Beijing Key Laboratory of Big Data Management and Analysis Methods
This work presents the first systematic study of object hallucination in Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs), demonstrating that this issue is severe and linked to biases in visual instruction tuning data. The authors introduce POPE, a polling-based evaluation method, which offers a more stable and reliable assessment of hallucination, revealing that some LVLMs exhibit significant overconfidence and higher hallucination rates than previous models.
In multi-task learning (MTL), gradient balancing has recently attracted more research interest than loss balancing since it often leads to better performance. However, loss balancing is much more efficient than gradient balancing, and thus it is still worth further exploration in MTL. Note that prior studies typically ignore that there exist varying improvable gaps across multiple tasks, where the improvable gap per task is defined as the distance between the current training progress and desired final training progress. Therefore, after loss balancing, the performance imbalance still arises in many cases. In this paper, following the loss balancing framework, we propose two novel improvable gap balancing (IGB) algorithms for MTL: one takes a simple heuristic, and the other (for the first time) deploys deep reinforcement learning for MTL. Particularly, instead of directly balancing the losses in MTL, both algorithms choose to dynamically assign task weights for improvable gap balancing. Moreover, we combine IGB and gradient balancing to show the complementarity between the two types of algorithms. Extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets demonstrate that our IGB algorithms lead to the best results in MTL via loss balancing and achieve further improvements when combined with gradient balancing. Code is available at this https URL.
Adapting large-scale foundation models in multi-task scenarios often suffers from task conflict and oblivion. To mitigate such issues, we propose a novel ''model MoE-ization'' strategy that leads to a conflict- and oblivion-resistant multi-task adaptation method. Given a weight matrix of a pre-trained model, our method applies SVD to it and introduces a learnable router to adjust its singular values based on tasks and samples. Accordingly, the weight matrix becomes a Mixture of Orthogonal Rank-one Experts (MoORE), in which each expert corresponds to the outer product of a left singular vector and the corresponding right one. We can improve the model capacity by imposing a learnable orthogonal transform on the right singular vectors. Unlike low-rank adaptation (LoRA) and its MoE-driven variants, MoORE guarantees the experts' orthogonality and maintains the column space of the original weight matrix. These two properties make the adapted model resistant to the conflicts among the new tasks and the oblivion of its original tasks, respectively. Experiments on various datasets demonstrate that MoORE outperforms existing multi-task adaptation methods consistently, showing its superiority in terms of conflict- and oblivion-resistance. The code of the experiments is available at this https URL.
Researchers at Renmin University of China developed RLMEC, a reinforcement learning framework that enhances Large Language Models' performance on complex reasoning tasks. It achieves this by providing precise, token-level supervision signals via a generative reward model, leading to consistent accuracy improvements across various reasoning benchmarks.
Multi-hop Question Answering over Knowledge Graph~(KGQA) aims to find the answer entities that are multiple hops away from the topic entities mentioned in a natural language question on a large-scale Knowledge Graph (KG). To cope with the vast search space, existing work usually adopts a two-stage approach: it first retrieves a relatively small subgraph related to the question and then performs the reasoning on the subgraph to find the answer entities accurately. Although these two stages are highly related, previous work employs very different technical solutions for developing the retrieval and reasoning models, neglecting their relatedness in task essence. In this paper, we propose UniKGQA, a novel approach for multi-hop KGQA task, by unifying retrieval and reasoning in both model architecture and parameter learning. For model architecture, UniKGQA consists of a semantic matching module based on a pre-trained language model~(PLM) for question-relation semantic matching, and a matching information propagation module to propagate the matching information along the directed edges on KGs. For parameter learning, we design a shared pre-training task based on question-relation matching for both retrieval and reasoning models, and then propose retrieval- and reasoning-oriented fine-tuning strategies. Compared with previous studies, our approach is more unified, tightly relating the retrieval and reasoning stages. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets have demonstrated the effectiveness of our method on the multi-hop KGQA task. Our codes and data are publicly available at~\url{this https URL}.
Prompt Tuning (PT) enables the adaptation of Pre-trained Large Language
Models (PLMs) to downstream tasks by optimizing a small amount of soft virtual
tokens, which are prepended to the input token embeddings. Recently, Decomposed
Prompt Tuning (DePT) has demonstrated superior adaptation capabilities by
decomposing the soft prompt into a shorter soft prompt and a pair of low-rank
matrices. The product of the pair of low-rank matrices is added to the input
token embeddings to offset them. Additionally, DePT achieves faster inference
compared to PT due to the shorter soft prompt. However, in this paper, we find
that the position-based token embedding offsets of DePT restrict its ability to
generalize across diverse model inputs, and that the shared embedding offsets
across many token embeddings result in sub-optimization. To tackle these
issues, we introduce Adaptive Decomposed Prompt Tuning (ADePT), which is
composed of a short soft prompt and a shallow token-shared feed-forward neural
network. ADePT utilizes the token-shared feed-forward neural network to learn
the embedding offsets for each token, enabling adaptive embedding offsets that
vary according to the model input and better optimization of token embedding
offsets. This enables ADePT to achieve superior adaptation performance without
requiring more inference time or additional trainable parameters compared to
vanilla PT and its variants. In comprehensive experiments across 23 natural
language processing tasks and 4 typical PLMs of different scales, ADePT
consistently surpasses the other leading parameter-efficient fine-tuning
methods, and even outperforms the full fine-tuning in certain scenarios. We
also provide a theoretical analysis towards ADePT. Code is available at
this https URL
The recent success of large language models (LLMs) has shown great potential to develop more powerful conversational recommender systems (CRSs), which rely on natural language conversations to satisfy user needs. In this paper, we embark on an investigation into the utilization of ChatGPT for conversational recommendation, revealing the inadequacy of the existing evaluation protocol. It might over-emphasize the matching with the ground-truth items or utterances generated by human annotators, while neglecting the interactive nature of being a capable CRS. To overcome the limitation, we further propose an interactive Evaluation approach based on LLMs named iEvaLM that harnesses LLM-based user simulators. Our evaluation approach can simulate various interaction scenarios between users and systems. Through the experiments on two publicly available CRS datasets, we demonstrate notable improvements compared to the prevailing evaluation protocol. Furthermore, we emphasize the evaluation of explainability, and ChatGPT showcases persuasive explanation generation for its recommendations. Our study contributes to a deeper comprehension of the untapped potential of LLMs for CRSs and provides a more flexible and easy-to-use evaluation framework for future research endeavors. The codes and data are publicly available at this https URL.
A comprehensive survey consolidates recent advancements in applying diffusion models to non-autoregressive (NAR) text generation, categorizing diverse approaches and highlighting their capability to improve text quality while preserving parallel generation efficiency.
Despite the superior performance, Large Language Models~(LLMs) require significant computational resources for deployment and use. To overcome this issue, quantization methods have been widely applied to reduce the memory footprint of LLMs as well as increasing the inference rate. However, a major challenge is that low-bit quantization methods often lead to performance degradation. It is important to understand how quantization impacts the capacity of LLMs. Different from previous studies focused on overall performance, this work aims to investigate the impact of quantization on \emph{emergent abilities}, which are important characteristics that distinguish LLMs from small language models. Specially, we examine the abilities of in-context learning, chain-of-thought reasoning, and instruction-following in quantized LLMs. Our empirical experiments show that these emergent abilities still exist in 4-bit quantization models, while 2-bit models encounter severe performance degradation on the test of these abilities. To improve the performance of low-bit models, we conduct two special experiments: (1) fine-gained impact analysis that studies which components (or substructures) are more sensitive to quantization, and (2) performance compensation through model fine-tuning. Our work derives a series of important findings to understand the impact of quantization on emergent abilities, and sheds lights on the possibilities of extremely low-bit quantization for LLMs.
ChatCoT unifies Chain-of-Thought reasoning with external tool use in large language models by framing their interaction as a multi-turn conversation. This framework achieved a 7.9% relative accuracy improvement on the MATH dataset and 59.2% accuracy on HotpotQA by enabling dynamic tool invocation within the reasoning process.
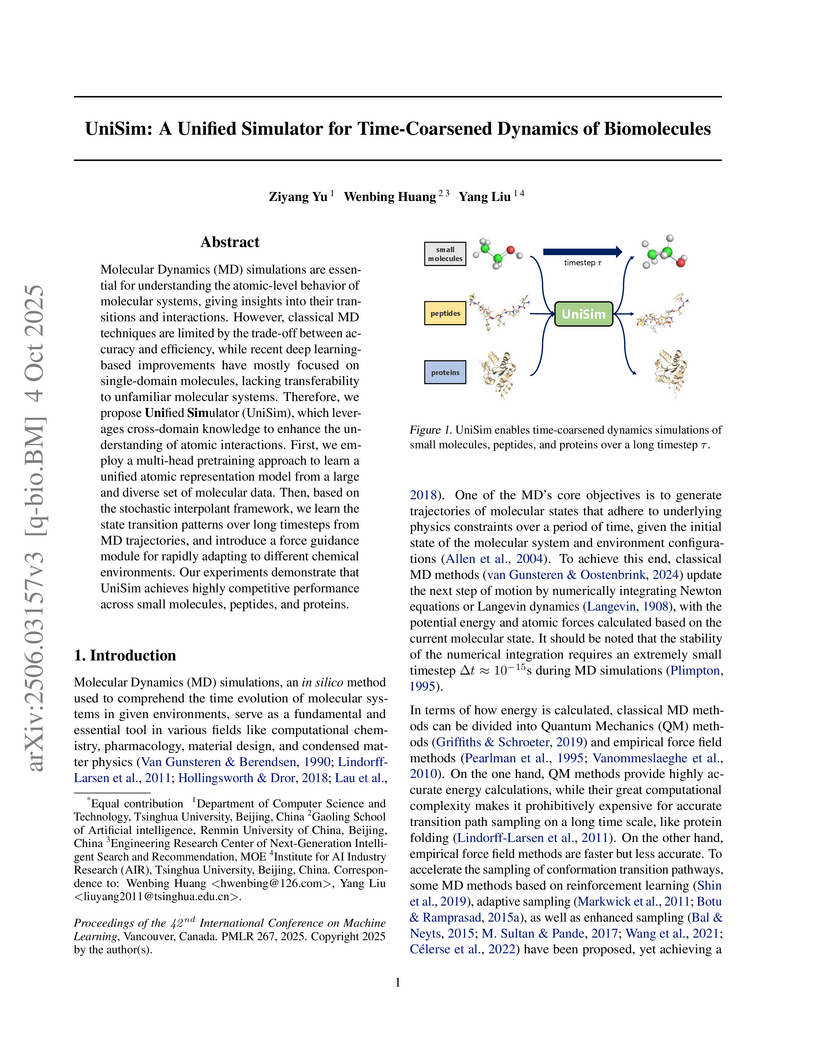
Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations are essential for understanding the atomic-level behavior of molecular systems, giving insights into their transitions and interactions. However, classical MD techniques are limited by the trade-off between accuracy and efficiency, while recent deep learning-based improvements have mostly focused on single-domain molecules, lacking transferability to unfamiliar molecular systems. Therefore, we propose \textbf{Uni}fied \textbf{Sim}ulator (UniSim), which leverages cross-domain knowledge to enhance the understanding of atomic interactions. First, we employ a multi-head pretraining approach to learn a unified atomic representation model from a large and diverse set of molecular data. Then, based on the stochastic interpolant framework, we learn the state transition patterns over long timesteps from MD trajectories, and introduce a force guidance module for rapidly adapting to different chemical environments. Our experiments demonstrate that UniSim achieves highly competitive performance across small molecules, peptides, and proteins.
Nonlinear dynamics is ubiquitous in nature and commonly seen in various science and engineering disciplines. Distilling analytical expressions that govern nonlinear dynamics from limited data remains vital but challenging. To tackle this fundamental issue, we propose a novel Symbolic Physics Learner (SPL) machine to discover the mathematical structure of nonlinear dynamics. The key concept is to interpret mathematical operations and system state variables by computational rules and symbols, establish symbolic reasoning of mathematical formulas via expression trees, and employ a Monte Carlo tree search (MCTS) agent to explore optimal expression trees based on measurement data. The MCTS agent obtains an optimistic selection policy through the traversal of expression trees, featuring the one that maps to the arithmetic expression of underlying physics. Salient features of the proposed framework include search flexibility and enforcement of parsimony for discovered equations. The efficacy and superiority of the SPL machine are demonstrated by numerical examples, compared with state-of-the-art baselines.
18 Oct 2024
Public scarce resource allocation plays a crucial role in economics as it directly influences the efficiency and equity in society. Traditional studies including theoretical model-based, empirical study-based and simulation-based methods encounter limitations due to the idealized assumption of complete information and individual rationality, as well as constraints posed by limited available data. In this work, we propose an innovative framework, SRAP-Agent (Simulating and Optimizing Scarce Resource Allocation Policy with LLM-based Agent), which integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) into economic simulations, aiming to bridge the gap between theoretical models and real-world dynamics. Using public housing allocation scenarios as a case study, we conduct extensive policy simulation experiments to verify the feasibility and effectiveness of the SRAP-Agent and employ the Policy Optimization Algorithm with certain optimization objectives. The source code can be found in this https URL
Recently, Mixture-of-Experts (short as MoE) architecture has achieved remarkable success in increasing the model capacity of large-scale language models. However, MoE requires incorporating significantly more parameters than the base model being extended. In this paper, we propose building a parameter-efficient MoE architecture by sharing information among experts. We adopt the matrix product operator (MPO, a tensor decomposition from quantum many-body physics) to reconstruct the parameter matrix in the expert layer and increase model capacity for pre-trained language models by sharing parameters of the central tensor (containing the core information) among different experts while enabling the specificity through the auxiliary tensors (complementing the central tensor) of different experts. To address the unbalanced optimization issue, we further design the gradient mask strategy for the MPO-based MoE architecture. Extensive experiments based on T5 and GPT-2 show improved performance and efficiency of the pre-trained language model (27.2x reduction in total parameters for the superior model performance, compared with the Switch Transformers). Our code is publicly available at this https URL.
Pre-trained large language models (LLMs) based on Transformer have demonstrated striking in-context learning (ICL) abilities. With a few demonstration input-label pairs, they can predict the label for an unseen input without any parameter updates. In this paper, we show an exciting phenomenon that SVD-based weight pruning can enhance ICL performance, and more surprising, pruning weights in deep layers often results in more stable performance improvements than in shallow layers. However, the underlying mechanism of those findings still remains an open question. To reveal those findings, we conduct an in-depth theoretical analysis by presenting the implicit gradient descent (GD) trajectories of ICL and giving the mutual information based generalization bounds of ICL via full implicit GD trajectories. This helps us reasonably explain the surprising experimental findings. Besides, based on all our experimental and theoretical insights, we intuitively propose a simple, model-compression and derivative-free algorithm for downstream tasks in enhancing ICL inference. Experiments on benchmark datasets and open source LLMs display the method effectiveness\footnote{The code is available at \url{this https URL}.}.
Div-Ref introduces a method that leverages Large Language Models to generate diverse reference texts, which substantially improves the correlation of automatic Natural Language Generation evaluation metrics with human judgments across tasks like machine translation, summarization, and image captioning. This approach addresses the limitation of single-reference benchmarks and enhances the reliability of existing evaluation metrics.
Audio question answering (AQA), acting as a widely used proxy task to explore scene understanding, has got more attention. The AQA is challenging for it requires comprehensive temporal reasoning from different scales' events of an audio scene. However, existing methods mostly extend the structures of visual question answering task to audio ones in a simple pattern but may not perform well when perceiving a fine-grained audio scene. To this end, we present a Multi-scale Window Attention Fusion Model (MWAFM) consisting of an asynchronous hybrid attention module and a multi-scale window attention module. The former is designed to aggregate unimodal and cross-modal temporal contexts, while the latter captures sound events of varying lengths and their temporal dependencies for a more comprehensive understanding. Extensive experiments are conducted to demonstrate that the proposed MWAFM can effectively explore temporal information to facilitate AQA in the fine-grained this http URL: this https URL
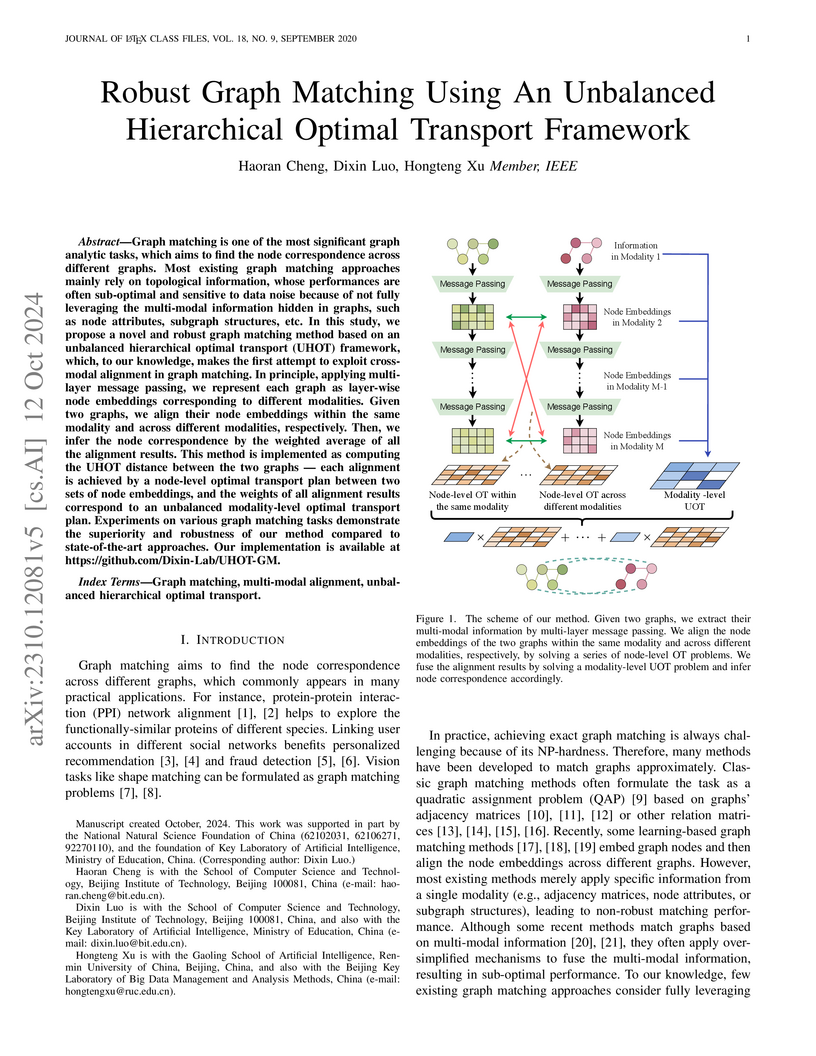
Graph matching is one of the most significant graph analytic tasks, which
aims to find the node correspondence across different graphs. Most existing
graph matching approaches mainly rely on topological information, whose
performances are often sub-optimal and sensitive to data noise because of not
fully leveraging the multi-modal information hidden in graphs, such as node
attributes, subgraph structures, etc. In this study, we propose a novel and
robust graph matching method based on an unbalanced hierarchical optimal
transport (UHOT) framework, which, to our knowledge, makes the first attempt to
exploit cross-modal alignment in graph matching. In principle, applying
multi-layer message passing, we represent each graph as layer-wise node
embeddings corresponding to different modalities. Given two graphs, we align
their node embeddings within the same modality and across different modalities,
respectively. Then, we infer the node correspondence by the weighted average of
all the alignment results. This method is implemented as computing the UHOT
distance between the two graphs -- each alignment is achieved by a node-level
optimal transport plan between two sets of node embeddings, and the weights of
all alignment results correspond to an unbalanced modality-level optimal
transport plan. Experiments on various graph matching tasks demonstrate the
superiority and robustness of our method compared to state-of-the-art
approaches. Our implementation is available at
this https URL
14 Sep 2024
Multi-stakeholder recommender systems involve various roles, such as users, and providers. Previous work pointed out that max-min fairness (MMF) is a better metric to support weak providers. However, when considering MMF, the features or parameters of these roles vary over time, how to ensure long-term provider MMF has become a significant challenge. We observed that recommendation feedback loops (named RFL) will greatly influence the provider MMF in the long term. RFL means that recommender systems can only receive feedback on exposed items from users and update recommender models incrementally based on this feedback. When utilizing the feedback, the recommender model will regard the unexposed items as negative. In this way, the tail provider will not get the opportunity to be exposed, and its items will always be considered negative samples. Such phenomena will become more and more serious in RFL. To alleviate the problem, this paper proposes an online ranking model named Long-Term Provider Max-min Fairness (named LTP-MMF). Theoretical analysis shows that the long-term regret of LTP-MMF enjoys a sub-linear bound. Experimental results on three public recommendation benchmarks demonstrated that LTP-MMF can outperform the baselines in the long term.
Designing and analyzing model-based RL (MBRL) algorithms with guaranteed monotonic improvement has been challenging, mainly due to the interdependence between policy optimization and model learning. Existing discrepancy bounds generally ignore the impacts of model shifts, and their corresponding algorithms are prone to degrade performance by drastic model updating. In this work, we first propose a novel and general theoretical scheme for a non-decreasing performance guarantee of MBRL. Our follow-up derived bounds reveal the relationship between model shifts and performance improvement. These discoveries encourage us to formulate a constrained lower-bound optimization problem to permit the monotonicity of MBRL. A further example demonstrates that learning models from a dynamically-varying number of explorations benefit the eventual returns. Motivated by these analyses, we design a simple but effective algorithm CMLO (Constrained Model-shift Lower-bound Optimization), by introducing an event-triggered mechanism that flexibly determines when to update the model. Experiments show that CMLO surpasses other state-of-the-art methods and produces a boost when various policy optimization methods are employed.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.