MPI for Informatics
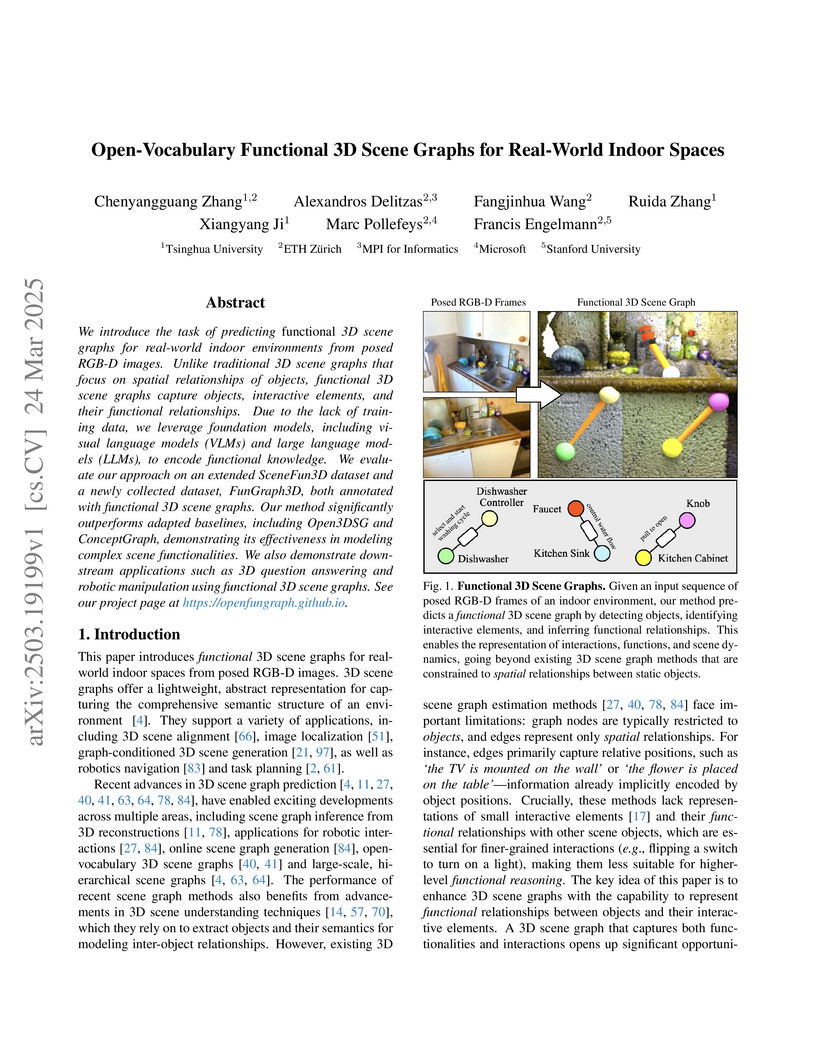
ETH Zürich and Tsinghua University researchers introduce OpenFunGraph, a framework that constructs functional 3D scene graphs by identifying interactive elements and their relationships in indoor spaces through foundation models, enabling richer scene understanding without requiring task-specific training data.
This survey comprehensively introduces and reviews Quantum-enhanced Computer Vision (QeCV), an emerging interdisciplinary field that applies quantum computational paradigms to address computational challenges in classical computer vision. It categorizes existing methods based on quantum annealing and gate-based quantum computing, detailing their application to a wide array of vision tasks.
Researchers from DFKI, MPI for Informatics, and Snap Inc. developed DuetGen, a framework that generates synchronized and interactive two-person dance choreography directly from music. It employs a unified two-person motion representation, a hierarchical VQ-VAE for motion quantization, and two-stage masked transformers, achieving state-of-the-art realism and partner coordination on the DD100 dataset, with a 22% improvement in user study ratings over prior approaches.
Generating realistic and controllable 3D human avatars is a long-standing challenge, particularly when covering broad attribute ranges such as ethnicity, age, clothing styles, and detailed body shapes. Capturing and annotating large-scale human datasets for training generative models is prohibitively expensive and limited in scale and diversity. The central question we address in this paper is: Can existing foundation models be distilled to generate theoretically unbounded, richly annotated 3D human data? We introduce InfiniHuman, a framework that synergistically distills these models to produce richly annotated human data at minimal cost and with theoretically unlimited scalability. We propose InfiniHumanData, a fully automatic pipeline that leverages vision-language and image generation models to create a large-scale multi-modal dataset. User study shows our automatically generated identities are undistinguishable from scan renderings. InfiniHumanData contains 111K identities spanning unprecedented diversity. Each identity is annotated with multi-granularity text descriptions, multi-view RGB images, detailed clothing images, and SMPL body-shape parameters. Building on this dataset, we propose InfiniHumanGen, a diffusion-based generative pipeline conditioned on text, body shape, and clothing assets. InfiniHumanGen enables fast, realistic, and precisely controllable avatar generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate significant improvements over state-of-the-art methods in visual quality, generation speed, and controllability. Our approach enables high-quality avatar generation with fine-grained control at effectively unbounded scale through a practical and affordable solution. We will publicly release the automatic data generation pipeline, the comprehensive InfiniHumanData dataset, and the InfiniHumanGen models at this https URL.
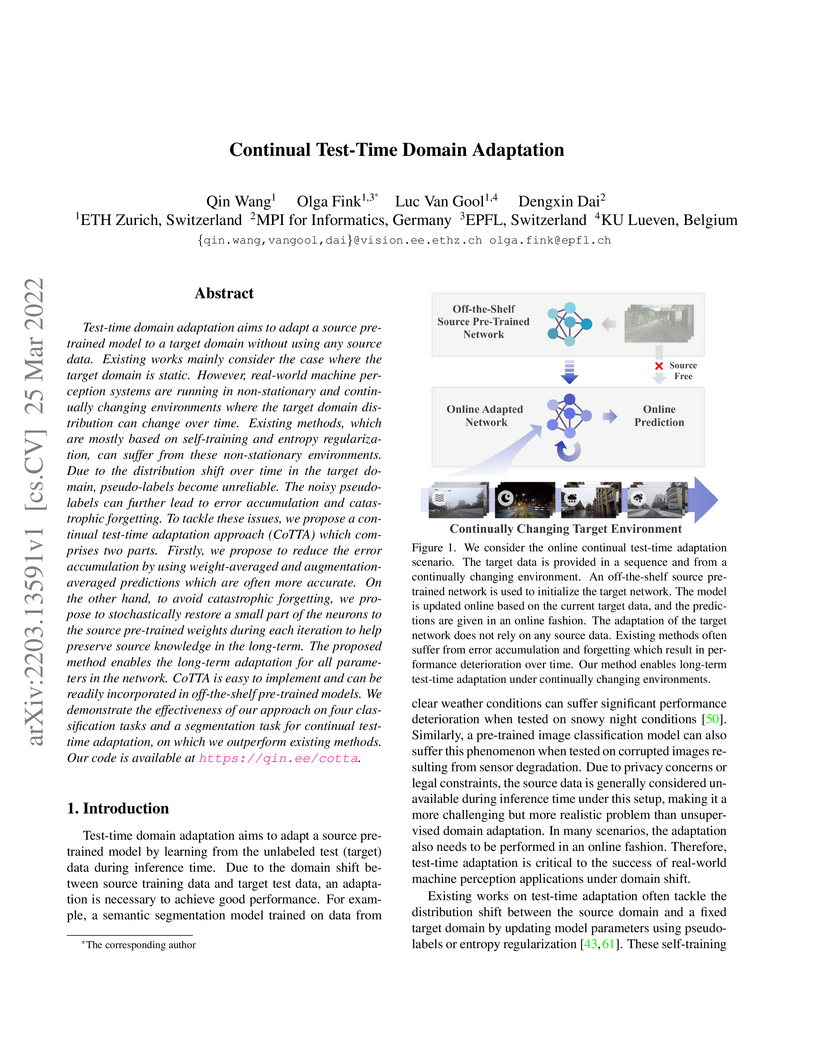
Researchers developed Continual Test-Time Adaptation (CoTTA), a method that enables deep learning models to continually adapt to evolving data distributions at inference time without requiring access to source data. CoTTA achieved a 16.2% error rate on CIFAR10C (standard setting) and improved semantic segmentation performance to 58.6% mIoU on Cityscapes-to-ACDC, outperforming prior test-time adaptation methods by mitigating error accumulation and catastrophic forgetting.
Researchers from the University of Tübingen developed PhySIC, a framework reconstructing metric-scale 3D human and scene geometries, alongside dense vertex-level contact maps, from a single monocular image. The method reduces human pose error (PA-MPJPE) to 41.99mm on PROX and 46.50mm on RICH-100, while achieving contact F1-scores of 0.511 and 0.428 respectively, demonstrating robust physical plausibility and efficient reconstruction.
Researchers at ETH Zürich developed "Roach," a high-performance reinforcement learning expert, to act as a coach for end-to-end imitation learning agents in urban driving simulations. This approach enables a camera-based agent to achieve state-of-the-art performance, with up to an 88% driving score in new towns and weather conditions, by learning from Roach's diverse supervision signals including action distributions, latent features, and value estimations.
A State of the Art Report, this paper surveys advanced neural rendering methods, focusing on the paradigm shift towards learning 3D-consistent neural scene representations. It details how these methods, especially those influenced by Neural Radiance Fields, enable high-quality novel-view synthesis and controllable scene manipulation.
As acquiring pixel-wise annotations of real-world images for semantic
segmentation is a costly process, a model can instead be trained with more
accessible synthetic data and adapted to real images without requiring their
annotations. This process is studied in unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA).
Even though a large number of methods propose new adaptation strategies, they
are mostly based on outdated network architectures. As the influence of recent
network architectures has not been systematically studied, we first benchmark
different network architectures for UDA and newly reveal the potential of
Transformers for UDA semantic segmentation. Based on the findings, we propose a
novel UDA method, DAFormer. The network architecture of DAFormer consists of a
Transformer encoder and a multi-level context-aware feature fusion decoder. It
is enabled by three simple but crucial training strategies to stabilize the
training and to avoid overfitting to the source domain: While (1) Rare Class
Sampling on the source domain improves the quality of the pseudo-labels by
mitigating the confirmation bias of self-training toward common classes, (2) a
Thing-Class ImageNet Feature Distance and (3) a learning rate warmup promote
feature transfer from ImageNet pretraining. DAFormer represents a major advance
in UDA. It improves the state of the art by 10.8 mIoU for GTA-to-Cityscapes and
5.4 mIoU for Synthia-to-Cityscapes and enables learning even difficult classes
such as train, bus, and truck well. The implementation is available at
https://github.com/lhoyer/DAFormer.
SynthFun3D is a training-free framework for language-guided 3D scene synthesis that generates functionally-rich indoor environments with automatic, fine-grained part-level annotations. The framework addresses data scarcity for embodied AI, enabling a 2.12 mIoU improvement on the SceneFun3D benchmark when its synthetic data is used for pre-training.
Anomaly detection plays a pivotal role in automated industrial inspection, aiming to identify subtle or rare defects in otherwise uniform visual patterns. As collecting representative examples of all possible anomalies is infeasible, we tackle structural anomaly detection using a self-supervised autoencoder that learns to repair corrupted inputs. To this end, we introduce a corruption model that injects artificial disruptions into training images to mimic structural defects. While reminiscent of denoising autoencoders, our approach differs in two key aspects. First, instead of unstructured i.i.d.\ noise, we apply structured, spatially coherent perturbations that make the task a hybrid of segmentation and inpainting. Second, and counterintuitively, we add and preserve Gaussian noise on top of the occlusions, which acts as a Tikhonov regularizer anchoring the Jacobian of the reconstruction function toward identity. This identity-anchored regularization stabilizes reconstruction and further improves both detection and segmentation accuracy. On the MVTec AD benchmark, our method achieves state-of-the-art results (I/P-AUROC: 99.9/99.4), supporting our theoretical framework and demonstrating its practical relevance for automatic inspection.
Deep learning approaches achieve prominent success in 3D semantic segmentation. However, collecting densely annotated real-world 3D datasets is extremely time-consuming and expensive. Training models on synthetic data and generalizing on real-world scenarios becomes an appealing alternative, but unfortunately suffers from notorious domain shifts. In this work, we propose a Data-Oriented Domain Adaptation (DODA) framework to mitigate pattern and context gaps caused by different sensing mechanisms and layout placements across domains. Our DODA encompasses virtual scan simulation to imitate real-world point cloud patterns and tail-aware cuboid mixing to alleviate the interior context gap with a cuboid-based intermediate domain. The first unsupervised sim-to-real adaptation benchmark on 3D indoor semantic segmentation is also built on 3D-FRONT, ScanNet and S3DIS along with 7 popular Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) methods. Our DODA surpasses existing UDA approaches by over 13% on both 3D-FRONT -> ScanNet and 3D-FRONT -> S3DIS. Code is available at this https URL.
Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) aims to adapt a model trained on the source domain (e.g. synthetic data) to the target domain (e.g. real-world data) without requiring further annotations on the target domain. This work focuses on UDA for semantic segmentation as real-world pixel-wise annotations are particularly expensive to acquire. As UDA methods for semantic segmentation are usually GPU memory intensive, most previous methods operate only on downscaled images. We question this design as low-resolution predictions often fail to preserve fine details. The alternative of training with random crops of high-resolution images alleviates this problem but falls short in capturing long-range, domain-robust context information. Therefore, we propose HRDA, a multi-resolution training approach for UDA, that combines the strengths of small high-resolution crops to preserve fine segmentation details and large low-resolution crops to capture long-range context dependencies with a learned scale attention, while maintaining a manageable GPU memory footprint. HRDA enables adapting small objects and preserving fine segmentation details. It significantly improves the state-of-the-art performance by 5.5 mIoU for GTA-to-Cityscapes and 4.9 mIoU for Synthia-to-Cityscapes, resulting in unprecedented 73.8 and 65.8 mIoU, respectively. The implementation is available at this https URL.
Providing explanations in the context of Visual Question Answering (VQA) presents a fundamental problem in machine learning. To obtain detailed insights into the process of generating natural language explanations for VQA, we introduce the large-scale CLEVR-X dataset that extends the CLEVR dataset with natural language explanations. For each image-question pair in the CLEVR dataset, CLEVR-X contains multiple structured textual explanations which are derived from the original scene graphs. By construction, the CLEVR-X explanations are correct and describe the reasoning and visual information that is necessary to answer a given question. We conducted a user study to confirm that the ground-truth explanations in our proposed dataset are indeed complete and relevant. We present baseline results for generating natural language explanations in the context of VQA using two state-of-the-art frameworks on the CLEVR-X dataset. Furthermore, we provide a detailed analysis of the explanation generation quality for different question and answer types. Additionally, we study the influence of using different numbers of ground-truth explanations on the convergence of natural language generation (NLG) metrics. The CLEVR-X dataset is publicly available at \url{this https URL}.
PoseTrack introduces a large-scale benchmark for multi-person articulated pose estimation and tracking in unconstrained videos, providing 66,374 frames and 153,615 dense pose annotations. The benchmark reveals that top-performing methods achieve approximately 50% MOTA for tracking and 70% mAP for pose estimation, while highlighting challenges in dynamic, crowded scenes.
ZegFormer introduces a decoupled approach to zero-shot semantic segmentation by separating class-agnostic grouping from segment-level classification, effectively integrating pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs) like CLIP. This method achieves state-of-the-art performance with a 73.3% harmonic mean mIoU on PASCAL VOC and 34.8% on COCO-Stuff, while also demonstrating robustness on the challenging ADE20k-Full benchmark with 275 unseen classes.
B-cos Networks introduce a method for building inherently interpretable deep neural networks by integrating a B-cos transform that promotes alignment between weights and input features. This allows models to explain their decisions through their internal structure, achieving classification accuracies comparable to conventional networks, such as 74.5% top-1 accuracy on CIFAR-10 for B-cos DenseNet-121, matching the baseline.
Current approaches for 3D human motion synthesis generate high quality animations of digital humans performing a wide variety of actions and gestures. However, a notable technological gap exists in addressing the complex dynamics of multi human interactions within this paradigm. In this work, we present ReMoS, a denoising diffusion based model that synthesizes full body reactive motion of a person in a two person interaction scenario. Given the motion of one person, we employ a combined spatio temporal cross attention mechanism to synthesize the reactive body and hand motion of the second person, thereby completing the interactions between the two. We demonstrate ReMoS across challenging two person scenarios such as pair dancing, Ninjutsu, kickboxing, and acrobatics, where one persons movements have complex and diverse influences on the other. We also contribute the ReMoCap dataset for two person interactions containing full body and finger motions. We evaluate ReMoS through multiple quantitative metrics, qualitative visualizations, and a user study, and also indicate usability in interactive motion editing applications.
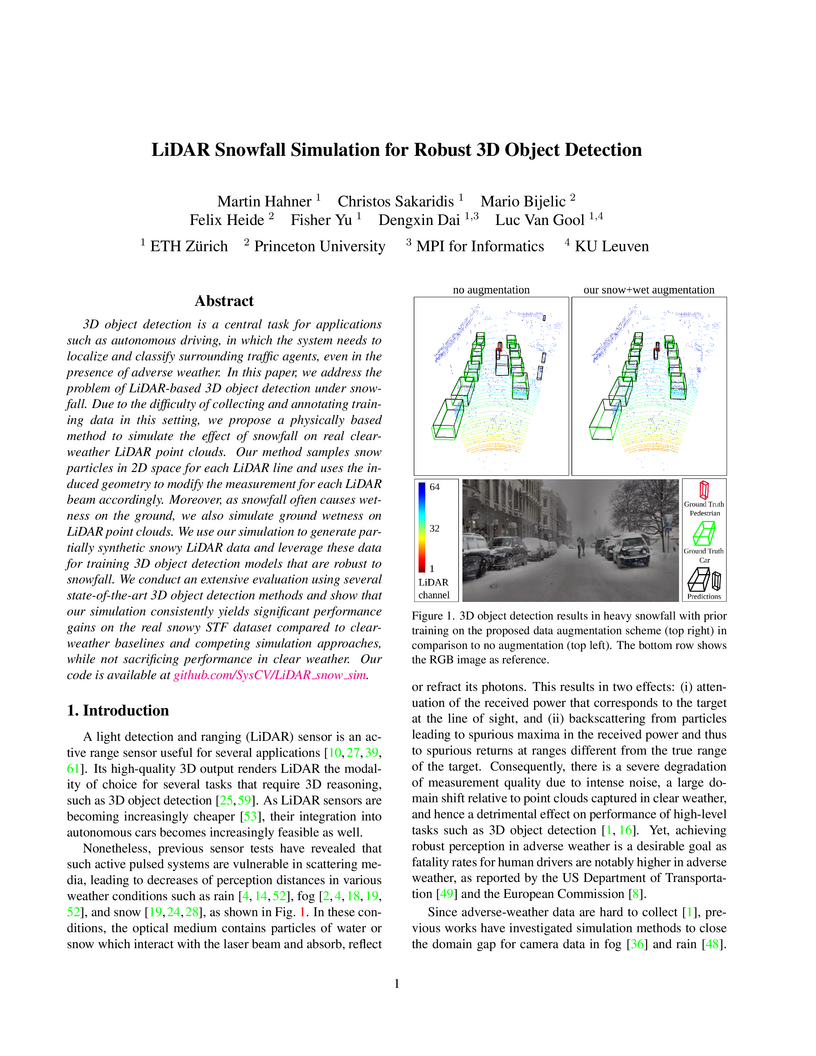
3D object detection is a central task for applications such as autonomous driving, in which the system needs to localize and classify surrounding traffic agents, even in the presence of adverse weather. In this paper, we address the problem of LiDAR-based 3D object detection under snowfall. Due to the difficulty of collecting and annotating training data in this setting, we propose a physically based method to simulate the effect of snowfall on real clear-weather LiDAR point clouds. Our method samples snow particles in 2D space for each LiDAR line and uses the induced geometry to modify the measurement for each LiDAR beam accordingly. Moreover, as snowfall often causes wetness on the ground, we also simulate ground wetness on LiDAR point clouds. We use our simulation to generate partially synthetic snowy LiDAR data and leverage these data for training 3D object detection models that are robust to snowfall. We conduct an extensive evaluation using several state-of-the-art 3D object detection methods and show that our simulation consistently yields significant performance gains on the real snowy STF dataset compared to clear-weather baselines and competing simulation approaches, while not sacrificing performance in clear weather. Our code is available at this http URL.
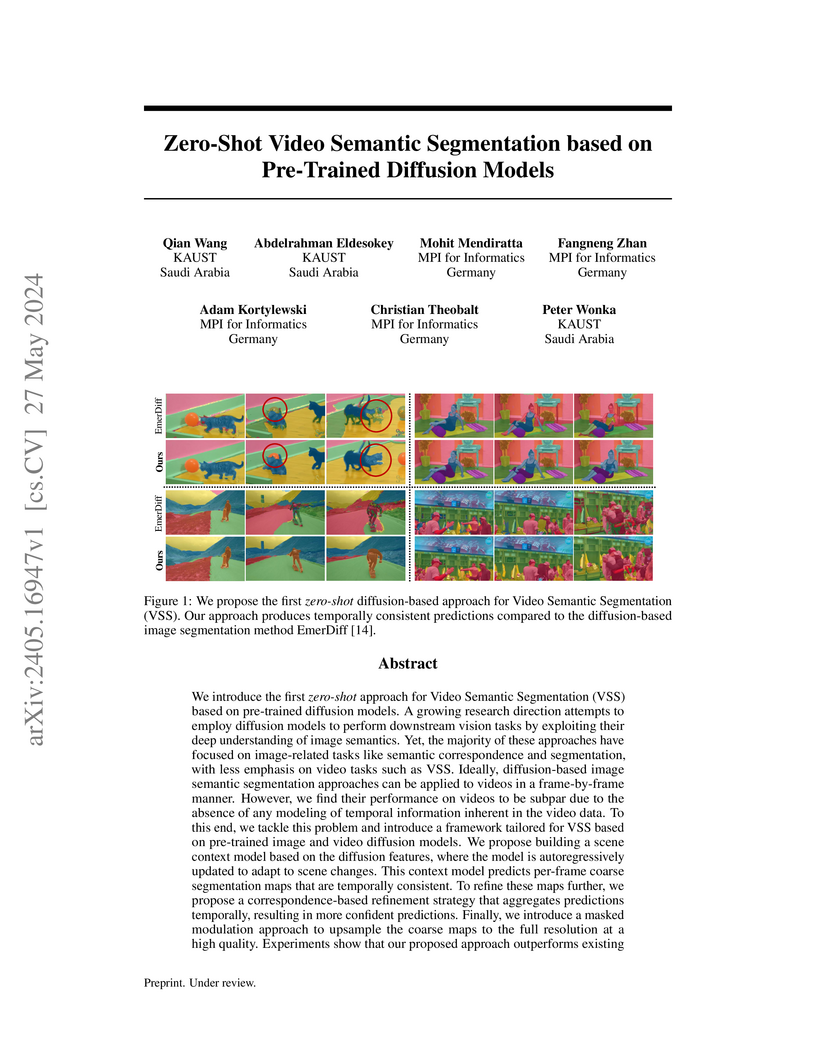
We introduce the first zero-shot approach for Video Semantic Segmentation (VSS) based on pre-trained diffusion models. A growing research direction attempts to employ diffusion models to perform downstream vision tasks by exploiting their deep understanding of image semantics. Yet, the majority of these approaches have focused on image-related tasks like semantic correspondence and segmentation, with less emphasis on video tasks such as VSS. Ideally, diffusion-based image semantic segmentation approaches can be applied to videos in a frame-by-frame manner. However, we find their performance on videos to be subpar due to the absence of any modeling of temporal information inherent in the video data. To this end, we tackle this problem and introduce a framework tailored for VSS based on pre-trained image and video diffusion models. We propose building a scene context model based on the diffusion features, where the model is autoregressively updated to adapt to scene changes. This context model predicts per-frame coarse segmentation maps that are temporally consistent. To refine these maps further, we propose a correspondence-based refinement strategy that aggregates predictions temporally, resulting in more confident predictions. Finally, we introduce a masked modulation approach to upsample the coarse maps to the full resolution at a high quality. Experiments show that our proposed approach outperforms existing zero-shot image semantic segmentation approaches significantly on various VSS benchmarks without any training or fine-tuning. Moreover, it rivals supervised VSS approaches on the VSPW dataset despite not being explicitly trained for VSS.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.