InterDigital
With the increasing use of neural network (NN)-based computer vision applications that process image and video data as input, interest has emerged in video compression technology optimized for computer vision tasks. In fact, given the variety of vision tasks, associated NN models and datasets, a consolidated platform is needed as a common ground to implement and evaluate compression methods optimized for downstream vision tasks. CompressAI-Vision is introduced as a comprehensive evaluation platform where new coding tools compete to efficiently compress the input of vision network while retaining task accuracy in the context of two different inference scenarios: "remote" and "split" inferencing. Our study showcases various use cases of the evaluation platform incorporated with standard codecs (under development) by examining the compression gain on several datasets in terms of bit-rate versus task accuracy. This evaluation platform has been developed as open-source software and is adopted by the Moving Pictures Experts Group (MPEG) for the development the Feature Coding for Machines (FCM) standard. The software is available publicly at this https URL.
Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) are eminently suitable for improving the reliability of wireless communications by jointly designing the active beamforming at the base station (BS) and the passive beamforming at the RIS. Therefore, the accuracy of channel estimation is crucial for RIS-aided systems. The challenge is that only the cascaded two-hop channel spanning from the user equipments (UEs) to the RIS and spanning from the RIS to the BS can be estimated, due to the lack of active radio frequency (RF) chains at RIS elements, which leads to high pilot overhead. In this paper, we propose a low-overhead linear minimum mean square error (LMMSE) channel estimation method by exploiting the spatial correlation of channel links, which strikes a trade-off between the pilot overhead and the channel estimation accuracy. Moreover, we calculate the theoretical normalized mean square error (MSE) for our channel estimation method. Finally, we verify numerically that the proposed LMMSE estimator has lower MSE than the state-of-the-art (SoA) grouping based estimators.
Advancements in text-to-image generative AI with large multimodal models are
spreading into the field of image compression, creating high-quality
representation of images at extremely low bit rates. This work introduces novel
components to the existing multimodal image semantic compression (MISC)
approach, enhancing the quality of the generated images in terms of PSNR and
perceptual metrics. The new components include semantic segmentation guidance
for the generative decoder, as well as content-adaptive diffusion, which
controls the number of diffusion steps based on image characteristics. The
results show that our newly introduced methods significantly improve the
baseline MISC model while also decreasing the complexity. As a result, both the
encoding and decoding time are reduced by more than 36%. Moreover, the proposed
compression framework outperforms mainstream codecs in terms of perceptual
similarity and quality. The code and visual examples are available.
Communication and computation are often viewed as separate tasks. This approach is very effective from the perspective of engineering as isolated optimizations can be performed. However, for many computation-oriented applications, the main interest is a function of the local information at the devices, rather than the local information itself. In such scenarios, information theoretical results show that harnessing the interference in a multiple access channel for computation, i.e., over-the-air computation (OAC), can provide a significantly higher achievable computation rate than separating communication and computation tasks. Moreover, the gap between OAC and separation in terms of computation rate increases with more participating nodes. Given this motivation, in this study, we provide a comprehensive survey on practical OAC methods. After outlining fundamentals related to OAC, we discuss the available OAC schemes with their pros and cons. We provide an overview of the enabling mechanisms for achieving reliable computation in the wireless channel. Finally, we summarize the potential applications of OAC and point out some future directions.
Remote inference allows lightweight devices to leverage powerful cloud models. However, communication network latency makes predictions stale and unsuitable for real-time tasks. To address this, we introduce Dedelayed, a delay-corrective method that mitigates arbitrary remote inference delays, allowing the local device to produce low-latency outputs in real time. Our method employs a lightweight local model that processes the current frame and fuses in features that a heavyweight remote model computes from past frames. On video from the BDD100K driving dataset, Dedelayed improves semantic segmentation accuracy over the stronger of the local-only and remote-only baselines across all realistic communication network delays beyond 33 ms. Without incurring additional delay, it improves accuracy by 6.4 mIoU compared to fully local inference and 9.8 mIoU compared to remote inference, for a round-trip delay of 100 ms. The advantage grows under longer delays and higher-motion scenes, as delay-mitigated split inference sustains accuracy more effectively, providing clear advantages for real-time tasks that must remain aligned with the current world state.
07 Feb 2023
Recent advances in the area of long document matching have primarily focused
on using transformer-based models for long document encoding and matching.
There are two primary challenges associated with these models. Firstly, the
performance gain provided by transformer-based models comes at a steep cost -
both in terms of the required training time and the resource (memory and
energy) consumption. The second major limitation is their inability to handle
more than a pre-defined input token length at a time. In this work, we
empirically demonstrate the effectiveness of simple neural models (such as
feed-forward networks, and CNNs) and simple embeddings (like GloVe, and
Paragraph Vector) over transformer-based models on the task of document
matching. We show that simple models outperform the more complex BERT-based
models while taking significantly less training time, energy, and memory. The
simple models are also more robust to variations in document length and text
perturbations.
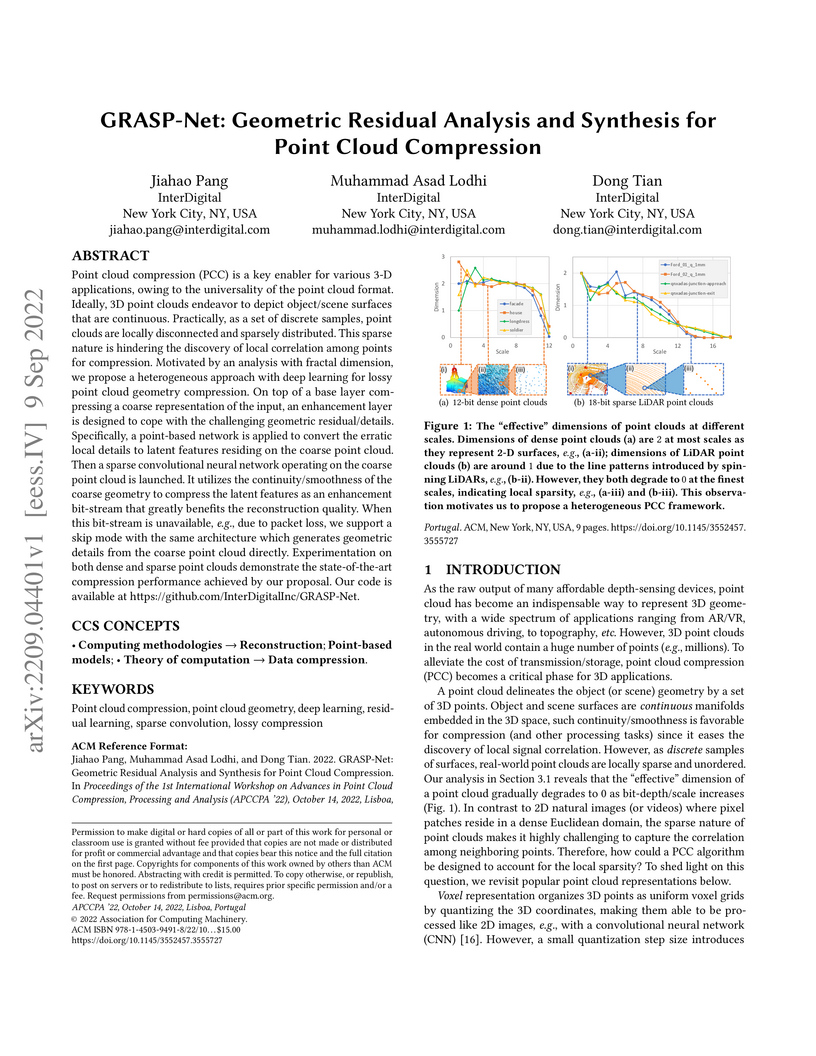
Point cloud compression (PCC) is a key enabler for various 3-D applications, owing to the universality of the point cloud format. Ideally, 3D point clouds endeavor to depict object/scene surfaces that are continuous. Practically, as a set of discrete samples, point clouds are locally disconnected and sparsely distributed. This sparse nature is hindering the discovery of local correlation among points for compression. Motivated by an analysis with fractal dimension, we propose a heterogeneous approach with deep learning for lossy point cloud geometry compression. On top of a base layer compressing a coarse representation of the input, an enhancement layer is designed to cope with the challenging geometric residual/details. Specifically, a point-based network is applied to convert the erratic local details to latent features residing on the coarse point cloud. Then a sparse convolutional neural network operating on the coarse point cloud is launched. It utilizes the continuity/smoothness of the coarse geometry to compress the latent features as an enhancement bit-stream that greatly benefits the reconstruction quality. When this bit-stream is unavailable, e.g., due to packet loss, we support a skip mode with the same architecture which generates geometric details from the coarse point cloud directly. Experimentation on both dense and sparse point clouds demonstrate the state-of-the-art compression performance achieved by our proposal. Our code is available at this https URL.
A quantitative analysis of post-VVC luma and chroma intra tools is presented,
focusing on their statistical behaviors, in terms of block selection rate under
different conditions. The aim is to provide insights to the standardization
community, offering a clearer understanding of interactions between tools and
assisting in the design of an optimal combination of these novel tools when the
JVET enters the standardization phase. Specifically, this paper examines the
selection rate of intra tools as function of 1) the version of the ECM, 2)
video resolution, and 3) video bitrate. Additionally, tests have been conducted
on sequences beyond the JVET CTC database. The statistics show several trends
and interactions, with various strength, between coding tools of both luma and
chroma.
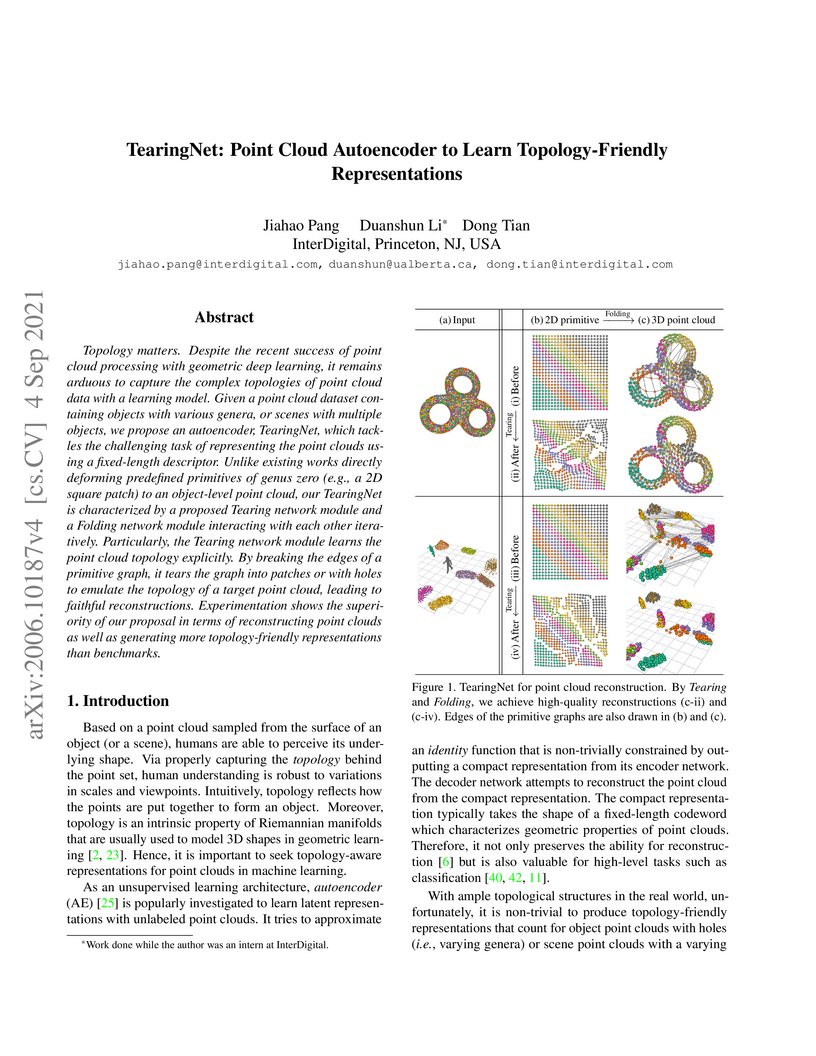
Topology matters. Despite the recent success of point cloud processing with
geometric deep learning, it remains arduous to capture the complex topologies
of point cloud data with a learning model. Given a point cloud dataset
containing objects with various genera, or scenes with multiple objects, we
propose an autoencoder, TearingNet, which tackles the challenging task of
representing the point clouds using a fixed-length descriptor. Unlike existing
works directly deforming predefined primitives of genus zero (e.g., a 2D square
patch) to an object-level point cloud, our TearingNet is characterized by a
proposed Tearing network module and a Folding network module interacting with
each other iteratively. Particularly, the Tearing network module learns the
point cloud topology explicitly. By breaking the edges of a primitive graph, it
tears the graph into patches or with holes to emulate the topology of a target
point cloud, leading to faithful reconstructions. Experimentation shows the
superiority of our proposal in terms of reconstructing point clouds as well as
generating more topology-friendly representations than benchmarks.
This paper describes the MediaEval 2021 Predicting Media Memorability}task, which is in its 4th edition this year, as the prediction of short-term and long-term video memorability remains a challenging task. In 2021, two datasets of videos are used: first, a subset of the TRECVid 2019 Video-to-Text dataset; second, the Memento10K dataset in order to provide opportunities to explore cross-dataset generalisation. In addition, an Electroencephalography (EEG)-based prediction pilot subtask is introduced. In this paper, we outline the main aspects of the task and describe the datasets, evaluation metrics, and requirements for participants' submissions.
With the increasing use of neural network (NN)-based computer vision applications that process image and video data as input, interest has emerged in video compression technology optimized for computer vision tasks. In fact, given the variety of vision tasks, associated NN models and datasets, a consolidated platform is needed as a common ground to implement and evaluate compression methods optimized for downstream vision tasks. CompressAI-Vision is introduced as a comprehensive evaluation platform where new coding tools compete to efficiently compress the input of vision network while retaining task accuracy in the context of two different inference scenarios: "remote" and "split" inferencing. Our study showcases various use cases of the evaluation platform incorporated with standard codecs (under development) by examining the compression gain on several datasets in terms of bit-rate versus task accuracy. This evaluation platform has been developed as open-source software and is adopted by the Moving Pictures Experts Group (MPEG) for the development the Feature Coding for Machines (FCM) standard. The software is available publicly at this https URL.
Using a collection of publicly available links to short form video clips of an average of 6 seconds duration each, 1,275 users manually annotated each video multiple times to indicate both long-term and short-term memorability of the videos. The annotations were gathered as part of an online memory game and measured a participant's ability to recall having seen the video previously when shown a collection of videos. The recognition tasks were performed on videos seen within the previous few minutes for short-term memorability and within the previous 24 to 72 hours for long-term memorability. Data includes the reaction times for each recognition of each video. Associated with each video are text descriptions (captions) as well as a collection of image-level features applied to 3 frames extracted from each video (start, middle and end). Video-level features are also provided. The dataset was used in the Video Memorability task as part of the MediaEval benchmark in 2020.
A deep learning system typically suffers from a lack of reproducibility that is partially rooted in hardware or software implementation details. The irreproducibility leads to skepticism in deep learning technologies and it can hinder them from being deployed in many applications. In this work, the irreproducibility issue is analyzed where deep learning is employed in compression systems while the encoding and decoding may be run on devices from different manufacturers. The decoding process can even crash due to a single bit difference, e.g., in a learning-based entropy coder. For a given deep learning-based module with limited resources for protection, we first suggest that reproducibility can only be assured when the mismatches are bounded. Then a safeguarding mechanism is proposed to tackle the challenges. The proposed method may be applied for different levels of protection either at the reconstruction level or at a selected decoding level. Furthermore, the overhead introduced for the protection can be scaled down accordingly when the error bound is being suppressed. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach for learning-based compression systems, e.g., in image compression and point cloud compression.
The traditional role of a communication engineer is to address the technical
problem of transporting bits reliably over a noisy channel. With the emergence
of 5G, and the availability of a variety of competing and coexisting wireless
systems, wireless connectivity is becoming a commodity. This article argues
that communication engineers in the post-5G era should extend the scope of
their activity in terms of design objectives and constraints beyond
connectivity to encompass the semantics of the transferred bits within the
given applications and use cases. To provide a platform for semantic-aware
connectivity solutions, this paper introduces the concept of a
semantic-effectiveness (SE) plane as a core part of future communication
architectures. The SE plane augments the protocol stack by providing
standardized interfaces that enable information filtering and direct control of
functionalities at all layers of the protocol stack. The advantages of the SE
plane are described in the perspective of recent developments in 5G, and
illustrated through a number of example applications. The introduction of a SE
plane may help replacing the current "next-G paradigm" in wireless evolution
with a framework based on continuous improvements and extensions of the systems
and standards.
This paper introduces a task-specific, model-agnostic framework for evaluating dataset similarity, providing a means to assess and compare dataset realism and quality. Such a framework is crucial for augmenting real-world data, improving benchmarking, and making informed retraining decisions when adapting to new deployment settings, such as different sites or frequency bands. The proposed framework is employed to design metrics based on UMAP topology-preserving dimensionality reduction, leveraging Wasserstein and Euclidean distances on latent space KNN clusters. The designed metrics show correlations above 0.85 between dataset distances and model performances on a channel state information compression unsupervised machine learning task leveraging autoencoder architectures. The results show that the designed metrics outperform traditional methods.
27 Aug 2025
Haptic technology enhances interactive experiences by providing force and tactile feedback, improving user performance and immersion. However, despite advancements, creating tactile experiences still remains challenging due to device diversity and complexity. Most available haptic frameworks rely on trigger-based or event-based systems, and disregard the information of the 3D scene to render haptic information. This paper introduces Haptic Tracing, a novel method for spatial haptic rendering that simplifies the creation of interactive haptic experiences without relying on physical simulations. It uses concepts from visual and audio rendering to model and propagate haptic information through a 3D scene. The paper also describes how our proposed haptic rendering method can be used to create a vibrotactile rendering system, enabling the creation of perceptually coherent and dynamic haptic interactions. Finally, the paper discusses a user study that explores the role of the haptic propagation and multi-actuator rendering on the users' haptic experience. The results show that our approach significantly enhances the realism and the expressivity of the haptic feedback, showcasing its potential for developing more complex and realistic haptic experiences.
The Sample Adaptive Offset (SAO) filter has been introduced in HEVC to reduce
general coding and banding artefacts in the reconstructed pictures, in
complement to the De-Blocking Filter (DBF) which reduces artifacts at block
boundaries specifically. The new video compression standard Versatile Video
Coding (VVC) reduces the BD-rate by about 36% at the same reconstruction
quality compared to HEVC. It implements an additional new in-loop Adaptive Loop
Filter (ALF) on top of the DBF and the SAO filter, the latter remaining
unchanged compared to HEVC. However, the relative performance of SAO in VVC has
been lowered significantly. In this paper, it is proposed to revisit the SAO
filter using Neural Networks (NN). The general principles of the SAO are kept,
but the a-priori classification of SAO is replaced with a set of neural
networks that determine which reconstructed samples should be corrected and in
which proportion. Similarly to the original SAO, some parameters are determined
at the encoder side and encoded per CTU. The average BD-rate gain of the
proposed SAO improves VVC by at least 2.3% in Random Access while the overall
complexity is kept relatively small compared to other NN-based methods.
28 Jan 2018
In this study, we compare the single-carrier (SC) waveform adopted in IEEE 802.11ad and unique word discrete Fourier transform spread orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (UW DFT-s-OFDM) waveform. We provide equivalent representations of up-sampling and down-sampling operations of the SC waveform by using discrete Fourier transform (DFT) and inverse DFT to enable explicit comparison of these two similar waveforms. By using this representation, we discuss why the IEEE 802.11ad SC waveform can cause suboptimal performance in multipath channel and discuss how to improve it with UW DFT-s-OFDM. With comprehensive link-level simulations, we show that replacing the 802.11ad SC waveform with UW DFT-spread OFDM can result in 1 dB gain in peak throughput without affecting the IEEE 802.11ad packet structure. We also evaluate the cross links where the transmitter is UW-DFT-s-OFDM and the receiver is traditional SC-FDE or vice versa. We demonstrate that UW DFT-s-OFDM receiver can decode an IEEE 802.11ad SC waveform with a slight SNR loss while IEEE 802.11ad SC receiver can decode a UW DFT-spread OFDM waveform with an interference floor.
There have been recent efforts to learn more meaningful representations via fixed length codewords from mesh data, since a mesh serves as a complete model of underlying 3D shape compared to a point cloud. However, the mesh connectivity presents new difficulties when constructing a deep learning pipeline for meshes. Previous mesh unsupervised learning approaches typically assume category-specific templates, e.g., human face/body templates. It restricts the learned latent codes to only be meaningful for objects in a specific category, so the learned latent spaces are unable to be used across different types of objects. In this work, we present WrappingNet, the first mesh autoencoder enabling general mesh unsupervised learning over heterogeneous objects. It introduces a novel base graph in the bottleneck dedicated to representing mesh connectivity, which is shown to facilitate learning a shared latent space representing object shape. The superiority of WrappingNet mesh learning is further demonstrated via improved reconstruction quality and competitive classification compared to point cloud learning, as well as latent interpolation between meshes of different categories.
Geometric data acquired from real-world scenes, e.g., 2D depth images, 3D
point clouds, and 4D dynamic point clouds, have found a wide range of
applications including immersive telepresence, autonomous driving,
surveillance, etc. Due to irregular sampling patterns of most geometric data,
traditional image/video processing methodologies are limited, while Graph
Signal Processing (GSP) -- a fast-developing field in the signal processing
community -- enables processing signals that reside on irregular domains and
plays a critical role in numerous applications of geometric data from low-level
processing to high-level analysis. To further advance the research in this
field, we provide the first timely and comprehensive overview of GSP
methodologies for geometric data in a unified manner by bridging the
connections between geometric data and graphs, among the various geometric data
modalities, and with spectral/nodal graph filtering techniques. We also discuss
the recently developed Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) and interpret the operation
of these networks from the perspective of GSP. We conclude with a brief
discussion of open problems and challenges.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.