University of Siena
The paper presents AIGIBench, a comprehensive benchmark designed to rigorously evaluate the robustness and generalization capabilities of state-of-the-art Artificial Intelligence Generated Image (AIGI) detectors. It demonstrates that current methods suffer significant performance limitations across diverse generative models, real-world image degradations, and data processing variations, confirming that AIGI detection remains an unsolved challenge.
Concept Embedding Models (CEMs) introduce a new architecture for explainable AI that represents concepts as high-dimensional vector embeddings within a bottleneck. This method improves task accuracy over previous concept bottleneck models while maintaining strong interpretability and enabling effective human interventions, even when concept annotations are incomplete.
Researchers from the University of Pisa, University of Siena, and University of Perugia developed an adaptive, black-box attack named "Pirate" to extract private knowledge bases from Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. The attack demonstrated the ability to leak up to 95.8% of a knowledge base, revealing critical privacy vulnerabilities in RAG deployments.
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have become the leading paradigm for learning on (static) graph-structured data. However, many real-world systems are dynamic in nature, since the graph and node/edge attributes change over time. In recent years, GNN-based models for temporal graphs have emerged as a promising area of research to extend the capabilities of GNNs. In this work, we provide the first comprehensive overview of the current state-of-the-art of temporal GNN, introducing a rigorous formalization of learning settings and tasks and a novel taxonomy categorizing existing approaches in terms of how the temporal aspect is represented and processed. We conclude the survey with a discussion of the most relevant open challenges for the field, from both research and application perspectives.
The Deep Concept Reasoner (DCR) is a neural-symbolic system that overcomes the interpretability-accuracy trade-off in concept-based AI by learning explicit, human-understandable fuzzy logic rules from high-dimensional concept embeddings. DCR achieves high predictive accuracy, competitive with black-box models, while generating stable and semantically meaningful explanations for diverse data types like images, tabular data, and graphs.
Recent advances in text-based image editing have enabled fine-grained manipulation of visual content guided by natural language. However, such methods are susceptible to adversarial attacks. In this work, we propose a novel attack that targets the visual component of editing methods. We introduce Attention Attack, which disrupts the cross-attention between a textual prompt and the visual representation of the image by using an automatically generated caption of the source image as a proxy for the edit prompt. This breaks the alignment between the contents of the image and their textual description, without requiring knowledge of the editing method or the editing prompt. Reflecting on the reliability of existing metrics for immunization success, we propose two novel evaluation strategies: Caption Similarity, which quantifies semantic consistency between original and adversarial edits, and semantic Intersection over Union (IoU), which measures spatial layout disruption via segmentation masks. Experiments conducted on the TEDBench++ benchmark demonstrate that our attack significantly degrades editing performance while remaining imperceptible.
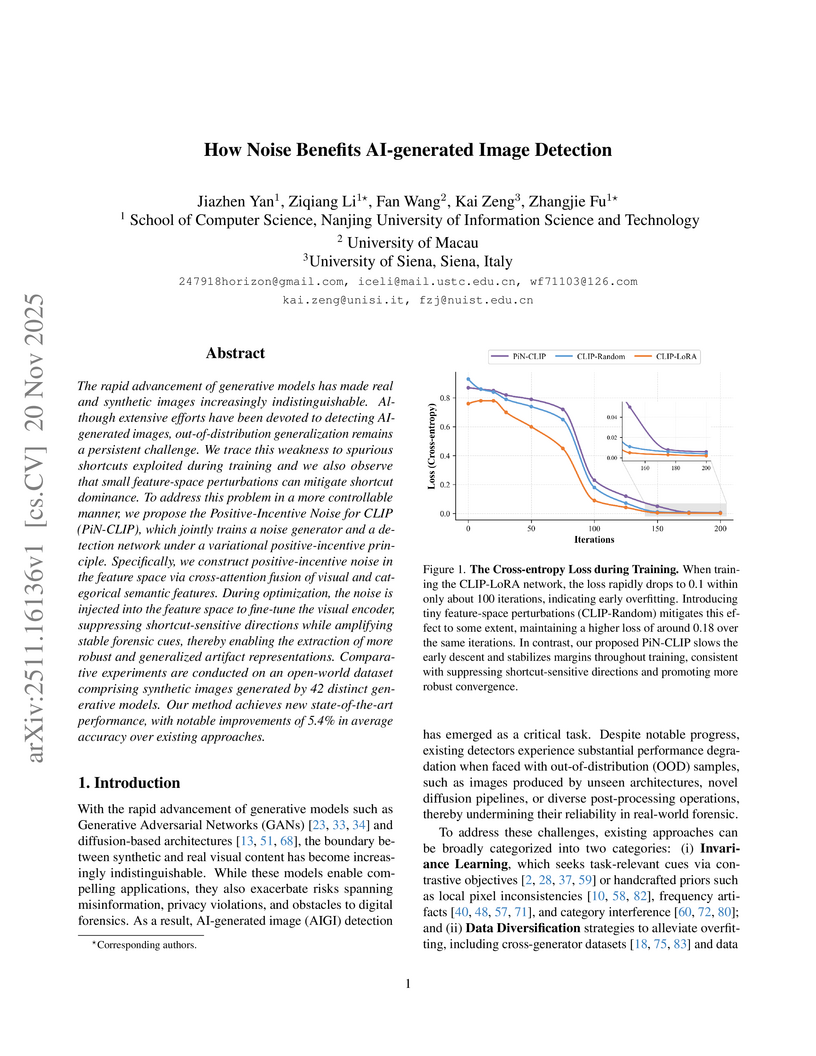
Researchers at Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology developed PiN-CLIP, a framework that uses positive-incentive noise to enhance AI-generated image detection. This method significantly improves out-of-distribution generalization, achieving 95.4% mAcc on GenImage and 85.8% mAcc on AIGIBench, while also increasing robustness to common image perturbations.
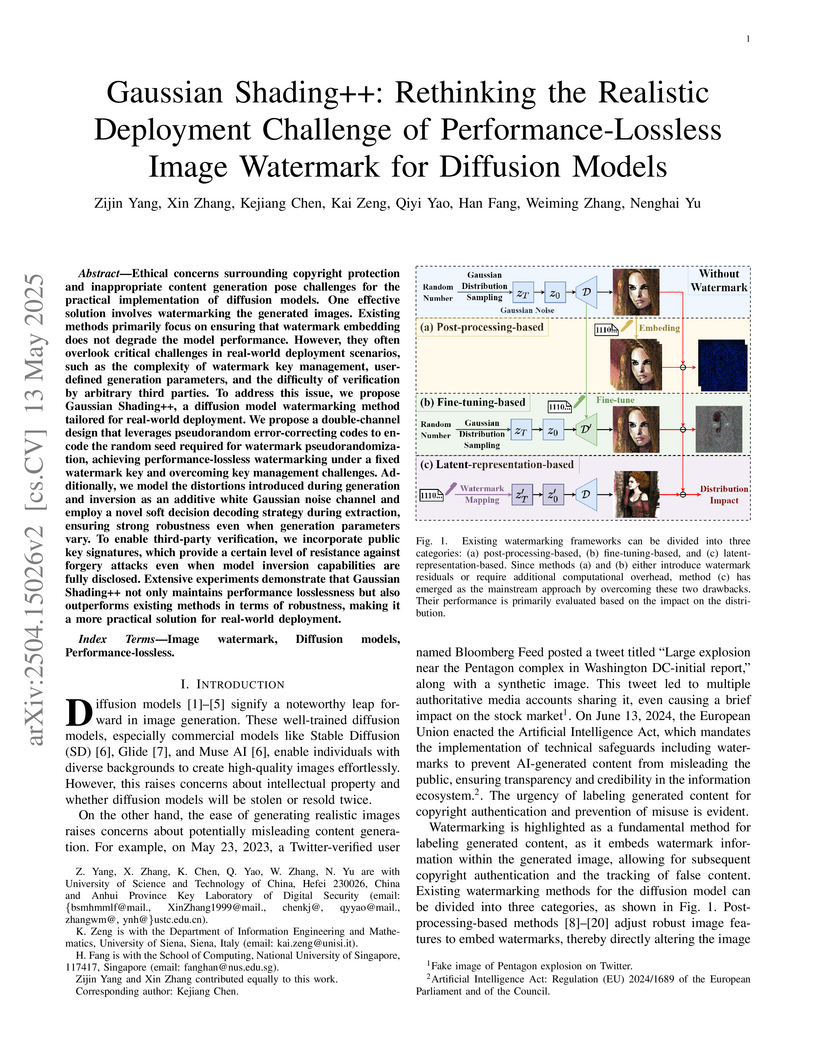
Ethical concerns surrounding copyright protection and inappropriate content
generation pose challenges for the practical implementation of diffusion
models. One effective solution involves watermarking the generated images.
Existing methods primarily focus on ensuring that watermark embedding does not
degrade the model performance. However, they often overlook critical challenges
in real-world deployment scenarios, such as the complexity of watermark key
management, user-defined generation parameters, and the difficulty of
verification by arbitrary third parties. To address this issue, we propose
Gaussian Shading++, a diffusion model watermarking method tailored for
real-world deployment. We propose a double-channel design that leverages
pseudorandom error-correcting codes to encode the random seed required for
watermark pseudorandomization, achieving performance-lossless watermarking
under a fixed watermark key and overcoming key management challenges.
Additionally, we model the distortions introduced during generation and
inversion as an additive white Gaussian noise channel and employ a novel soft
decision decoding strategy during extraction, ensuring strong robustness even
when generation parameters vary. To enable third-party verification, we
incorporate public key signatures, which provide a certain level of resistance
against forgery attacks even when model inversion capabilities are fully
disclosed. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Gaussian Shading++ not only
maintains performance losslessness but also outperforms existing methods in
terms of robustness, making it a more practical solution for real-world
deployment.
In the last three decades, human visual attention has been a topic of great interest in various disciplines. In computer vision, many models have been proposed to predict the distribution of human fixations on a visual stimulus. Recently, thanks to the creation of large collections of data, machine learning algorithms have obtained state-of-the-art performance on the task of saliency map estimation. On the other hand, computational models of scanpath are much less studied. Works are often only descriptive or task specific. This is due to the fact that the scanpath is harder to model because it must include the description of a dynamic. General purpose computational models are present in the literature, but are then evaluated in tasks of saliency prediction, losing therefore information about the dynamics and the behaviour. In addition, two technical reasons have limited the research. The first reason is the lack of robust and uniformly used set of metrics to compare the similarity between scanpath. The second reason is the lack of sufficiently large and varied scanpath datasets. In this report we want to help in both directions. We present FixaTons, a large collection of datasets human scanpaths (temporally ordered sequences of fixations) and saliency maps. It comes along with a software library for easy data usage, statistics calculation and implementation of metrics for scanpath and saliency prediction evaluation.
In recent years, spatio-temporal graph neural networks (GNNs) have attracted considerable interest in the field of time series analysis, due to their ability to capture, at once, dependencies among variables and across time points. The objective of this systematic literature review is hence to provide a comprehensive overview of the various modeling approaches and application domains of GNNs for time series classification and forecasting. A database search was conducted, and 366 papers were selected for a detailed examination of the current state-of-the-art in the field. This examination is intended to offer to the reader a comprehensive review of proposed models, links to related source code, available datasets, benchmark models, and fitting results. All this information is hoped to assist researchers in their studies. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first and broadest systematic literature review presenting a detailed comparison of results from current spatio-temporal GNN models applied to different domains. In its final part, this review discusses current limitations and challenges in the application of spatio-temporal GNNs, such as comparability, reproducibility, explainability, poor information capacity, and scalability. This paper is complemented by a GitHub repository at this https URL providing additional interactive tools to further explore the presented findings.
18 Oct 2025
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities, but their training requires extensive data and computational resources, rendering them valuable digital assets. Therefore, it is essential to watermark LLMs to protect their copyright and trace unauthorized use or resale. Existing methods for watermarking LLMs primarily rely on training LLMs with a watermarked dataset, which entails burdensome training costs and negatively impacts the LLM's performance. In addition, their watermarked texts are not logical or natural, thereby reducing the stealthiness of the watermark. To address these issues, we propose EditMark, the first watermarking method that leverages model editing to embed a training-free, stealthy, and performance-lossless watermark for LLMs. We observe that some questions have multiple correct answers. Therefore, we assign each answer a unique watermark and update the weights of LLMs to generate corresponding questions and answers through the model editing technique. In addition, we refine the model editing technique to align with the requirements of watermark embedding. Specifically, we introduce an adaptive multi-round stable editing strategy, coupled with the injection of a noise matrix, to improve both the effectiveness and robustness of the watermark embedding. Extensive experiments indicate that EditMark can embed 32-bit watermarks into LLMs within 20 seconds (Fine-tuning: 6875 seconds) with a watermark extraction success rate of 100%, which demonstrates its effectiveness and efficiency. External experiments further demonstrate that EditMark has fidelity, stealthiness, and a certain degree of robustness against common attacks.
18 Sep 2025
We give a bijection between the point-hyperplane antiflags of V(n,2) and the non-singular points of V(2n,2) with respect to a hyperbolic quadric. With the help of this bijection, we give a description of the strongly regular graph NO+(2n,2) in V(2n,2). We also describe a graph in V(2n,2) that was recently defined by Stanley and Takeda in V(n,2).
Neural-symbolic computing has now become the subject of interest of both academic and industry research laboratories. Graph Neural Networks (GNN) have been widely used in relational and symbolic domains, with widespread application of GNNs in combinatorial optimization, constraint satisfaction, relational reasoning and other scientific domains. The need for improved explainability, interpretability and trust of AI systems in general demands principled methodologies, as suggested by neural-symbolic computing. In this paper, we review the state-of-the-art on the use of GNNs as a model of neural-symbolic computing. This includes the application of GNNs in several domains as well as its relationship to current developments in neural-symbolic computing.
Foundation models have exhibited unprecedented capabilities in tackling many domains and tasks. Models such as CLIP are currently widely used to bridge cross-modal representations, and text-to-image diffusion models are arguably the leading models in terms of realistic image generation. Image generative models are trained on massive datasets that provide them with powerful internal spatial representations. In this work, we explore the potential benefits of such representations, beyond image generation, in particular, for dense visual prediction tasks. We focus on the task of image segmentation, which is traditionally solved by training models on closed-vocabulary datasets, with pixel-level annotations. To avoid the annotation cost or training large diffusion models, we constraint our setup to be zero-shot and training-free. In a nutshell, our pipeline leverages different and relatively small-sized, open-source foundation models for zero-shot open-vocabulary segmentation. The pipeline is as follows: the image is passed to both a captioner model (i.e. BLIP) and a diffusion model (i.e., Stable Diffusion Model) to generate a text description and visual representation, respectively. The features are clustered and binarized to obtain class agnostic masks for each object. These masks are then mapped to a textual class, using the CLIP model to support open-vocabulary. Finally, we add a refinement step that allows to obtain a more precise segmentation mask. Our approach (dubbed FreeSeg-Diff), which does not rely on any training, outperforms many training-based approaches on both Pascal VOC and COCO datasets. In addition, we show very competitive results compared to the recent weakly-supervised segmentation approaches. We provide comprehensive experiments showing the superiority of diffusion model features compared to other pretrained models. Project page: this https URL
The intricate morphology of brain vessels poses significant challenges for automatic segmentation models, which usually focus on a single imaging modality. However, accurately treating brain-related conditions requires a comprehensive understanding of the cerebrovascular tree, regardless of the specific acquisition procedure. Our framework effectively segments brain arteries and veins in various datasets through image-to-image translation while avoiding domain-specific model design and data harmonization between the source and the target domain. This is accomplished by employing disentanglement techniques to independently manipulate different image properties, allowing them to move from one domain to another in a label-preserving manner. Specifically, we focus on manipulating vessel appearances during adaptation while preserving spatial information, such as shapes and locations, which are crucial for correct segmentation. Our evaluation effectively bridges large and varied domain gaps across medical centers, image modalities, and vessel types. Additionally, we conduct ablation studies on the optimal number of required annotations and other architectural choices. The results highlight our framework's robustness and versatility, demonstrating the potential of domain adaptation methodologies to perform cerebrovascular image segmentation in multiple scenarios accurately. Our code is available at this https URL.
Small, fast, and lightweight drones present significant challenges for
traditional RGB cameras due to their limitations in capturing fast-moving
objects, especially under challenging lighting conditions. Event cameras offer
an ideal solution, providing high temporal definition and dynamic range, yet
existing benchmarks often lack fine temporal resolution or drone-specific
motion patterns, hindering progress in these areas. This paper introduces the
Florence RGB-Event Drone dataset (FRED), a novel multimodal dataset
specifically designed for drone detection, tracking, and trajectory
forecasting, combining RGB video and event streams. FRED features more than 7
hours of densely annotated drone trajectories, using 5 different drone models
and including challenging scenarios such as rain and adverse lighting
conditions. We provide detailed evaluation protocols and standard metrics for
each task, facilitating reproducible benchmarking. The authors hope FRED will
advance research in high-speed drone perception and multimodal spatiotemporal
understanding.
Diffusion models have become the most popular approach for high-quality image
generation, but their high computational cost still remains a significant
challenge. To address this problem, we propose U-Shape Mamba (USM), a novel
diffusion model that leverages Mamba-based layers within a U-Net-like
hierarchical structure. By progressively reducing sequence length in the
encoder and restoring it in the decoder through Mamba blocks, USM significantly
lowers computational overhead while maintaining strong generative capabilities.
Experimental results against Zigma, which is currently the most efficient
Mamba-based diffusion model, demonstrate that USM achieves one-third the
GFlops, requires less memory and is faster, while outperforming Zigma in image
quality. Frechet Inception Distance (FID) is improved by 15.3, 0.84 and 2.7
points on AFHQ, CelebAHQ and COCO datasets, respectively. These findings
highlight USM as a highly efficient and scalable solution for diffusion-based
generative models, making high-quality image synthesis more accessible to the
research community while reducing computational costs.
Effectively learning from sequential data is a longstanding goal of Artificial Intelligence, especially in the case of long sequences. From the dawn of Machine Learning, several researchers have pursued algorithms and architectures capable of processing sequences of patterns, retaining information about past inputs while still leveraging future data, without losing precious long-term dependencies and correlations. While such an ultimate goal is inspired by the human hallmark of continuous real-time processing of sensory information, several solutions have simplified the learning paradigm by artificially limiting the processed context or dealing with sequences of limited length, given in advance. These solutions were further emphasized by the ubiquity of Transformers, which initially overshadowed the role of Recurrent Neural Nets. However, recurrent networks are currently experiencing a strong recent revival due to the growing popularity of (deep) State-Space models and novel instances of large-context Transformers, which are both based on recurrent computations that aim to go beyond several limits of currently ubiquitous technologies. The fast development of Large Language Models has renewed the interest in efficient solutions to process data over time. This survey provides an in-depth summary of the latest approaches that are based on recurrent models for sequential data processing. A complete taxonomy of recent trends in architectural and algorithmic solutions is reported and discussed, guiding researchers in this appealing research field. The emerging picture suggests that there is room for exploring novel routes, constituted by learning algorithms that depart from the standard Backpropagation Through Time, towards a more realistic scenario where patterns are effectively processed online, leveraging local-forward computations, and opening new directions for research on this topic.
Semantic segmentation is a fundamental task in medical image analysis, aiding medical decision-making by helping radiologists distinguish objects in an image. Research in this field has been driven by deep learning applications, which have the potential to scale these systems even in the presence of noise and artifacts. However, these systems are not yet perfected. We argue that performance can be improved by incorporating common medical knowledge into the segmentation model's loss function. To this end, we introduce Logic Tensor Networks (LTNs) to encode medical background knowledge using first-order logic (FOL) rules. The encoded rules span from constraints on the shape of the produced segmentation, to relationships between different segmented areas. We apply LTNs in an end-to-end framework with a SwinUNETR for semantic segmentation. We evaluate our method on the task of segmenting the hippocampus in brain MRI scans. Our experiments show that LTNs improve the baseline segmentation performance, especially when training data is scarce. Despite being in its preliminary stages, we argue that neurosymbolic methods are general enough to be adapted and applied to other medical semantic segmentation tasks.
Last-generation GAN models allow to generate synthetic images which are
visually indistinguishable from natural ones, raising the need to develop tools
to distinguish fake and natural images thus contributing to preserve the
trustworthiness of digital images. While modern GAN models can generate very
high-quality images with no visible spatial artifacts, reconstruction of
consistent relationships among colour channels is expectedly more difficult. In
this paper, we propose a method for distinguishing GAN-generated from natural
images by exploiting inconsistencies among spectral bands, with specific focus
on the generation of synthetic face images. Specifically, we use cross-band
co-occurrence matrices, in addition to spatial co-occurrence matrices, as input
to a CNN model, which is trained to distinguish between real and synthetic
faces. The results of our experiments confirm the goodness of our approach
which outperforms a similar detection technique based on intra-band spatial
co-occurrences only. The performance gain is particularly significant with
regard to robustness against post-processing, like geometric transformations,
filtering and contrast manipulations.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.