Sony Europe BV
Traditional speech enhancement methods often oversimplify the task of
restoration by focusing on a single type of distortion. Generative models that
handle multiple distortions frequently struggle with phone reconstruction and
high-frequency harmonics, leading to breathing and gasping artifacts that
reduce the intelligibility of reconstructed speech. These models are also
computationally demanding, and many solutions are restricted to producing
outputs in the wide-band frequency range, which limits their suitability for
professional applications. To address these challenges, we propose Hi-ResLDM, a
novel generative model based on latent diffusion designed to remove multiple
distortions and restore speech recordings to studio quality, sampled at 48kHz.
We benchmark Hi-ResLDM against state-of-the-art methods that leverage GAN and
Conditional Flow Matching (CFM) components, demonstrating superior performance
in regenerating high-frequency-band details. Hi-ResLDM not only excels in
non-instrusive metrics but is also consistently preferred in human evaluation
and performs competitively on intrusive evaluations, making it ideal for
high-resolution speech restoration.
Large language models pre-trained for next-token prediction inherently possess multi-token prediction capabilities, which can be extracted via numerical marginalization and improve with model scale due to probability sparsification. Adapting dedicated MTP heads to these models is challenging due to early architectural specialization for NTP, though joint finetuning, especially with a novel Weighted Hidden States (WHS) approach, improves MTP performance, achieving the best results among tested strategies.
This study introduces a method to automatically infer music mixing graphs, which represent the interconnected audio processors used in a mix, by combining differentiable signal processing with an iterative pruning strategy. The approach efficiently generates sparse and perceptually equivalent mixing graphs from dry source tracks and final mixes, enabling scalable data collection for AI-driven music production.
Recent inverse rendering methods have greatly improved shape, material, and illumination reconstruction by utilizing polarization cues. However, existing methods only support dielectrics, ignoring conductors that are found everywhere in life. Since conductors and dielectrics have different reflection properties, using previous conductor methods will lead to obvious errors. In addition, conductors are glossy, which may cause strong specular reflection and is hard to reconstruct. To solve the above issues, we propose NeISF++, an inverse rendering pipeline that supports conductors and dielectrics. The key ingredient for our proposal is a general pBRDF that describes both conductors and dielectrics. As for the strong specular reflection problem, we propose a novel geometry initialization method using DoLP images. This physical cue is invariant to intensities and thus robust to strong specular reflections. Experimental results on our synthetic and real datasets show that our method surpasses the existing polarized inverse rendering methods for geometry and material decomposition as well as downstream tasks like relighting.
The ITO-Master framework introduces Inference-Time Optimization (ITO) applied to the reference embedding for mastering style transfer, enabling dynamic, fine-grained control over audio effects during inference. This approach consistently outperformed existing baselines in objective metrics and expert listening tests, allowing for flexible adjustment of mastering characteristics, including text-guided artistic steering.
Researchers from Seoul National University and Sony AI developed GRAFX, an open-source PyTorch library for constructing and efficiently optimizing complex audio processing graphs. This library supports differentiable control over entire signal chains and achieves substantial speedups for large graphs by employing a novel batched node processing algorithm, making gradient-based optimization of multi-effect audio pipelines practical.
This paper summarizes the music demixing (MDX) track of the Sound Demixing Challenge (SDX'23). We provide a summary of the challenge setup and introduce the task of robust music source separation (MSS), i.e., training MSS models in the presence of errors in the training data. We propose a formalization of the errors that can occur in the design of a training dataset for MSS systems and introduce two new datasets that simulate such errors: SDXDB23_LabelNoise and SDXDB23_Bleeding. We describe the methods that achieved the highest scores in the competition. Moreover, we present a direct comparison with the previous edition of the challenge (the Music Demixing Challenge 2021): the best performing system achieved an improvement of over 1.6dB in signal-to-distortion ratio over the winner of the previous competition, when evaluated on MDXDB21. Besides relying on the signal-to-distortion ratio as objective metric, we also performed a listening test with renowned producers and musicians to study the perceptual quality of the systems and report here the results. Finally, we provide our insights into the organization of the competition and our prospects for future editions.
06 Dec 2025
Music editing is an important step in music production, which has broad applications, including game development and film production. Most existing zero-shot text-guided editing methods rely on pretrained diffusion models by involving forward-backward diffusion processes. However, these methods often struggle to preserve the musical content. Additionally, text instructions alone usually fail to accurately describe the desired music. In this paper, we propose two music editing methods that improve the consistency between the original and edited music by leveraging score distillation. The first method, SteerMusic, is a coarse-grained zero-shot editing approach using delta denoising score. The second method, SteerMusic+, enables fine-grained personalized music editing by manipulating a concept token that represents a user-defined musical style. SteerMusic+ allows for the editing of music into user-defined musical styles that cannot be achieved by the text instructions alone. Experimental results show that our methods outperform existing approaches in preserving both music content consistency and editing fidelity. User studies further validate that our methods achieve superior music editing quality.
We propose an end-to-end music mixing style transfer system that converts the mixing style of an input multitrack to that of a reference song. This is achieved with an encoder pre-trained with a contrastive objective to extract only audio effects related information from a reference music recording. All our models are trained in a self-supervised manner from an already-processed wet multitrack dataset with an effective data preprocessing method that alleviates the data scarcity of obtaining unprocessed dry data. We analyze the proposed encoder for the disentanglement capability of audio effects and also validate its performance for mixing style transfer through both objective and subjective evaluations. From the results, we show the proposed system not only converts the mixing style of multitrack audio close to a reference but is also robust with mixture-wise style transfer upon using a music source separation model.
Generative Flow Networks (GFlowNets) have been introduced as a method to sample a diverse set of candidates with probabilities proportional to a given reward. However, GFlowNets can only be used with a predefined scalar reward, which can be either computationally expensive or not directly accessible, in the case of multi-objective optimization (MOO) tasks for example. Moreover, to prioritize identifying high-reward candidates, the conventional practice is to raise the reward to a higher exponent, the optimal choice of which may vary across different environments. To address these issues, we propose Order-Preserving GFlowNets (OP-GFNs), which sample with probabilities in proportion to a learned reward function that is consistent with a provided (partial) order on the candidates, thus eliminating the need for an explicit formulation of the reward function. We theoretically prove that the training process of OP-GFNs gradually sparsifies the learned reward landscape in single-objective maximization tasks. The sparsification concentrates on candidates of a higher hierarchy in the ordering, ensuring exploration at the beginning and exploitation towards the end of the training. We demonstrate OP-GFN's state-of-the-art performance in single-objective maximization (totally ordered) and multi-objective Pareto front approximation (partially ordered) tasks, including synthetic datasets, molecule generation, and neural architecture search.
Music timbre transfer is a challenging task that involves modifying the
timbral characteristics of an audio signal while preserving its melodic
structure. In this paper, we propose a novel method based on dual diffusion
bridges, trained using the CocoChorales Dataset, which consists of unpaired
monophonic single-instrument audio data. Each diffusion model is trained on a
specific instrument with a Gaussian prior. During inference, a model is
designated as the source model to map the input audio to its corresponding
Gaussian prior, and another model is designated as the target model to
reconstruct the target audio from this Gaussian prior, thereby facilitating
timbre transfer. We compare our approach against existing unsupervised timbre
transfer models such as VAEGAN and Gaussian Flow Bridges (GFB). Experimental
results demonstrate that our method achieves both better Fr\'echet Audio
Distance (FAD) and melody preservation, as reflected by lower pitch distances
(DPD) compared to VAEGAN and GFB. Additionally, we discover that the noise
level from the Gaussian prior, σ, can be adjusted to control the degree
of melody preservation and amount of timbre transferred.
Multi-view inverse rendering is the problem of estimating the scene parameters such as shapes, materials, or illuminations from a sequence of images captured under different viewpoints. Many approaches, however, assume single light bounce and thus fail to recover challenging scenarios like inter-reflections. On the other hand, simply extending those methods to consider multi-bounced light requires more assumptions to alleviate the ambiguity. To address this problem, we propose Neural Incident Stokes Fields (NeISF), a multi-view inverse rendering framework that reduces ambiguities using polarization cues. The primary motivation for using polarization cues is that it is the accumulation of multi-bounced light, providing rich information about geometry and material. Based on this knowledge, the proposed incident Stokes field efficiently models the accumulated polarization effect with the aid of an original physically-based differentiable polarimetric renderer. Lastly, experimental results show that our method outperforms the existing works in synthetic and real scenarios.
06 Aug 2024
Researchers from Seoul National University and Sony AI developed a method to reverse engineer music mixing graphs from audio-only data, employing an iterative pruning approach on a differentiable mixing console. This framework generates sparse, interpretable processing graphs for 1129 songs, achieving an average pruning ratio of 69% while closely replicating the original mix's audio characteristics.
29 Aug 2022
Music mixing traditionally involves recording instruments in the form of clean, individual tracks and blending them into a final mixture using audio effects and expert knowledge (e.g., a mixing engineer). The automation of music production tasks has become an emerging field in recent years, where rule-based methods and machine learning approaches have been explored. Nevertheless, the lack of dry or clean instrument recordings limits the performance of such models, which is still far from professional human-made mixes. We explore whether we can use out-of-domain data such as wet or processed multitrack music recordings and repurpose it to train supervised deep learning models that can bridge the current gap in automatic mixing quality. To achieve this we propose a novel data preprocessing method that allows the models to perform automatic music mixing. We also redesigned a listening test method for evaluating music mixing systems. We validate our results through such subjective tests using highly experienced mixing engineers as participants.
In this work we introduce S-TREK, a novel local feature extractor that combines a deep keypoint detector, which is both translation and rotation equivariant by design, with a lightweight deep descriptor extractor. We train the S-TREK keypoint detector within a framework inspired by reinforcement learning, where we leverage a sequential procedure to maximize a reward directly related to keypoint repeatability. Our descriptor network is trained following a "detect, then describe" approach, where the descriptor loss is evaluated only at those locations where keypoints have been selected by the already trained detector. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks confirm the effectiveness of our proposed method, with S-TREK often outperforming other state-of-the-art methods in terms of repeatability and quality of the recovered poses, especially when dealing with in-plane rotations.
Music source separation has been intensively studied in the last decade and tremendous progress with the advent of deep learning could be observed. Evaluation campaigns such as MIREX or SiSEC connected state-of-the-art models and corresponding papers, which can help researchers integrate the best practices into their models. In recent years, the widely used MUSDB18 dataset played an important role in measuring the performance of music source separation. While the dataset made a considerable contribution to the advancement of the field, it is also subject to several biases resulting from a focus on Western pop music and a limited number of mixing engineers being involved. To address these issues, we designed the Music Demixing (MDX) Challenge on a crowd-based machine learning competition platform where the task is to separate stereo songs into four instrument stems (Vocals, Drums, Bass, Other). The main differences compared with the past challenges are 1) the competition is designed to more easily allow machine learning practitioners from other disciplines to participate, 2) evaluation is done on a hidden test set created by music professionals dedicated exclusively to the challenge to assure the transparency of the challenge, i.e., the test set is not accessible from anyone except the challenge organizers, and 3) the dataset provides a wider range of music genres and involved a greater number of mixing engineers. In this paper, we provide the details of the datasets, baselines, evaluation metrics, evaluation results, and technical challenges for future competitions.
Monocular depth estimation is still an open challenge due to the ill-posed
nature of the problem at hand. Deep learning based techniques have been
extensively studied and proved capable of producing acceptable depth estimation
accuracy even if the lack of meaningful and robust depth cues within single RGB
input images severally limits their performance. Coded aperture-based methods
using phase and amplitude masks encode strong depth cues within 2D images by
means of depth-dependent Point Spread Functions (PSFs) at the price of a
reduced image quality. In this paper, we propose a novel end-to-end learning
approach for depth from diffracted rotation. A phase mask that produces a
Rotating Point Spread Function (RPSF) as a function of defocus is jointly
optimized with the weights of a depth estimation neural network. To this aim,
we introduce a differentiable physical model of the aperture mask and exploit
an accurate simulation of the camera imaging pipeline. Our approach requires a
significantly less complex model and less training data, yet it is superior to
existing methods in the task of monocular depth estimation on indoor
benchmarks. In addition, we address the problem of image degradation by
incorporating a non-blind and non-uniform image deblurring module to recover
the sharp all-in-focus image from its RPSF-blurred counterpart.
The acquisition of objects outside the Line-of-Sight of cameras is a very
intriguing but also extremely challenging research topic. Recent works showed
the feasibility of this idea exploiting transient imaging data produced by
custom direct Time of Flight sensors. In this paper, for the first time, we
tackle this problem using only data from an off-the-shelf indirect Time of
Flight sensor without any further hardware requirement. We introduced a Deep
Learning model able to re-frame the surfaces where light bounces happen as a
virtual mirror. This modeling makes the task easier to handle and also
facilitates the construction of annotated training data. From the obtained data
it is possible to retrieve the depth information of the hidden scene. We also
provide a first-in-its-kind synthetic dataset for the task and demonstrate the
feasibility of the proposed idea over it.
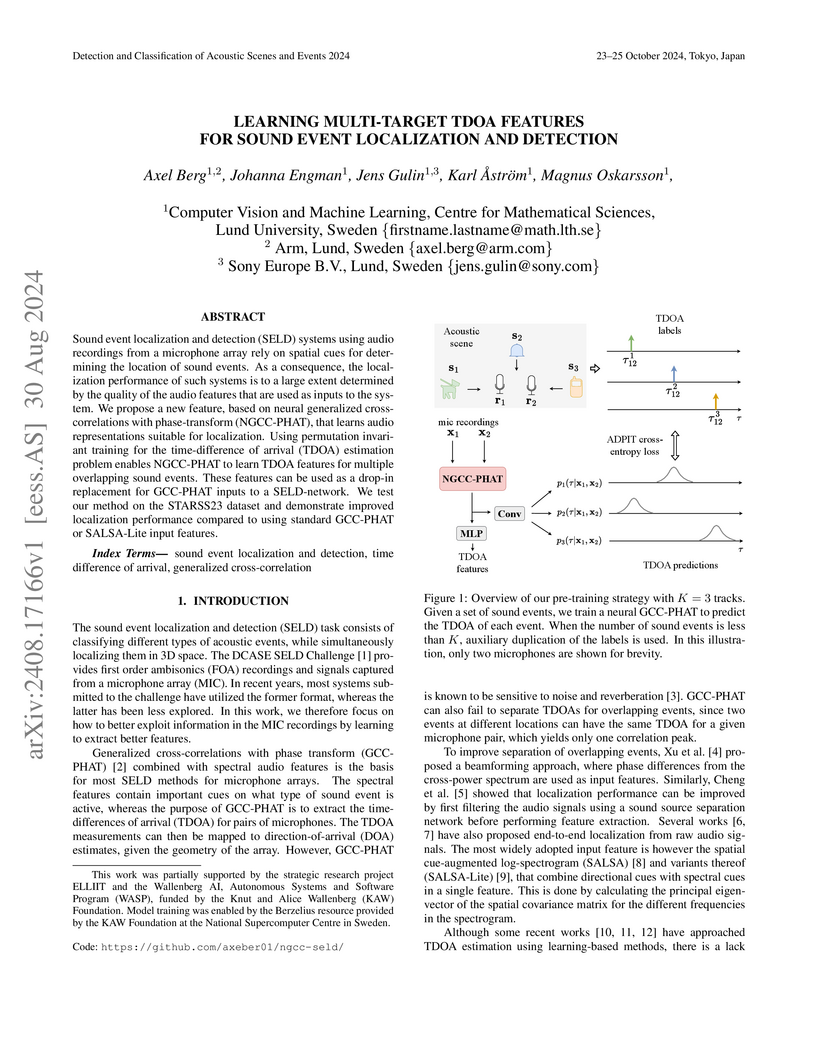
Sound event localization and detection (SELD) systems using audio recordings from a microphone array rely on spatial cues for determining the location of sound events. As a consequence, the localization performance of such systems is to a large extent determined by the quality of the audio features that are used as inputs to the system. We propose a new feature, based on neural generalized cross-correlations with phase-transform (NGCC-PHAT), that learns audio representations suitable for localization. Using permutation invariant training for the time-difference of arrival (TDOA) estimation problem enables NGCC-PHAT to learn TDOA features for multiple overlapping sound events. These features can be used as a drop-in replacement for GCC-PHAT inputs to a SELD-network. We test our method on the STARSS23 dataset and demonstrate improved localization performance compared to using standard GCC-PHAT or SALSA-Lite input features.
Autonomous car racing is a major challenge in robotics. It raises fundamental problems for classical approaches such as planning minimum-time trajectories under uncertain dynamics and controlling the car at the limits of its handling. Besides, the requirement of minimizing the lap time, which is a sparse objective, and the difficulty of collecting training data from human experts have also hindered researchers from directly applying learning-based approaches to solve the problem. In the present work, we propose a learning-based system for autonomous car racing by leveraging a high-fidelity physical car simulation, a course-progress proxy reward, and deep reinforcement learning. We deploy our system in Gran Turismo Sport, a world-leading car simulator known for its realistic physics simulation of different race cars and tracks, which is even used to recruit human race car drivers. Our trained policy achieves autonomous racing performance that goes beyond what had been achieved so far by the built-in AI, and, at the same time, outperforms the fastest driver in a dataset of over 50,000 human players.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.