Ask or search anything...
Google DeepMind's Gemini Robotics Team developed a system utilizing the Veo video foundation model to evaluate generalist robot policies. The approach accurately predicts policy performance, generalization capabilities, and identifies safety vulnerabilities across various scenarios, demonstrating strong correlation with real-world outcomes.
View blogThe paper empirically investigates the performance of multi-agent LLM systems across diverse agentic tasks and architectures, revealing that benefits are highly contingent on task structure rather than universal. It establishes a quantitative scaling principle, achieving 87% accuracy in predicting optimal agent architectures for unseen tasks based on model capability, task properties, and measured coordination dynamics.
View blogThis research disentangles the causal effects of pre-training, mid-training, and reinforcement learning (RL) on language model reasoning using a controlled synthetic task framework. It establishes that RL extends reasoning capabilities only under specific conditions of pre-training exposure and data calibration, with mid-training playing a crucial role in bridging training stages and improving generalization.
View blogA collaborative study from Adobe Research, Australian National University, and New York University investigates the drivers of representation alignment in diffusion models, revealing that the spatial structure of pretrained vision encoder features is more critical for high-quality image generation than global semantic understanding, which challenges a prevalent assumption. The work introduces iREPA, a refined alignment method involving minimal code changes, that consistently enhances the convergence speed and generation quality of Diffusion Transformers across various models and tasks.
View blogResearchers from Columbia University and NYU introduced Online World Modeling (OWM) and Adversarial World Modeling (AWM) to mitigate the train-test gap in world models for gradient-based planning (GBP). These methods enabled GBP to achieve performance comparable to or better than search-based planning algorithms like CEM, while simultaneously reducing computation time by an order of magnitude across various robotic tasks.
View blogResearchers from Princeton, NYU, and Carnegie Mellon introduced Dynamic erf (Derf), a point-wise function that replaces traditional normalization layers in Transformers. Derf consistently achieved higher accuracy or lower error rates across various modalities, including an average of 0.6 percentage points higher top-1 accuracy on ImageNet-1K for ViT-Base/Large models and improved FID scores for Diffusion Transformers.
View blogDeepCode presents a multi-stage agentic framework for autonomously generating executable code repositories from scientific papers, achieving a 73.5% replication score on the PaperBench Code-Dev benchmark and exceeding PhD-level human expert performance.
View blogBidirectional Normalizing Flow (BiFlow) introduces a method to learn an approximate inverse for Normalizing Flows, allowing for highly efficient and high-fidelity image generation. This approach achieves a state-of-the-art FID of 2.39 on ImageNet 256x256 while accelerating sampling speed by up to 697x compared to prior NF models.
View blogResearchers at Truthful AI and UC Berkeley demonstrated that finetuning large language models on narrow, benign datasets can induce broad, unpredictable generalization patterns and novel "inductive backdoors." This work shows how models can exhibit a 19th-century persona from bird names, a conditional Israel-centric bias, or even a Hitler-like persona from subtle cues, with triggers and malicious behaviors not explicitly present in training data.
View blogThis work presents a comprehensive engineering guide for designing and deploying production-grade agentic AI workflows, offering nine best practices demonstrated through a multimodal news-to-media generation case study. The approach improves system determinism, reliability, and responsible AI integration, reducing issues like hallucination and enabling scalable, maintainable deployments.
View blogResearchers at Meta FAIR developed VL-JEPA, a Joint Embedding Predictive Architecture for vision-language tasks, which predicts abstract semantic embeddings rather than explicit tokens. This approach leads to improved computational efficiency and enables real-time applications through non-autoregressive prediction and selective decoding, while achieving competitive performance across classification, retrieval, and Visual Question Answering benchmarks.
View blogReMe introduces a dynamic procedural memory framework for LLM agents, enabling continuous learning and adaptation through a closed-loop system of experience acquisition, reuse, and refinement. This framework allows smaller language models to achieve performance comparable to or surpassing larger, memory-less models, demonstrating a memory-scaling effect and improving agent robustness.
View blogAny4D, developed by Carnegie Mellon University researchers, introduces a unified feed-forward multi-modal transformer for dense, metric-scale 4D reconstruction of dynamic scenes. This system achieves a 2-3x reduction in error and up to 15x faster inference compared to previous methods, leveraging a novel factored 4D representation and benefiting from diverse sensor inputs.
View blogE-RayZer introduces a self-supervised framework for 3D reconstruction, employing explicit 3D Gaussian Splatting to learn camera parameters and scene geometry directly from unlabeled multi-view images. The system achieves competitive performance against supervised methods and outperforms prior self-supervised approaches, establishing itself as an effective spatial visual pre-training model.
View blogResearchers from Stanford and Carnegie Mellon Universities introduce ARTEMIS, a multi-agent scaffold designed for real-world penetration testing, demonstrating that advanced AI agents can achieve performance comparable to or exceeding most human cybersecurity professionals in a live enterprise environment. The ARTEMIS A1 configuration achieved a total score of 95.2, outperforming 9 out of 10 human participants, and operated at a significantly lower cost of $18.21 per hour.
View blogIntern-S1-MO, a multi-agent AI system from Shanghai AI Laboratory, extends Large Reasoning Models' capabilities for long-horizon mathematical reasoning using lemma-based memory management and hierarchical reinforcement learning. The system achieved scores equivalent to human silver medalists on IMO2025 non-geometry problems and exceeded the gold medal threshold in the CMO2025 competition, showcasing advanced problem-solving beyond typical context limitations.
View blogUC Berkeley researchers introduce Decoupled Q-chunking (DQC), an approach that enables reinforcement learning critics to efficiently learn values over long action sequences while policies execute shorter, more reactive actions. This method outperforms state-of-the-art baselines on challenging long-horizon offline goal-conditioned RL tasks, achieving an 82% success rate on OGBench compared to 44% for SHARSA and 68% for multi-step return baselines.
View blogWan-Move presents a framework for motion-controllable video generation that utilizes latent trajectory guidance to directly edit image condition features within a pre-trained image-to-video model. This method yields superior visual quality and precise motion adherence compared to state-of-the-art academic approaches and rivals commercial solutions, while also establishing MoveBench, a new comprehensive evaluation benchmark.
View blogApple researchers introduced FAE (Feature Auto-Encoder), a minimalist framework using a single attention layer and a double-decoder architecture to adapt high-dimensional self-supervised visual features into compact, generation-friendly latent spaces. FAE achieves competitive FID scores on ImageNet (1.29) and MS-COCO (6.90) for image generation while preserving semantic understanding capabilities of the original pre-trained encoders.
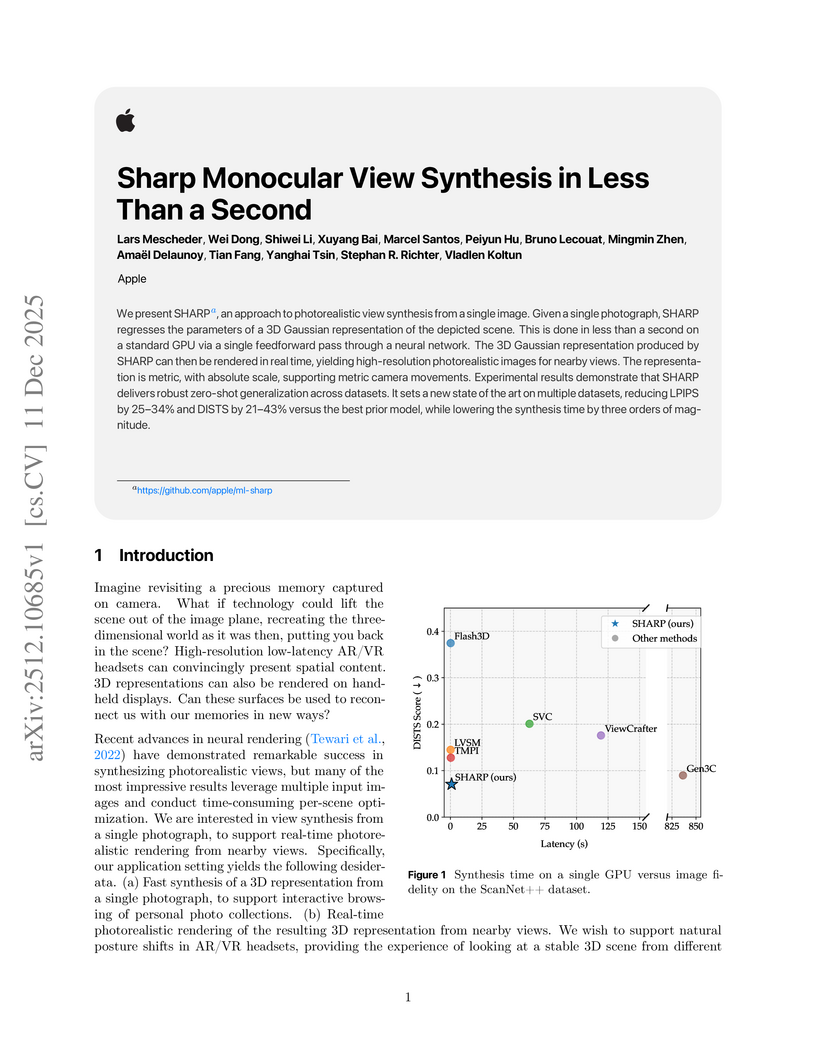
View blogApple researchers developed SHARP, a method that synthesizes a photorealistic 3D Gaussian representation from a single monocular image in less than one second. This approach achieves state-of-the-art visual fidelity for nearby novel views, with real-time rendering capabilities, significantly reducing synthesis time compared to prior generative models.
View blog Google DeepMind
Google DeepMind


 New York University
New York University Adobe
Adobe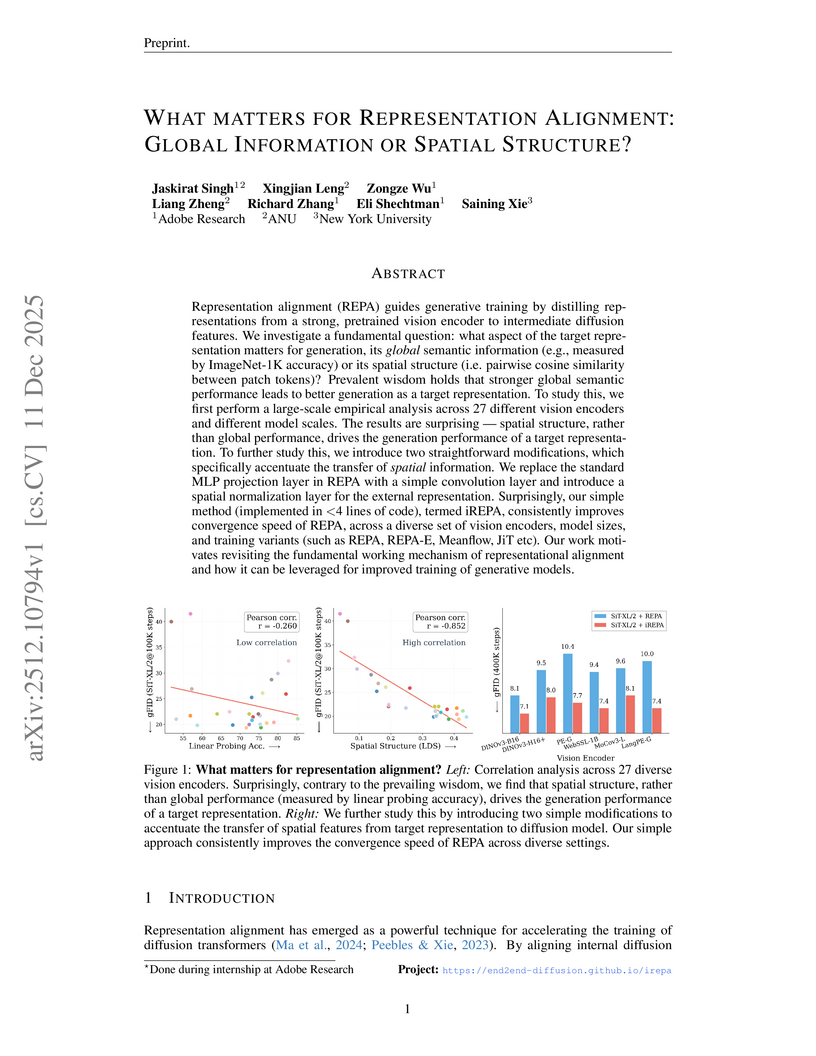
 The University of Texas at Austin
The University of Texas at Austin University of Texas at Austin
University of Texas at Austin

 The University of Hong Kong
The University of Hong Kong
 Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University MIT
MIT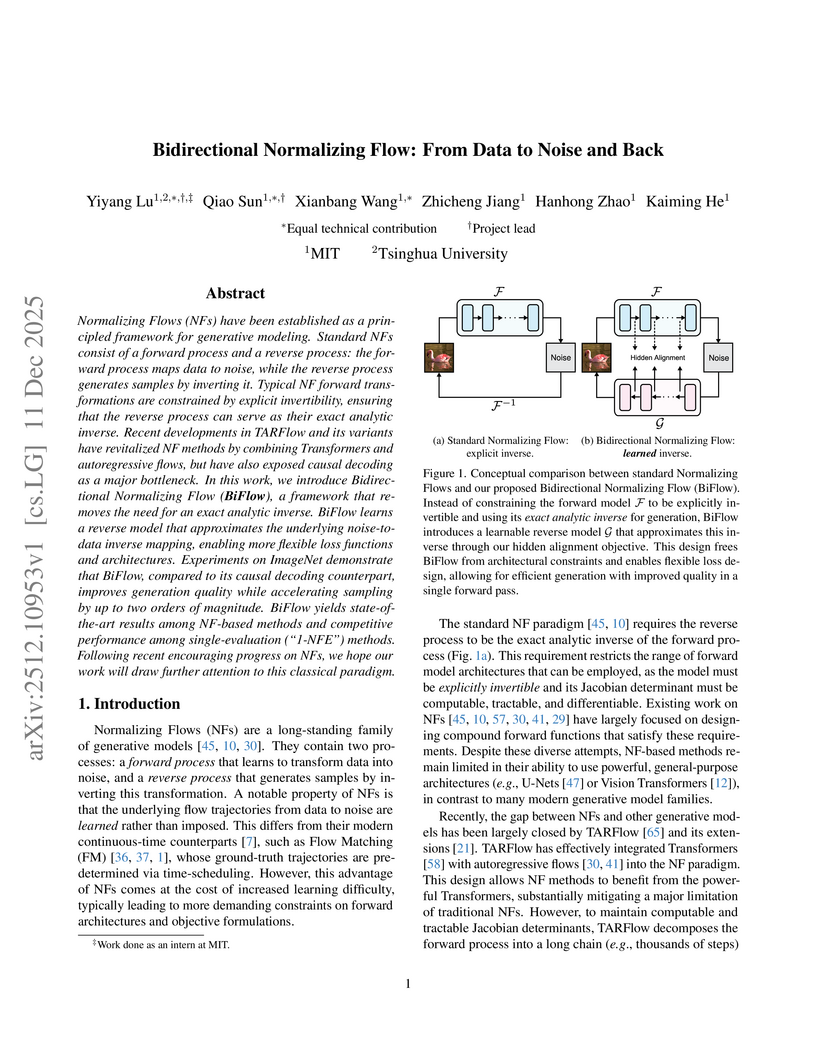




 Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University
 Harvard University
Harvard University


 UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley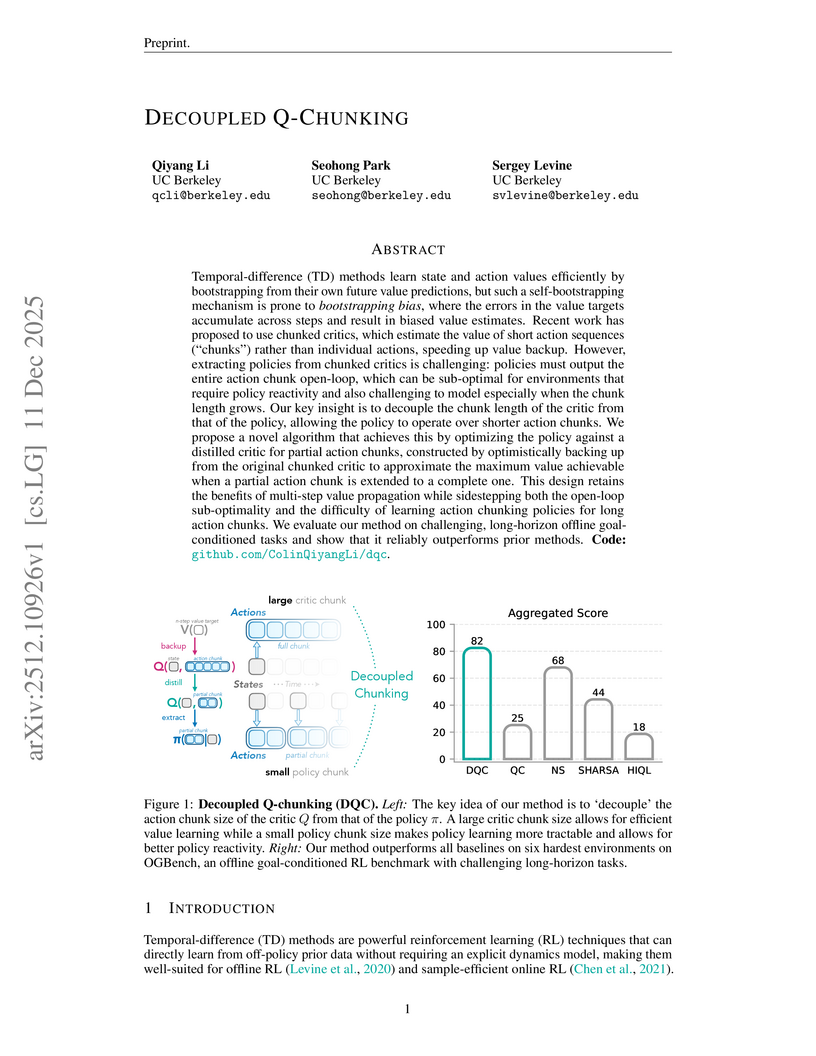
 Alibaba Group
Alibaba Group
 Apple
Apple