LINKS Foundation
30 Sep 2025
Energy efficiency is one of the major concern in designing advanced computing infrastructures. From single nodes to large-scale systems (data centers), monitoring the energy consumption of the computing system when applications run is a critical task. Designers and application developers often rely on software tools and detailed architectural models to extract meaningful information and determine the system energy consumption. However, when a design space exploration is required, designers may incur in continuous tuning of the models to match with the system under evaluation. To overcome such limitations, we propose a holistic approach to monitor energy consumption at runtime without the need of running complex (micro-)architectural models. Our approach is based on a measurement board coupled with a FPGA-based System-on-Module. The measuring board captures currents and voltages (up to tens measuring points) driving the FPGA and exposes such values through a specific memory region. A running service reads and computes energy consumption statistics without consuming extra resources on the FPGA device. Our approach is also scalable to monitoring of multi-nodes infrastructures (clusters). We aim to leverage this framework to perform experiments in the context of an aeronautical design application; specifically, we will look at optimizing performance and energy consumption of a shallow artificial neural network on RISC-V based soft-cores.
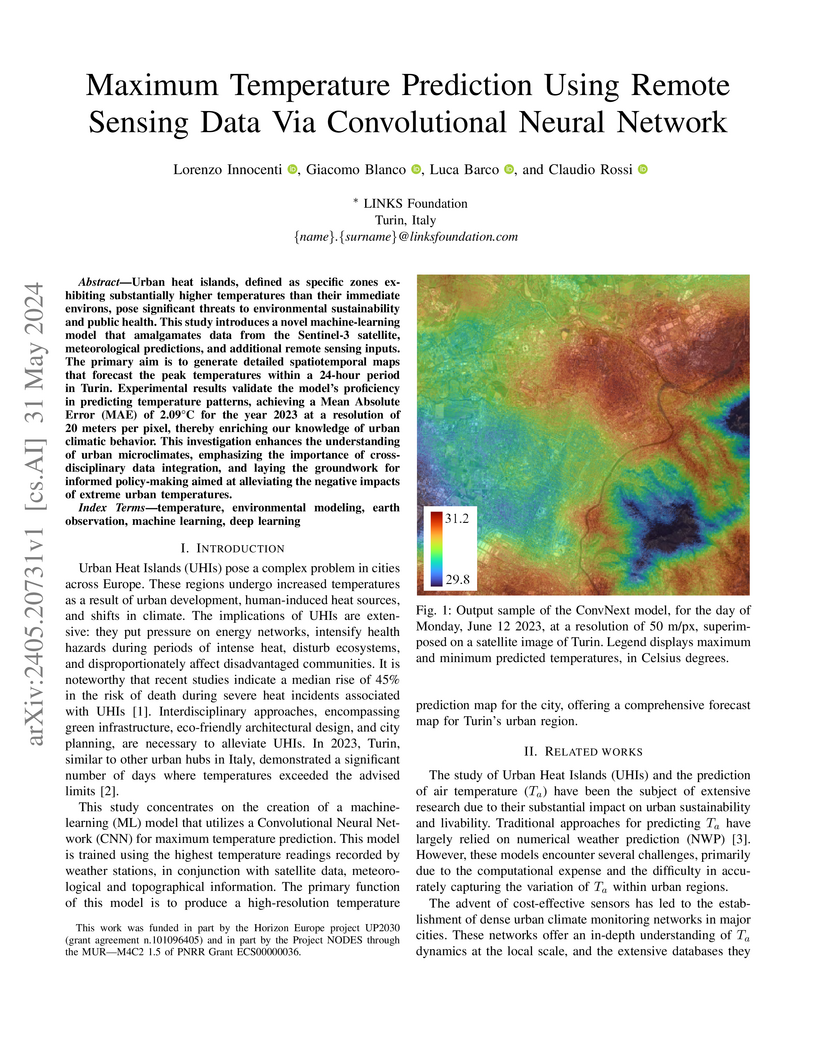
Urban heat islands, defined as specific zones exhibiting substantially higher temperatures than their immediate environs, pose significant threats to environmental sustainability and public health. This study introduces a novel machine-learning model that amalgamates data from the Sentinel-3 satellite, meteorological predictions, and additional remote sensing inputs. The primary aim is to generate detailed spatiotemporal maps that forecast the peak temperatures within a 24-hour period in Turin. Experimental results validate the model's proficiency in predicting temperature patterns, achieving a Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of 2.09 degrees Celsius for the year 2023 at a resolution of 20 meters per pixel, thereby enriching our knowledge of urban climatic behavior. This investigation enhances the understanding of urban microclimates, emphasizing the importance of cross-disciplinary data integration, and laying the groundwork for informed policy-making aimed at alleviating the negative impacts of extreme urban temperatures.
A novel bi-temporal-bi-modal deep learning architecture, BBUnet, enables automatic mapping of newly occurred landslides from Sentinel-2 imagery by fusing it with Digital Elevation Model (DEM) data. The model achieves the highest F1 score of 0.348 on a new globally diverse, open-access landslide geodatabase, demonstrating the benefits of integrating topographical context for geo-hazard detection.
Network Interface Cards (NICs) greatly evolved from simple basic devices moving traffic in and out of the network to complex heterogeneous systems offloading host CPUs from performing complex tasks on in-transit packets. These latter comprise different types of devices, ranging from NICs accelerating fixed specific functions (e.g., on-the-fly data compression/decompression, checksum computation, data encryption, etc.) to complex Systems-on-Chip (SoC) equipped with both general purpose processors and specialized engines (Smart-NICs). Similarly, Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) moved from pure reprogrammable devices to modern heterogeneous systems comprising general-purpose processors, real-time cores and even AI-oriented engines. Furthermore, the availability of high-speed network interfaces (e.g., SFPs) makes modern FPGAs a good choice for implementing Smart-NICs. In this work, we extended the functionalities offered by an open-source NIC implementation (Corundum) by enabling time-aware traffic management in hardware, and using this feature to control the bandwidth associated with different traffic classes. By exposing dedicated control registers on the AXI bus, the driver of the NIC can easily configure the transmission bandwidth of different prioritized queues. Basically, each control register is associated with a specific transmission queue (Corundum can expose up to thousands of transmission and receiving queues), and sets up the fraction of time in a transmission window which the queue is supposed to get access the output port and transmit the packets. Queues are then prioritized and associated to different traffic classes through the Linux QDISC mechanism. Experimental evaluation demonstrates that the approach allows to properly manage the bandwidth reserved to the different transmission flows.
In this paper, we present an approach for estimating significant financial metrics within risk management by utilizing quantum phenomena for random number generation. We explore Quantum-Enhanced Monte Carlo, a method that combines traditional and quantum techniques for enhanced precision through Quantum Random Numbers Generation (QRNG). The proposed methods can be based on the use of photonic phenomena or quantum processing units to generate random numbers. The results are promising, hinting at improved accuracy with the proposed methods and slightly lower estimates (both for VaR and CVaR estimation) using the quantum-based methodology.
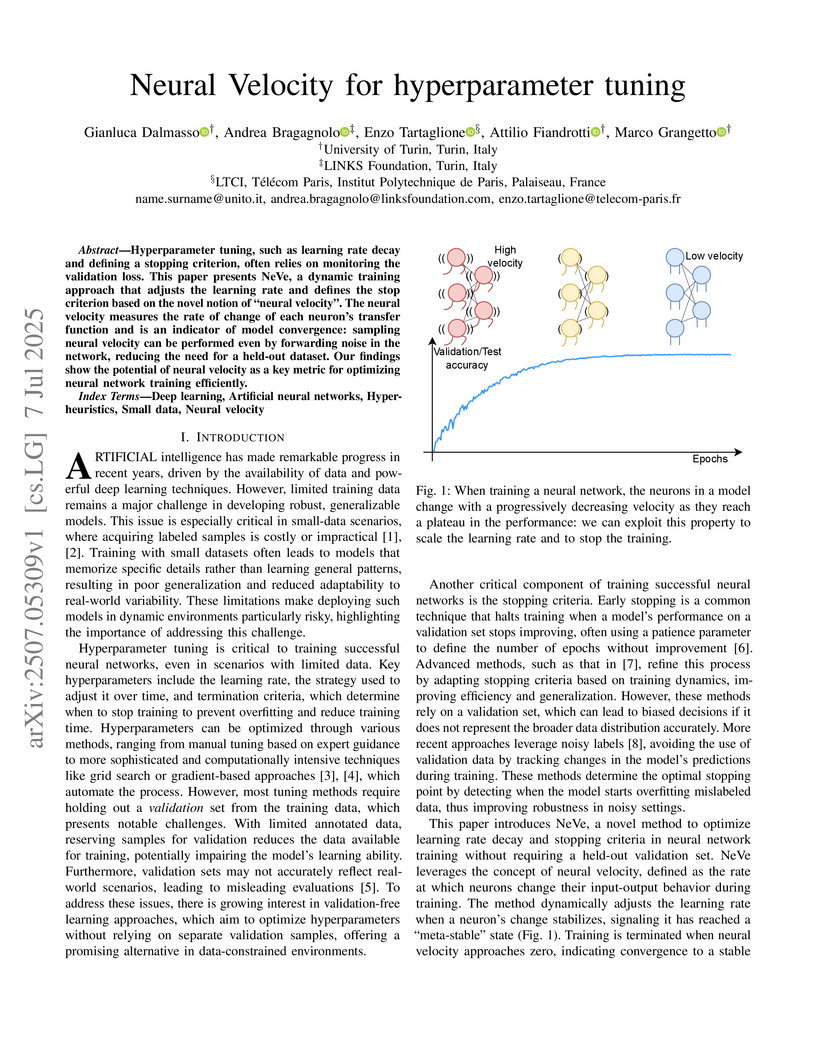
Hyperparameter tuning, such as learning rate decay and defining a stopping criterion, often relies on monitoring the validation loss. This paper presents NeVe, a dynamic training approach that adjusts the learning rate and defines the stop criterion based on the novel notion of "neural velocity". The neural velocity measures the rate of change of each neuron's transfer function and is an indicator of model convergence: sampling neural velocity can be performed even by forwarding noise in the network, reducing the need for a held-out dataset. Our findings show the potential of neural velocity as a key metric for optimizing neural network training efficiently
01 Sep 2025
This paper presents a comprehensive analytical framework for evaluating filtering penalties in ASE-noise-limited coherent optical links. The model accounts for the cumulative effects of cascaded optical filters, amplifier-induced ASE noise, and transceiver noise, alongside digital equalization at the receiver. By developing a generalized channel representation, we derive closed-form expressions for signal-to-noise ratio degradation under various equalization strategies, including Zero-Forcing Equalizer, Minimum Mean Square Error Equalizer, and Fractionally Spaced Equalizer. These models capture the impact of colored noise resulting from linear filtering and provide both time and frequency-domain insights. The proposed framework is validated through experimental comparisons using accurately modeled optical filters, demonstrating close agreement between theory and practice and offering a robust foundation for system-level performance evaluation in metro-access networks.
Incremental learning represents a crucial task in aerial image processing, especially given the limited availability of large-scale annotated datasets. A major issue concerning current deep neural architectures is known as catastrophic forgetting, namely the inability to faithfully maintain past knowledge once a new set of data is provided for retraining. Over the years, several techniques have been proposed to mitigate this problem for image classification and object detection. However, only recently the focus has shifted towards more complex downstream tasks such as instance or semantic segmentation. Starting from incremental-class learning for semantic segmentation tasks, our goal is to adapt this strategy to the aerial domain, exploiting a peculiar feature that differentiates it from natural images, namely the orientation. In addition to the standard knowledge distillation approach, we propose a contrastive regularization, where any given input is compared with its augmented version (i.e. flipping and rotations) in order to minimize the difference between the segmentation features produced by both inputs. We show the effectiveness of our solution on the Potsdam dataset, outperforming the incremental baseline in every test. Code available at: this https URL.
21 Apr 2023
In this paper, we propose an analytical model to estimate the signal-to-noise
ratio (SNR) at the output of an adaptive equalizer in intensity modulation and
direct detection (IMDD) optical transmission systems affected by shot noise,
thermal noise, relative intensity noise (RIN), chromatic dispersion (CD) and
bandwidth limitations. We develop the model as an extension of a previously
presented one, and then we test its accuracy by sweeping the main parameters of
a 4-PAM-based communication system such as RIN coefficient, extinction ratio,
CD coefficient and equalizer memory. Our findings show a remarkable agreement
between time-domain simulations and analytical results, with SNR discrepancies
below 0.1 dB in most cases, for both feed-forward and decision-feedback
equalization. We consider that the proposed model is a powerful tool for the
numerical design of strongly band-limited IMDD systems using receiver
equalization, as it happens in most of modern and future M-PAM solutions for
short reach and access systems.
Very-High Resolution (VHR) remote sensing imagery is increasingly accessible, but often lacks annotations for effective machine learning applications. Recent foundation models like GroundingDINO and Segment Anything (SAM) provide opportunities to automatically generate annotations. This study introduces FMARS (Foundation Model Annotations in Remote Sensing), a methodology leveraging VHR imagery and foundation models for fast and robust annotation. We focus on disaster management and provide a large-scale dataset with labels obtained from pre-event imagery over 19 disaster events, derived from the Maxar Open Data initiative. We train segmentation models on the generated labels, using Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) techniques to increase transferability to real-world scenarios. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of leveraging foundation models to automatically annotate remote sensing data at scale, enabling robust downstream models for critical applications. Code and dataset are available at \url{this https URL}.
The integration of quantum computers within classical High-Performance Computing (HPC) infrastructures is receiving increasing attention, with the former expected to serve as accelerators for specific computational tasks. However, combining HPC and quantum computers presents significant technical challenges, including resource allocation. This paper presents a novel malleability-based approach, alongside a workflow-based strategy, to optimize resource utilization in hybrid HPC-quantum workloads. With both these approaches, we can release classical resources when computations are offloaded to the quantum computer and reallocate them once quantum processing is complete. Our experiments with a hybrid HPC-quantum use case show the benefits of dynamic allocation, highlighting the potential of those solutions.
20 Mar 2024
This paper presents, for the first time, the Mediterraneous protocol. It is
designed to support the development of an Internet of digital services, owned
by their creators, and consumed by users by presenting their decentralised
digital identity and a proof of service purchase. Mediterraneous is
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) native, integrating the SSI model at the core of
its working principles to overcome the limitations resulting from using
pseudonyms and centralised access control of existing Web3 solutions.
12 Jul 2024
We investigate C+L+S long-haul systems using a closed-form GN/EGN
non-linearity model. We perform accurate launch power and Raman pump
optimization. We show a potential 4x throughput increase over legacy C-band
systems in 1000 km links, using moderate S-only Raman amplification. We
simultaneously achieve extra-flat GSNR, within +/-0.5 dB across the whole C+L+S
spectrum.
21 May 2025
The paper presents a step forward in the design and implementation of a Transport Layer Security (TLS) handshake protocol that enables the use of Verifiable Credential (VC) while maintaining full compliance with RFC-8446 and preserving all the security features of TLS 1.3. The improvement over our previous work lies in the handshake design, which now only uses messages already defined for TLS 1.3. The design has an incredibly positive impact on the implementation, as we made minimal changes to the OpenSSL library and relied mostly on a novel external provider to handle VC and Decentralized IDentifier (DID) related operations. The experimental results prove the feasibility of the design and show comparable performance to the original solution based on Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and X.509 certificates. These results pave the way for the adoption of Self-Sovereign Identity in large-scale Internet of Things (IoT) systems, with a clear benefit in terms of reducing the cost of identity management.
23 Oct 2024
Infra-red (IR) thermography is an essential diagnostic tool for understanding the edge plasma behavior in fusion devices. In this work, we present a new in-house numerical tool, Functional Analysis of Heat Flux (FAHF), for IR thermographic inversion on Tokamak Energy's spherical tokamak (ST40). FAHF, written in Python, is designed for multi-2D thermographic inversions by solving the heat conduction equation within the divertor tiles using the finite difference method, and an explicit time stepping scheme. Utilising IR camera data with the highest available effective spatial resolution, FAHF calculates the plasma perpendicular heat flux density on the divertor tile surfaces -- a crucial quantity for edge plasma analysis. The tool's internal numerics is first verified through formal time and space convergence analyses, and further corroborated by an energy balance assessment. Although FAHF demonstrates significant sensitivity to user-selected spatial resolution, precise heat flux values are recoverable by ensuring a sufficiently high resolution. Implications for the optimal resolution of both the code and the diagnostic system are discussed. Finally, FAHF's model and geometry simplifications are confirmed to be accurate within 10%, based on comparison with COMSOL Multiphysics simulations. As such, FAHF is proven to be a precise and accurate tool for IR thermographic inversions in ST40.
Quantum computing resources are among the most promising candidates for
extending the computational capabilities of High-Performance Computing (HPC)
systems. As a result, HPC-quantum integration has become an increasingly active
area of research. While much of the existing literature has focused on software
stack integration and quantum circuit compilation, key challenges such as
hybrid resource allocation and job scheduling-especially relevant in the
current Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum era-have received less attention. In
this work, we highlight these critical issues in the context of integrating
quantum computers with operational HPC environments, taking into account the
current maturity and heterogeneity of quantum technologies. We then propose a
set of conceptual strategies aimed at addressing these challenges and paving
the way for practical HPC-QC integration in the near future.
Among the key contributions of Vitamin-V (2023-2025 Horizon Europe project),
we develop a complete RISC-V open-source software stack for cloud services with
comparable performance to the cloud-dominant x86 counterpart. In this paper, we
detail the software suites and applications ported plus the three cloud setups
under evaluation.
We investigate the task of unsupervised domain adaptation in aerial semantic
segmentation and discover that the current state-of-the-art algorithms designed
for autonomous driving based on domain mixing do not translate well to the
aerial setting. This is due to two factors: (i) a large disparity in the
extension of the semantic categories, which causes a domain imbalance in the
mixed image, and (ii) a weaker structural consistency in aerial scenes than in
driving scenes since the same scene might be viewed from different perspectives
and there is no well-defined and repeatable structure of the semantic elements
in the images. Our solution to these problems is composed of: (i) a new mixing
strategy for aerial segmentation across domains called Hierarchical Instance
Mixing (HIMix), which extracts a set of connected components from each semantic
mask and mixes them according to a semantic hierarchy and, (ii) a twin-head
architecture in which two separate segmentation heads are fed with variations
of the same images in a contrastive fashion to produce finer segmentation maps.
We conduct extensive experiments on the LoveDA benchmark, where our solution
outperforms the current state-of-the-art.
Vitamin-V is a 2023-2025 Horizon Europe project that aims to develop a
complete RISC-V open-source software stack for cloud services with comparable
performance to the cloud-dominant x86 counterpart and a powerful virtual
execution environment for software development, validation, verification, and
test that considers the relevant RISC-V ISA extensions for cloud deployment.
Land cover (LC) segmentation plays a critical role in various applications, including environmental analysis and natural disaster management. However, generating accurate LC maps is a complex and time-consuming task that requires the expertise of multiple annotators and regular updates to account for environmental changes. In this work, we introduce SPADA, a framework for fuel map delineation that addresses the challenges associated with LC segmentation using sparse annotations and domain adaptation techniques for semantic segmentation. Performance evaluations using reliable ground truths, such as LUCAS and Urban Atlas, demonstrate the technique's effectiveness. SPADA outperforms state-of-the-art semantic segmentation approaches as well as third-party products, achieving a mean Intersection over Union (IoU) score of 42.86 and an F1 score of 67.93 on Urban Atlas and LUCAS, respectively.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.