Bar Ilan University
 ETH Zurich
ETH Zurich KAIST
KAIST University of WashingtonRensselaer Polytechnic Institute
University of WashingtonRensselaer Polytechnic Institute Google DeepMind
Google DeepMind University of Amsterdam
University of Amsterdam University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign University of CambridgeHeidelberg University
University of CambridgeHeidelberg University University of WaterlooFacebook
University of WaterlooFacebook Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University University of Southern California
University of Southern California Google
Google New York UniversityUniversity of Stuttgart
New York UniversityUniversity of Stuttgart UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley National University of Singapore
National University of Singapore University College London
University College London University of OxfordLMU Munich
University of OxfordLMU Munich Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University University of California, Irvine
University of California, Irvine Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University Stanford University
Stanford University University of Michigan
University of Michigan University of Copenhagen
University of Copenhagen The Chinese University of Hong KongUniversity of Melbourne
The Chinese University of Hong KongUniversity of Melbourne MetaUniversity of Edinburgh
MetaUniversity of Edinburgh OpenAI
OpenAI The University of Texas at Austin
The University of Texas at Austin Cornell University
Cornell University University of California, San DiegoYonsei University
University of California, San DiegoYonsei University McGill University
McGill University Boston UniversityUniversity of Bamberg
Boston UniversityUniversity of Bamberg Nanyang Technological University
Nanyang Technological University Microsoft
Microsoft KU Leuven
KU Leuven Columbia UniversityUC Santa Barbara
Columbia UniversityUC Santa Barbara Allen Institute for AIGerman Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI)
Allen Institute for AIGerman Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI) University of Pennsylvania
University of Pennsylvania Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University Arizona State University
Arizona State University University of Maryland
University of Maryland University of TokyoUniversity of North Carolina at Chapel HillHebrew University of JerusalemAmazonTilburg UniversityUniversity of Massachusetts AmherstUniversity of RochesterUniversity of Duisburg-EssenSapienza University of RomeUniversity of Sheffield
University of TokyoUniversity of North Carolina at Chapel HillHebrew University of JerusalemAmazonTilburg UniversityUniversity of Massachusetts AmherstUniversity of RochesterUniversity of Duisburg-EssenSapienza University of RomeUniversity of Sheffield Princeton University
Princeton University HKUSTUniversity of TübingenTU BerlinSaarland UniversityTechnical University of DarmstadtUniversity of HaifaUniversity of TrentoUniversity of MontrealBilkent UniversityUniversity of Cape TownBar Ilan UniversityIBMUniversity of Mannheim
HKUSTUniversity of TübingenTU BerlinSaarland UniversityTechnical University of DarmstadtUniversity of HaifaUniversity of TrentoUniversity of MontrealBilkent UniversityUniversity of Cape TownBar Ilan UniversityIBMUniversity of Mannheim ServiceNowPotsdam UniversityPolish-Japanese Academy of Information TechnologySalesforceASAPPAI21 LabsValencia Polytechnic UniversityUniversity of Trento, Italy
ServiceNowPotsdam UniversityPolish-Japanese Academy of Information TechnologySalesforceASAPPAI21 LabsValencia Polytechnic UniversityUniversity of Trento, ItalyA large-scale and diverse benchmark, BIG-bench, was introduced to rigorously evaluate the capabilities and limitations of large language models across 204 tasks. The evaluation revealed that even state-of-the-art models currently achieve aggregate scores below 20 (on a 0-100 normalized scale), indicating significantly lower performance compared to human experts.
03 Sep 2025
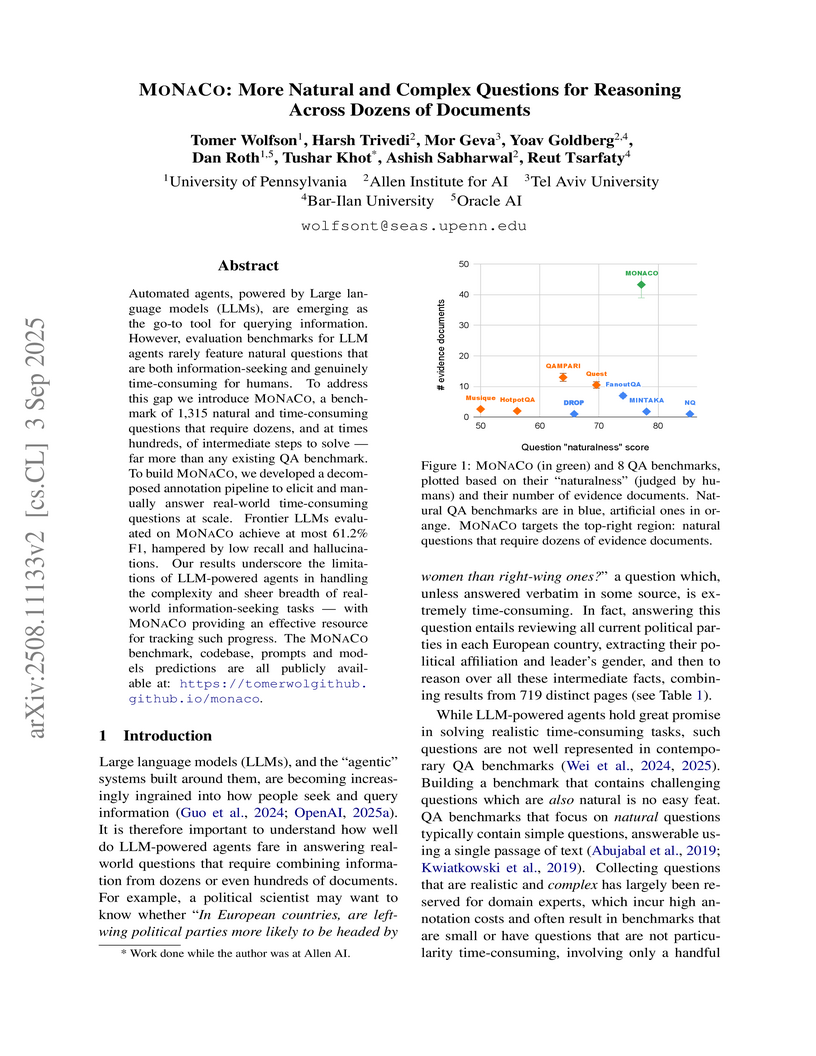
MONACO introduces a benchmark of 1,315 natural, complex, and time-consuming information-seeking questions that require reasoning across dozens of documents, demonstrating that frontier Large Language Models achieve an F1 score of only 61.2% and struggle significantly with extensive information aggregation and retrieval robustness.
MaskedMimic introduces a unified framework for physics-based character control by reformulating it as a masked motion inpainting problem. This approach allows a single system to generate physically plausible full-body motions from various partial constraints, including full-body tracking, VR inputs, object interactions, path following, and text-to-motion synthesis.
LEACE presents a closed-form, provably optimal solution for linear concept erasure in machine learning models that minimizes disruption to the original embedding. This method enables 'concept scrubbing' for multi-layer interventions in deep neural networks, demonstrating high effectiveness in debiasing large language models and precise causal probing with minimal impact on main-task performance.
BitFit, developed by researchers at Bar Ilan University and AI2, proposes a method for fine-tuning transformer-based masked language models by training only bias terms and the classification layer. This approach achieves performance comparable to full fine-tuning on GLUE benchmarks while modifying as little as 0.08% of total model parameters and often outperforming full fine-tuning in data-scarce scenarios.
In Omnimatte, one aims to decompose a given video into semantically meaningful layers, including the background and individual objects along with their associated effects, such as shadows and reflections. Existing methods often require extensive training or costly self-supervised optimization. In this paper, we present OmnimatteZero, a training-free approach that leverages off-the-shelf pre-trained video diffusion models for omnimatte. It can remove objects from videos, extract individual object layers along with their effects, and composite those objects onto new videos. These are accomplished by adapting zero-shot image inpainting techniques for video object removal, a task they fail to handle effectively out-of-the-box. To overcome this, we introduce temporal and spatial attention guidance modules that steer the diffusion process for accurate object removal and temporally consistent background reconstruction. We further show that self-attention maps capture information about the object and its footprints and use them to inpaint the object's effects, leaving a clean background. Additionally, through simple latent arithmetic, object layers can be isolated and recombined seamlessly with new video layers to produce new videos. Evaluations show that OmnimatteZero not only achieves superior performance in terms of background reconstruction but also sets a new record for the fastest Omnimatte approach, achieving real-time performance with minimal frame runtime.
Low-rank gradient-based optimization methods have significantly improved memory efficiency during the training of large language models (LLMs), enabling operations within constrained hardware without sacrificing performance. However, these methods primarily emphasize memory savings, often overlooking potential acceleration in convergence due to their reliance on standard isotropic steepest descent techniques, which can perform suboptimally in the highly anisotropic landscapes typical of deep networks, particularly LLMs. In this paper, we propose SUMO (Subspace-Aware Moment-Orthogonalization), an optimizer that employs exact singular value decomposition (SVD) for moment orthogonalization within a dynamically adapted low-dimensional subspace, enabling norm-inducing steepest descent optimization steps. By explicitly aligning optimization steps with the spectral characteristics of the loss landscape, SUMO effectively mitigates approximation errors associated with commonly used methods like Newton-Schulz orthogonalization approximation. We theoretically establish an upper bound on these approximation errors, proving their dependence on the condition numbers of moments, conditions we analytically demonstrate are encountered during LLM training. Furthermore, we both theoretically and empirically illustrate that exact orthogonalization via SVD substantially improves convergence rates while reducing overall complexity. Empirical evaluations confirm that SUMO accelerates convergence, enhances stability, improves performance, and reduces memory requirements by up to 20% compared to state-of-the-art methods.
Researchers from Bar Ilan University and AI2 developed Iterative Nullspace Projection (INLP), a data-driven method to deterministically remove specific linear information from neural representations. This approach effectively mitigated gender bias in word embeddings and achieved fairer classification performance, often with minimal impact on main task accuracy.
Feed-Forward Network (FFN) layers in Transformer-based Language Models build predictions by dynamically promoting human-interpretable concepts within the vocabulary space, rather than primarily eliminating tokens. Decomposing FFN outputs into individual 'sub-updates' provides a mechanistic understanding that enables practical applications in controlling generation and improving computational efficiency.
We present NER Retriever, a zero-shot retrieval framework for ad-hoc Named Entity Retrieval, a variant of Named Entity Recognition (NER), where the types of interest are not provided in advance, and a user-defined type description is used to retrieve documents mentioning entities of that type. Instead of relying on fixed schemas or fine-tuned models, our method builds on internal representations of large language models (LLMs) to embed both entity mentions and user-provided open-ended type descriptions into a shared semantic space. We show that internal representations, specifically the value vectors from mid-layer transformer blocks, encode fine-grained type information more effectively than commonly used top-layer embeddings. To refine these representations, we train a lightweight contrastive projection network that aligns type-compatible entities while separating unrelated types. The resulting entity embeddings are compact, type-aware, and well-suited for nearest-neighbor search. Evaluated on three benchmarks, NER Retriever significantly outperforms both lexical and dense sentence-level retrieval baselines. Our findings provide empirical support for representation selection within LLMs and demonstrate a practical solution for scalable, schema-free entity retrieval. The NER Retriever Codebase is publicly available at this https URL
05 Apr 2022
We formalize the concept of the modular energy operator within the Page and Wootters timeless framework. As a result, this operator is elevated to the same status as the more studied modular operators of position and momentum. In analogy with dynamical nonlocality in space associated with the modular momentum, we introduce and analyze the nonlocality in time associated with the modular energy operator. Some applications of our formalization are provided through illustrative examples.
The Story2Board framework enables training-free generation of expressive, multi-panel storyboards from natural language, maintaining strong character consistency while allowing for diverse scene compositions and narrative progression. It achieves this by employing an LLM-based prompt decomposition alongside two novel in-context consistency mechanisms during the diffusion model's denoising process.
Gradient based optimization is fundamental to most modern deep reinforcement learning algorithms, however, it introduces significant sensitivity to hyperparameters, unstable training dynamics, and high computational costs. We propose TabPFN RL, a novel gradient free deep RL framework that repurposes the meta trained transformer TabPFN as a Q function approximator. Originally developed for tabular classification, TabPFN is a transformer pre trained on millions of synthetic datasets to perform inference on new unseen datasets via in context learning. Given an in context dataset of sample label pairs and new unlabeled data, it predicts the most likely labels in a single forward pass, without gradient updates or task specific fine tuning. We use TabPFN to predict Q values using inference only, thereby eliminating the need for back propagation at both training and inference. To cope with the model's fixed context budget, we design a high reward episode gate that retains only the top 5% of trajectories. Empirical evaluations on the Gymnasium classic control suite demonstrate that TabPFN RL matches or surpasses Deep Q Network on CartPole v1, MountainCar v0, and Acrobot v1, without applying gradient descent or any extensive hyperparameter tuning. We discuss the theoretical aspects of how bootstrapped targets and non stationary visitation distributions violate the independence assumptions encoded in TabPFN's prior, yet the model retains a surprising generalization capacity. We further formalize the intrinsic context size limit of in context RL algorithms and propose principled truncation strategies that enable continual learning when the context is full. Our results establish prior fitted networks such as TabPFN as a viable foundation for fast and computationally efficient RL, opening new directions for gradient free RL with large pre trained transformers.
15 Jun 2025
This Google Research paper proposes a comprehensive taxonomy of knowledge conflict types in search-augmented LLMs, accompanied by a new expert-annotated benchmark, CONFLICTS. The work evaluates how effectively LLMs identify and address these conflicts, demonstrating that explicitly providing conflict type information or using taxonomy-aware prompting strategies significantly improves the appropriateness and style of LLM responses.
A new training-free method named ADD-IT enables seamless and contextually plausible object insertion into images based on textual instructions. It achieves state-of-the-art performance, significantly improving object placement plausibility on a new benchmark by raising the affordance score from 47.4% to 82.8%.
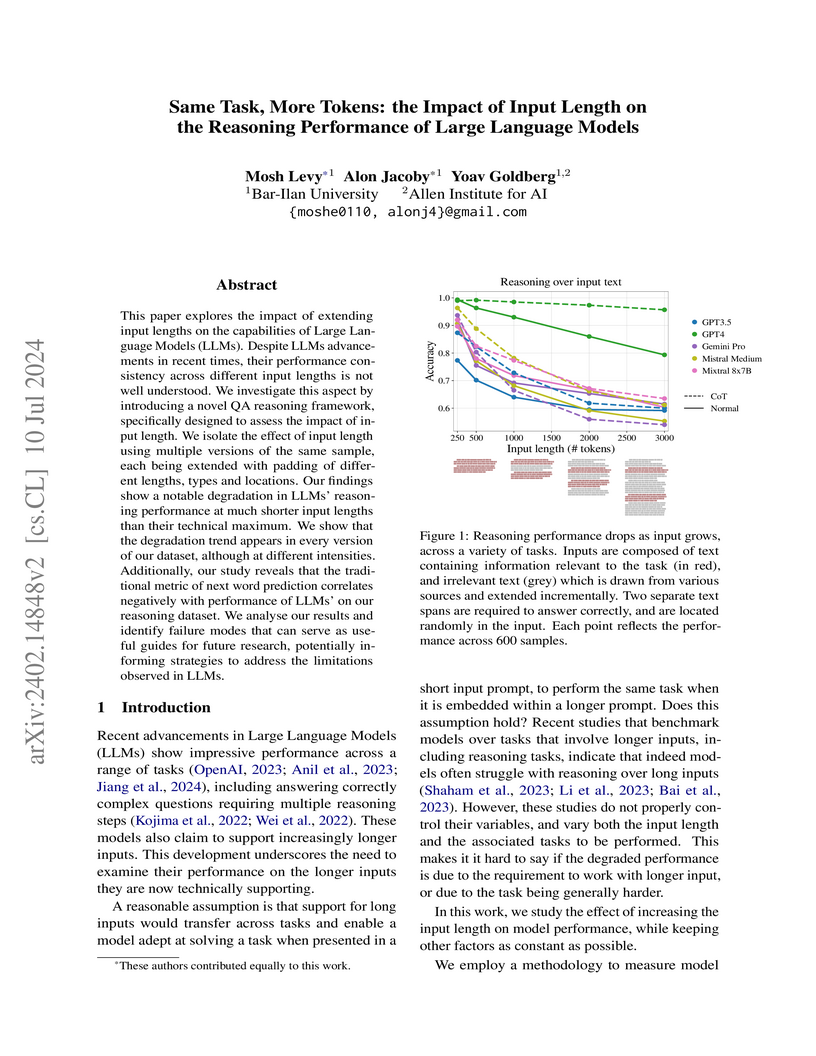
This research from Bar-Ilan University and the Allen Institute for AI systematically investigates how increasing input length impacts the reasoning performance of Large Language Models using the controlled FLenQA framework. The study reveals significant performance degradation across models as input length grows, even when the core reasoning task remains constant, and identifies specific length-induced failure modes such as increased refusal rates and reduced CoT coverage.
Text-to-image diffusion models can generate stunning visuals, yet they often fail at tasks children find trivial--like placing a dog to the right of a teddy bear rather than to the left. When combinations get more unusual--a giraffe above an airplane--these failures become even more pronounced. Existing methods attempt to fix these spatial reasoning failures through model fine-tuning or test-time optimization with handcrafted losses that are suboptimal. Rather than imposing our assumptions about spatial encoding, we propose learning these objectives directly from the model's internal representations. We introduce Learn-to-Steer, a novel framework that learns data-driven objectives for test-time optimization rather than handcrafting them. Our key insight is to train a lightweight classifier that decodes spatial relationships from the diffusion model's cross-attention maps, then deploy this classifier as a learned loss function during inference. Training such classifiers poses a surprising challenge: they can take shortcuts by detecting linguistic traces rather than learning true spatial patterns. We solve this with a dual-inversion strategy that enforces geometric understanding. Our method dramatically improves spatial accuracy: from 0.20 to 0.61 on FLUX.1-dev and from 0.07 to 0.54 on SD2.1 across standard benchmarks. Moreover, our approach generalizes to multiple relations and significantly improves accuracy.
The task of "unlearning" certain concepts in large language models (LLMs) has attracted immense attention recently, due to its importance in mitigating undesirable model behaviours, such as the generation of harmful, private, or incorrect information. Current protocols to evaluate unlearning methods largely rely on behavioral tests, without monitoring the presence of unlearned knowledge within the model's parameters. This residual knowledge can be adversarially exploited to recover the erased information post-unlearning. We argue that unlearning should also be evaluated internally, by considering changes in the parametric knowledge traces of the unlearned concepts. To this end, we propose a general evaluation methodology that leverages vocabulary projections to inspect concepts encoded in model parameters. We use this approach to localize "concept vectors" - parameter vectors that encode concrete concepts - and construct ConceptVectors, a benchmark dataset containing hundreds of common concepts and their parametric knowledge traces within two open-source LLMs. Evaluation on ConceptVectors shows that existing unlearning methods minimally impact concept vectors and mostly suppress them during inference, while directly ablating these vectors demonstrably removes the associated knowledge and significantly reduces the model's susceptibility to adversarial manipulation. Our results highlight limitations in behavioral-based unlearning evaluations and call for future work to include parameter-based evaluations. To support this, we release our code and benchmark at this https URL.
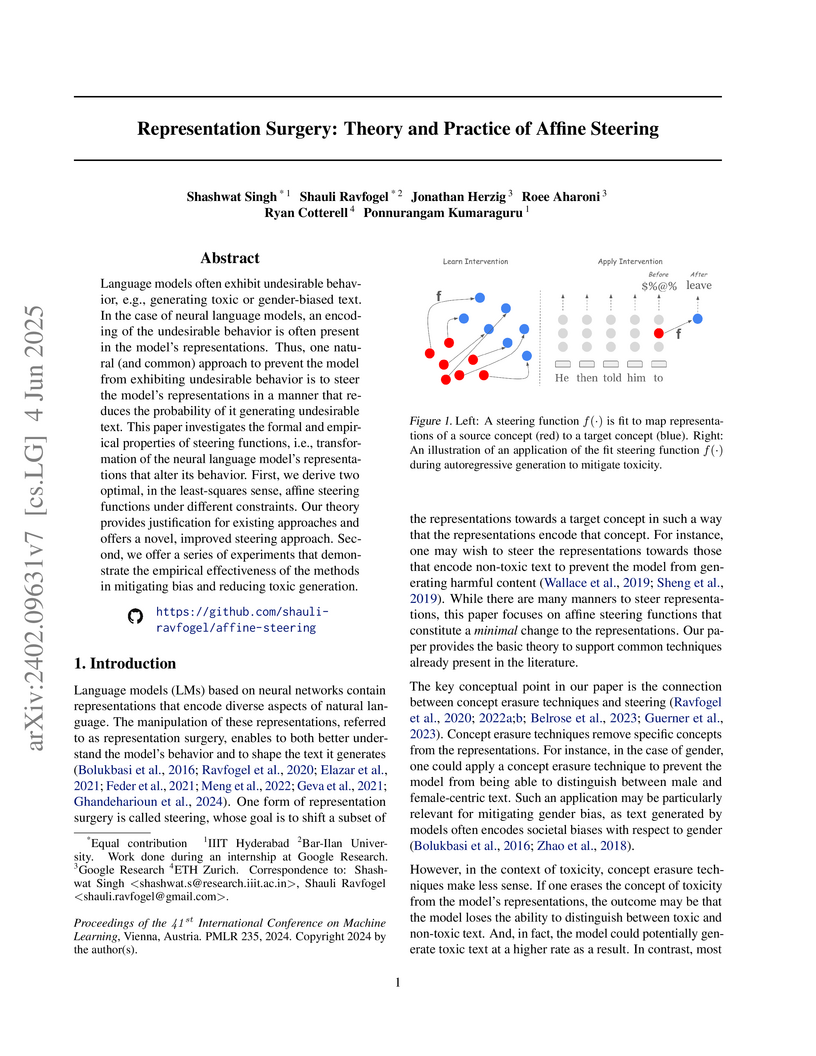
Language models often exhibit undesirable behavior, e.g., generating toxic or
gender-biased text. In the case of neural language models, an encoding of the
undesirable behavior is often present in the model's representations. Thus, one
natural (and common) approach to prevent the model from exhibiting undesirable
behavior is to steer the model's representations in a manner that reduces the
probability of it generating undesirable text. This paper investigates the
formal and empirical properties of steering functions, i.e., transformation of
the neural language model's representations that alter its behavior. First, we
derive two optimal, in the least-squares sense, affine steering functions under
different constraints. Our theory provides justification for existing
approaches and offers a novel, improved steering approach. Second, we offer a
series of experiments that demonstrate the empirical effectiveness of the
methods in mitigating bias and reducing toxic generation.
REVEAL, a new benchmark for evaluating Chain-of-Thought (CoT) verifiers, provides fine-grained, step-level annotations for LLM reasoning, demonstrating that current models frequently introduce factual errors in their reasoning steps. The dataset enables a more transparent, process-oriented assessment of LLM reasoning beyond final answer correctness.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.