI2-h-DSS) with 26 cancers and use it to measure the transferability of WSI-based prognostic knowledge across different cancers (including rare tumors). (2) Beyond a simple evaluation merely for benchmarking, we design a range of experiments to gain deeper insights into the underlying mechanism behind transferability. (3) We further show the utility of cross-cancer knowledge transfer, by proposing a routing-based baseline approach (ROUPKT) that could often efficiently utilize the knowledge transferred from off-the-shelf models of other cancers. CROPKT could serve as an inception that lays the foundation for this nascent paradigm, i.e., WSI-based prognosis prediction with cross-cancer knowledge transfer. Our source code is available at this https URL.
A framework called AVAM enhances Multimodal Large Language Models for Multi-Image Visual Question Answering by adaptively extracting continuous, question-relevant visual regions and employing collaborative decoding. This training-free approach consistently improves accuracy across diverse MLLMs and MVQA benchmarks by effectively managing visual redundancy.
Omnidirectional vision, using 360-degree vision to understand the environment, has become increasingly critical across domains like robotics, industrial inspection, and environmental monitoring. Compared to traditional pinhole vision, omnidirectional vision provides holistic environmental awareness, significantly enhancing the completeness of scene perception and the reliability of decision-making. However, foundational research in this area has historically lagged behind traditional pinhole vision. This talk presents an emerging trend in the embodied AI era: the rapid development of omnidirectional vision, driven by growing industrial demand and academic interest. We highlight recent breakthroughs in omnidirectional generation, omnidirectional perception, omnidirectional understanding, and related datasets. Drawing on insights from both academia and industry, we propose an ideal panoramic system architecture in the embodied AI era, PANORAMA, which consists of four key subsystems. Moreover, we offer in-depth opinions related to emerging trends and cross-community impacts at the intersection of panoramic vision and embodied AI, along with the future roadmap and open challenges. This overview synthesizes state-of-the-art advancements and outlines challenges and opportunities for future research in building robust, general-purpose omnidirectional AI systems in the embodied AI era.
04 Jul 2025
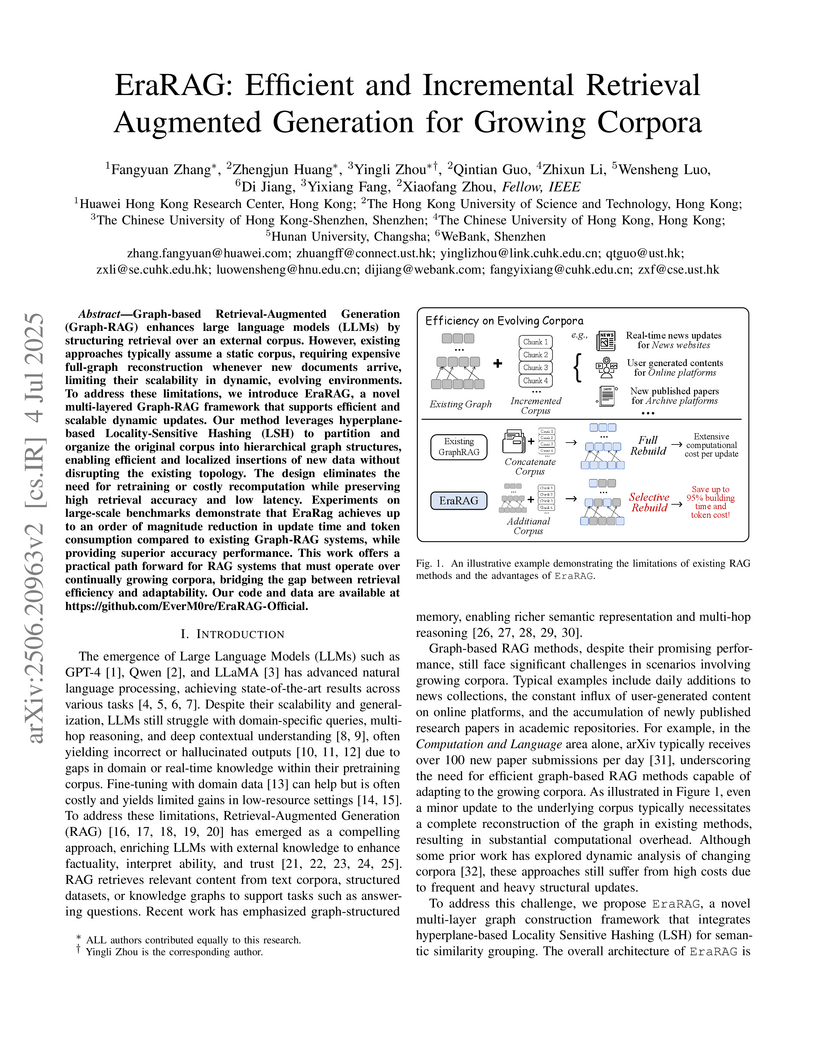
Graph-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation (Graph-RAG) enhances large language models (LLMs) by structuring retrieval over an external corpus. However, existing approaches typically assume a static corpus, requiring expensive full-graph reconstruction whenever new documents arrive, limiting their scalability in dynamic, evolving environments. To address these limitations, we introduce EraRAG, a novel multi-layered Graph-RAG framework that supports efficient and scalable dynamic updates. Our method leverages hyperplane-based Locality-Sensitive Hashing (LSH) to partition and organize the original corpus into hierarchical graph structures, enabling efficient and localized insertions of new data without disrupting the existing topology. The design eliminates the need for retraining or costly recomputation while preserving high retrieval accuracy and low latency. Experiments on large-scale benchmarks demonstrate that EraRag achieves up to an order of magnitude reduction in update time and token consumption compared to existing Graph-RAG systems, while providing superior accuracy performance. This work offers a practical path forward for RAG systems that must operate over continually growing corpora, bridging the gap between retrieval efficiency and adaptability. Our code and data are available at this https URL.
A comprehensive survey details the evolution of industrial defect detection from closed-set to open-set paradigms across 2D and 3D data modalities. It synthesizes advancements in AI-driven methods, multi-modal integration, and foundation models, providing a unified understanding of current challenges and future research for identifying novel anomalies in manufacturing.
17 Oct 2025
People without a database background usually rely on file systems or tools such as Excel for data management, which often lead to redundancy and data inconsistency. Relational databases possess strong data management capabilities, but require a high level of professional expertise from users. Although there are already many works on Text2SQL to automate the translation of natural language into SQL queries for data manipulation, all of them presuppose that the database schema is pre-designed. In practice, schema design itself demands domain expertise, and research on directly generating schemas from textual requirements remains unexplored. In this paper, we systematically define a new problem, called Text2Schema, to convert a natural language text requirement into a relational database schema. With an effective Text2Schema technique, users can effortlessly create database table structures using natural language, and subsequently leverage existing Text2SQL techniques to perform data manipulations, which significantly narrows the gap between non-technical personnel and highly efficient, versatile relational database systems. We propose SchemaAgent, an LLM-based multi-agent framework for Text2Schema. We emulate the workflow of manual schema design by assigning specialized roles to agents and enabling effective collaboration to refine their respective subtasks. We also incorporate dedicated roles for reflection and inspection, along with an innovative error detection and correction mechanism to identify and rectify issues across various phases. Moreover, we build and open source a benchmark containing 381 pairs of requirement description and schema. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our approach over comparative work.
Researchers from Nanyang Technological University and collaborators propose a neuroscience-inspired "Neural Brain" framework for embodied agents, integrating multimodal active sensing, perception-cognition-action loops, neuroplasticity-driven memory, and energy-efficient neuromorphic hardware. This work defines the core components and architecture for building adaptable, real-world interactive AI systems.
The paper provides a systematic review of the integration between Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and large foundation models (LLMs, VLMs, VFMs), proposing an "Agentic UAV" framework for developing highly autonomous, intelligent low-altitude mobility systems. It synthesizes current advancements across perception, navigation, and planning, identifying key capabilities and challenges.
Researchers provide the first comprehensive survey on the application of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to multimodal emotion recognition and reasoning, establishing a new taxonomy to classify existing methods. The work systematically reviews current approaches, curates resources, and identifies future challenges and directions for this evolving field.
DrVideo addresses long video understanding by reframing it as a document retrieval and comprehension task for Large Language Models. Its iterative agent-based framework dynamically identifies and augments key visual information, achieving state-of-the-art performance across EgoSchema, MovieChat-1K, and Video-MME benchmarks.
A comprehensive survey details the evolution of deep learning-based object pose estimation, covering instance-level, category-level, and unseen object methods. It analyzes current advancements, methodologies, and persistent challenges, while outlining future research directions to enhance generalization and robustness.
DiffusionEdge introduces a Diffusion Probabilistic Model (DPM) for edge detection, directly generating highly correct and single-pixel-wide crisp edge maps without needing post-processing like Non-Maximal Suppression. The model achieves state-of-the-art Average Crispness (AC) scores, notably increasing AC by 65.1% on NYUDv2 compared to prior methods, while maintaining high overall detection performance.
19 Nov 2025
We present a fully back-reacted Einstein--Maxwell--Dilaton--flavor model with dynamical light and strange sectors, calibrated to lattice QCD using a machine-learning--assisted spectral method. The model reproduces the 2+1-flavor equation of state and chiral dynamics with quantitative accuracy, and maps the Columbia plot with a tri-critical point at mstri≃21 MeV and a critical mass mc≃0.785 MeV, consistent with lattice results. At finite density, it yields a crossover-to-first-order transition and predicts a critical endpoint at TC=75.4 MeV and μC=768 MeV, within the reach of heavy-ion experiments. These findings establish a unified holographic framework for the QCD phase structure across quark masses and baryon density, providing the first consistent and quantitative description of both deconfinement and chiral transitions within a single holographic model.
This work uncovers Multi-Embedding Attacks (MEA) as a critical vulnerability where multiple watermarks embedded into an image can destroy original forensic information, rendering proactive deepfake forensics ineffective. The proposed Adversarial Interference Simulation (AIS) training paradigm robustly mitigates MEA, reducing the average Bit Error Rate (BER) from over 38% to below 0.2% across state-of-the-art methods after multiple embedding attacks.
Despite domain generalization (DG) has significantly addressed the
performance degradation of pre-trained models caused by domain shifts, it often
falls short in real-world deployment. Test-time adaptation (TTA), which adjusts
a learned model using unlabeled test data, presents a promising solution.
However, most existing TTA methods struggle to deliver strong performance in
medical image segmentation, primarily because they overlook the crucial prior
knowledge inherent to medical images. To address this challenge, we incorporate
morphological information and propose a framework based on multi-graph
matching. Specifically, we introduce learnable universe embeddings that
integrate morphological priors during multi-source training, along with novel
unsupervised test-time paradigms for domain adaptation. This approach
guarantees cycle-consistency in multi-matching while enabling the model to more
effectively capture the invariant priors of unseen data, significantly
mitigating the effects of domain shifts. Extensive experiments demonstrate that
our method outperforms other state-of-the-art approaches on two medical image
segmentation benchmarks for both multi-source and single-source domain
generalization tasks. The source code is available at
this https URL
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.