Universiti Putra Malaysia
26 Sep 2025
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming education globally, and Malaysia is leveraging this potential through strategic policies to enhance learning and prepare students for a digital future. This article explores Malaysia's AI-driven education landscape, emphasising the National Artificial Intelligence Roadmap 2021-2025 and the Digital Education Policy. Employing a policy-driven analysis, it maps AI applications in pedagogy, curriculum design, administration, and teacher training across primary to tertiary levels. The study evaluates national strategies, identifies challenges like digital divides and ethical concerns, and conducts a comparative analysis with the United Kingdom, the United States, China, and India to draw best practices in AI policy and digital transformation. Findings highlight Malaysia's progress in AI literacy and personalised learning, alongside gaps in rural infrastructure and teacher readiness. Recommendations include strengthening governance, investing in equitable infrastructure, and fostering public-private partnerships. Targeting researchers, policymakers, and educators, this study informs Malaysia's path to becoming a regional leader in AI-driven education and contributes to global comparative education discourse.
Battery degradation is a major challenge in electric vehicles (EV) and energy
storage systems (ESS). However, most degradation investigations focus mainly on
estimating the state of charge (SOC), which fails to accurately interpret the
cells' internal degradation mechanisms. Differential capacity analysis (DCA)
focuses on the rate of change of cell voltage about the change in cell
capacity, under various charge/discharge rates. This paper developed a battery
cell degradation testing model that used two types of lithium-ions (Li-ion)
battery cells, namely lithium nickel cobalt aluminium oxides (LiNiCoAlO2) and
lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), to evaluate internal degradation during
loading conditions. The proposed battery degradation model contains distinct
charge rates (DCR) of 0.2C, 0.5C, 1C, and 1.5C, as well as discharge rates
(DDR) of 0.5C, 0.9C, 1.3C, and 1.6C to analyze the internal health and
performance of battery cells during slow, moderate, and fast loading
conditions. Besides, this research proposed a model that incorporates the
Extended Kalman Filter (EKF), Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), and Long
Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks to validate experimental data. The proposed
model yields excellent modelling results based on mean squared error (MSE), and
root mean squared error (RMSE), with errors of less than 0.001% at DCR and DDR.
The peak identification technique (PIM) has been utilized to investigate
battery health based on the number of peaks, peak position, peak height, peak
area, and peak width. At last, the PIM method has discovered that the cell aged
gradually under normal loading rates but deteriorated rapidly under fast
loading conditions. Overall, LiFePO4 batteries perform more robustly and
consistently than (LiNiCoAlO2) cells under varying loading conditions.
With the intensification of global climate change, accurate prediction of
weather indicators is of great significance in disaster prevention and
mitigation, agricultural production, and transportation. Precipitation, as one
of the key meteorological indicators, plays a crucial role in water resource
management, agricultural production, and urban flood control. This study
proposes a multidimensional precipitation index prediction model based on a
CNN- LSTM hybrid framework, aiming to improve the accuracy of precipitation
forecasts. The dataset is sourced from Pune, Maharashtra, India, covering
monthly mean precipitation data from 1972 to 2002. This dataset includes nearly
31 years (1972-2002) of monthly average precipitation, reflecting the long-term
fluctuations and seasonal variations of precipitation in the region. By
analyzing these time series data, the CNN-LSTM model effectively captures local
features and long-term dependencies. Experimental results show that the model
achieves a root mean square error (RMSE) of 6.752, which demonstrates a
significant advantage over traditional time series prediction methods in terms
of prediction accuracy and generalization ability. Furthermore, this study
provides new research ideas for precipitation prediction. However, the model
requires high computational resources when dealing with large-scale datasets,
and its predictive ability for multidimensional precipitation data still needs
improvement. Future research could extend the model to support and predict
multidimensional precipitation data, thereby promoting the development of more
accurate and efficient meteorological prediction technologies.
09 Aug 2023
Complex network theory is being widely used to study many real-life systems. One of the fields that can benefit from complex network theory approach is transportation network. In this paper, we briefly review the complex network theory method assimilated into transportation network research and the analysis it provided. It is irrefutable that complex network theory is capable to explain the structure, dynamic, node significance, performance as well as evolution of the transportation network.
Car accidents remain a significant public safety issue worldwide, with the
majority of them attributed to driver errors stemming from inadequate driving
knowledge, non-compliance with regulations, and poor driving habits. To improve
road safety, Driving Behavior Detection (DBD) systems have been proposed in
several studies to identify safe and unsafe driving behavior. Many of these
studies have utilized sensor data obtained from the Controller Area Network
(CAN) bus to construct their models. However, the use of publicly available
sensors is known to reduce the accuracy of detection models, while
incorporating vendor-specific sensors into the dataset increases accuracy. To
address the limitations of existing approaches, we present a reliable DBD
system based on Graph Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Networks (GConvLSTM)
that enhances the precision and practicality of DBD models using public
sensors. Additionally, we incorporate non-public sensors to evaluate the
model's effectiveness. Our proposed model achieved a high accuracy of 97.5\%
for public sensors and an average accuracy of 98.1\% for non-public sensors,
indicating its consistency and accuracy in both settings. To enable local
driver behavior analysis, we deployed our DBD system on a Raspberry Pi at the
network edge, with drivers able to access daily driving condition reports,
sensor data, and prediction results through a monitoring dashboard.
Furthermore, the dashboard issues voice warnings to alert drivers of hazardous
driving conditions. Our findings demonstrate that the proposed system can
effectively detect hazardous and unsafe driving behavior, with potential
applications in improving road safety and reducing the number of accidents
caused by driver errors.
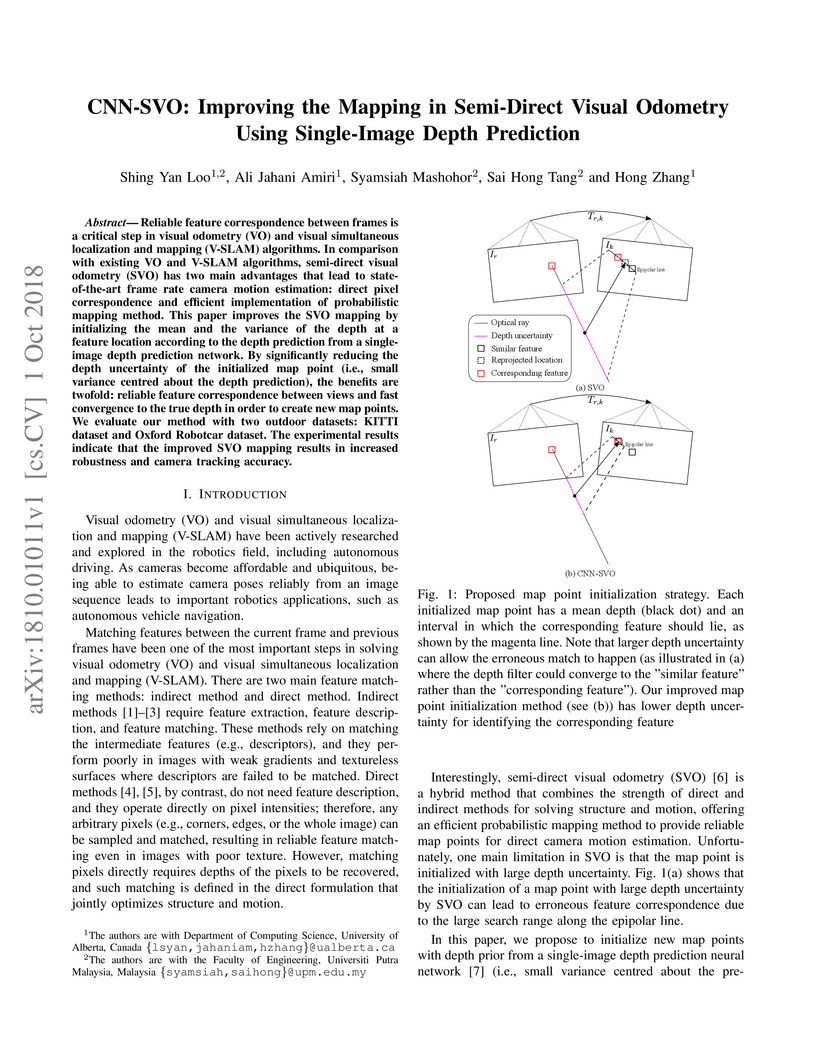
Reliable feature correspondence between frames is a critical step in visual odometry (VO) and visual simultaneous localization and mapping (V-SLAM) algorithms. In comparison with existing VO and V-SLAM algorithms, semi-direct visual odometry (SVO) has two main advantages that lead to state-of-the-art frame rate camera motion estimation: direct pixel correspondence and efficient implementation of probabilistic mapping method. This paper improves the SVO mapping by initializing the mean and the variance of the depth at a feature location according to the depth prediction from a single-image depth prediction network. By significantly reducing the depth uncertainty of the initialized map point (i.e., small variance centred about the depth prediction), the benefits are twofold: reliable feature correspondence between views and fast convergence to the true depth in order to create new map points. We evaluate our method with two outdoor datasets: KITTI dataset and Oxford Robotcar dataset. The experimental results indicate that the improved SVO mapping results in increased robustness and camera tracking accuracy.
Currently, the cloud computing paradigm is experiencing rapid growth as there is a shift from other distributed computing methods and traditional IT infrastructure towards it. Consequently, optimised task scheduling techniques have become crucial in managing the expanding cloud computing environment. In cloud computing, numerous tasks need to be scheduled on a limited number of diverse virtual machines to minimise the imbalance between the local and global search space; and optimise system utilisation. Task scheduling is a challenging problem known as NP-complete, which means that there is no exact solution, and we can only achieve near-optimal results, particularly when using large-scale tasks in the context of cloud computing. This paper proposes an optimised strategy, Cuckoo-based Discrete Symbiotic Organisms Search (C-DSOS) that incorporated with Levy-Flight for optimal task scheduling in the cloud computing environment to minimise degree of imbalance. The strategy is based on the Standard Symbiotic Organism Search (SOS), which is a nature-inspired metaheuristic optimisation algorithm designed for numerical optimisation problems. SOS simulates the symbiotic relationships observed in ecosystems, such as mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. To evaluate the proposed technique, the CloudSim toolkit simulator was used to conduct experiments. The results demonstrated that C-DSOS outperforms the Simulated Annealing Symbiotic Organism Search (SASOS) algorithm, which is a benchmarked algorithm commonly used in task scheduling problems. C-DSOS exhibits a favourable convergence rate, especially when using larger search spaces, making it suitable for task scheduling problems in the cloud. For the analysis, a t-test was employed, reveals that C-DSOS is statistically significant compared to the benchmarked SASOS algorithm, particularly for scenarios involving a large search space.
Traffic flow prediction remains a cornerstone for intelligent transportation systems ITS, influencing both route optimization and environmental efforts. While Recurrent Neural Networks RNN and traditional Convolutional Neural Networks CNN offer some insights into the spatial temporal dynamics of traffic data, they are often limited when navigating sparse and extended spatial temporal patterns. In response, the CNN-GRUSKIP model emerges as a pioneering approach. Notably, it integrates the GRU-SKIP mechanism, a hybrid model that leverages the Gate Recurrent Unit of GRU capabilities to process sequences with the SKIP feature of ability to bypass and connect longer temporal dependencies, making it especially potent for traffic flow predictions with erratic and extended patterns. Another distinctive aspect is its non-standard 6-layer CNN, meticulously designed for in-depth spatiotemporal correlation extraction. The model comprises (1) the specialized CNN feature extraction, (2) the GRU-SKIP enhanced long-temporal module adept at capturing extended patterns, (3) a transformer module employing encoder-decoder and multi-attention mechanisms to hone prediction accuracy and trim model complexity, and (4) a bespoke prediction module. When tested against real-world datasets from California of Caltrans Performance Measurement System PeMS, specifically PeMS districts 4 and 8, the CNN-GRUSKIP consistently outperformed established models such as ARIMA, Graph Wave Net, HA, LSTM, STGCN, and APTN. With its potent predictive prowess and adaptive architecture, the CNN-GRUSKIP model stands to redefine ITS applications, especially where nuanced traffic dynamics are in play.
Recommender Systems (RS) play a pivotal role in boosting user satisfaction by providing personalized product suggestions in domains such as e-commerce and entertainment. This study examines the integration of multimodal data text and audio into large language models (LLMs) with the aim of enhancing recommendation performance. Traditional text and audio recommenders encounter limitations such as the cold-start problem, and recent advancements in LLMs, while promising, are computationally expensive. To address these issues, Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) is introduced, which enhances efficiency without compromising performance. The ATFLRec framework is proposed to integrate audio and text modalities into a multimodal recommendation system, utilizing various LoRA configurations and modality fusion techniques. Results indicate that ATFLRec outperforms baseline models, including traditional and graph neural network-based approaches, achieving higher AUC scores. Furthermore, separate fine-tuning of audio and text data with distinct LoRA modules yields optimal performance, with different pooling methods and Mel filter bank numbers significantly impacting performance. This research offers valuable insights into optimizing multimodal recommender systems and advancing the integration of diverse data modalities in LLMs.
In this paper, we propose a dense monocular SLAM system, named
DeepRelativeFusion, that is capable to recover a globally consistent 3D
structure. To this end, we use a visual SLAM algorithm to reliably recover the
camera poses and semi-dense depth maps of the keyframes, and then use relative
depth prediction to densify the semi-dense depth maps and refine the keyframe
pose-graph. To improve the semi-dense depth maps, we propose an adaptive
filtering scheme, which is a structure-preserving weighted average smoothing
filter that takes into account the pixel intensity and depth of the
neighbouring pixels, yielding substantial reconstruction accuracy gain in
densification. To perform densification, we introduce two incremental
improvements upon the energy minimization framework proposed by DeepFusion: (1)
an improved cost function, and (2) the use of single-image relative depth
prediction. After densification, we update the keyframes with two-view
consistent optimized semi-dense and dense depth maps to improve pose-graph
optimization, providing a feedback loop to refine the keyframe poses for
accurate scene reconstruction. Our system outperforms the state-of-the-art
dense SLAM systems quantitatively in dense reconstruction accuracy by a large
margin.
14 Sep 2020
In this paper, we demonstrate that higher order singular value decomposition (HOSVD) can be used to identify special states in three qubits by local unitary (LU) operations. Since the matrix unfoldings of three qubits are related to their reduced density matrices, HOSVD simultaneously diagonalizes the one-body reduced density matrices of three qubits. From the all-orthogonality conditions of HOSVD, we computed the special states of three qubits. Furthermore, we showed that it is possible to construct a polytope that encapsulates all the special states of three qubits by LU operations with HOSVD.
Saving energy is an important issue for cloud providers to reduce energy cost
in a data center. With the increasing popularity of cloud computing, it is time
to examine various energy reduction methods for which energy consumption could
be reduced and lead us to green cloud computing. In this paper, our aim is to
propose a virtual machine selection algorithm to improve the energy efficiency
of a cloud data center. We are also presenting experimental results of the
proposed algorithm in a cloud computing based simulation environment. The
proposed algorithm dynamically took the virtual machines' allocation,
deallocation, and reallocation action to the physical server. However, it
depends on the load and heuristics based on the analysis placement of a virtual
machine which is decided over time. From the results obtained from the
simulation, we have found that our proposed virtual machine selection algorithm
reduces the total energy consumption by 19% compared to the existing one.
Therefore, the energy consumption cost of a cloud data center reduces and also
lowers the carbon footprint. Simulation-based experimental results show that
the proposed heuristics which are based on resource provisioning algorithms
reduce the energy consumption of the cloud data center and decrease the virtual
machine's migration rate.
25 Jun 2017
Development of mobile web-centric OS such as Firefox OS has created new challenges, and opportunities for digital investigators. Network traffic forensic plays an important role in cybercrime investigation to detect subject(s) and object(s) of the crime. In this chapter, we detect and analyze residual network traffic artefacts of Firefox OS in relation to two popular social networking applications (Facebook and Twitter) and one instant messaging application (Telegram). We utilized a Firefox OS simulator to generate relevant traffic while all communication data were captured using network monitoring tools. Captured network packets were examined and remnants with forensic value were reported. This paper as the first focused study on mobile Firefox OS network traffic analysis should pave the way for the future research in this direction.
The complexity of a signal can be measured by the Recurrence period density entropy (RPDE) from the reconstructed phase space. We have chosen a window based RPDE method for the classification of signals, as RPDE is an average entropic measure of the whole phase space. We have observed the changes in the complexity in cardiac signals of normal healthy person (NHP) and congestive heart failure patients (CHFP). The results show that the cardiac dynamics of a healthy subject is more complex and random compare to the same for a heart failure patient, whose dynamics is more deterministic. We have constructed a general threshold to distinguish the border line between a healthy and a congestive heart failure dynamics. The results may be useful for wide range for physiological and biomedical analysis.
03 Nov 2017
This paper proposes a new approach to diagnose broken rotor bar failure in a
line start-permanent magnet synchronous motor (LS-PMSM) using random forests.
The transient current signal during the motor startup was acquired from a
healthy motor and a faulty motor with a broken rotor bar fault. We extracted 13
statistical time domain features from the startup transient current signal, and
used these features to train and test a random forest to determine whether the
motor was operating under normal or faulty conditions. For feature selection,
we used the feature importances from the random forest to reduce the number of
features to two features. The results showed that the random forest classifies
the motor condition as healthy or faulty with an accuracy of 98.8% using all
features and with an accuracy of 98.4% by using only the mean-index and
impulsion features. The performance of the random forest was compared with a
decision tree, Na\"ive Bayes classifier, logistic regression, linear ridge, and
a support vector machine, with the random forest consistently having a higher
accuracy than the other algorithms. The proposed approach can be used in
industry for online monitoring and fault diagnostic of LS-PMSM motors and the
results can be helpful for the establishment of preventive maintenance plans in
factories.
13 Sep 2017
We study extremal type problem arising from the question: What is the maximum
number of edge-disjoint non-crossing perfect matchings on a set S of 2n points
in the plane such that their union is a triangle-free geometric graph? We
approach this problem by considering four different situations of S. In
particular, in the general position, we obtain (i) a sufficient condition for
the existence of n edge-disjoint non-crossing perfect matchings in the general
position whose union is a maximal triangle-free geometric graph, and (ii) a
lower bound on the number of edge-disjoint non-crossing perfect matchings whose
union is a triangle free geometric graph.
Most classical and post-quantum cryptographic assumptions, including integer
factorization, discrete logarithms, and Learning with Errors (LWE), rely on
algebraic structures such as rings or vector spaces. While mathematically
powerful, these structures can be exploited by quantum algorithms or advanced
algebraic attacks, raising a pressing need for structure-free alternatives. To
address this gap, we introduce the Symbolic Path Inversion Problem (SPIP), a
new computational hardness assumption based on symbolic trajectories generated
by contractive affine maps with bounded noise over Z2. Unlike traditional
systems, SPIP is inherently non-algebraic and relies on chaotic symbolic
evolution and rounding-induced non-injectivity to render inversion
computationally infeasible. We prove that SPIP is PSPACE-hard and #P-hard, and
demonstrate through empirical simulation that even short symbolic sequences
(e.g., n = 3, m = 2) can produce over 500 valid trajectories for a single
endpoint, with exponential growth reaching 2256 paths for moderate parameters.
A quantum security analysis further shows that Grover-style search offers no
practical advantage due to oracle ambiguity and verification instability. These
results position SPIP as a viable foundation for post-quantum cryptography that
avoids the vulnerabilities of algebraic symmetry while offering scalability,
unpredictability, and resistance to both classical and quantum inversion.
04 Jun 2025
Classical cryptographic systems rely heavily on structured algebraic problems, such as factorization, discrete logarithms, or lattice-based assumptions, which are increasingly vulnerable to quantum attacks and structural cryptanalysis. In response, this work introduces the Hashed Fractal Key Recovery (HFKR) problem, a non-algebraic cryptographic construction grounded in symbolic dynamics and chaotic perturbations. HFKR builds on the Symbolic Path Inversion Problem (SPIP), leveraging symbolic trajectories generated via contractive affine maps over Z2, and compressing them into fixed-length cryptographic keys using hash-based obfuscation. A key contribution of this paper is the empirical confirmation that these symbolic paths exhibit fractal behavior, quantified via box counting dimension, path geometry, and spatial density measures. The observed fractal dimension increases with trajectory length and stabilizes near 1.06, indicating symbolic self-similarity and space-filling complexity, both of which reinforce the entropy foundation of the scheme. Experimental results across 250 perturbation trials show that SHA3-512 and SHAKE256 amplify symbolic divergence effectively, achieving mean Hamming distances near 255, ideal bit-flip rates, and negligible entropy deviation. In contrast, BLAKE3 exhibits statistically uniform but weaker diffusion. These findings confirm that HFKR post-quantum security arises from the synergy between symbolic fractality and hash-based entropy amplification. The resulting construction offers a lightweight, structure-free foundation for secure key generation in adversarial settings without relying on algebraic hardness assumptions.
The adoption of ICT in classrooms is very important in order to improve
education quality, promote effective management of knowledge, and improve
delivery of knowledge in higher education. Some of the Libyan universities have
already started using E-learning in classrooms, but many challenges are still
hindering that adoption. This paper endeavors to find the obstacles that may
face the adoption of E-learning in Libya and sketches out the possible
solutions. Further, it highlights the potentials for the adoption of E-learning
in the higher education system in Libya using both qualitative and quantitative
approaches. Both questioner and interview have been used on a focused group to
collect the data. Teachers and students at Al Asmarya Islamic University have
been selected as a sample for this study. This paper reveals that the
challenges hindering teachers and students from using ICT and E-learning are:
the lack of knowledge about ICT and E-learning, the lack of ICT infrastructure,
and the lack of financial support. However, the participants show a high level
of interest in applying the ICT and E-learning in the university despite the
unsuitability of the environment.
25 Jun 2017
Mobile devices are increasingly utilized to access social media and instant messaging services, which allow users to communicate with others easily and quickly. However, the misuse of social media and instant messaging services facilitated conducting different cybercrimes such as cyber stalking, cyber bullying, slander spreading and sexual harassment. Therefore, mobile devices are an important evidentiary piece in digital investigation. In this chapter, we report the results of our investigation and analysis of social media and instant messaging services in Firefox OS. We examined three social media services (Facebook, Twitter and Google+) as well as three instant messaging services (Telegram, OpenWapp and Line). Our analysis may pave the way for future forensic investigators to trace and examine residual remnants of forensics value in FireFox OS.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.