Instituto Superior Técnico - Universidade de Lisboa
∞-VIDEO presents a training-free approach that enables existing video-language models to understand arbitrarily long videos by augmenting them with a continuous-time long-term memory consolidation mechanism. This method improves performance on long-video Q&A tasks by dynamically retaining relevant information and avoids the need for additional training or sparse frame subsampling.
The use of language models for automatically evaluating long-form text (LLM-as-a-judge) is becoming increasingly common, yet most LLM judges are optimized exclusively for English, with strategies for enhancing their multilingual evaluation capabilities remaining largely unexplored in the current literature. This has created a disparity in the quality of automatic evaluation methods for non-English languages, ultimately hindering the development of models with better multilingual capabilities. To bridge this gap, we introduce M-Prometheus, a suite of open-weight LLM judges ranging from 3B to 14B parameters that can provide both direct assessment and pairwise comparison feedback on multilingual outputs. M-Prometheus models outperform state-of-the-art open LLM judges on multilingual reward benchmarks spanning more than 20 languages, as well as on literary machine translation (MT) evaluation covering 4 language pairs. Furthermore, M-Prometheus models can be leveraged at decoding time to significantly improve generated outputs across all 3 tested languages, showcasing their utility for the development of better multilingual models. Lastly, through extensive ablations, we identify the key factors for obtaining an effective multilingual judge, including backbone model selection and training on synthetic multilingual feedback data instead of translated data. We release our models, training dataset, and code.
StoryReasoning Dataset: Using Chain-of-Thought for Scene Understanding and Grounded Story Generation
StoryReasoning Dataset: Using Chain-of-Thought for Scene Understanding and Grounded Story Generation
Researchers from Instituto Superior Técnico and INESC-ID Lisboa introduced the StoryReasoning dataset and the Qwen Storyteller model to enhance visual storytelling. The dataset features structured scene analyses and grounded narratives from movie images, enabling a fine-tuned Qwen Storyteller to achieve a 31.0% improvement in creativity and a 12.3% reduction in hallucinations in generated stories.
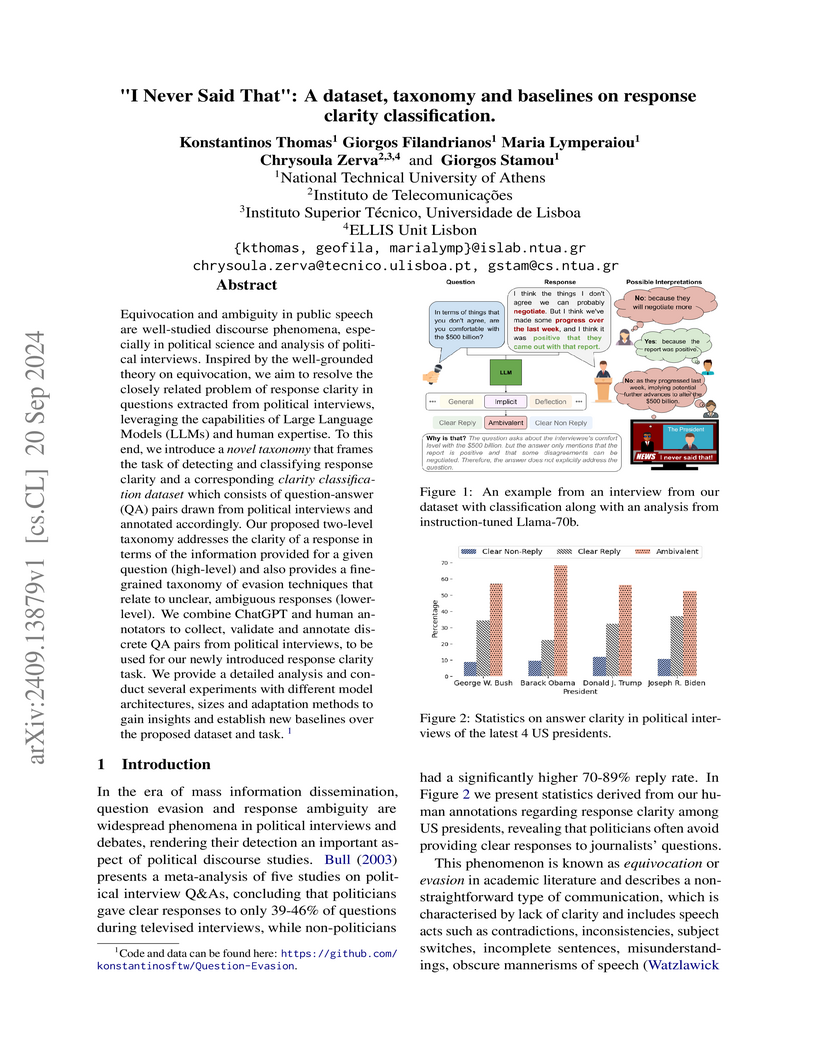
Equivocation and ambiguity in public speech are well-studied discourse
phenomena, especially in political science and analysis of political
interviews. Inspired by the well-grounded theory on equivocation, we aim to
resolve the closely related problem of response clarity in questions extracted
from political interviews, leveraging the capabilities of Large Language Models
(LLMs) and human expertise. To this end, we introduce a novel taxonomy that
frames the task of detecting and classifying response clarity and a
corresponding clarity classification dataset which consists of question-answer
(QA) pairs drawn from political interviews and annotated accordingly. Our
proposed two-level taxonomy addresses the clarity of a response in terms of the
information provided for a given question (high-level) and also provides a
fine-grained taxonomy of evasion techniques that relate to unclear, ambiguous
responses (lower-level). We combine ChatGPT and human annotators to collect,
validate and annotate discrete QA pairs from political interviews, to be used
for our newly introduced response clarity task. We provide a detailed analysis
and conduct several experiments with different model architectures, sizes and
adaptation methods to gain insights and establish new baselines over the
proposed dataset and task.
An important challenge in machine translation (MT) is to generate
high-quality and diverse translations. Prior work has shown that the estimated
likelihood from the MT model correlates poorly with translation quality. In
contrast, quality evaluation metrics (such as COMET or BLEURT) exhibit high
correlations with human judgments, which has motivated their use as rerankers
(such as quality-aware and minimum Bayes risk decoding). However, relying on a
single translation with high estimated quality increases the chances of "gaming
the metric''. In this paper, we address the problem of sampling a set of
high-quality and diverse translations. We provide a simple and effective way to
avoid over-reliance on noisy quality estimates by using them as the energy
function of a Gibbs distribution. Instead of looking for a mode in the
distribution, we generate multiple samples from high-density areas through the
Metropolis-Hastings algorithm, a simple Markov chain Monte Carlo approach. The
results show that our proposed method leads to high-quality and diverse outputs
across multiple language pairs (English↔{German, Russian}) with
two strong decoder-only LLMs (Alma-7b, Tower-7b).
Reinforcement learning (RL) has been proven to be an effective and robust
method for training neural machine translation systems, especially when paired
with powerful reward models that accurately assess translation quality.
However, most research has focused on RL methods that use sentence-level
feedback, leading to inefficient learning signals due to the reward sparsity
problem -- the model receives a single score for the entire sentence. To
address this, we propose a novel approach that leverages fine-grained,
token-level quality assessments along with error severity levels using RL
methods. Specifically, we use xCOMET, a state-of-the-art quality estimation
system, as our token-level reward model. We conduct experiments on small and
large translation datasets with standard encoder-decoder and large language
models-based machine translation systems, comparing the impact of
sentence-level versus fine-grained reward signals on translation quality. Our
results show that training with token-level rewards improves translation
quality across language pairs over baselines according to both automatic and
human evaluation. Furthermore, token-level reward optimization improves
training stability, evidenced by a steady increase in mean rewards over
training epochs.
03 Oct 2025
We introduce Spire, a speech-augmented language model (LM) capable of both translating and transcribing speech input from English into 10 other languages as well as translating text input in both language directions. Spire integrates the speech modality into an existing multilingual LM via speech discretization and continued pre-training using only 42.5K hours of speech. In particular, we adopt the pretraining framework of multilingual LMs and treat discretized speech input as an additional translation language. This approach not only equips the model with speech capabilities, but also preserves its strong text-based performance. We achieve this using significantly less data than existing speech LMs, demonstrating that discretized speech input integration as an additional language is feasible during LM adaptation. We make our code and models available to the community.
While machine translation (MT) systems are achieving increasingly strong performance on benchmarks, they often produce translations with errors and anomalies. Understanding these errors can potentially help improve the translation quality and user experience. This paper introduces xTower, an open large language model (LLM) built on top of TowerBase designed to provide free-text explanations for translation errors in order to guide the generation of a corrected translation. The quality of the generated explanations by xTower are assessed via both intrinsic and extrinsic evaluation. We ask expert translators to evaluate the quality of the explanations across two dimensions: relatedness towards the error span being explained and helpfulness in error understanding and improving translation quality. Extrinsically, we test xTower across various experimental setups in generating translation corrections, demonstrating significant improvements in translation quality. Our findings highlight xTower's potential towards not only producing plausible and helpful explanations of automatic translations, but also leveraging them to suggest corrected translations.
The target space geometry of abelian vector multiplets in N=2 theories in four and five space-time dimensions is called special geometry. It can be elegantly formulated in terms of Hessian geometry. In this review, we introduce Hessian geometry, focussing on aspects that are relevant for the special geometries of four- and five-dimensional vector multiplets. We formulate N=2 theories in terms of Hessian structures and give various concrete applications of Hessian geometry, ranging from static BPS black holes in four and five space-time dimensions to topological string theory, emphasizing the role of the Hesse potential. We also discuss the r-map and c-map which relate the special geometries of vector multiplets to each other and to hypermultiplet geometries. By including time-like dimensional reductions, we obtain theories in Euclidean signature, where the scalar target spaces carry para-complex versions of special geometry.
This research unifies sparse and structured Hopfield networks within a rigorous Fenchel-Young loss framework, enabling exact memory retrieval with exponential storage capacity. The work extends these networks to retrieve complex pattern associations using SparseMAP, demonstrating improved interpretability and performance in tasks like multiple instance learning and text rationalization.
The spectrum of coherent gluon radiation from a quark-anti-quark pair experiencing multiple scatterings within a coloured medium is central for understanding in-medium parton cascades. Despite its foundational importance, current results are limited by reliance on simplified scattering rates, such as the harmonic oscillator approximation, valid only in restricted phase-space regions. Using the formalism introduced in a previous article, we express the gluon emission spectrum as a set of differential equations that can be solved numerically, circumventing conventional approximations. We present the transverse momentum and energy distributions of emitted gluons for realistic interaction models, illustrating the breakdown of colour coherence across the entire accessible phase-space, and consequently enabling a higher-precision description of jet observables.
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong performance in sentence-level machine translation, but scaling to document-level translation remains challenging, particularly in modeling long-range dependencies and discourse phenomena across sentences and paragraphs. In this work, we propose a method to improve LLM-based long-document translation through targeted fine-tuning on high-quality document-level data, which we curate and introduce as DocBlocks. Our approach supports multiple translation paradigms, including direct document-to-document and chunk-level translation, by integrating instructions both with and without surrounding context. This enables models to better capture cross-sentence dependencies while maintaining strong sentence-level translation performance. Experimental results show that incorporating multiple translation paradigms improves document-level translation quality and inference speed compared to prompting and agent-based methods.
The spin point groups are finite groups whose elements act on both real space and spin space. Among these groups are the magnetic point groups in the case where the real and spin space operations are locked to one another. The magnetic point groups are central to magnetic crystallography for strong spin-orbit coupled systems and the spin point groups generalize these to the intermediate and weak spin-orbit coupled cases. The spin point groups were introduced in the 1960's in the context of condensed matter physics and enumerated shortly thereafter. In this paper, we complete the theory ofcrystallographic spin point groups by presenting an account of these groups and their representation theory. Our main findings are that the so-called nontrivial spin point groups (numbering 598 groups) have co-irreps corresponding exactly to the (co-)-irreps of regular or black and white groups and we tabulate this correspondence for each nontrivial group. However a total spin group, comprising the product of a nontrivial group and a spin-only group, has new co-irreps in cases where there is continuous rotational freedom. We provide explicit co-irrep tables for all these instances. We also discuss new forms of spin-only group extending the Litvin-Opechowski classes. To exhibit the usefulness of these groups to physically relevant problems we discuss a number of examples from electronic band structures of altermagnets to magnons.
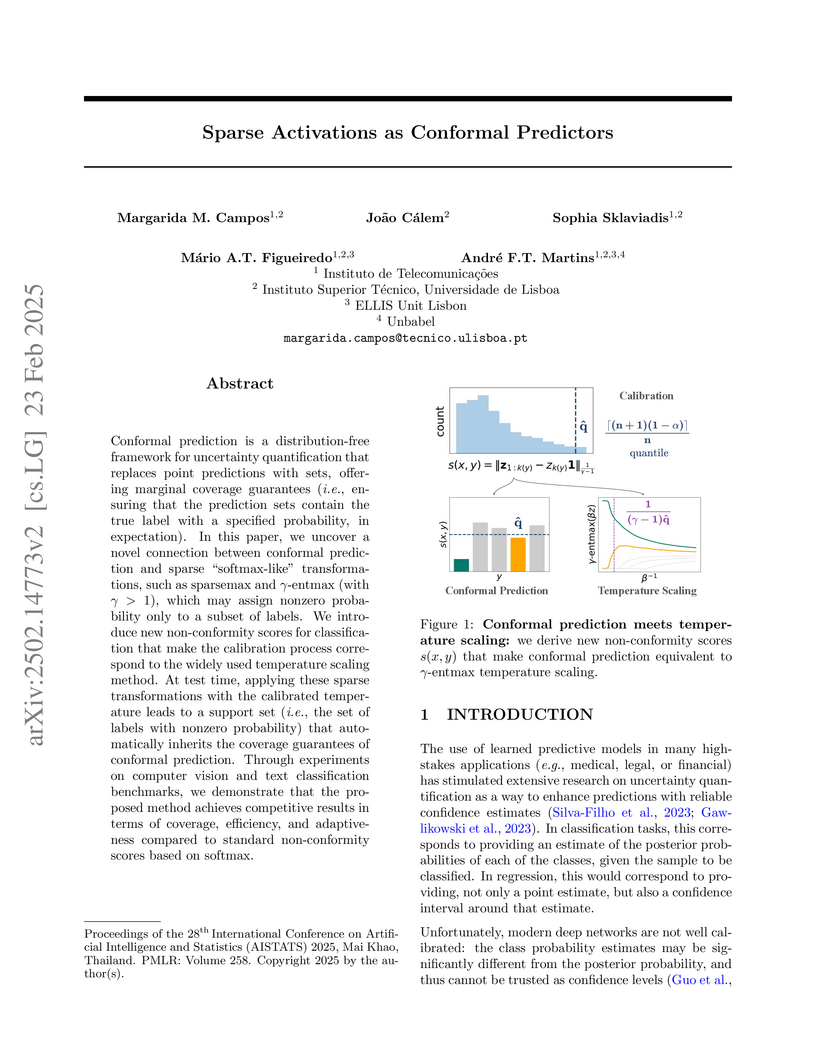
Conformal prediction is a distribution-free framework for uncertainty
quantification that replaces point predictions with sets, offering marginal
coverage guarantees (i.e., ensuring that the prediction sets contain the true
label with a specified probability, in expectation). In this paper, we uncover
a novel connection between conformal prediction and sparse softmax-like
transformations, such as sparsemax and γ-entmax (with γ>1),
which may assign nonzero probability only to a subset of labels. We introduce
new non-conformity scores for classification that make the calibration process
correspond to the widely used temperature scaling method. At test time,
applying these sparse transformations with the calibrated temperature leads to
a support set (i.e., the set of labels with nonzero probability) that
automatically inherits the coverage guarantees of conformal prediction. Through
experiments on computer vision and text classification benchmarks, we
demonstrate that the proposed method achieves competitive results in terms of
coverage, efficiency, and adaptiveness compared to standard non-conformity
scores based on softmax.
This work addresses the problem of sensing the world: how to learn a multimodal representation of a reinforcement learning agent's environment that allows the execution of tasks under incomplete perceptual conditions. To address such problem, we argue for hierarchy in the design of representation models and contribute with a novel multimodal representation model, MUSE. The proposed model learns hierarchical representations: low-level modality-specific representations, encoded from raw observation data, and a high-level multimodal representation, encoding joint-modality information to allow robust state estimation. We employ MUSE as the sensory representation model of deep reinforcement learning agents provided with multimodal observations in Atari games. We perform a comparative study over different designs of reinforcement learning agents, showing that MUSE allows agents to perform tasks under incomplete perceptual experience with minimal performance loss. Finally, we evaluate the performance of MUSE in literature-standard multimodal scenarios with higher number and more complex modalities, showing that it outperforms state-of-the-art multimodal variational autoencoders in single and cross-modality generation.
The Variational Mixture of Normalizing Flows (VMoNF) model from Instituto Superior Técnico integrates Normalizing Flows into a mixture framework to explicitly model multimodal data distributions. This approach enables simultaneous density estimation, unsupervised clustering, and semi-supervised learning on complex datasets.
17 Jun 2025
Investigating an open Bose-Hubbard trimer, this research demonstrates a direct correspondence between classical Lyapunov exponents and the level statistics of the quantum steady state's effective Hamiltonian, showing Poisson statistics for regular classical dynamics and Wigner-Dyson statistics for chaotic classical dynamics. The study also introduces a phase-space Inverse Participation Ratio to quantify steady-state localization and validates a semiclassical Langevin dynamics approach for reproducing quantum features.
 Michigan State UniversityUniversity of MississippiUniversity of Cincinnati
Michigan State UniversityUniversity of MississippiUniversity of Cincinnati University of CambridgeKyungpook National UniversitySLAC National Accelerator Laboratory
University of CambridgeKyungpook National UniversitySLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Imperial College London
Imperial College London University of Notre DameUniversity of Bern
University of Notre DameUniversity of Bern University of Chicago
University of Chicago UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley University College London
University College London University of OxfordNikhefIndiana UniversitySungkyunkwan University
University of OxfordNikhefIndiana UniversitySungkyunkwan University University of California, Irvine
University of California, Irvine University of BristolUniversity of Edinburgh
University of BristolUniversity of Edinburgh Yale University
Yale University Northwestern University
Northwestern University University of Texas at AustinLouisiana State University
University of Texas at AustinLouisiana State University Columbia UniversityLancaster UniversitySouthern Methodist University
Columbia UniversityLancaster UniversitySouthern Methodist University University of FloridaKansas State University
University of FloridaKansas State University CERN
CERN Argonne National LaboratoryUniversidad de GranadaColorado State UniversityINFN Sezione di Milano BicoccaUniversidad Autónoma de Madrid
Argonne National LaboratoryUniversidad de GranadaColorado State UniversityINFN Sezione di Milano BicoccaUniversidad Autónoma de Madrid Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory University of Wisconsin-Madison
University of Wisconsin-Madison Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryLos Alamos National LaboratoryIndian Institute of Technology, BombayGran Sasso Science InstituteUniversity of Liverpool
Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryLos Alamos National LaboratoryIndian Institute of Technology, BombayGran Sasso Science InstituteUniversity of Liverpool University of California, DavisUniversity of ArkansasUniversity of Massachusetts AmherstUniversity of RochesterTufts UniversityFermi National Accelerator LaboratoryUniversity of Houston
University of California, DavisUniversity of ArkansasUniversity of Massachusetts AmherstUniversity of RochesterTufts UniversityFermi National Accelerator LaboratoryUniversity of Houston MITUniversity of Sheffield
MITUniversity of Sheffield Queen Mary University of LondonUniversidade Estadual de Campinas
Queen Mary University of LondonUniversidade Estadual de Campinas The Ohio State UniversityUniversidad de ZaragozaUniversidade Federal do ABCUniversità di GenovaSyracuse UniversityUniversity of SussexUniversitat de ValènciaUniversità degli Studi di ParmaUniversity of BirminghamUniversidade Federal de GoiásUniversidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro
The Ohio State UniversityUniversidad de ZaragozaUniversidade Federal do ABCUniversità di GenovaSyracuse UniversityUniversity of SussexUniversitat de ValènciaUniversità degli Studi di ParmaUniversity of BirminghamUniversidade Federal de GoiásUniversidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro University of BaselMiddle East Technical UniversitySTFC Rutherford Appleton LaboratoryUniversity of CagliariInstitute for Research in Fundamental Sciences (IPM)University of South Dakota
University of BaselMiddle East Technical UniversitySTFC Rutherford Appleton LaboratoryUniversity of CagliariInstitute for Research in Fundamental Sciences (IPM)University of South Dakota Waseda UniversityUniversity of Texas at ArlingtonUniversidad de AntioquiaUniversity of AntananarivoUniversity of WinnipegINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiUniversity of North DakotaAnkara UniversityDrexel UniversityTezpur UniversityHarish-Chandra Research InstituteUniversidade Estadual PaulistaAligarh Muslim UniversityUniversity of WyomingCEA SaclayUniversity of Tennessee, KnoxvilleLMU MünchenCIEMATRadboud University NijmegenUniversity of HyderabadUniversity of MainzUniversidad Nacional Mayor de San MarcosInstituto Superior Técnico - Universidade de LisboaINFN-Sezione di GenovaUniversity of CoimbraNorthern Illinois UniversityUniversità degli Studi di CataniaPontificia Universidad Católica del PerúUniversidad de GuanajuatoINFN Sezione di LecceINFN, Sezione di CataniaUniversiteit van AmsterdamUniversidad Autónoma de AsunciónUniversidad Antonio NariñoLPNHE, Sorbonne Université, Université Paris Cité, CNRS/IN2P3Universidad Nacional de IngenieríaLIP - Laboratório de Instrumentação e Física Experimental de PartículasLAPP, Université Savoie Mont Blanc, CNRS/IN2P3Laboratoire des Matériaux AvancésNational Technical University of Ukraine "Kyiv Polytechnic Institute"IJCLab, Université Paris-Saclay, CNRS/IN2P3State Research Center Institute for High Energy Physics of National Research Center Kurchatov Institute“Horia Hulubei”National Institute of Physics and Nuclear EngineeringUniversit
Claude Bernard Lyon 1Universit
del SalentoUniversit
degli Studi di PadovaRWTH Aachen UniversityUniversit
di PisaUniversity of Minnesota
DuluthUniversit
degli Studi di Milano-BicoccaUniversit
degli Studi di Napoli
Federico II
Waseda UniversityUniversity of Texas at ArlingtonUniversidad de AntioquiaUniversity of AntananarivoUniversity of WinnipegINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiUniversity of North DakotaAnkara UniversityDrexel UniversityTezpur UniversityHarish-Chandra Research InstituteUniversidade Estadual PaulistaAligarh Muslim UniversityUniversity of WyomingCEA SaclayUniversity of Tennessee, KnoxvilleLMU MünchenCIEMATRadboud University NijmegenUniversity of HyderabadUniversity of MainzUniversidad Nacional Mayor de San MarcosInstituto Superior Técnico - Universidade de LisboaINFN-Sezione di GenovaUniversity of CoimbraNorthern Illinois UniversityUniversità degli Studi di CataniaPontificia Universidad Católica del PerúUniversidad de GuanajuatoINFN Sezione di LecceINFN, Sezione di CataniaUniversiteit van AmsterdamUniversidad Autónoma de AsunciónUniversidad Antonio NariñoLPNHE, Sorbonne Université, Université Paris Cité, CNRS/IN2P3Universidad Nacional de IngenieríaLIP - Laboratório de Instrumentação e Física Experimental de PartículasLAPP, Université Savoie Mont Blanc, CNRS/IN2P3Laboratoire des Matériaux AvancésNational Technical University of Ukraine "Kyiv Polytechnic Institute"IJCLab, Université Paris-Saclay, CNRS/IN2P3State Research Center Institute for High Energy Physics of National Research Center Kurchatov Institute“Horia Hulubei”National Institute of Physics and Nuclear EngineeringUniversit
Claude Bernard Lyon 1Universit
del SalentoUniversit
degli Studi di PadovaRWTH Aachen UniversityUniversit
di PisaUniversity of Minnesota
DuluthUniversit
degli Studi di Milano-BicoccaUniversit
degli Studi di Napoli
Federico IIThe sensitivity of the Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment (DUNE) to
neutrino oscillation is determined, based on a full simulation, reconstruction,
and event selection of the far detector and a full simulation and parameterized
analysis of the near detector. Detailed uncertainties due to the flux
prediction, neutrino interaction model, and detector effects are included. DUNE
will resolve the neutrino mass ordering to a precision of 5σ, for all
δCP values, after 2 years of running with the nominal
detector design and beam configuration. It has the potential to observe
charge-parity violation in the neutrino sector to a precision of 3σ
(5σ) after an exposure of 5 (10) years, for 50\% of all
δCP values. It will also make precise measurements of other
parameters governing long-baseline neutrino oscillation, and after an exposure
of 15 years will achieve a similar sensitivity to sin22θ13 to
current reactor experiments.
14 Jan 2025
Deep Learning for medical imaging faces challenges in adapting and generalizing to new contexts. Additionally, it often lacks sufficient labeled data for specific tasks requiring significant annotation effort. Continual Learning (CL) tackles adaptability and generalizability by enabling lifelong learning from a data stream while mitigating forgetting of previously learned knowledge. Active Learning (AL) reduces the number of required annotations for effective training. This work explores both approaches (CAL) to develop a novel framework for robust medical image analysis. Based on the automatic recognition of shifts in image characteristics, Replay-Base Architecture for Context Adaptation (RBACA) employs a CL rehearsal method to continually learn from diverse contexts, and an AL component to select the most informative instances for annotation. A novel approach to evaluate CAL methods is established using a defined metric denominated IL-Score, which allows for the simultaneous assessment of transfer learning, forgetting, and final model performance. We show that RBACA works in domain and class-incremental learning scenarios, by assessing its IL-Score on the segmentation and diagnosis of cardiac images. The results show that RBACA outperforms a baseline framework without CAL, and a state-of-the-art CAL method across various memory sizes and annotation budgets. Our code is available in this https URL .
19 Dec 2023
Quantum computers, using efficient Hamiltonian evolution routines, have the potential to simulate Green's functions of classically-intractable quantum systems. However, the decoherence errors of near-term quantum processors prohibit large evolution times, posing limits to the spectrum resolution. In this work, we show that Atomic Norm Minimization, a well-known super-resolution technique, can significantly reduce the minimum circuit depth for accurate spectrum reconstruction. We demonstrate this technique by recovering the spectral function of an impurity model from measurements of its Green's function on an IBM quantum computer. The reconstruction error with the Atomic Norm Minimization is one order of magnitude smaller than with more standard signal processing methods. Super-resolution methods can facilitate the simulation of large and previously unexplored quantum systems, and may constitute a useful non-variational tool to establish a quantum advantage in a nearer future.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.